On the heels of SpaceX’s last launch of 2021, which rounded out a record-breaking year and marked the 100th successful Falcon booster landing, the time has come to look at what the new year might hold for the world’s most prolific commercial launch provider and its workhorse rockets.
Thanks in part to a number of delays that pushed a significant portion of SpaceX’s planned 2021 launches into next year, the company’s 2022 launch manifest is bigger than any other year in its already impressive history. In 2021, having completed 31 orbital launches, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 was the single most launched rocket in the world – beating out several Russian and Chinese rockets operated by each country’s national space agency. On its own, Falcon 9 launched six more times than the entire country of Russia.
However, despite how impressive SpaceX’s performance was this year, all evidence suggests that 2022 could see almost twice as many Falcon launches as 2021.
That information comes from unofficial manifests maintained by fans and followers, who collate dozens of different reports, press releases, and rumors to create a rough picture of upcoming launch plans. Of course, the farther away any given launch is; the more likely it will be significantly delayed. Even official information from SpaceX itself would not be able to accurately predict how many launches it will conduct over a year or more, but the manifests are still useful tools for rough predictions.
In general, short of a major launch failure grounding a given rocket or some other unforeseen catastrophe (2021’s semiconductor supply issues, for example), unofficial manifests have been maybe 60-80% accurate. In the case of 2022, two such well-maintained manifests agree that SpaceX has approximately 40 launches currently scheduled next year – including up to 5 Falcon Heavy missions and at least 35 Falcon 9 launches. SpaceX has never had more launches scheduled in a single year. Simultaneously, after SpaceX’s 2021 performance, 2022 is the first time it’s been possible to seriously believe that the company might actually be able to complete 40 commercial launches in one year. And even then, that figure is still only part of the story.

Starlink
In 2021, SpaceX completed 17 successful dedicated Starlink missions, launching just shy of 1000 satellites – 989 to be exact – in a single year. In the first five months of 2021, before unknown issues caused an unintended Starlink launch hiatus, SpaceX completed 13 of those dedicated Starlink launches. In other words, if satellite production had kept up with SpaceX’s Falcon fleet, the company was technically on track to complete more than 30 Starlink launches in a single year, which – combined with all other missions – would have amounted to a total of 43 launches in 2021.
That specificity is important because – save for a single Starlink mission – the ~40 commercial launches on SpaceX’s 2022 manifest entirely exclude Starlink launches. Given that skipping or intentionally throttling a full year of Starlink launches is simply out of the question for SpaceX, that means that the company has approximately 40 commercial missions to launch on top of one or two dozen potential Starlink V1.5 missions. Assuming that Starlink V1.5 production remains somewhat constrained relative to Starlink V1.0, which peaked at an implied average of more than 1800 satellites per year in H1 2021, it might be reasonable to expect up to 20 (rather than 30) Starlink V1.5 launches in 2022 if production remains steady.
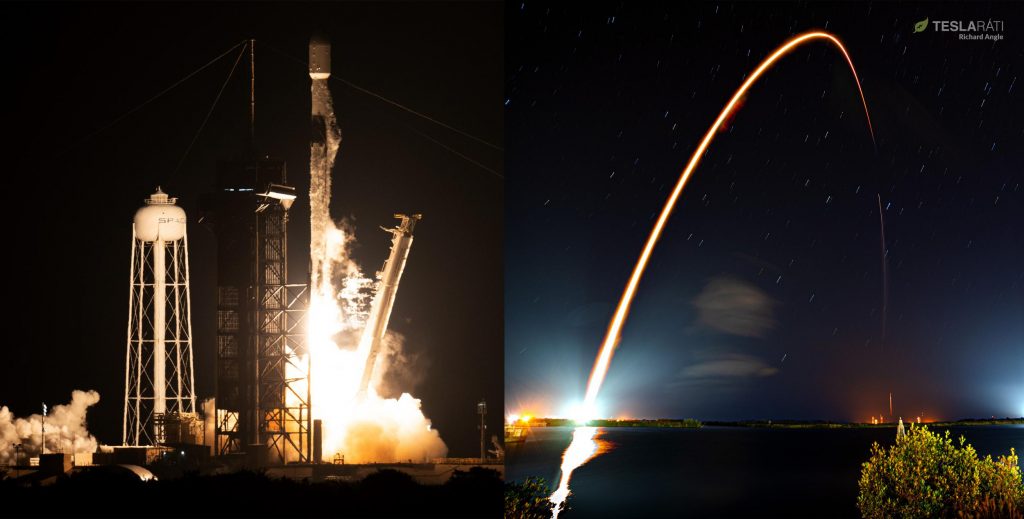



Combined, that means that SpaceX’s nominal 2022 manifest might actually include up to 60 Falcon launches. The question, then, is whether there is any chance at all for SpaceX to actually complete an average of more than one launch per week next year. Conveniently, SpaceX itself seemingly answered that question just this month. In December 2021, the company – pushing all three of its orbital pads to their limits – completed a record five Falcon 9 launches. Technically, it actually completed those five launches in a mere 19 days. Including NASA’s DART mission, which SpaceX launched on November 24th, the company ultimately launched six Falcon 9 rockets in less than four weeks (27 days).
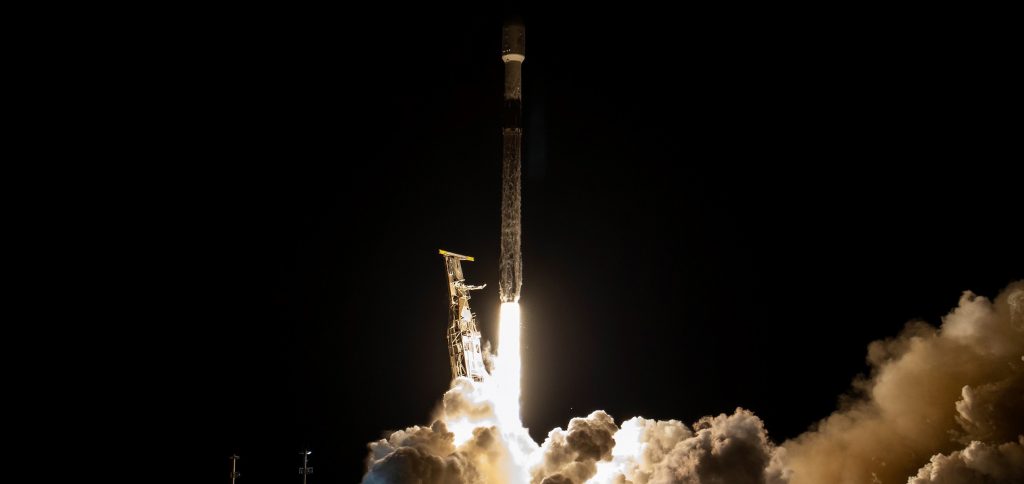
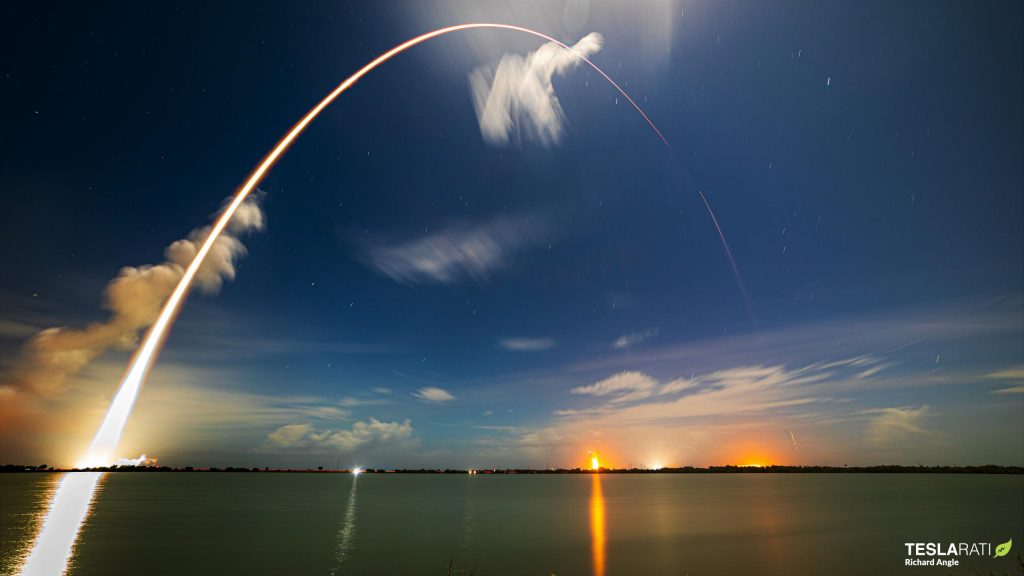



Given the company’s recent cadence records and the turnaround records of each of the three pads used to achieve them, it’s clear that SpaceX could technically repeat that feat – a burst of five launches in 3-4 weeks – every month. Obviously, that’s easier said than done and it’s inherently unlikely for a record-breaking monthly launch cadence to become the norm immediately after, but the achievement still demonstrates that SpaceX is technically capable of launching five times in three weeks and then being ready to do so again by the start of the next month.
Averaged over 2022, 5 launches per month would equate to 60 launches per year. In other words, while unlikely, it’s by no means impossible for SpaceX to replicate 2021’s Starlink launch cadence and simultaneously complete as many as 40 commercial launches. In reality, a more plausible outcome for 2022 might be 5-10 commercial launches slipping into 2023 and SpaceX ultimately completing around 30-35 commercial launches and ~15 dedicated Starlink missions for a total of 45-50 – still an extraordinary hypothetical achievement by any measure. Going off of recent trends, which have seen SpaceX’s annual cadence grow from 21 (2018) and 26 (2020) to 31 (2021), 35-40 launches would be a still more conservative estimate for 2022.
Regardless, even excluding Starship, the year is set to be quite the spectacle for SpaceX. The 40 commercial missions tentatively on the company’s manifest include two Crew Dragon NASA astronaut launches, one or two private Crew Dragon missions to the International Space Station, up to 3 commercial Moon landers, a Korean Moon orbiter, NASA’s Psyche asteroid explorer, and as many as five or six Falcon Heavy launches.

Elon Musk
What is Digital Optimus? The new Tesla and xAI project explained
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Tesla and xAI announced their groundbreaking joint project, Digital Optimus, also nicknamed “Macrohard” in a humorous jab at Microsoft, earlier this week.
This software-based AI agent is designed to automate complex office workflows by observing and replicating human interactions with computers. As the first major outcome of Tesla’s $2 billion investment in xAI, it represents a powerful fusion of hardware efficiency and advanced reasoning.
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Macrohard or Digital Optimus is a joint xAI-Tesla project, coming as part of Tesla’s investment agreement with xAI.
Grok is the master conductor/navigator with deep understanding of the world to direct digital Optimus, which is processing and actioning the past 5 secs of…
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 11, 2026
Tesla’s specialized AI acts as “System 1”—the fast, instinctive executor—processing the past five seconds of real-time computer screen video along with keyboard and mouse actions to perform immediate tasks.
xAI’s Grok model serves as “System 2,” the strategic “master conductor” or navigator, providing high-level reasoning, world understanding, and directional oversight, much like an advanced turn-by-turn navigation system.
When combined, the two can create a powerful AI-based assistant that can complete everything from accounting work to HR tasks.
Will Tesla join the fold? Predicting a triple merger with SpaceX and xAI
The system runs primarily on Tesla’s low-cost AI4 inference chip, minimizing expensive Nvidia resources from xAI for competitive, real-time performance.
Elon Musk described it as “the only real-time smart AI system” capable, in principle, of emulating the functions of entire companies, handling everything from accounting and HR to repetitive digital operations.
Timelines point to swift deployment. Announced just days ago, Musk expects Digital Optimus to be ready for user experience within about six months, targeting rollout around September 2026.
It will integrate into all AI4-equipped Tesla vehicles, enabling parked cars to handle office work during downtime. Millions of dedicated units are also planned for deployment at Supercharger stations, tapping into roughly 7 gigawatts of available power.
Oh and it works in all AI4-equipped cars, so your car can do office work for you when not driving.
We’re also deploying millions of dedicated Digital Optimus units in the field at Superchargers where we have ~7 gigawatts of available power.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 12, 2026
Digital Optimus directly supports Tesla’s broader autonomy strategy. It leverages the same end-to-end neural networks, computer vision, and real-time decision-making tech that power Full Self-Driving (FSD) software and the physical Optimus humanoid robot.
By repurposing idle vehicle compute and extending AI4 hardware beyond driving, the project scales Tesla’s autonomy ecosystem from roads to digital workspaces.
As a virtual counterpart to physical Optimus, it divides labor: software agents manage screen-based tasks while humanoid robots tackle physical ones, accelerating Tesla’s vision of general-purpose AI for productivity, Robotaxi fleets, and beyond.
In essence, Digital Optimus bridges Tesla’s vehicle and robotics autonomy with enterprise-scale AI, promising massive efficiency gains. No other company currently matches its real-time capabilities on such accessible hardware.
It really could be one of the most crucial developments Tesla and xAI begin to integrate, as it could revolutionize how people work and travel.
News
Tesla adds awesome new driving feature to Model Y
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.

Tesla is adding an awesome new driving feature to Model Y vehicles, effective on Juniper-updated models considered model year 2026 or newer.
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.
Tesla writes in the release notes for the feature:
“Your Tesla now provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.”
🚨 Tesla has added a new “Comfort Braking” update with 2026.8
“Your Tesla provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.” https://t.co/afqCpBSVeA pic.twitter.com/C6MRmzfzls
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
Interestingly, we’re not too sure what catalyzed Tesla to try to improve braking smoothness, because it hasn’t seemed overly abrupt or rough from my perspective. Although the brake pedal in my Model Y is rarely used due to Regenerative Braking, it seems Tesla wanted to try to make the ride comfort even smoother for owners.
There is always room for improvement, though, and it seems that there is a way to make braking smoother for passengers while the vehicle is coming to a stop.
This is far from the first time Tesla has attempted to improve its ride comfort through Over-the-Air updates, as it has rolled out updates to improve regenerative braking performance, handling while using Full Self-Driving, improvements to Steer-by-Wire to Cybertruck, and even recent releases that have combatted Active Road Noise.
Tesla holds a unique ability to change the functionality of its vehicles through software updates, which have come in handy for many things, including remedying certain recalls and shipping new features to the Full Self-Driving suite.
Tesla seems to have the most seamless OTA processes, as many automakers have the ability to ship improvements through a simple software update.
We’re really excited to test the update, so when we get an opportunity to try out Comfort Braking when it makes it to our Model Y.
News
Tesla finally brings a Robotaxi update that Android users will love
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android.

Tesla is finally bringing an update of its Robotaxi platform that Android users will love — mostly because it seems like they will finally be able to use the ride-hailing platform that the company has had active since last June.
Based on a decompile of software version 26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app, Tesla looks to be ready to roll out access to Android users.
According to the breakdown, performed by Tesla App Updates, the company is preparing to roll out an Android version of the app as it is developing several features for that operating system.
🚨 It looks like Tesla is preparing to launch the Robotaxi app for Android users at last!
A decompile of v26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app shows some progress on the Android side for Robotaxi 🤖 🚗 https://t.co/mThmoYuVLy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android:
“Strings like notification_channel_robotaxid_trip_name and android_native_alicorn_eta_text show exactly how Tesla plans to replicate the iOS Live Activities experience. Instead of standard push alerts, Android users are getting a persistent, dynamically updating notification channel.”
This is a big step forward for several reasons. From a face-value perspective, Tesla is finally ready to offer Robotaxi to Android users.
The company has routinely prioritized Apple releases because there is a higher concentration of iPhone users in its ownership base. Additionally, the development process for Apple is simply less laborious.
Tesla is working to increase Android capabilities in its vehicles
Secondly, the Robotaxi rollout has been a typical example of “slowly then all at once.”
Tesla initially released Robotaxi access to a handful of media members and influencers. Eventually, it was expanded to more users, so that anyone using an iOS device could download the app and hail a semi-autonomous ride in Austin or the Bay Area.
Opening up the user base to Android users may show that Tesla is preparing to allow even more users to utilize its Robotaxi platform, and although it seems to be a few months away from only offering fully autonomous rides to anyone with app access, the expansion of the user base to an entirely different user base definitely seems like its a step in the right direction.










