
News
SpaceX aims to launch critical Crew Dragon abort test before the end of 2019
SpaceX has applied for an FCC Special Temporary Authority license to authorize rocket communications during what is likely Crew Dragon’s In-Flight Abort (IFA) test, now scheduled to occur no earlier than November 23rd.
In line with recent comments from SpaceX executives, a November or December In-Flight Abort test would almost certainly preclude Crew Dragon from launching with astronauts in 2019, pushing the Demo-2 mission into the Q1 2020. Nevertheless, it would serve as a good sign that Crew Dragon remains on track if SpaceX can complete the critical abort test – meant to prove that Dragon can whisk astronauts away from a failing rocket at any point during launch – before the year is out.
The FCC application describes “SpaceX Mission 1357” launch from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex 39A, leased by SpaceX and primarily dedicated to launches involving either Falcon Heavy or Crew Dragon. Most tellingly, the STA request describes the mission as involving a “simulated orbital second stage”, an unusual phrase for SpaceX applications that almost certainly reveals it to be Crew Dragon’s IFA.
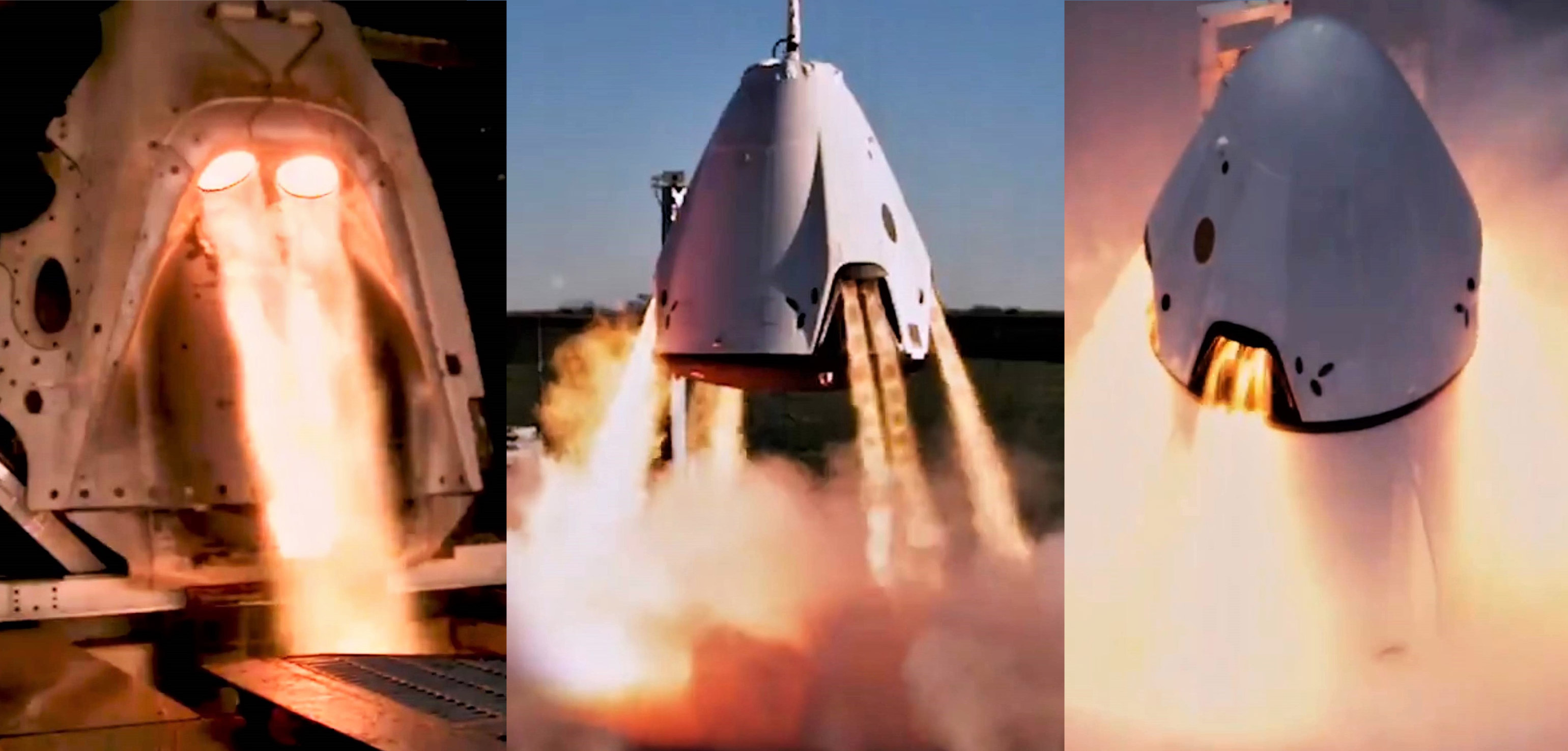
In the history of Falcon 9, all booster launches from Florida or California have carried functional Falcon upper stages. The FCC application’s “simulated” descriptor implies that this particular mission’s upper stage will not actually be capable of flight – a fact Elon Musk confirmed for the In-Flight Abort test in February 2019. Although the upper stage will otherwise be orbit-capable, the stage on Crew Dragon’s abort test is never meant to ignite and will thus feature a mass simulator in place of a functioning Merlin Vacuum (MVac) engine. A flight-proven Falcon 9 Block 5 booster – likely B1046.4 – will power the mission and both it and the upper stage are very unlikely to survive.
During the In-Flight Abort test, the Falcon 9 stack will lift off like any other launch, flying for approximately 60-70 seconds on a normal trajectory. Shortly thereafter, during a period of peak aerodynamic stress known as Max-Q, Crew Dragon’s SuperDraco abort system will somehow be triggered, causing the spacecraft to rapidly speed away from what it perceives to be a failing rocket. As Crew Dragon departs its perch atop Falcon 9’s upper stage, the rocket’s top will be instantly subjected to a supersonic windstream, akin to smashing into a brick wall. If the upper stage is quickly torn away, the booster will find its large, hollow interstage subjected to the same windstream, likely tearing it apart. The mission will undoubtedly be a spectacle regardless of how things transpire.

This filing comes ahead of the imminent resolution of a multi-month investigation to determine the cause of an anomaly that resulted in the loss of the DM-1 Crew Dragon capsule during a static fire test in April 2019. With that investigation nearly wrapped up and the Florida Department of Environmental Protection declaring “no further action” required with clean up efforts, as reported by Florida Today, SpaceX is likely ready to begin prelaunch preparations for Crew Dragon’s next major milestones.
SpaceX recently posted a video highlighting extensive testing of Crew Dragon’s SuperDraco abort system, noting the thrusters’ ability to propel a Crew Dragon capsule half a mile away from a failing rocket in just 7.5 seconds. SpaceX has performed more than 700 successful static fires, ranging from individual double-engine powerpack tests to a 2015 pad-abort test and integrated hover testing before propulsive Crew Dragon landing development was canceled in 2017.
The late-2019 IFA launch window means that a 2019 crewed Dragon debut is more or less impossible. Nevertheless, if SpaceX can successfully complete Crew Dragon’s IFA test in November or December, chances are good that there will be opportunities to attempt Crew Dragon’s crewed launch debut sometime in Q1 2020.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.
News
Tesla launches in India with Model Y, showing pricing will be biggest challenge
Tesla finally got its Model Y launched in India, but it will surely come at a price for consumers.
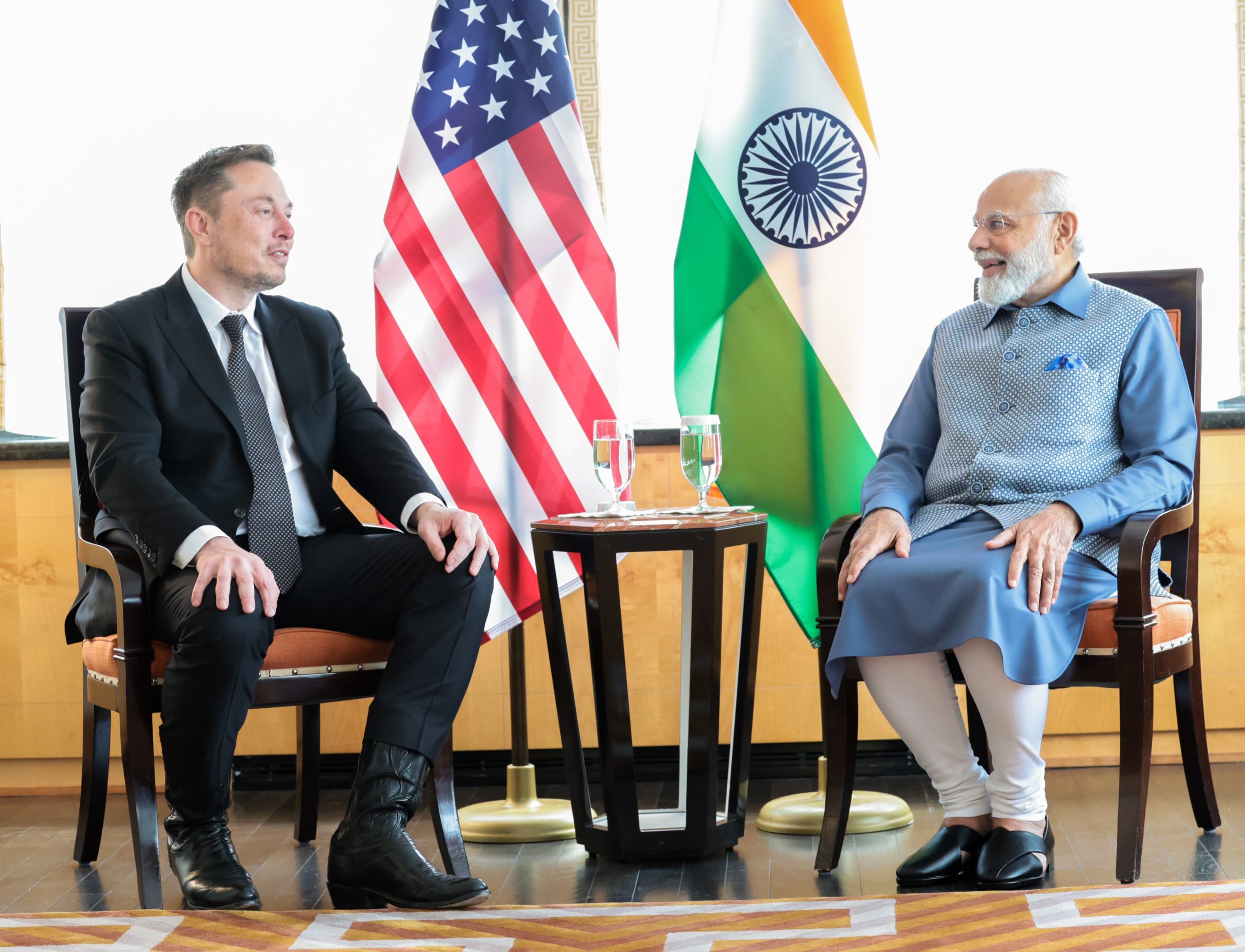

Tesla has officially launched in India following years of delays, as it brought its Model Y to the market for the first time on Tuesday.
However, the launch showed that pricing is going to be its biggest challenge. The all-electric Model Y is priced significantly higher than in other major markets in which Tesla operates.
On Tuesday, Tesla’s Model Y went up for sale for 59,89,000 rupees for the Rear-Wheel Drive configuration, while the Long Range Rear-Wheel Drive was priced at 67,89,000.
This equates to $69,686 for the RWD and $78,994 for the Long Range RWD, a substantial markup compared to what these cars sell for in the United States.
🚨 Here’s the difference in price for the Tesla Model Y in the U.S. compared to India.
🚨 59,89,000 is $69,686
🚨 67,89,000 is $78,994 pic.twitter.com/7EUzyWLcED— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 15, 2025
Deliveries are currently scheduled for the third quarter, and it will be interesting to see how many units they can sell in the market at this price point.
The price includes tariffs and additional fees that are applied by the Indian government, which has aimed to work with foreign automakers to come to terms on lower duties that increase vehicle cost.
Tesla Model Y seen testing under wraps in India ahead of launch
There is a chance that these duties will be removed, which would create a more stable and affordable pricing model for Tesla in the future. President Trump and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi continue to iron out those details.
Maharashtra Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis said to reporters outside the company’s new outlet in the region (via Reuters):
“In the future, we wish to see R&D and manufacturing done in India, and I am sure at an appropriate stage, Tesla will think about it.”
It appears to be eerily similar to the same “game of chicken” Tesla played with Indian government officials for the past few years. Tesla has always wanted to enter India, but was unable to do so due to these import duties.
India wanted Tesla to commit to building a Gigafactory in the country, but Tesla wanted to test demand first.
It seems this could be that demand test, and the duties are going to have a significant impact on what demand will actually be.
Elon Musk
Tesla ups Robotaxi fare price to another comical figure with service area expansion
Tesla upped its fare price for a Robotaxi ride from $4.20 to, you guessed it, $6.90.

Tesla has upped its fare price for the Robotaxi platform in Austin for the first time since its launch on June 22. The increase came on the same day that Tesla expanded its Service Area for the Robotaxi ride-hailing service, offering rides to a broader portion of the city.
The price is up from $4.20, a figure that many Tesla fans will find amusing, considering CEO Elon Musk has used that number, as well as ’69,’ as a light-hearted attempt at comedy over the past several years.
Musk confirmed yesterday that Tesla would up the price per ride from that $4.20 point to $6.90. Are we really surprised that is what the company decided on, as the expansion of the Service Area also took effect on Monday?
But the price is now a princely $6.90, as foretold in the prophecy 😂
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) July 14, 2025
The Service Area expansion was also somewhat of a joke too, especially considering the shape of the new region where the driverless service can travel.
I wrote yesterday about how it might be funny, but in reality, it is more of a message to competitors that Tesla can expand in Austin wherever it wants at any time.
Tesla’s Robotaxi expansion wasn’t a joke, it was a warning to competitors
It was only a matter of time before the Robotaxi platform would subject riders to a higher, flat fee for a ride. This is primarily due to two reasons: the size of the access program is increasing, and, more importantly, the service area is expanding in size.
Tesla has already surpassed Waymo in Austin in terms of its service area, which is roughly five square miles larger. Waymo launched driverless rides to the public back in March, while Tesla’s just became available to a small group in June. Tesla has already expanded it, allowing new members to hail a ride from a driverless Model Y nearly every day.
The Robotaxi app is also becoming more robust as Tesla is adding new features with updates. It has already been updated on two occasions, with the most recent improvements being rolled out yesterday.
Tesla updates Robotaxi app with several big changes, including wider service area
News
Tesla Model Y and Model 3 dominate U.S. EV sales despite headwinds
Tesla’s two mainstream vehicles accounted for more than 40% of all EVs sold in the United States in Q2 2025.

Tesla’s Model Y and Model 3 remained the top-selling electric vehicles in the U.S. during Q2 2025, even as the broader EV market dipped 6.3% year-over-year.
The Model Y logged 86,120 units sold, followed by the Model 3 at 48,803. This means that Tesla’s two mainstream vehicles accounted for 43% of all EVs sold in the United States during the second quarter, as per data from Cox Automotive.
Tesla leads amid tax credit uncertainty and a tough first half
Tesla’s performance in Q2 is notable given a series of hurdles earlier in the year. The company temporarily paused Model Y deliveries in Q1 as it transitioned to the production of the new Model Y, and its retail presence was hit by protests and vandalism tied to political backlash against CEO Elon Musk. The fallout carried into Q2, yet Tesla’s two mass-market vehicles still outsold the next eight EVs combined.
Q2 marked just the third-ever YoY decline in quarterly EV sales, totaling 310,839 units. Electric vehicle sales, however, were still up 4.9% from Q1 and reached a record 607,089 units in the first half of 2025. Analysts also expect a surge in Q3 as buyers rush to qualify for federal EV tax credits before they expire on October 1, Cox Automotive noted in a post.
Legacy rivals gain ground, but Tesla holds its commanding lead
General Motors more than doubled its EV volume in the first half of 2025, selling over 78,000 units and boosting its EV market share to 12.9%. Chevrolet became the second-best-selling EV brand, pushing GM past Ford and Hyundai. Tesla, however, still retained a commanding 44.7% electric vehicle market share despite a 12% drop in in Q2 revenue, following a decline of almost 9% in Q1.
Incentives reached record highs in Q2, averaging 14.8% of transaction prices, roughly $8,500 per vehicle. As government support winds down, the used EV market is also gaining momentum, with over 100,000 used EVs sold in Q2.
Q2 2025 Kelley Blue Book EV Sales Report by Simon Alvarez on Scribd
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoTesla debuts hands-free Grok AI with update 2025.26: What you need to know
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 Elon Musk5 days ago
Elon Musk5 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales















