

News
SpaceX fires up redesigned Crew Dragon as NASA reveals SuperDraco thruster “flaps”
On November 13th, SpaceX revealed that a planned static fire test of a Crew Dragon’s powerful abort thrusters was completed without issue, a strong sign that the company has successfully redesigned the spacecraft to prevent a catastrophic April 2019 explosion from reoccurring.
Pending a far more extensive analysis, Wednesday’s static fire should leave SpaceX on track to perform Crew Dragon’s next major flight test before the end of 2019.
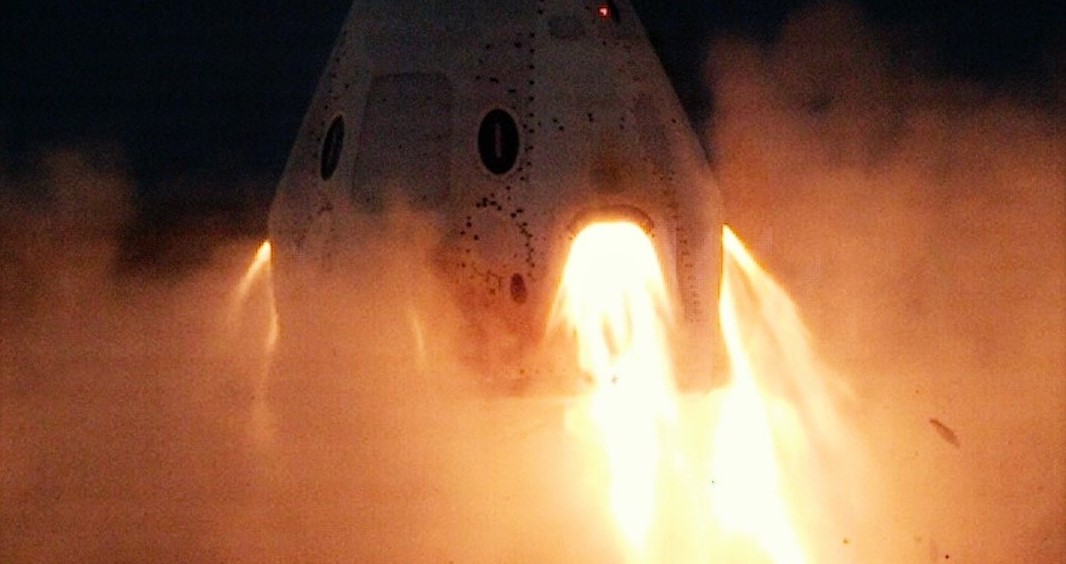
In an unexpected flourish of transparency, SpaceX and NASA published photos of the Crew Dragon capsule’s static fire test just a few hours after it was completed, an excellent sign that the ‘quick-look’ data analysis immediately following the test was extremely positive. Spaceflight Now was first to visually confirm that the test had occurred, publishing a photo that revealed a whitish cloud of smoke produced by the static fire around 3:15 pm EST (20:15 UTC).
Had a failure similar to the April 2019 explosion occurred, that cloud would have likely been tinged red by unburnt dinitrogen tetroxide (NTO) oxidizer, and the different appearance of November 13th’s exhaust cloud was seen as the first tentative sign that this static fire had gone more successfully.
Alongside photos of the SuperDraco thruster test published by NASA and SpaceX shortly after its conclusion, SpaceX confirmed that the test was completed without issue. Regardless of whether everything performed exactly as intended, this means that factory-fresh Crew Dragon capsule C205 made it through the test unscathed, likely securing SpaceX and NASA a large volume of uninterrupted telemetry data, as well as the hardware itself.
Just hours after C205’s static fire was completed, NASA published a detailed update, confirming that the tests were finished without any immediately apparent issues.
NASA described the test in much more detail than SpaceX, noting that it began with the ignition of two of Crew Dragon’s 16 Draco maneuvering thrusters, each performing two one-second burns. C205’s eight SuperDraco abort thrusters subsequently ignited and burned for a total of ~9 seconds to simulate required abort performance, followed by the reignition of two Draco thrusters immediately after SuperDraco cutoff.
Each capable of producing several dozen pounds of thrust, both Crew and Cargo Dragon use Draco thrusters to orient themselves in orbit, rendezvous with the International Space Station, and lower their orbits to reenter Earth’s atmosphere. Crew Dragon’s Draco thrusters are also designed to control its attitude during abort scenarios, stabilizing and flipping the spacecraft to prevent a loss of control and ensure proper orientation during emergency parachute deployment. The Draco firings during Crew Dragon’s November 13th static fire were meant to simulate that additional use-case.
Aside from verifying that SpaceX has successfully redesigned Crew Dragon to mitigate the failure mode that caused capsule C201’s catastrophic explosion in April 2019, the Draco static fires specifically mirrored the burns Crew Dragon C205 will need to perform to successfully complete its In-Flight Abort (IFA) test. As noted by NASA and SpaceX, with the static fire complete, both teams will now comb through the data produced, inspect Crew Dragon to verify its health and the performance of its redesigned high-flow pressurization system, and perform any necessary refurbishment.
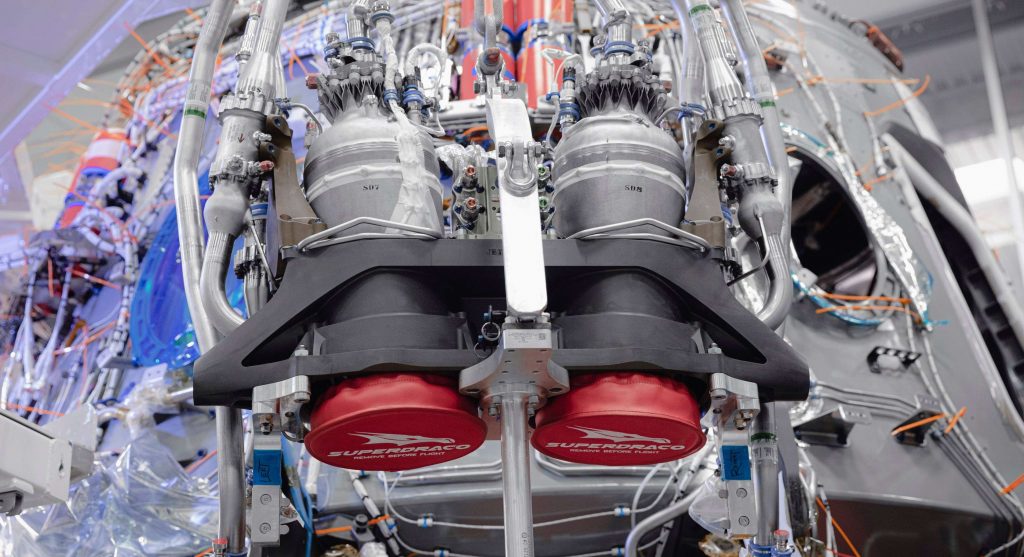
SuperDraco’s mystery “flaps”
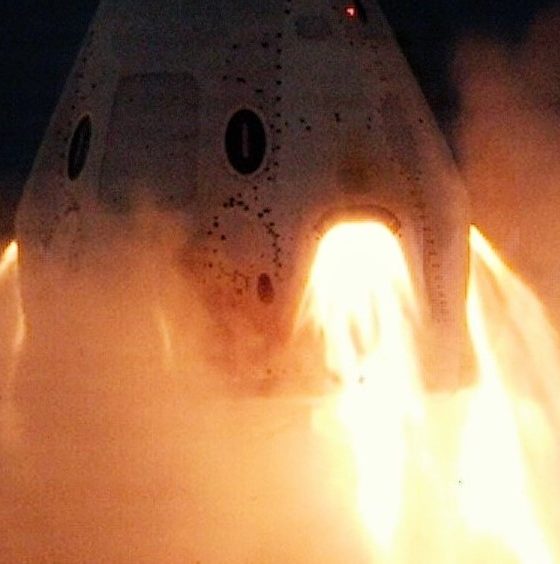
NASA’s post on Crew Dragon’s static fire revealed another thoroughly intriguing detail: the SpaceX spacecraft’s SuperDraco thrusters apparently have flaps! A bit of retroactive speculation suggests that SuperDracos are closed out with plugs of some sort to create a seal against the environment before Crew Dragon is rolled out to the launch pad. Perhaps, in the event of a SuperDraco ignition, SpaceX included actuating flaps as a method of resealing those thrusters prior to splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean.
“Immediately after the SuperDracos shut down, two Dracos thrusters fired and all eight SuperDraco flaps closed, mimicking the sequence required to reorient the spacecraft in-flight to a parachute deploy attitude and close the flaps prior to reentry. The full sequence, from SuperDraco startup to flap closure, spanned approximately 70 seconds.”
NASA, November 13th, 2019

Given that the obvious utility of those flaps appears to be extremely limited and their associated actuators have to survive the 9+ consecutive seconds of hellish conditions in the event of an actual abort, it seems like an excessively complicated system to include on Crew Dragon. Nevertheless, the ability to guarantee that SuperDracos are water-sealed before splashdown would almost without a doubt make Crew Dragon far easier to refurbish and reuse.
The SuperDraco flaps may also be a holdover from before propulsive Crew Dragon landings were canceled, although the use-cases for such a system still remain unclear. The flaps’ raison d’etre could even be as simple as preventing water intrusion that might otherwise cause Dragon to sink after splashdown.
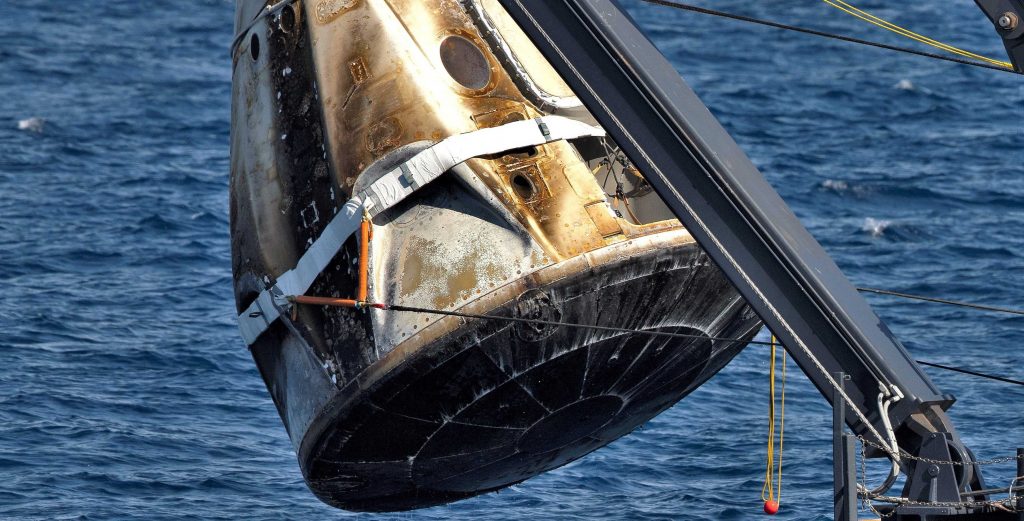

Regardless of why they exist, NASA indicates that SpaceX’s November 13th static fire proved that they worked exactly as expected, closing soon after the simulated abort burn to seal Crew Dragon against water intrusion. If NASA and SpaceX’s deep-dive inspections and data analysis uncover no red flags, it’s extremely likely that SpaceX will able to launch C205 for its In-Flight Abort test some 4-8 weeks from now.
If the IFA also goes as planned, Crew Dragon could be ready for its inaugural NASA astronaut launch as early as February or March 2020.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
Tesla adds awesome new driving feature to Model Y
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.

Tesla is adding an awesome new driving feature to Model Y vehicles, effective on Juniper-updated models considered model year 2026 or newer.
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.
Tesla writes in the release notes for the feature:
“Your Tesla now provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.”
🚨 Tesla has added a new “Comfort Braking” update with 2026.8
“Your Tesla provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.” https://t.co/afqCpBSVeA pic.twitter.com/C6MRmzfzls
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
Interestingly, we’re not too sure what catalyzed Tesla to try to improve braking smoothness, because it hasn’t seemed overly abrupt or rough from my perspective. Although the brake pedal in my Model Y is rarely used due to Regenerative Braking, it seems Tesla wanted to try to make the ride comfort even smoother for owners.
There is always room for improvement, though, and it seems that there is a way to make braking smoother for passengers while the vehicle is coming to a stop.
This is far from the first time Tesla has attempted to improve its ride comfort through Over-the-Air updates, as it has rolled out updates to improve regenerative braking performance, handling while using Full Self-Driving, improvements to Steer-by-Wire to Cybertruck, and even recent releases that have combatted Active Road Noise.
Tesla holds a unique ability to change the functionality of its vehicles through software updates, which have come in handy for many things, including remedying certain recalls and shipping new features to the Full Self-Driving suite.
Tesla seems to have the most seamless OTA processes, as many automakers have the ability to ship improvements through a simple software update.
We’re really excited to test the update, so when we get an opportunity to try out Comfort Braking when it makes it to our Model Y.
News
Tesla finally brings a Robotaxi update that Android users will love
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android.

Tesla is finally bringing an update of its Robotaxi platform that Android users will love — mostly because it seems like they will finally be able to use the ride-hailing platform that the company has had active since last June.
Based on a decompile of software version 26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app, Tesla looks to be ready to roll out access to Android users.
According to the breakdown, performed by Tesla App Updates, the company is preparing to roll out an Android version of the app as it is developing several features for that operating system.
🚨 It looks like Tesla is preparing to launch the Robotaxi app for Android users at last!
A decompile of v26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app shows some progress on the Android side for Robotaxi 🤖 🚗 https://t.co/mThmoYuVLy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android:
“Strings like notification_channel_robotaxid_trip_name and android_native_alicorn_eta_text show exactly how Tesla plans to replicate the iOS Live Activities experience. Instead of standard push alerts, Android users are getting a persistent, dynamically updating notification channel.”
This is a big step forward for several reasons. From a face-value perspective, Tesla is finally ready to offer Robotaxi to Android users.
The company has routinely prioritized Apple releases because there is a higher concentration of iPhone users in its ownership base. Additionally, the development process for Apple is simply less laborious.
Tesla is working to increase Android capabilities in its vehicles
Secondly, the Robotaxi rollout has been a typical example of “slowly then all at once.”
Tesla initially released Robotaxi access to a handful of media members and influencers. Eventually, it was expanded to more users, so that anyone using an iOS device could download the app and hail a semi-autonomous ride in Austin or the Bay Area.
Opening up the user base to Android users may show that Tesla is preparing to allow even more users to utilize its Robotaxi platform, and although it seems to be a few months away from only offering fully autonomous rides to anyone with app access, the expansion of the user base to an entirely different user base definitely seems like its a step in the right direction.
News
Lucid unveils Lunar Robotaxi in bid to challenge Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
Lucid’s Lunar robotaxi is gunning for Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering.jpg)
Lucid Group pulled back the curtain on its purpose-built autonomous robotaxi platform dubbed the Lunar Concept. Announced at its New York investor day event, Lunar is arguably the company’s most ambitious concept yet, and a direct line of sight toward the autonomous ride haling market that Tesla looks to control.
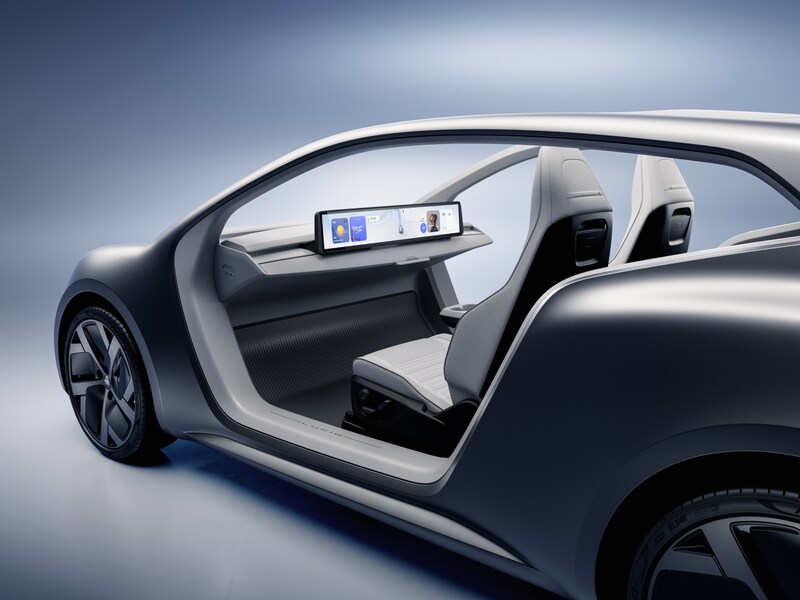

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
A comparison to Tesla’s Cybercab is unavoidable. The concept of a Tesla robotaxi was first introduced by Elon Musk back in April 2019 during an event dubbed “Autonomy Day,” where he envisioned a network of self-driving Tesla vehicles transporting passengers while not in use by their owners. That vision took another major step in October 2024 when, Musk unveiled the Cybercab at the Tesla “We, Robot” event held at Warner Bros. Studios in Burbank, California, where 20 concept Cybercabs autonomously drove around the studio lot giving rides to attendees.
Fast forward to today, and Tesla’s ambitions are finally materializing, but not without friction. As we recently reported, the Cybercab is being spotted with increasing frequency on public roads and across the grounds of Gigafactory Texas, suggesting that the company’s road testing and validation program is ramping meaningfully ahead of mass production. Tesla already operates a small scale robotaxi service in Austin using supervised Model Ys, but the Cybercab is designed from the ground up for high-volume, low-cost production, with Musk stating an eventual goal of producing one vehicle every 10 seconds.
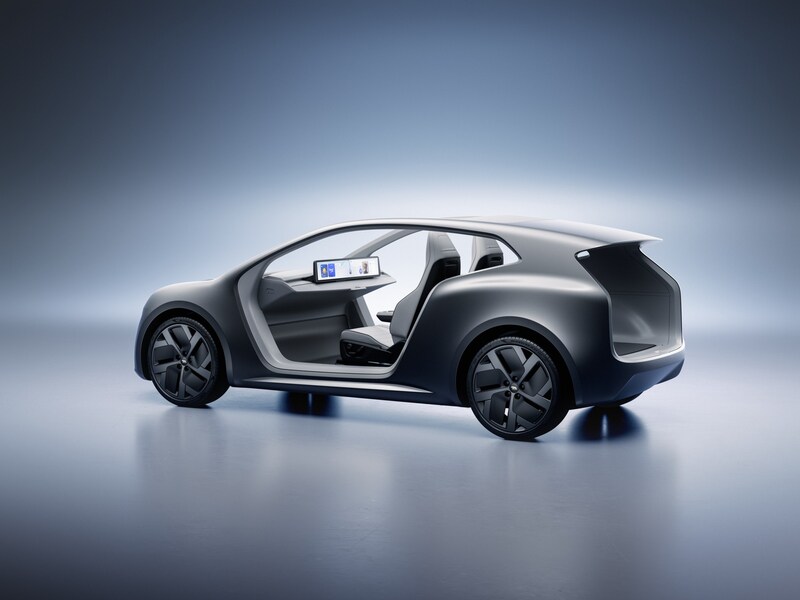

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
Into this landscape steps Lucid’s Lunar. Built on the company’s all-new Midsize EV platform, which will also underpin consumer SUVs starting below $50,000. The Lunar mirrors the Cybercab’s core philosophy of having two seats, no driver controls, and a focus on fleet economics. The platform introduces Lucid’s redesigned Atlas electric drive unit, engineered to be smaller, lighter, and cheaper to manufacture at scale.
Unlike Tesla’s strategy of building its own ride hailing network from scratch, Lucid is partnering with Uber. The companies are said to be in advanced discussions to deploy Midsize platform vehicles at large scale, with Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi publicly backing Lucid’s engineering credentials and autonomous-ready architecture.
In the investor day event, Lucid also outlined a recurring software revenue model, with an in-vehicle AI assistant and monthly autonomous driving subscriptions priced between $69 and $199. This can be seen as a nod to the software revenue stream that Tesla has long championed with its Full Self-Driving subscription.
Tesla’s Cybercab is targeting a price point below $30k and with operating costs as low as 20 cents per mile. But with regulatory hurdles still ahead, the window for competition is open. Lucid’s Lunar may not have a launch date yet, but it arrives at a pivotal moment, and when the robotaxi race is no longer viewed as hypothetical. Rather, every serious EV player needs to come to bat on the same plate that Tesla has had countless practice swings on over the last seven years.


![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





