

SpaceX
SpaceX’s Crew Dragon to launch astronauts in July, says Russian source
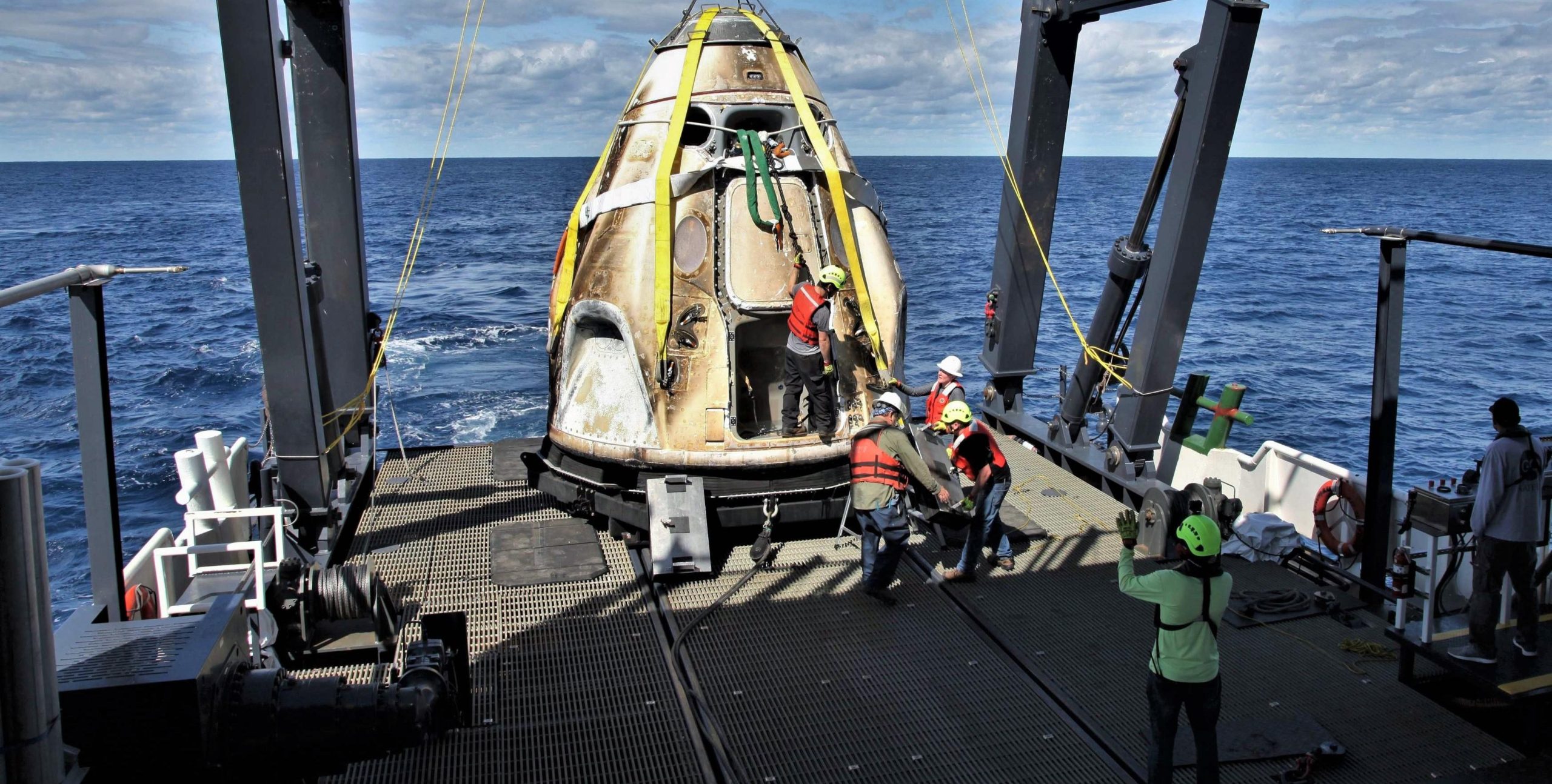
A source familiar with Russia’s aerospace industry recently informed state newspaper RIA Novosti that NASA has provided Russian space agency Roscosmos with an updated planning schedule for International Space Station (ISS) operations, including a preliminary target for SpaceX’s first Crew Dragon launch with astronauts aboard.
According to RIA’s source, NASA informed Roscosmos that the agency was tentatively planning for the launch of SpaceX’s Demonstration Mission 2 (DM-2) as early as July 25th, with the spacecraft departing the ISS, reentering the atmosphere, and safely returning astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley to Earth on August 5th. In a bizarre turn of events, Russian news agency TASS published a separate article barely 12 hours later, in which – once again – an anonymous space agency source told the outlet that “the [DM-2] launch of Crew Dragon is likely to be postponed to November”. For the time being, the reality likely stands somewhere in the middle.
While it’s hard not to jump to conclusions about the oddity of two wholly contradictory reports arising from similar sources in similar articles just half a day apart, it’s just as likely that the near-simultaneous publishing of both TASS and RIA stories is mainly a coincidence. At the same time, truth can be found in both comments made by the anonymous source(s), while they also offer a sort of best-case and worst-case scenario for the first crewed launch of SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft.
RIA began the series on March 22nd with a brief news blurb featuring one substantive quote from the aforementioned space industry source.
“The American side informed the Russian side that the launch of the [first crewed launch of] Dragon-2…to the ISS…is scheduled for July 25. The docking with the station is scheduled [to occur around one day later]. The separation from the ISS and return to Earth is expected on August 5,” the agency’s source said.
Put in a slightly different way, NASA informed Roscosmos that it had begun to loosely plan for the launch of SpaceX’s DM-2 no earlier than (NET) late July, much like NASA and SpaceX publicly announced that Crew Dragon’s DM-1 launch debut was scheduled NET January 17th as of early December 2018. DM-1’s actual debut wound up occurring on March 2nd, a delay of approximately six weeks. The cause(s) behind the discrepancy between NASA’s first serious planning date and the actual launch remains unknown but it’s safe to say that things took quite a bit longer than expected even after Crew Dragon and Falcon 9 were technically “go” for launch.
Although NASA and SpaceX now have the luxury of a vast cache of flight data and the practical experience derived from conducting Crew Dragon’s first – and nearly flawless – orbital launch and ISS rendezvous, Crew Dragon’s DM-2 mission remains an entirely different animal. Aside from requiring a number of significant hardware changes and introducing the visceral pressure of real human lives hanging in the balance, DM-2 will be a major first for the NASA after having spent the better part of eight years unable to launch its own astronauts into orbit.
A ‘race’ no more
Meanwhile, Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft – a companion to Crew Dragon under NASA’s Commercial Crew Program – has suffered multiple setbacks in 2019, reportedly pushing the vehicle’s uncrewed launch debut from April to NET August, a delay of at least four months. As a result, nothing short of severe anomalies during Crew Dragon hardware preparation and/or NASA’s reviews of DM-1 performance and DM-2 flight-readiness could prevent SpaceX from becoming the first commercial entity to build, launch, and operate a crewed spacecraft in the history of spaceflight.
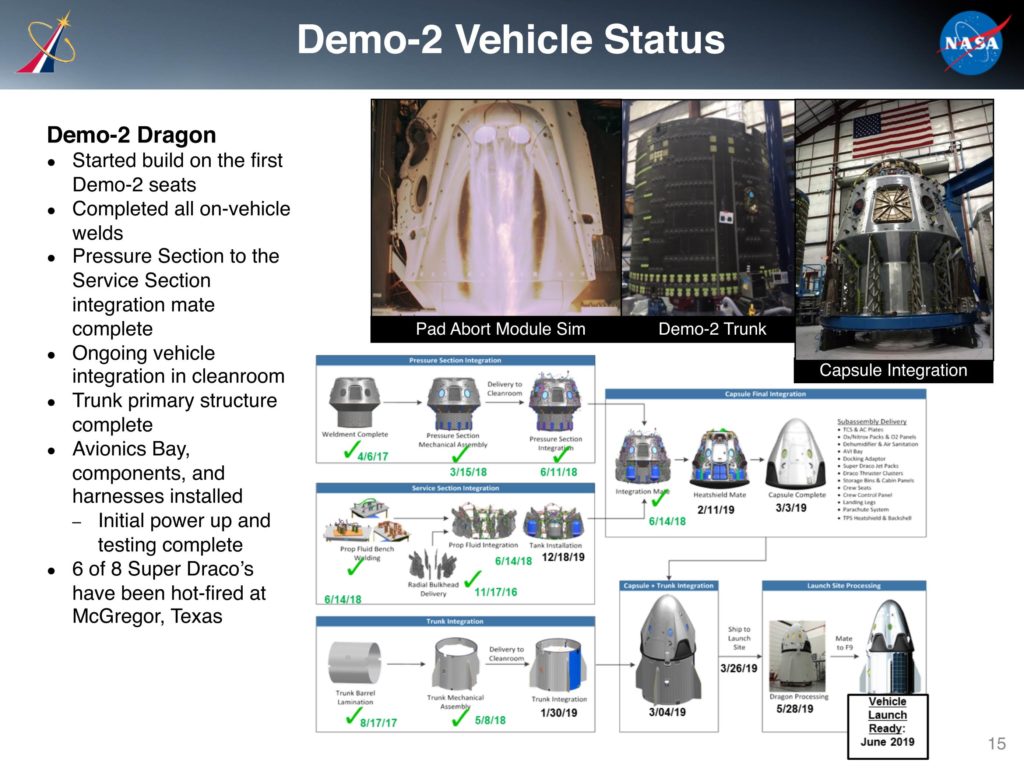

According to a December 2018 update provided during NASA’s quarterly Advisory Council meetings, the entirety of Crew Dragon DM-2’s manufacturing and integration may already be complete, with the capsule potentially heading to SpaceX’s Florida payload processing facilities later this week. NAC’s December 2018 dates did not, however, account for the DM-1 launch delays that shortly followed, plausibly impacting the completion of DM-2 integration and pad delivery to ensure that any potential anomalies experienced during Crew Dragon’s test flight could be resolved in Hawthorne, CA.
According to NASA and SpaceX, DM-2’s Crew Dragon will need to be retrofitted with thermal regulation hardware to prevent Draco thruster plumbing from freezing under a handful of specific conditions on orbit, as well as potential modifications to the craft’s parachute system and the installation of four windows instead of two. SpaceX will also need to install Crew Dragon’s first orbit-ready display and control hardware. Finally, SpaceX has opted to conduct an in-flight abort (IFA) test of Crew Dragon to verify that the spacecraft can safely carry astronauts to safety from the moment of launch to orbital insertion, a test that will have to be completed successfully and reviewed by NASA before the agency allows SpaceX to proceed with DM-2.

All of the above tasks – including major agency-wide reviews of Crew Dragon’s performance during its DM-1 debut – must be completed before SpaceX will be permitted to launch astronauts to the ISS, all of which inherently add some level of uncertainty to DM-2’s practical launch schedule. If all reviews and modifications proceed flawlessly, including a perfect in-flight abort test as early as late June, it’s possible that SpaceX and NASA could be prepared to launch Crew Dragon once more by the end of July.
In reality, it’s extremely unlikely that everything will proceed perfectly, as evidenced by the drawn-out process required for NASA and SpaceX to eventually reach flight-readiness prior to DM-1. If a significant number of challenges arise over the next few months of reviews and work, it’s not out of the question for DM-2’s launch to slip to Q4 2019 or Q1 2020. Splitting the difference, it would be safest to bet that Crew Dragon will lift off with astronauts aboard no earlier than August or September. Regardless, a great many exciting milestones are soon to come for SpaceX’s first human spaceflight program. Stay tuned as SpaceX prepares to ship the second flightworthy Crew Dragon to Florida.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

Elon Musk
Elon Musk shares updated Starship V3 maiden launch target date
The comment was posted on Musk’s official account on social media platform X.
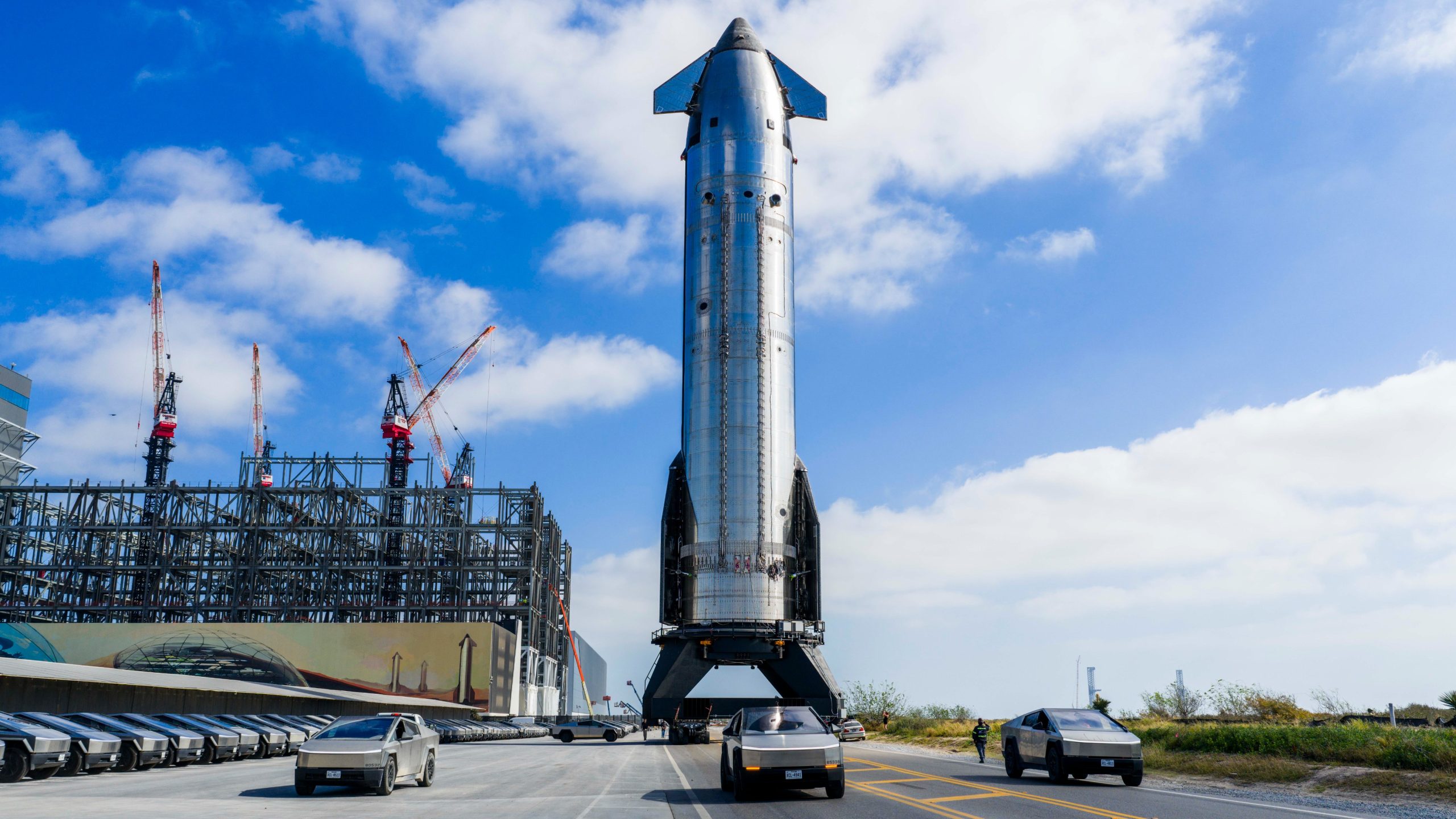

SpaceX CEO Elon Musk shared a brief Starship V3 update in a post on social media platform X, stating the next launch attempt of the spacecraft could take place in about four weeks.
The comment was posted on Musk’s official account on social media platform X.
Musk’s update suggests that Starship Flight 12 could target a launch around early April, though the schedule will depend on several remaining milestones at SpaceX’s Starbase launch facility in Texas.
Among the key steps is testing and certification of the site’s new launch tower, launch mount, and tank farm systems. These upgrades will support the next generation of Starship vehicles.
Booster 19 is expected to roll to the launch site and be placed on the launch mount before returning to the production facility to receive its 33 Raptor engines. The booster would then return for a static fire test, which could mark the first time a Super Heavy booster equipped with Raptor V3 engines is fired on the pad.
Ship 39 is expected to undergo a similar preparation process. The vehicle will likely return to the production site to receive its six engines before heading to Massey’s test site for static fire testing.
Once both stages are prepared, the booster and ship will roll out to the launch site for the first full stack of a V3 Super Heavy and V3 Starship. A full wet dress rehearsal is expected to follow before any launch attempt.
Elon Musk has previously shared how SpaceX plans to eventually recover Starship’s upper stage using the launch tower’s robotic arms. Musk noted that the company will only attempt to catch the Starship spacecraft after two successful soft landings in the ocean. The approach is intended to reduce risk before attempting a recovery over land.
“Should note that SpaceX will only try to catch the ship with the tower after two perfect soft landings in the ocean. The risk of the ship breaking up over land needs to be very low,” Musk wrote in a post on X.
Such a milestone would represent a major step toward the full reuse of the Starship system, which remains a central goal for SpaceX’s long-term launch strategy.
News
SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell details xAI power pledge at White House event
The commitment was announced during an event with United States President Donald Trump.

SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell stated that xAI will develop 1.2 gigawatts of power at its Memphis-area AI supercomputer site as part of the White House’s new “Ratepayer Protection Pledge.”
The commitment was announced during an event with United States President Donald Trump.
During the White House event, Shotwell stated that xAI’s AI data center near Memphis would include a major energy installation designed to support the facility’s power needs.
“As you know, xAI builds huge supercomputers and data centers and we build them fast. Currently, we’re building one on the Tennessee-Mississippi state line. As part of today’s commitment, we will take extensive additional steps to continue to reduce the costs of electricity for our neighbors…
“xAI will therefore commit to develop 1.2 GW of power as our supercomputer’s primary power source. That will be for every additional data center as well. We will expand what is already the largest global Megapack power installation in the world,” Shotwell said.
She added that the system would provide significant backup power capacity.
“The installation will provide enough backup power to power the city of Memphis, and more than sufficient energy to power the town of Southaven, Mississippi where the data center resides. We will build new substations and invest in electrical infrastructure to provide stability to the area’s grid.”
Shotwell also noted that xAI will be supporting the area’s water supply as well.
“We haven’t talked about it yet, but this is actually quite important. We will build state-of-the-art water recycling plants that will protect approximately 4.7 billion gallons of water from the Memphis aquifer each year. And we will employ thousands of American workers from around the city of Memphis on both sides of the TN-MS border,” she noted.
The Ratepayer Protection Pledge was introduced as part of the federal government’s effort to address concerns about rising electricity costs tied to large AI data centers, as noted in an Insider report. Under the agreement, companies developing major AI infrastructure projects committed to covering their own power generation needs and avoiding additional costs for local ratepayers.
Elon Musk
SpaceX to launch Starlink V2 satellites on Starship starting 2027
The update was shared by SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell and Starlink Vice President Mike Nicolls.

SpaceX is looking to start launching its next-generation Starlink V2 satellites in mid-2027 using Starship.
The update was shared by SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell and Starlink Vice President Mike Nicolls during remarks at Mobile World Congress (MWC) in Barcelona, Spain.
“With Starship, we’ll be able to deploy the constellation very quickly,” Nicolls stated. “Our goal is to deploy a constellation capable of providing global and contiguous coverage within six months, and that’s roughly 1,200 satellites.”
Nicolls added that once Starship is operational, it will be capable of launching approximately 50 of the larger, more powerful Starlink satellites at a time, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
The initial deployment of roughly 1,200 next-generation satellites is intended to establish global and contiguous coverage. After that phase, SpaceX plans to continue expanding the system to reach “truly global coverage, including the polar regions,” Nicolls said.
Currently, all Starlink satellites are launched on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket. The next-generation fleet will rely on Starship, which remains in development following a series of test flights in 2025. SpaceX is targeting its next Starship test flight, featuring an upgraded version of the rocket, as soon as this month.
Starlink is currently the largest satellite network in orbit, with nearly 10,000 satellites deployed. Bloomberg Intelligence estimates the business could generate approximately $9 billion in revenue for SpaceX in 2026.
Nicolls also confirmed that SpaceX is rebranding its direct-to-cell service as Starlink Mobile.
The service currently operates with 650 satellites capable of connecting directly to smartphones and has approximately 10 million monthly active users. SpaceX expects that figure to exceed 25 million monthly active users by the end of 2026.








