

News
Martian auroras offer clues to how the red planet lost its water
Aurorae are a dazzling light spectacle often visible at high-latitude locations here on Earth. They’re colorful and mesmerizing, but most of all, they’re mysterious.
A new study has found that this same phenomenon also happens on Mars. In research presented last week at the American Geophysical Union’s annual Fall meeting, scientists revealed that the most common form of Martian aurorae is called the proton aurora.
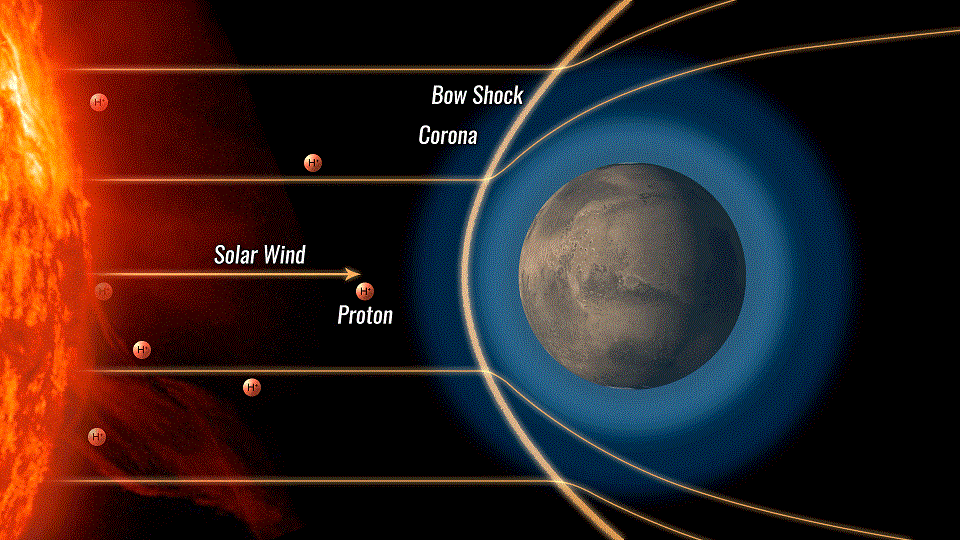
Just like the auroras we see here on Earth, proton aurorae are formed when the solar wind—a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun—interacts with the atmosphere. That interaction often manifests itself as a mesmerizing swirl of colored lights in the night sky.
On Mars, however, the auroras appear during the daytime and onlookers would need special ultraviolet glasses to see them. That’s because they’re invisible to the naked eye, but can be spotted with special UV instruments.

These auroras aren’t just a future Martian tourist attraction, they have a scientific value. We could better understand how Mars is losing water to space and more about how the planet’s climate is changing.
Proton auroras were first discovered in 2016 by NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) spacecraft. MAVEN is investigating how the Red Planet lost its atmosphere and water, ultimately transforming its climate from one that may have supported life to one that is inhospitable.
The observed aurora can help researchers track the amount of water lost since the auroras are related to water loss.
“In this new study using MAVEN/IUVS data from multiple Mars years, the team has found that periods of increased atmospheric escape correspond with increases in proton aurora occurrence and intensity,” Andréa Hughes of Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in Daytona Beach, Florida said in a news release.
Auroras on both planets start with the same source: the solar wind. On Earth, they appear when the solar wind slams into our planet’s magnetic field. High-energy collisions occur as the charged solar particles interact with particles of atmospheric gas. Each type of particle produces a different colored light in the sky.
Martian auroras start in much the same way, charged particles from the solar wind collide with a cloud of hydrogen that surrounds the red planet. When this happens, protons in the solar wind become neutral after stealing electrons from the hydrogen atoms. They then collide with other molecules in the Martian atmosphere, producing an ultraviolet glow.
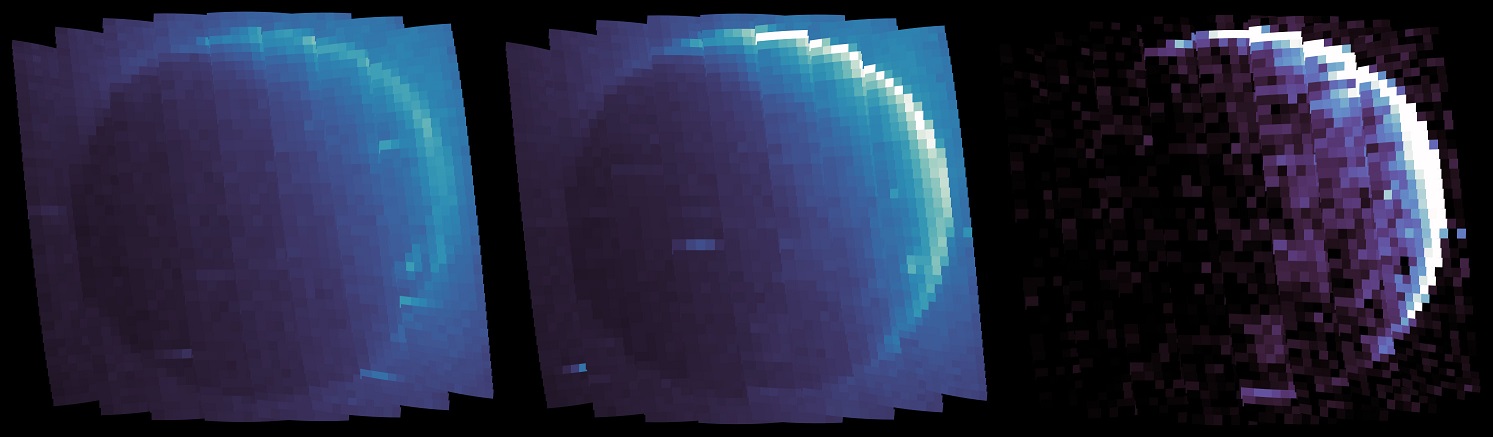
Since the hydrogen cloud surrounding the planet is created in part by water being lost to space, this could give scientists a way to measure the amount of water lost over time.
When the MAVEN team first observed the proton aurora, they thought they were witnessing an unusual phenomenon. “At first, we believed that these events were rather rare because we weren’t looking at the right times and places,” Mike Chaffin, a research scientist at the University of Colorado Boulder’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) said in a statement.
After Chaffin’s team took a closer look, they discovered that the proton auroras occur quite frequently, especially in the summer. This is probably due to seasonal variation in the hydrogen cloud that surrounds Mars. The team noted that during the Martian summer, the cloud lines up just right to produce near-constant auroras.
But that’s not all. The researchers also discovered that as temperatures climb during the summer, rising dust clouds would carry water vapor away from the planet’s surface. That water vapor is then broken down into its components: hydrogen and oxygen. As more hydrogen escapes into space, it enhances the hydrogen cloud enveloping Mars and ultimately leads to more frequent (and brighter) proton auroras.
“Observations of proton auroras at Mars provides a unique perspective of hydrogen and, therefore, water loss from the planet,” physicist Edwin Mierkiewicz of Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in Florida said in a statement.
“Through this research, we can gain a deeper understanding of the Sun’s interactions with the upper atmosphere of Mars and with similar bodies in our Solar System, or in another solar system, that lacks a global magnetic field.”
So, if we ever do make it to Mars, those first visitors are going to witness some truly out-of-this-world sights—as long as they packed their ultraviolet goggles.
News
Tesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
Tesla seems serious about expanding its Robotaxi service to several states in the coming months.

Tesla has initiated discussions with Arizona transportation regulators to certify its driverless Robotaxi service in the state, as per a recent report from Bloomberg News. The move follows Tesla’s launch of its Robotaxi pilot program in Austin, Texas, as well as CEO Elon Musk’s recent comments about the service’s expansion in the Bay Area.
The Arizona Department of Transportation confirmed to Bloomberg that Tesla has reached out to begin the certification process for autonomous ride-sharing operations in the state. While details remain limited, the outreach suggests that Tesla is serious about expanding its driverless Robotaxi service to several territories in the coming months.
The Arizona development comes as Tesla prepares to expand its service area in Austin this weekend, as per CEO Elon Musk in a post on X. Musk also stated that Tesla is targeting the San Francisco Bay Area as its next major market, with a potential launch “in a month or two,” pending regulatory approvals.
Tesla first launched its autonomous ride-hailing program on June 22 in Austin with a small fleet of Model Y vehicles, accompanied by a Tesla employee in the passenger seat to monitor safety. While still classified as a test, Musk has said the program will expand to about 1,000 vehicles in the coming months. Tesla will later upgrade its Robotaxi fleet with the Cyercab, a two-seater that is designed without a steering wheel.
Sightings of Cybercab castings around the Giga Texas complex suggests that Tesla may be ramping the initial trial production of the self-driving two-seater. Tesla, for its part, has noted in the past that volume production of the Cybercab is expected to start sometime next year.
In California, Tesla has already applied for a transportation charter-party carrier permit from the state’s Public Utilities Commission. The company is reportedly taking a phased approach to operating in California, with the Robotaxi service starting with pre-arranged rides for employees in vehicles with safety drivers.
News
Tesla sets November 6 date for 2025 Annual Shareholder Meeting
The automaker announced the date on Thursday in a Form 8-K.

Tesla has scheduled its 2025 annual shareholder meeting for November 6, addressing investor concerns that the company was nearing a legal deadline to hold the event.
The automaker announced the date on Thursday in a Form 8-K submitted to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The company also listed a new proposal submission deadline of July 31 for items to be included in the proxy statement.
Tesla’s announcement followed calls from a group of 27 shareholders, including the leaders of large public pension funds, which urged Tesla’s board to formally set the meeting date, as noted in a report from The Wall Street Journal.
The group noted that under Texas law, where Tesla is now incorporated, companies must hold annual meetings within 13 months of the last one if requested by shareholders. Tesla’s previous annual shareholder meeting was held on June 13, 2024, which placed the July 13 deadline in focus.
Tesla originally stated in its 2024 annual report that it would file its proxy statement by the end of April. However, an amended filing on April 30 indicated that the Board of Directors had not yet finalized a meeting date, at least at the time.
The April filing also confirmed that Tesla’s board had formed a special committee to evaluate certain matters related to CEO Elon Musk’s compensation plan. Musk’s CEO performance award remains at the center of a lengthy legal dispute in Delaware, Tesla’s former state of incorporation.
Due to the aftermath of Musk’s legal dispute about his compensation plan in Delaware, he has not been paid for his work at Tesla for several years. Musk, for his part, has noted that he is more concerned about his voting stake in Tesla than his actual salary.
At last year’s annual meeting, TSLA shareholders voted to reapprove Elon Musk’s compensation plan and ratified Tesla’s decision to relocate its legal domicile from Delaware to Texas.
Elon Musk
Grok coming to Tesla vehicles next week “at the latest:” Elon Musk
Grok’s rollout to Tesla vehicles is expected to begin next week at the latest.

Elon Musk announced on Thursday that Grok, the large language model developed by his startup xAI, will soon be available in Tesla vehicles. Grok’s rollout to Tesla vehicles is expected to begin next week at the latest, further deepening the ties between the two Elon Musk-led companies.
Tesla–xAI synergy
Musk confirmed the news on X shortly after livestreaming the release of Grok 4, xAI’s latest large language model. “Grok is coming to Tesla vehicles very soon. Next week at the latest,” Musk wrote in a post on social media platform X.
During the livestream, Musk and several members of the xAI team highlighted several upgrades to Grok 4’s voice capabilities and performance metrics, positioning the LLM as competitive with top-tier models from OpenAI and Google.
The in-vehicle integration of Grok marks a new chapter in Tesla’s AI development. While Tesla has long relied on in-house systems for autonomous driving and energy optimization, Grok’s integration would introduce conversational AI directly into its vehicles’ user experience. This integration could potentially improve customer interaction inside Tesla vehicles.
xAI and Tesla’s collaborative footprint
Grok’s upcoming rollout to Tesla vehicles adds to a growing business relationship between Tesla and xAI. Earlier this year, Tesla disclosed that it generated $198.3 million in revenue from commercial, consulting, and support agreements with xAI, as noted in a report from Bloomberg News. A large portion of that amount, however, came from the sale of Megapack energy storage systems to the artificial intelligence startup.
In July 2023, Musk polled X users about whether Tesla should invest $5 billion in xAI. While no formal investment has been made so far, 68% of poll participants voted yes, and Musk has since stated that the idea would be discussed with Tesla’s board.
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk20 hours ago
Elon Musk20 hours agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla’s Omead Afshar, known as Elon Musk’s right-hand man, leaves company: reports
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”

















