News
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk reveals next-generation Starlink satellite details
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk has revealed the first technical details about the company’s next-generation Starlink ‘Gen2’ satellite design, confirming that it will far outmatch the current generation of satellites by almost every measure.
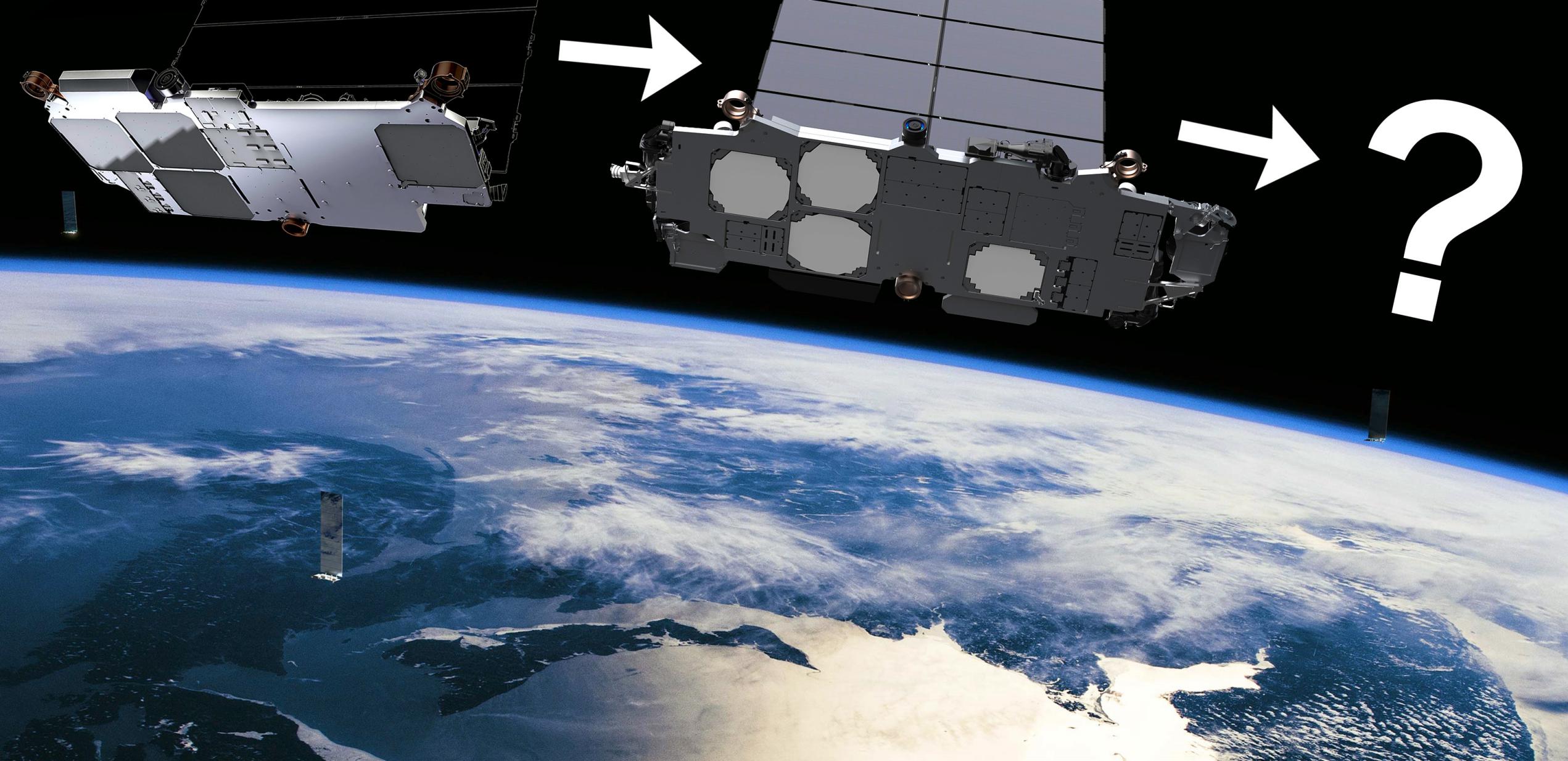
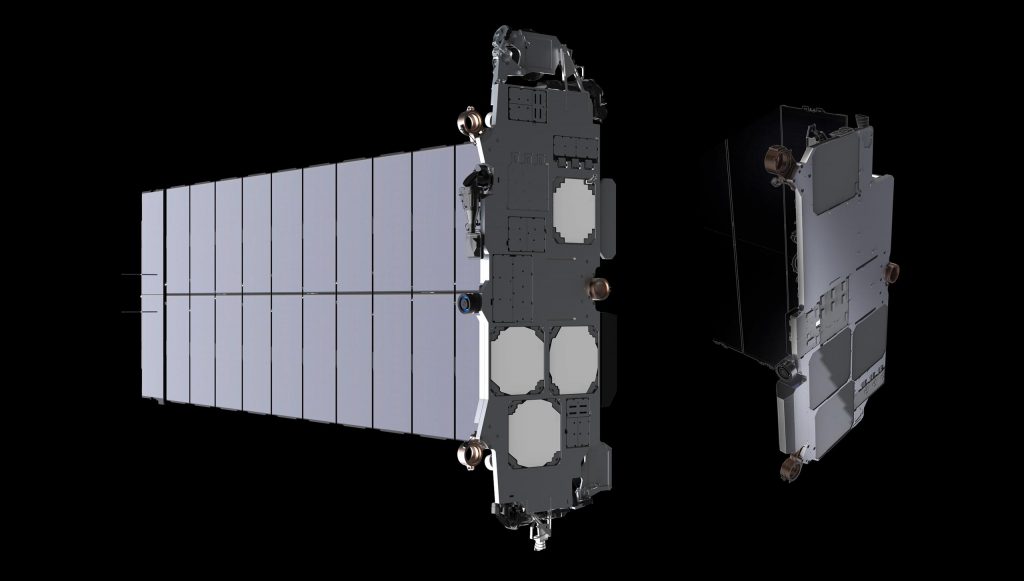
Speaking in an onsite interview and Starbase tour with YouTuber Tim Dodd (The Everyday Astronaut), Musk – largely unprovoked – revealed that SpaceX has already built at least one functional Starlink Gen2/V2.0 satellite prototype and shipped it to the South Texas Starship factory, where it is currently being stored. More importantly, Musk also provided the first direct specifications for the next-generation spacecraft, stating that each Starlink V2.0 satellite will weigh about 1.25 tons (~2750 lb), measure about seven meters (~23 ft) long, and be almost an order of magnitude more capable than the “Starlink 1” satellites they’ll ultimately supersede.
Almost ten months after SpaceX first revealed its updated plans for a next-generation, 30,000-satellite constellation, those details have confirmed a few key points of speculation about the future of Starlink.
The 1st #SpaceX #Starlink Gen 2 #satellite has been produced. It’s 7 meters long & 1.2 tons, @elonmusk says. Note: that’s 4-5X more massive than Gen 1!
Musk adds, the new version will be almost an order of magnitude more capable than Starlink 1 in terms of useful data throughput.— Stan Shull (@stanshull) May 26, 2022
Back in August 2021, I surmised that just like it has with Falcon 9, SpaceX would again try to optimize its new Starlink V2.0 satellite design to take maximum advantage of Starship’s launch performance. In an updated Starlink Gen2 filing, the company conveniently revealed that a version of the constellation optimized for Starship would be structured such that the rocket could launch an entire orbital plane (one ring of satellites spaced evenly around the Earth) in one go. In that constellation variant, all but ~500 (1.5%) of almost 30,000 spacecraft would be stationed in planes of 110 or 120 satellites, meaning that it was safe to assume that SpaceX meant that every Starship would nominally carry 110-120 satellites. Using Musk’s latest optimistic Starship performance estimate of 150 tons to low Earth orbit (LEO), that all but guaranteed that a Starship-optimized Starlink V2.0 satellite would weigh up to 1250 kilograms.
Musk has now explicitly confirmed that each Starlink V2.0 satellite will weigh… “about one and a quarter tons” or 1250 kilograms. Starlink V1.0 and V1.5 satellites weigh around 260 and 310 kilograms, respectively, meaning that Starlink V2.0 satellites will be about a bit more than four times heavier than V1.5 and a bit less than five times heavier than V1.0.
Musk also revealed that V2.0 satellites will be “almost an order of magnitude more capable than Starlink 1.” He refused to call that capability bandwidth or throughput, the traditional method of describing a communication satellite’s total performance, but Starlink V1.0 satellites are believed to have a total bandwidth of 18 gigabits per second (18 Gbps). As of today, it’s unknown if Starlink V1.5 – a significant upgrade – also added more bandwidth, nor if Musk was referring to that latest Starlink V1.x iteration. But even if he was comparing V2.0 with the earliest V1.0 satellites, it’s possible that each Starlink V2.0 satellite could add around 140-160 Gbps to the 30,000-satellite constellation.

Ultimately, specific numbers aren’t needed to emphasize the importance of the details Musk provided. If true, they mean that Starlink V2.0 will pack roughly twice as much usable bandwidth into a given unit of satellite mass compared to V1.x. Combined with the fact that Starship could offer ~10 times as much performance to LEO as Falcon 9, a single Starship launch could theoretically expand total network capacity roughly twenty times more than one Falcon 9 launch. For example, each Falcon 9 launch of 60 260-kilogram Starlink V1.0 satellites added about 1080 Gbps of instantaneous bandwidth to the constellation. A Starship launch of 120 1250-kilogram Starlink V2.0 satellites could add around 19,000 Gbps (19 terabits per second).
Even despite those massive advantages, SpaceX’s Starlink Gen2 ambitions still leave it no slack whatsoever. If the FCC approves its license request, SpaceX would need to launch half of the constellation within six years – equivalent to around 130 Starship launches or 22 Starship launches per year. In comparison, Falcon 9 – a rocket that’s ten times smaller, less reusable, and has been flying since 2010 – did not achieve 22 launches in one year until 2020. For Starship to have any hope of achieving the cadence Starlink Gen2 requires, SpaceX would have to ramp up launches of the largest rocket ever built at a truly miraculous pace and suffer very few failures or setbacks along the way.
As immense as the challenge may be, the potential rewards are just as high. A constellation of 30,000 Starlink V2.0 satellites – if spaced evenly around the Earth – could have a total bandwidth of ~1250 terabits per second (Tbps) available over land (excluding Antarctica) at any given second. Even if half of that bandwidth is needed for backhaul and routing, the total installed bandwidth of global internet infrastructure was estimated to be 600 Tbps in 2020. Starlink will always be bottlenecked by the number of satellites that can be simultaneously available over any single point on Earth, so the constellation will never be able to match a ground network 1:1 with the same installed capacity, but it’s safe to assume that Starlink Gen2 could serve tens or even hundreds of millions of users located anywhere on Earth if SpaceX is able to build it.

News
Tesla looks to upgrade Matrix Headlights with new features
According to the update, Tesla will work on improving the headlights when coming into contact with highly reflective objects, including road signs, traffic signs, and street lights. Additionally, pixel-level dimming will happen in two stages, whereas it currently performs with just one, meaning on or off.
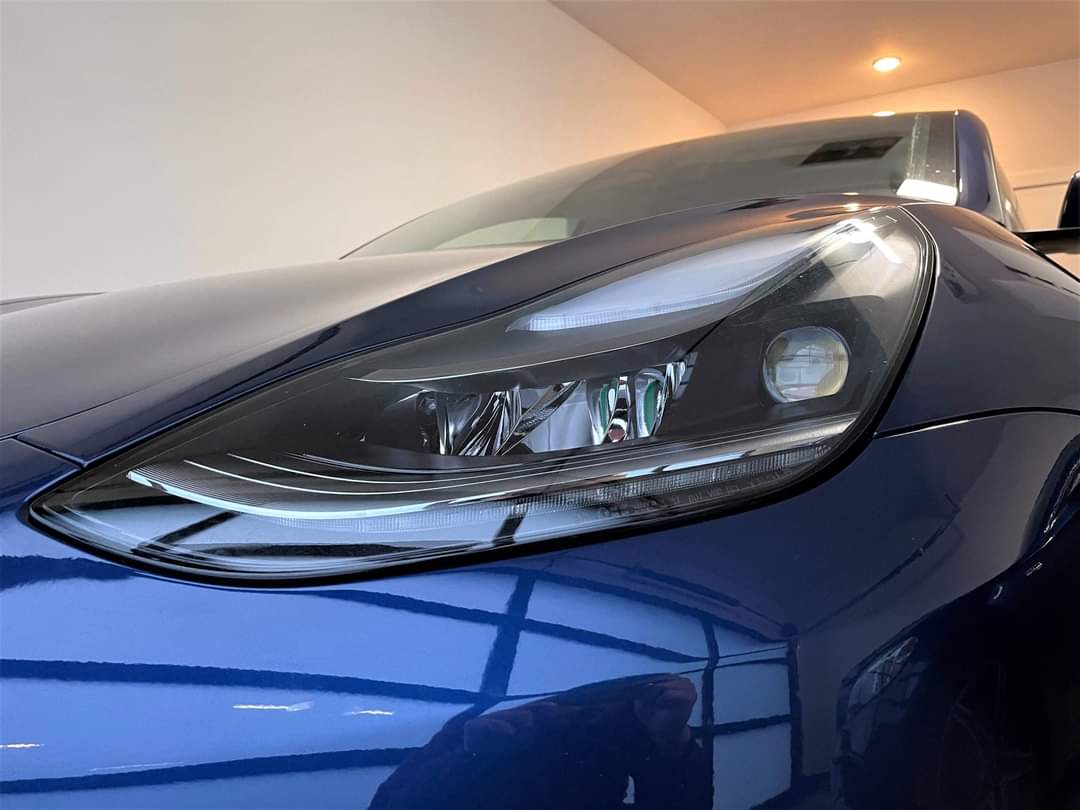

Tesla is looking to upgrade its Matrix Headlights, a unique and high-tech feature that is available on several of its vehicles. The headlights aim to maximize visibility for Tesla drivers while being considerate of oncoming traffic.
The Matrix Headlights Tesla offers utilize dimming of individual light pixels to ensure that visibility stays high for those behind the wheel, while also being considerate of other cars by decreasing the brightness in areas where other cars are traveling.
Here’s what they look like in action:
- Credit: u/ObjectiveScratch | Reddit
- Credit: u/ObjectiveScratch | Reddit
As you can see, the Matrix headlight system intentionally dims the area where oncoming cars would be impacted by high beams. This keeps visibility at a maximum for everyone on the road, including those who could be hit with bright lights in their eyes.
There are still a handful of complaints from owners, however, but Tesla appears to be looking to resolve these with the coming updates in a Software Version that is currently labeled 2026.2.xxx. The coding was spotted by X user BERKANT:
🚨 Tesla is quietly upgrading Matrix headlights.
Software https://t.co/pXEklQiXSq reveals a hidden feature:
matrix_two_stage_reflection_dip
This is a major step beyond current adaptive high beams.
What it means:
• The car detects highly reflective objects
Road signs,… pic.twitter.com/m5UpQJFA2n— BERKANT (@Tesla_NL_TR) February 24, 2026
According to the update, Tesla will work on improving the headlights when coming into contact with highly reflective objects, including road signs, traffic signs, and street lights. Additionally, pixel-level dimming will happen in two stages, whereas it currently performs with just one, meaning on or off.
Finally, the new system will prevent the high beams from glaring back at the driver. The system is made to dim when it recognizes oncoming cars, but not necessarily objects that could produce glaring issues back at the driver.
Tesla’s revolutionary Matrix headlights are coming to the U.S.
This upgrade is software-focused, so there will not need to be any physical changes or upgrades made to Tesla vehicles that utilize the Matrix headlights currently.
Elon Musk
xAI’s Grok approved for Pentagon classified systems: report
Under the agreement, Grok can be deployed in systems handling classified intelligence analysis, weapons development, and battlefield operations.

Elon Musk’s xAI has signed an agreement with the United States Department of Defense (DoD) to allow Grok to be used in classified military systems.
Previously, Anthropic’s Claude had been the only AI system approved for the most sensitive military work, but a dispute over usage safeguards has reportedly prompted the Pentagon to broaden its options, as noted in a report from Axios.
Under the agreement, Grok can be deployed in systems handling classified intelligence analysis, weapons development, and battlefield operations.
The publication reported that xAI agreed to the Pentagon’s requirement that its technology be usable for “all lawful purposes,” a standard Anthropic has reportedly resisted due to alleged ethical restrictions tied to mass surveillance and autonomous weapons use.
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth is scheduled to meet with Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei in what sources expect to be a tense meeting, with the publication hinting that the Pentagon could designate Anthropic a “supply chain risk” if the company does not lift its safeguards.
Axios stated that replacing Claude fully might be technically challenging even if xAI or other alternative AI systems take its place. That being said, other AI systems are already in use by the DoD.
Grok already operates in the Pentagon’s unclassified systems alongside Google’s Gemini and OpenAI’s ChatGPT. Google is reportedly close to an agreement that will result in Gemini being used for classified use, while OpenAI’s progress toward classified deployment is described as slower but still feasible.
The publication noted that the Pentagon continues talks with several AI companies as it prepares for potential changes in classified AI sourcing.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk denies Starlink’s price cuts are due to Amazon Kuiper
“This has nothing to do with Kuiper, we’re just trying to make Starlink more affordable to a broader audience,” Musk wrote in a post on X.

Elon Musk has pushed back on claims that Starlink’s recent price reductions are tied to Amazon’s Kuiper project.
In a post on X, Musk responded directly to a report suggesting that Starlink was cutting prices and offering free hardware to partners ahead of a planned IPO and increased competition from Kuiper.
“This has nothing to do with Kuiper, we’re just trying to make Starlink more affordable to a broader audience,” Musk wrote in a post on X. “The lower the cost, the more Starlink can be used by people who don’t have much money, especially in the developing world.”
The speculation originated from a post summarizing a report from The Information, which ran with the headline “SpaceX’s Starlink Makes Land Grab as Amazon Threat Looms.” The report stated that SpaceX is aggressively cutting prices and giving free hardware to distribution partners, which was interpreted as a reaction to Amazon’s Kuiper’s upcoming rollout and possible IPO.
In a way, Musk’s comments could be quite accurate considering Starlink’s current scale. The constellation currently has more than 9,700 satellites in operation today, making it by far the largest satellite broadband network in operation. It has also managed to grow its user base to 10 million active customers across more than 150 countries worldwide.
Amazon’s Kuiper, by comparison, has launched approximately 211 satellites to date, as per data from SatelliteMap.Space, some of which were launched by SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket. Starlink surpassed that number in early January 2020, during the early buildout of its first-generation network.
Lower pricing also aligns with Starlink’s broader expansion strategy. SpaceX continues to deploy satellites at a rapid pace using Falcon 9, and future launches aboard Starship are expected to significantly accelerate the constellation’s growth. A larger network improves capacity and global coverage, which can support a broader customer base.
In that context, price reductions can be viewed as a way to match expanding supply with growing demand. Musk’s companies have historically used aggressive pricing strategies to drive adoption at scale, particularly when vertical integration allows costs to decline over time.










