
News
NASA Mars rover promises blazing entrance after China, UAE make it to Mars orbit
The month of the robotic invasion of Mars is upon us. Seven months ago, the United States, China, and the United Arab Emirates launched missions on a 300 million mile (480 million kilometer) journey to Mars.
Last week, two of the three missions quietly arrived and inserted themselves into Mars orbit. The final spacecraft to arrive, NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance mission, however, will not go gently into the Martian atmosphere. On Thursday, February 18, NASA’s latest Mars mission destined to uncover evidence of ancient microbial life on the distant planet is set to touchdown following a spectacular display of extremely complex engineering.
Getting to Mars
Launching to the Red Planet is a strategic maneuver that can only be completed once every two years. This is due to the varying speeds and the elliptical shape of the planets’ orbits around the sun. The point at which Earth and Mars are aligned close enough to minimize travel time, called an opposition, occurs only once every two years.
The update that's rolling out to the fleet makes full use of the front and rear steering travel to minimize turning circle. In this case a reduction of 1.6 feet just over the air— Wes (@wmorrill3) April 16, 2024
The most recent opposition occurred in July 2020. Four international Mars missions were intended to leave Earth that summer, however, due to required further certification of parachutes the European Space Agency’s ExoMars Rosalind Franklin rover would have to wait for its launch opportunity during the next planetary opposition to occur in 2022. That left three robotic invaders from the United States, the United Arab Emirates, and China to escape Earth’s orbit and become interplanetary superstars.
Hope arrives to Mars
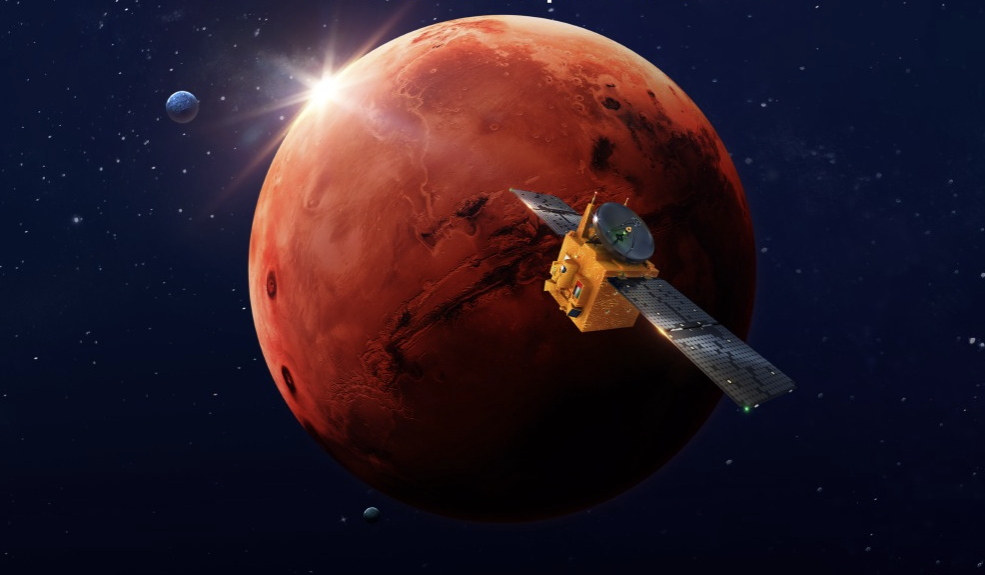
The United Arab Emirates Space Agency’s first-ever interplanetary mission, a spacecraft named Al-Amal, or the Hope Probe, was developed in collaboration between the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Center, Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado Boulder, Arizona State University, and the Space Sciences Lab at the University of California, Berkeley. It was launched on July 19, 2020, from Tanegashima Space Centre in Japan aboard an H2A202 rocket. On Tuesday, February 9, the Hope Probe was the first of the three missions to complete the journey to Mars and successfully insert itself into orbit.
The Hope Probe arrived to near-Mars orbit traveling approximately 75,000 mph (121,000 kph), far too fast to successfully achieve a safe Martian orbital insertion maneuver. In order to slow down to the approximate 11,000mph (18,000 kph) needed to be captured by Mars orbit, the spacecraft had to autonomously fire its main thrusters and perform a Mars Orbit Insertion burn lasting an agonizing 27 minutes. To compensate in the instance of a thruster failure, there was a backup safety protocol that would’ve doubled the length of the burn. After 27 grueling minutes, the Mohammad Bin Rashid Space Center located in Dubai reported that the maneuver was completed successfully and the Hope Probe had arrived at its final destination.
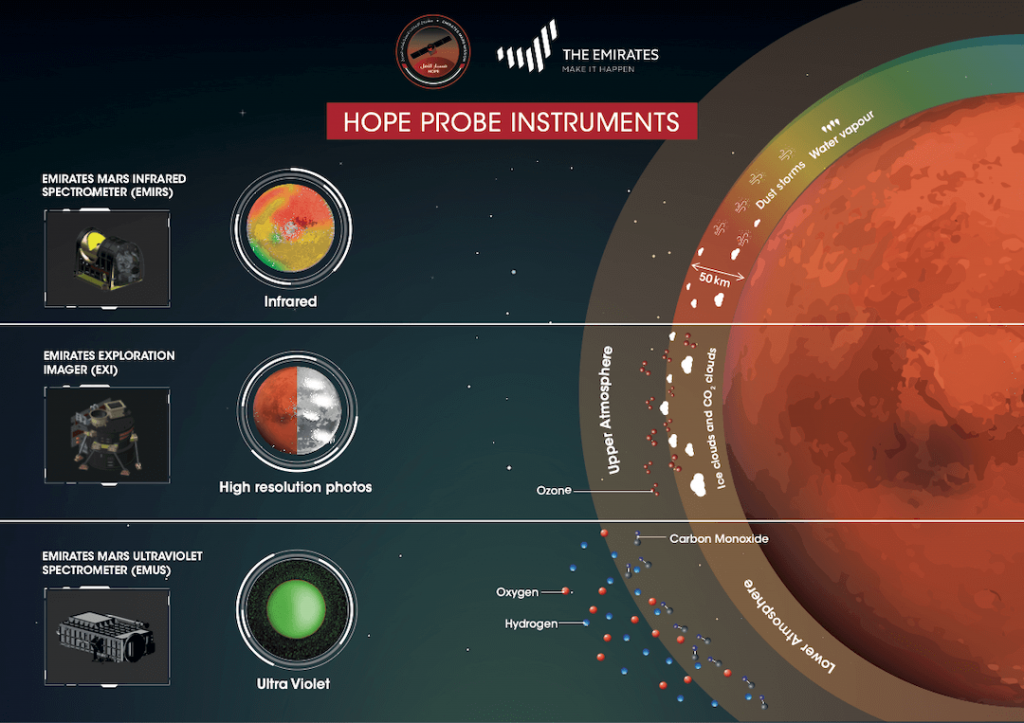
Unlike the American and Chinese missions to Mars which will land rovers on the surface, the United Arab Emirates’ Hope Probe will remain in Mars orbit for the duration of its mission – approximately two Martian years. The spacecraft is equipped with a suite of three instruments, two spectrometers – one infrared and one ultraviolet – to study the Martian atmosphere, and one imager to capture high-resolution images to study the surface from afar.
China’s Tianwen-1 Rover will hang out in orbit before landing in May
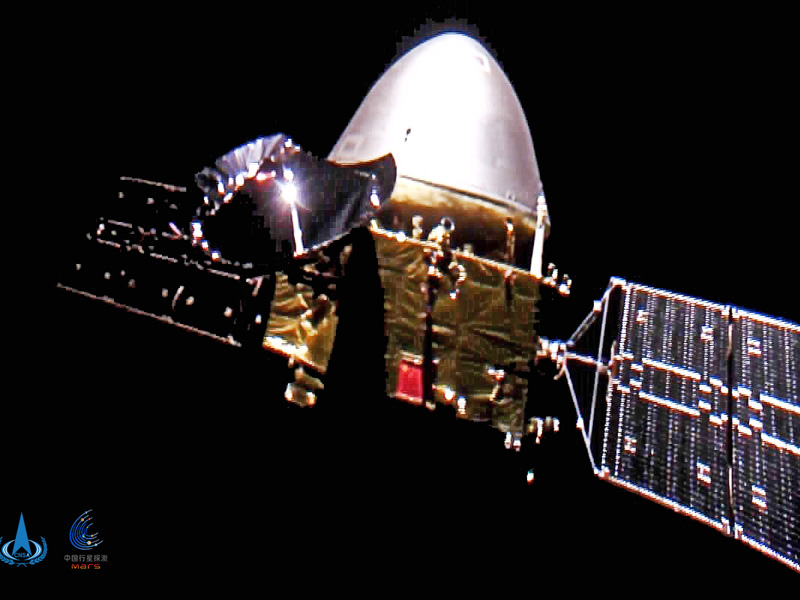
The same type of Mars Orbit Insertion maneuver was completed by China’s first interplanetary mission, the Tianwen-1 spacecraft. Launched from China on July 23, 2020, Tianwen-1 arrived at Mars orbit just one day after the Hope Probe on Wednesday, February 10.
The Tianwen-1 spacecraft had to autonomously complete an excruciating 11-minute “braking” burn to slow down which took it behind the planet as it was captured by Mars gravity and entered into orbit.
Like NASA’s Perseverance, the Tianwen-1 mission features a rover that will eventually land on the surface of Mars. The process to get the rover to the surface, however, varies from that of NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance mission.
The Tianwen-1 spacecraft is made of two components, an orbiter and a rover. Currently, it is planned that the orbiter will spend some time in Mars orbit for a period of comprehensive observation before attempting a landing of the rover in May. Ideally, the spacecraft will then touch down in a region known as Utopia Planitia.

The update that's rolling out to the fleet makes full use of the front and rear steering travel to minimize turning circle. In this case a reduction of 1.6 feet just over the air— Wes (@wmorrill3) April 16, 2024
Once the rover safely makes it to the surface it will initiate the investigation period of the mission. The rover carries a suite of scientific instruments that will be used to investigate the composition of the Martian surface searching for the potential distribution of water and ice. Similar to China’s Yutu 2 rover which is exploring the Moon, the Tianwen-1 rover also carries a panoramic camera to image the planet.
Perseverance and Ingenuity like no other
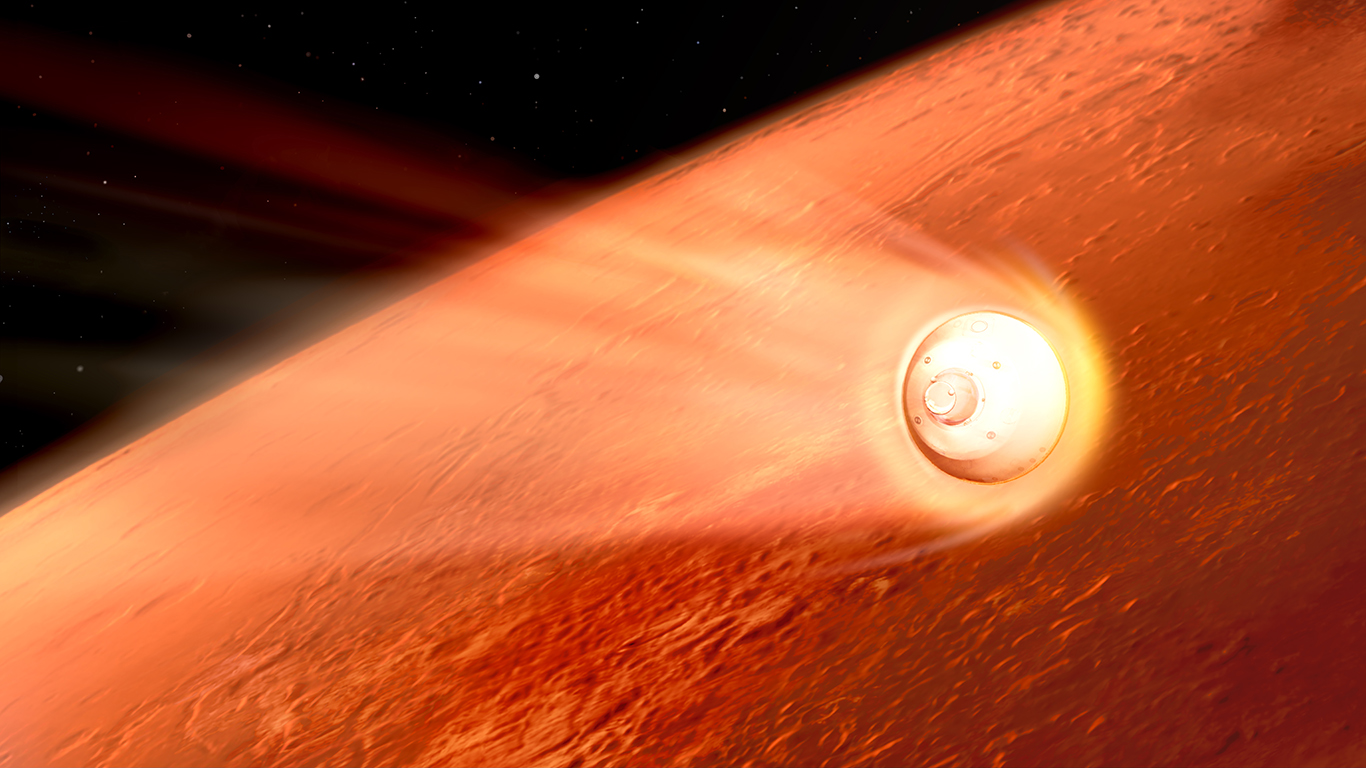
The last of the three Mars missions – NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance mission launched on July 30, 2020, from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas 5 rocket. As far as Mars arrivals go, the best has certainly been saved for last. Following the success of the other two missions from China and the United Arab Emirates, the stage is set for Perseverance to make its dramatic entrance.
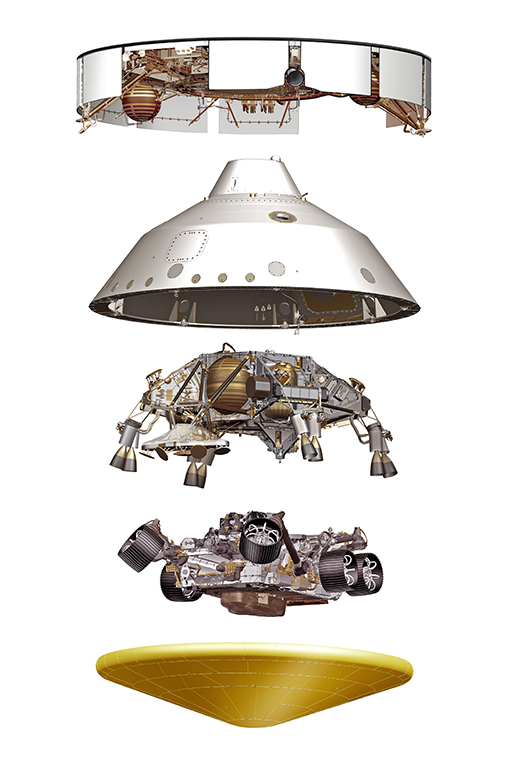

NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is by far the most ambitious mission to launch to Mars during the 2020 planetary transfer window. NASA is not attempting to land one, but two spacecraft on the surface of Mars. The $2.4 billion Mars 2020 mission is comprised of the Perseverance rover – powered by the heat produced by radioactive decay of Plutonium – and a first of its kind rotary helicopter called Ingenuity. It is scheduled to arrive in dramatic fashion on Thursday, February 18.
Rather than conducting a braking maneuver to slow down and enter Mars orbit, the Perseverance spacecraft will autonomously conduct the entry, descent, and landing (EDL) procedure – essentially going from traveling several thousand miles an hour to descending slowly under a parachute canopy to softly land in mere minutes.
The spacecraft – housed in a protective aeroshell with its robust heat shield facing the planet’s surface – will burst into Mars’ atmosphere traveling nearly 12,500 mph (20,000 kph). Once through, Pesevereance will ditch its heat shield and autonomously begin scanning the Martain terrain to determine its relative location and make adjustments to find an optimal landing spot. Then, a powered descent module will deploy transporting the rover the rest of the way down slowing to less than 2mph (3kph). Finally, the descent module will hover and deploy a complex harness system lowering Perseverance – and its stowaway, the Ingenuity helicopter – to the Martian surface for touchdown.
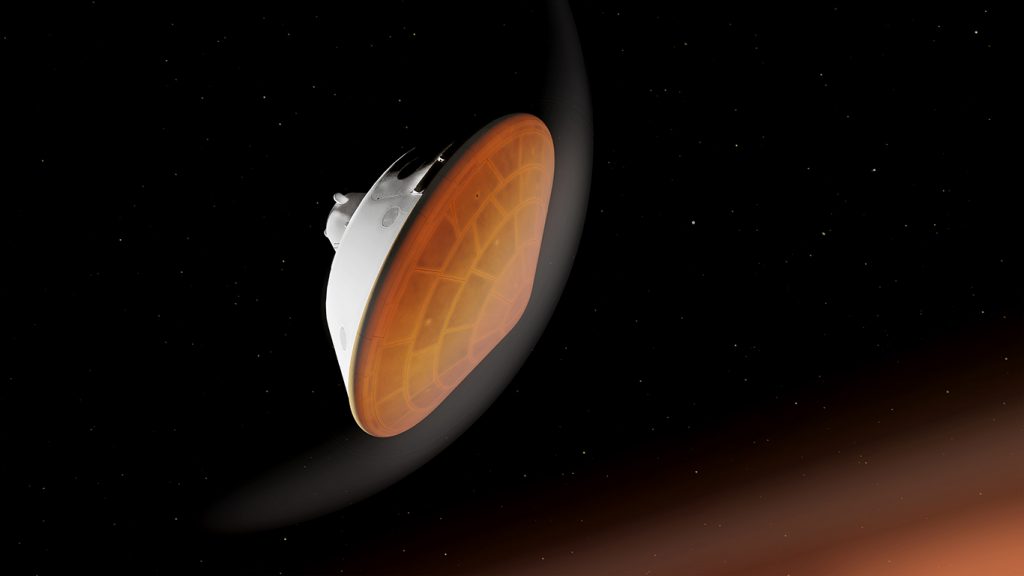

After seven months of interplanetary travel, it all comes down to the final seven minutes – the length of time the EDL process is expected to take. All spacecraft controllers back on Earth can do is watch and wait for that final telemetry reading indicating that Perseverance has successfully touched down. That is why this process has earned the nickname “seven minutes of terror.”
Beginning around 11:15 am PST (19:15 UTC) on Thursday, February 18th, NASA will provide live coverage of Perseverance’s landing attempt. The agency will carry the coverage on NASA TV and its website, as well as a number of other platforms including YouTube, Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitch, Daily Motion, Theta.TV, and NASA App.
Elon Musk
Tesla Supercharger Diner food menu gets a sneak peek as construction closes out
What are you ordering at the Tesla Diner?
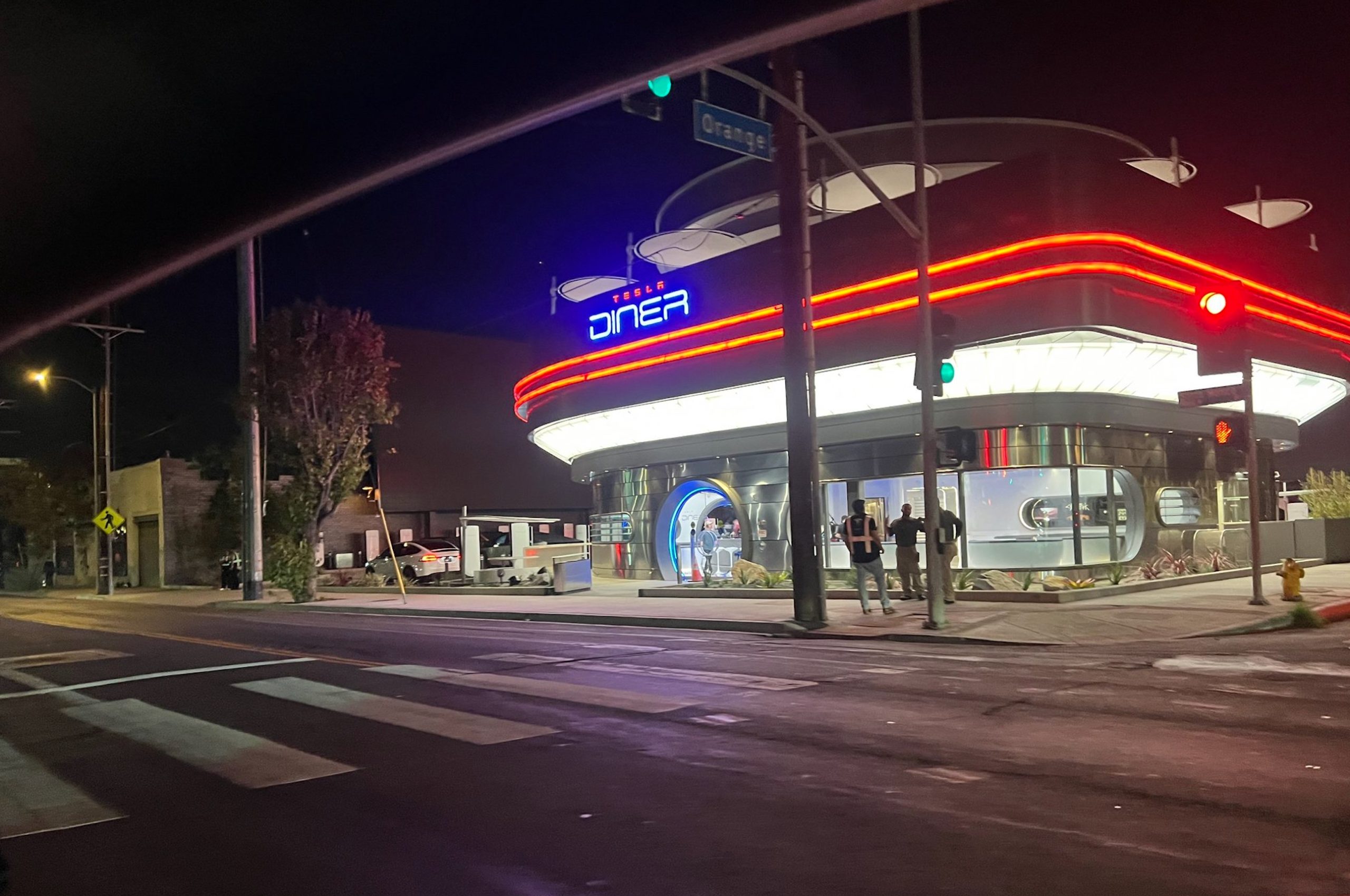

The Tesla Supercharger Diner in Los Angeles is nearing completion as construction appears to be winding down significantly. However, the more minor details, such as what the company will serve at its 50s-style diner for food, are starting to be revealed.
Tesla’s Supercharger Diner is set to open soon, seven years after CEO Elon Musk first drafted the idea in a post on X in 2018. Musk has largely come through on most of what he envisioned for the project: the diner, the massive movie screens, and the intended vibe are all present, thanks to the aerial and ground footage shared on social media.
We already know the Diner will be open 24/7, based on decals placed on the front door of the restaurant that were shared earlier this week. We assume that Tesla Optimus will come into play for these long and uninterrupted hours.
The Tesla Diner is basically finished—here’s what it looks like
As far as the food, Tesla does have an email also printed on the front door of the Diner, but we did not receive any response back (yet) about what cuisine it will be offering. We figured it would be nothing fancy and it would be typical diner staples: burgers, fries, wings, milkshakes, etc.
According to pictures taken by @Tesla_lighting_, which were shared by Not a Tesla App, the food will be just that: quick and affordable meals that diners do well. It’s nothing crazy, just typical staples you’d find at any diner, just with a Tesla twist:
Tesla Diner food:
• Burgers
• Fries
• Chicken Wings
• Hot Dogs
• Hand-spun milkshakes
• And more https://t.co/kzFf20YZQq pic.twitter.com/aRv02TzouY— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) July 17, 2025
As the food menu is finalized, we will be sure to share any details Tesla provides, including a full list of what will be served and its prices.
Additionally, the entire property appears to be nearing its final construction stages, and it seems it may even be nearing completion. The movie screens are already up and showing videos of things like SpaceX launches.
There are many cars already using the Superchargers at the restaurant, and employees inside the facility look to be putting the finishing touches on the interior.
🚨 Boots on the ground at the Tesla Diner:
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 17, 2025
It’s almost reminiscent of a Tesla version of a Buc-ee’s, a southern staple convenience store that offers much more than a traditional gas station. Of course, Tesla’s version is futuristic and more catered to the company’s image, but the idea is the same.
It’s a one-stop shop for anything you’d need to recharge as a Tesla owner. Los Angeles building permits have not yet revealed the date for the restaurant’s initial operation, but Tesla may have its eye on a target date that will likely be announced during next week’s Earnings Call.
News
Tesla’s longer Model Y did not scale back requests for this vehicle type from fans
Tesla fans are happy with the new Model Y, but they’re still vocal about the need for something else.

Tesla launched a slightly longer version of the Model Y all-electric crossover in China, and with it being extremely likely that the vehicle will make its way to other markets, including the United States, fans are still looking for something more.
The new Model Y L in China boasts a slightly larger wheelbase than its original version, giving slightly more interior room with a sixth seat, thanks to a third row.
Tesla exec hints at useful and potentially killer Model Y L feature
Tesla has said throughout the past year that it would focus on developing its affordable, compact models, which were set to begin production in the first half of the year. The company has not indicated whether it met that timeline or not, but many are hoping to see unveilings of those designs potentially during the Q3 earnings call.
However, the modifications to the Model Y, which have not yet been officially announced for any markets outside of China, still don’t seem to be what owners and fans are looking forward to. Instead, they are hoping for something larger.
A few months ago, I reported on the overall consensus within the Tesla community that the company needs a full-size SUV, minivan, or even a cargo van that would be ideal for camping or business use.
Tesla is missing one type of vehicle in its lineup and fans want it fast
That mentality still seems very present amongst fans and owners, who state that a full-size SUV with enough seating for a larger family, more capability in terms of cargo space for camping or business operation, and something to compete with gas cars like the Chevrolet Tahoe, Ford Expedition, or electric ones like the Volkswagen ID.BUZZ.
We asked the question on X, and Tesla fans were nearly unanimously in support of a larger SUV or minivan-type vehicle for the company’s lineup:
🚨 More and more people are *still* saying that, despite this new, longer Model Y, Tesla still needs a true three-row SUV
Do you agree? https://t.co/QmbRDcCE08 pic.twitter.com/p6m5zB4sDZ
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 16, 2025
Here’s what some of the respondents said:
100% agree, we need a larger vehicle.
Our model Y is quickly getting too small for our family of 5 as the kids grow. A slightly longer Y with an extra seat is nice but it’s not enough if you’re looking to take it on road trips/vacations/ kids sports gear etc.
Unfortunately we…
— Anthony Hunter (@_LiarsDice_) July 17, 2025
Had to buy a Kia Carnival Hybrid because Tesla doesn’t have a true 3 row vehicle with proper space and respectable range. pic.twitter.com/pzwFyHU8Gi
— Neil, like the astronaut (@Neileeyo) July 17, 2025
Agreed! I’m not sure who created this but I liked it enough to save it. pic.twitter.com/Sof5nMehjS
— 🦉Wise Words of Wisdom – Inspirational Quotes (IQ) (@WiseWordsIQ) July 16, 2025
Tesla is certainly aware that many of its owners would like the company to develop something larger that competes with the large SUVs on the market.
However, it has not stated that anything like that is in the current plans for future vehicles, as it has made a concerted effort to develop Robotaxi alongside the affordable, compact models that it claims are in development.
It has already unveiled the Robovan, a people-mover that can seat up to 20 passengers in a lounge-like interior.
The Robovan will be completely driverless, so it’s unlikely we will see it before the release of a fully autonomous Full Self-Driving suite from Tesla.
Energy
Tesla launches first Virtual Power Plant in UK – get paid to use solar
Tesla has launched its first-ever Virtual Power Plant program in the United Kingdom.
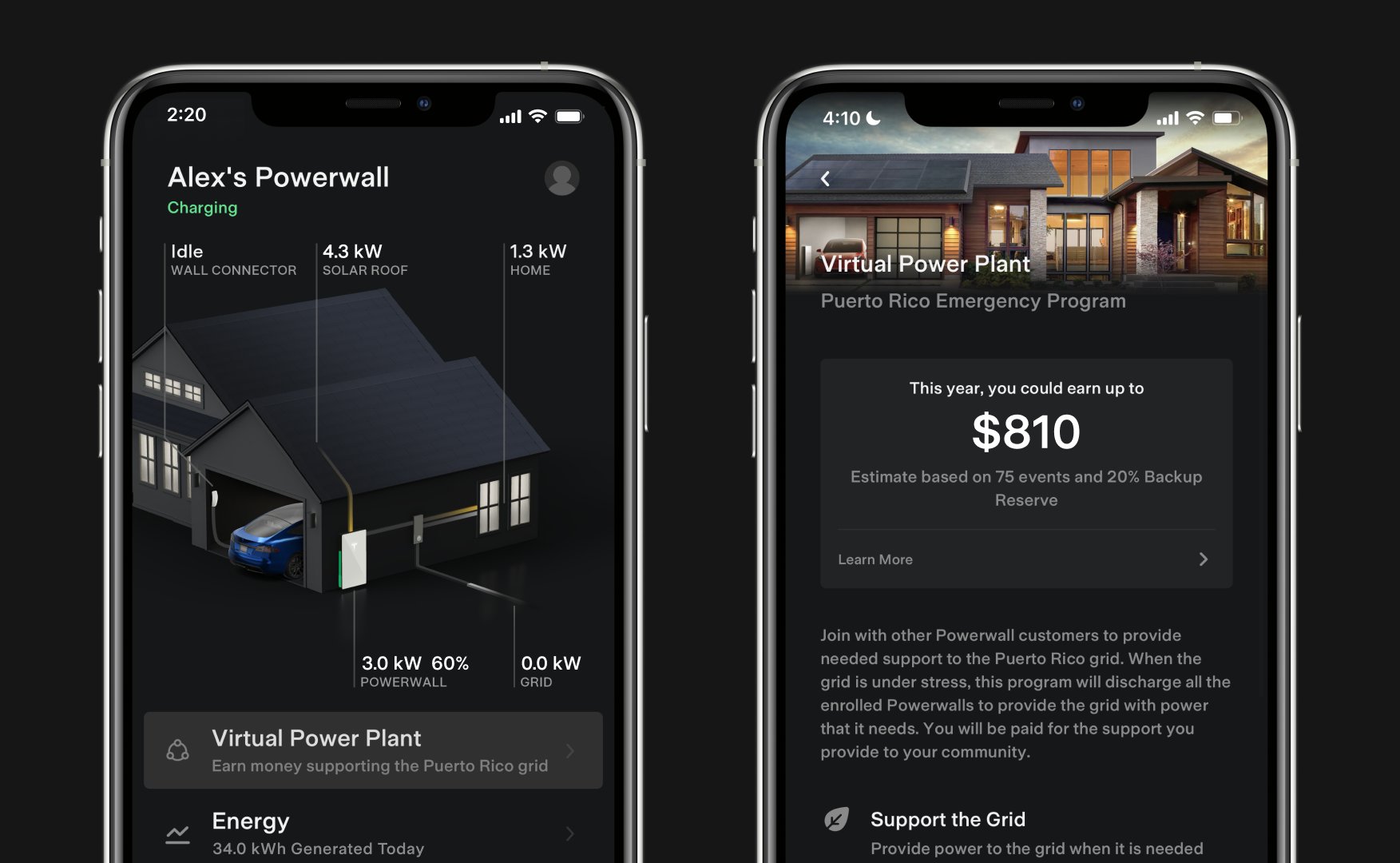
Tesla has launched its first-ever Virtual Power Plant program in the United Kingdom. This feature enables users of solar panels and energy storage systems to sell their excess energy back to the grid.
Tesla is utilizing Octopus Energy, a British renewable energy company that operates in multiple markets, including the UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, and the United States, as the provider for the VPP launch in the region.
The company states that those who enroll in the program can earn up to £300 per month.
Tesla has operated several VPP programs worldwide, most notably in California, Texas, Connecticut, and the U.S. territory of Puerto Rico. This is not the first time Tesla has operated a VPP outside the United States, as there are programs in Australia, Japan, and New Zealand.
This is its first in the UK:
Our first VPP in the UK
You can get paid to share your energy – store excess energy in your Powerwall & sell it back to the grid
You’re making £££ and the community is powered by clean energy
Win-win pic.twitter.com/evhMtJpgy1
— Tesla UK (@tesla_uk) July 17, 2025
Tesla is not the only company that is working with Octopus Energy in the UK for the VPP, as it joins SolarEdge, GivEnergy, and Enphase as other companies that utilize the Octopus platform for their project operations.
It has been six years since Tesla launched its first VPP, as it started its first in Australia back in 2019. In 2024, Tesla paid out over $10 million to those participating in the program.
Participating in the VPP program that Tesla offers not only provides enrolled individuals with the opportunity to earn money, but it also contributes to grid stabilization by supporting local energy grids.
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoWaymo responds to Tesla’s Robotaxi expansion in Austin with bold statement
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoTesla exec hints at useful and potentially killer Model Y L feature
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoElon Musk reveals SpaceX’s target for Starship’s 10th launch
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoTesla ups Robotaxi fare price to another comical figure with service area expansion
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoTesla’s longer Model Y did not scale back requests for this vehicle type from fans
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day ago“Worthy of respect:” Six-seat Model Y L acknowledged by Tesla China’s biggest rivals
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoFirst glimpse of Tesla Model Y with six seats and extended wheelbase
-
 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoElon Musk confirms Tesla is already rolling out a new feature for in-car Grok