SpaceX
SpaceX test fires twice-flown Falcon 9 for world’s first commercial Moon mission
Likely to be the third orbital-class launch for the booster in question, SpaceX’s next launch – led by primary customer Pasifik Satelit Nusantara (PSN) – has the potential to lay claim to multiple major spaceflight “firsts”, ranging from the first time a twice-flown Falcon 9 has launched on the East Coast to the world’s first attempt to land a commercial spacecraft on another planetary body – the Moon, in this case.
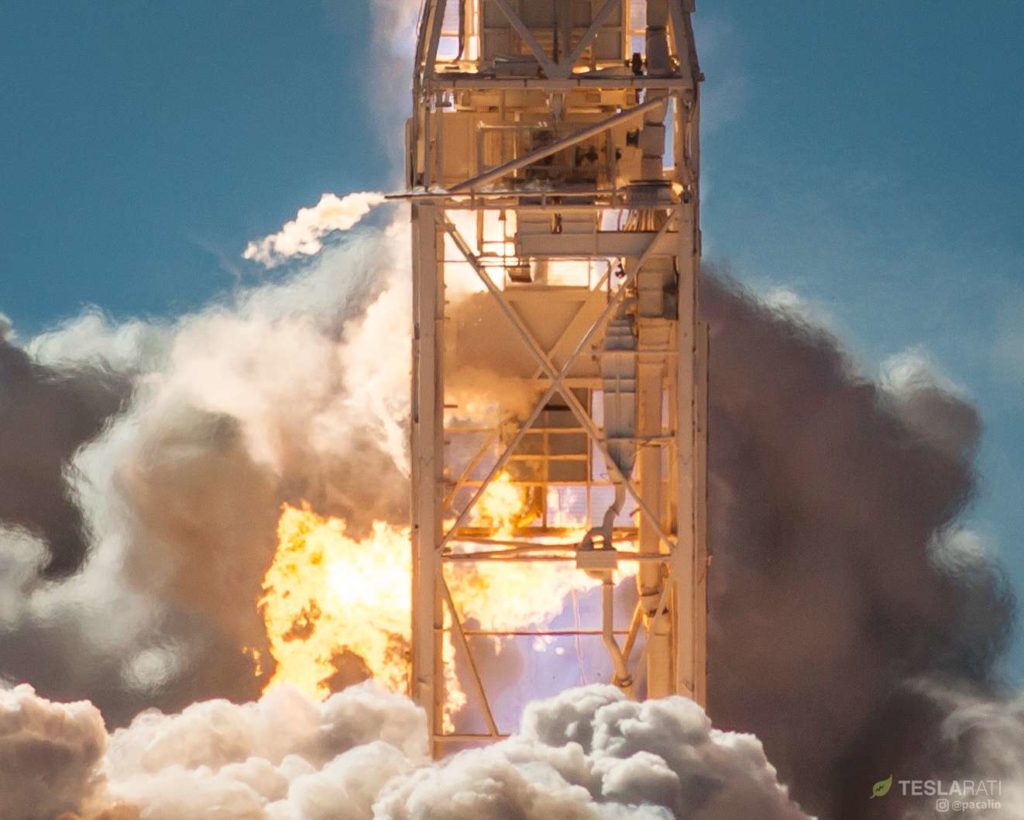
SpaceX has completed the final critical test milestone of the mission’s flight-proven Falcon 9, filling the rocket with propellant and successfully static firing the booster on the evening of February 18th. According to SpaceX, all remains on schedule for a February 21st launch attempt from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) Launch Complex 40 (LC-40), with liftoff currently targeted for 8:45 pm EDT (01:45 UTC).
Static fire test of Falcon 9 complete—targeting February 21 launch of Nusantara Satu from Pad 40 in Florida.
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) February 19, 2019
If all goes well, the launch of PSN satellite Nusantara Satu (formerly PSN-6; translation: “One Archipelago”) – carrying two copassenger spacecraft – could be an immensely significant moment for commercial spaceflight. Thanks to the support of rideshare provider Spaceflight Industries, those two passengers will be sent to high-energy geostationary orbits long relegated to dedicated launches of extremely large satellites, typically weighing multiple tons. While one could fairly argue that this is not the first time in history that a geostationary rideshare launch has occurred, it is almost certainly the first time that such a mission profile has been attempting for a commercial customer.
We are going to the moon! A 3D engine mount from RUAG Space will be the first 3D printed part on the moon. Our 3D part will support landing and lift off of Lunar Lander from @TeamSpaceIL. Congrats to our incredible engineers! pic.twitter.com/AbFZFD7GPB
— Peter Guggenbach (@PeterGuggenbach) February 11, 2019
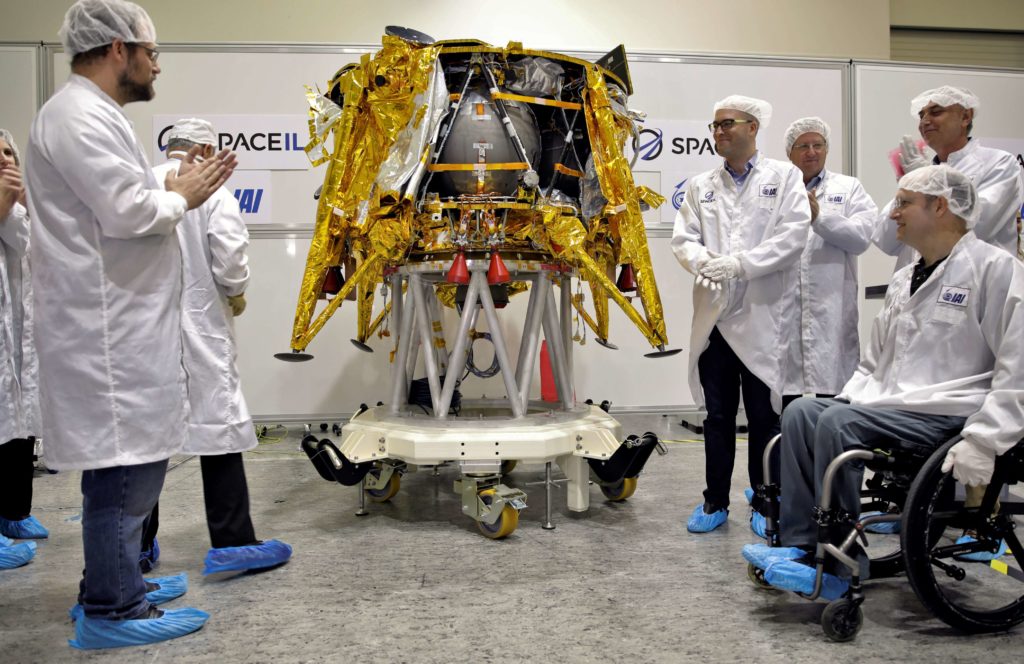
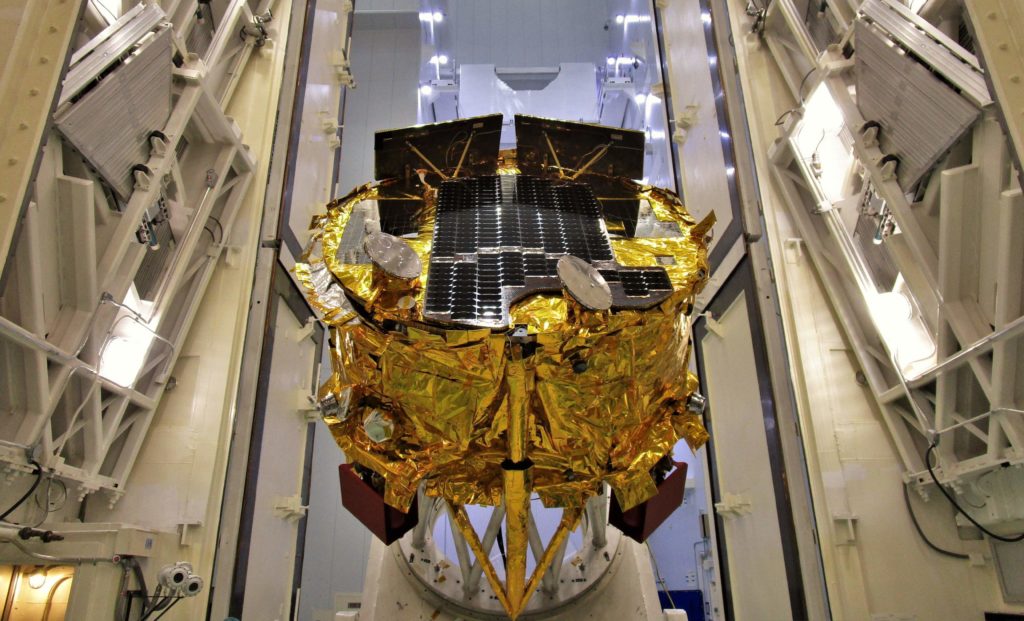
In this case, that commercial entity is the Israeli company SpaceIL in support of the world’s first commercially-developed Moon lander, a ~600 kg (1300 lb) spacecraft known as Beresheet (Hebrew for “In the beginning”). Designed by SpaceIL and constructed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), the craft has since been installed atop PSN-6 and encased in Falcon 9’s payload fairing along with one much smaller copassenger, an Air Force Research Laboratory-funded (AFRL) microsat known as “S5”. The latter spacecraft weighs roughly 60 kg (130 lb) and is an experiment designed to determine whether small satellites can be used in geostationary orbit (GEO), with S5 focusing on cataloging and tracking GEOsats.
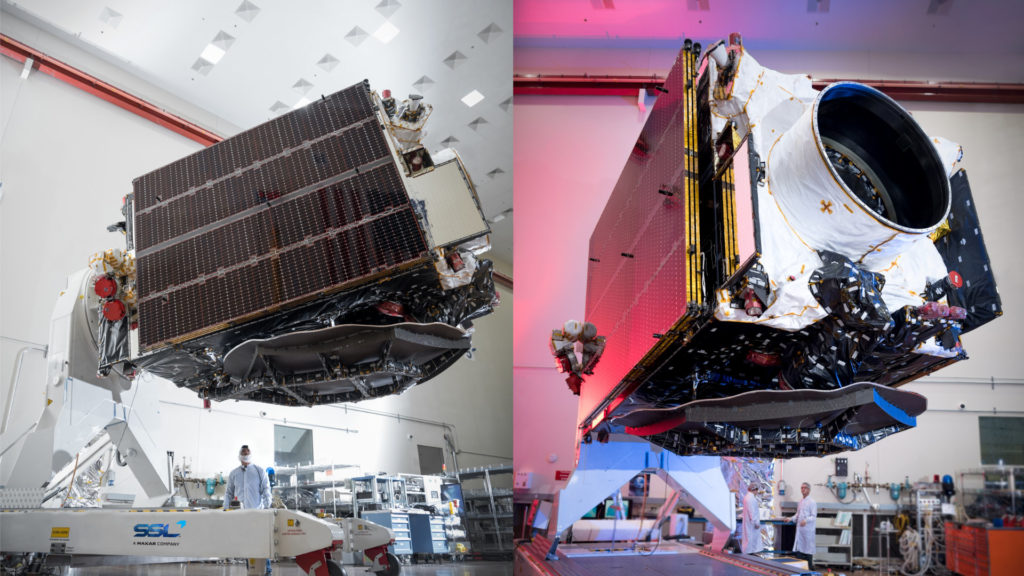
- PSN-6, an SSL-built communications satellite weighing several thousand kilograms, arrived in Florida roughly 10 days ago. (SSL)
- The Air Force Research Lab’s S5 smallsat. (Blue Canyon)
- Beresheet is seen here prior to the spacecraft’s flight from Israel to Florida. (SpaceIL/IAI)
- After arriving in Florida, Spaceflight was tasked with integrating Beresheet with PSN-6. (SpaceIL/Spaceflight)
Spaceflight Industries aims for new market creation
Shepherded by rideshare industry leader Spaceflight, the PSN-6 rideshare – known by the company as GTO-1 – has the potential to open up a new and highly useful realm of spaceflight previously all but closed off to customers lacking tens of millions of dollars for launch costs. While it’s unclear how exactly Spaceflight worked with SSL and/or PSN to make it happen, the mission profile and its potential are both fascinating and complex.
“What we’re doing with [GTO-1] is really cool, cause this is a type of mission that hasn’t really been available [commercially] in the past – taking a ride all the way to GEO and then separating in GEO as an independent spacecraft . . . We’re really excited about testing the market and proving – really, making – a new market here with the GEO [and GTO] rideshare.” – Ryan Olcott, Spaceflight (Jan. 2019)
In a late-January interview with Spaceflight’s Mission Director Ryan Olcott, the senior manager was audibly excited about the future potential of Spaceflight’s new GTO (and GEO) offerings and the many ways that they could change the game for a number of companies and startups with far smaller but no less capable spacecraft. Including startups Astranis and Terran Orbital and industry stalwart SSL, interest in small geostationary satellites has never been higher, and a number of pathfinder missions in 2020 and 2021 – if successful or at least promising – could mark a paradigm shift for the geostationary satellite communications industry as a whole. Often sized perfectly (100-500 kg) for a handful of in-development smallsat launch vehicles like Relativity’s Terran, Firefly’s Beta, and ABL Space’s RS-1, it will likely be several years before those new rockets are capable of reliably supporting these much smaller launches, leaving rideshare missions as the only real route for interested customers until the early to mid 2020s.
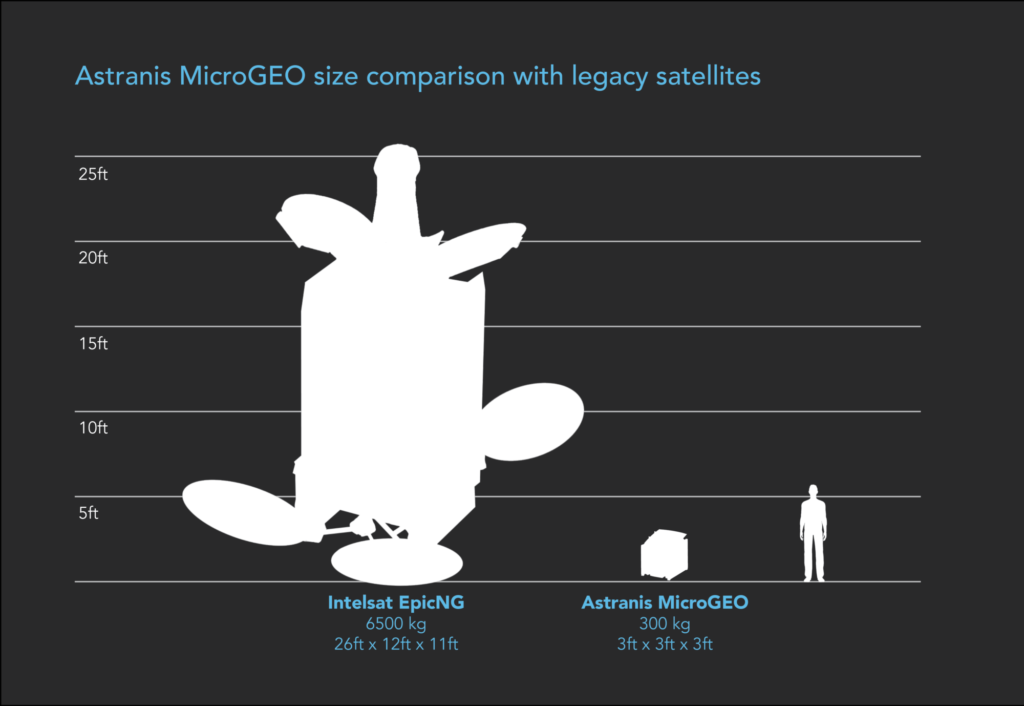
- Astranis’ “MicroGEO” offering compared beside one of the largest geostationary satellite buses. (Astranis)
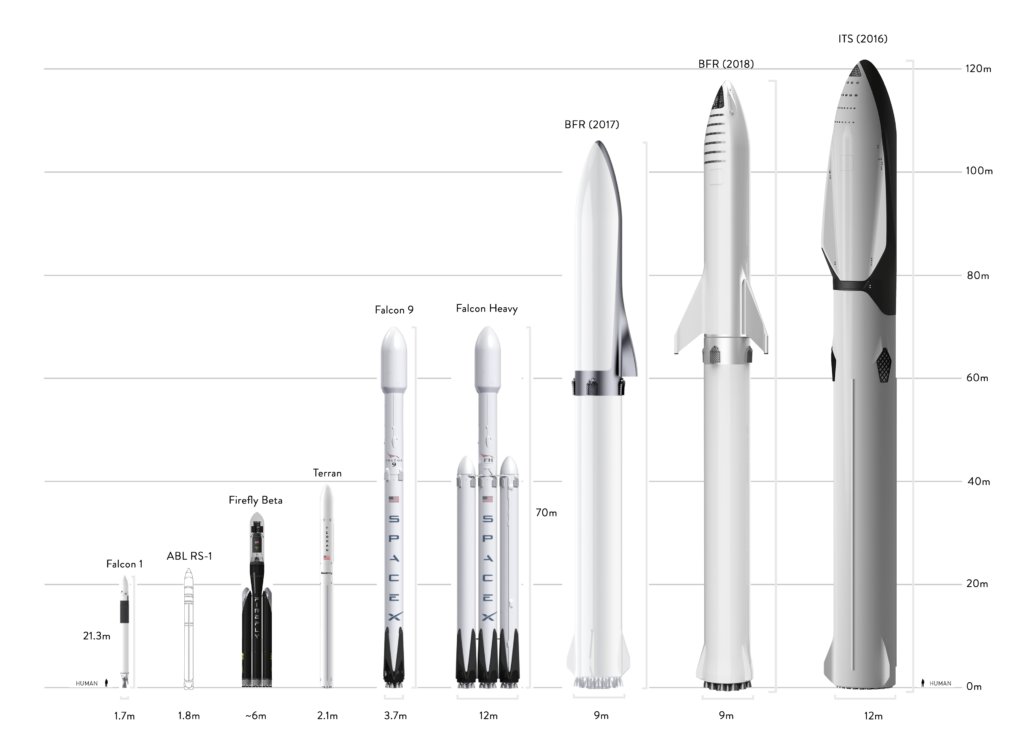
- The change in scale between ITS, BFR, and BFR 2018 is significant. (Teslarati)
- A render of Spaceflight’s SSO-A dispensers attached to Falcon 9’s second stage.
- Falcon 9 B1046 lifts off for the third time with Spaceflight’s SSO-A rideshare mission. (Pauline Acalin)
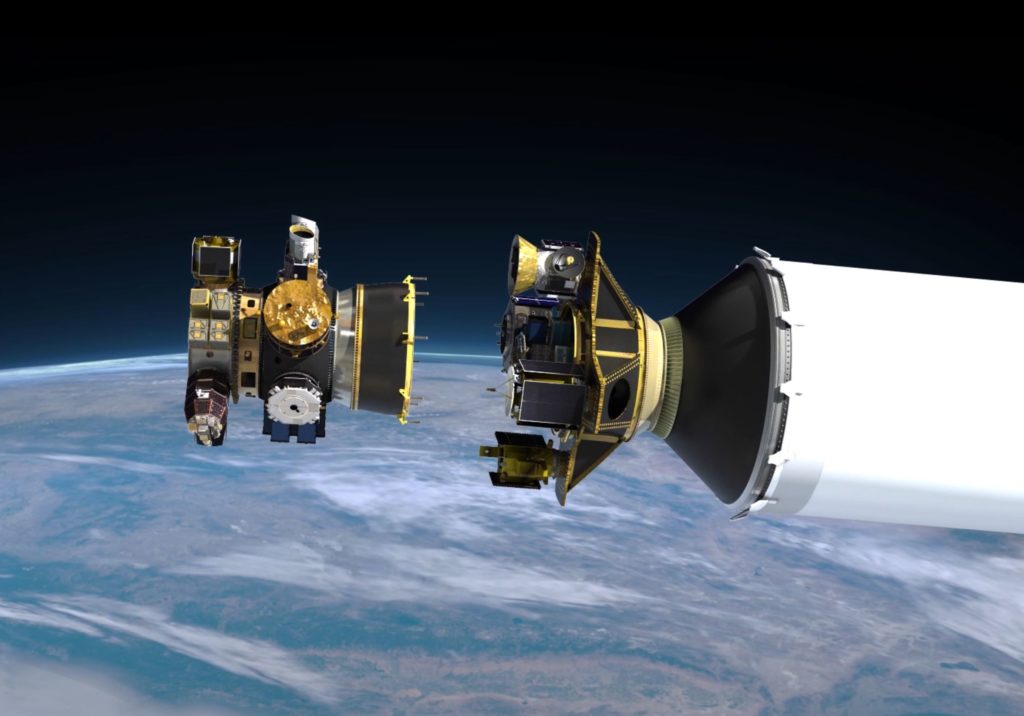
In the process of undertaking this milestone geostationary rideshare, Spaceflight had to design, build, and test custom hardware needed to protect the AFRL’s S5 spacecraft on its multi-week ridealong from geostationary transfer orbit to PSN-6’s geostationary orbit destination, as well as unique mounting hardware needed to load SpaceIL’s Beresheet spacecraft atop the main satellite host. In fact, GTO-1’s mission profile is impressively complex, requiring multiple mission-specific maneuvers and separation events to detach Beresheet shortly after the entourage separates from Falcon 9, carry S5 to a geostationary graveyard orbit (GEO + ~300 km) to separate Spaceflight’s custom hardware, return to a lower orbit to deploy the Air Force satellite, and finally insert PSN-6 into its final operational orbit.
“We actually have to open up our adapter system to allow the [AFRL S5] spacecraft to come out, so we have about a half-day time window that we’re aiming for where we will separate the top off of our cone adapter system and then drop [the orbit] back down a little bit [because we can’t drop that junk off in GEO – you have to use the GEO graveyard slot].” – Ryan Olcott, Spaceflight

“GTO is pretty cool because you can do all sorts of positive C3 missions [to] Lagrange points or just about [anywhere] in the solar system you want to go to … With SpaceIL, potentially in the future [Spaceflight will also] be able to partner with them to bring things to the Moon if they’ve got customers that want to bring payloads to the Moon.” – Ryan Olcott, Spaceflight
The fact that the first primary passenger (by weight) of GTO-1 is a mission as groundbreaking as the commercial Beresheet Moon lander is also by no means a coincidence according to Ostello, a feeling that was rapidly backed up by an agreement between IAI and European company OHB to potentially use Beresheet-derived landers to deliver European payloads to the Moon. Ostello expressed a similar interest and optimism a few weeks prior to that announcement. While not directly involving Spaceflight, the fact that IAI (Beresheet’s manufacturer) is interested in producing more landers for other customers essentially opens the door for Spaceflight or other commercial or governmental entities to purchase future landers for customer payloads or arrange their launch to the Moon.
Second time’s the third-time charm
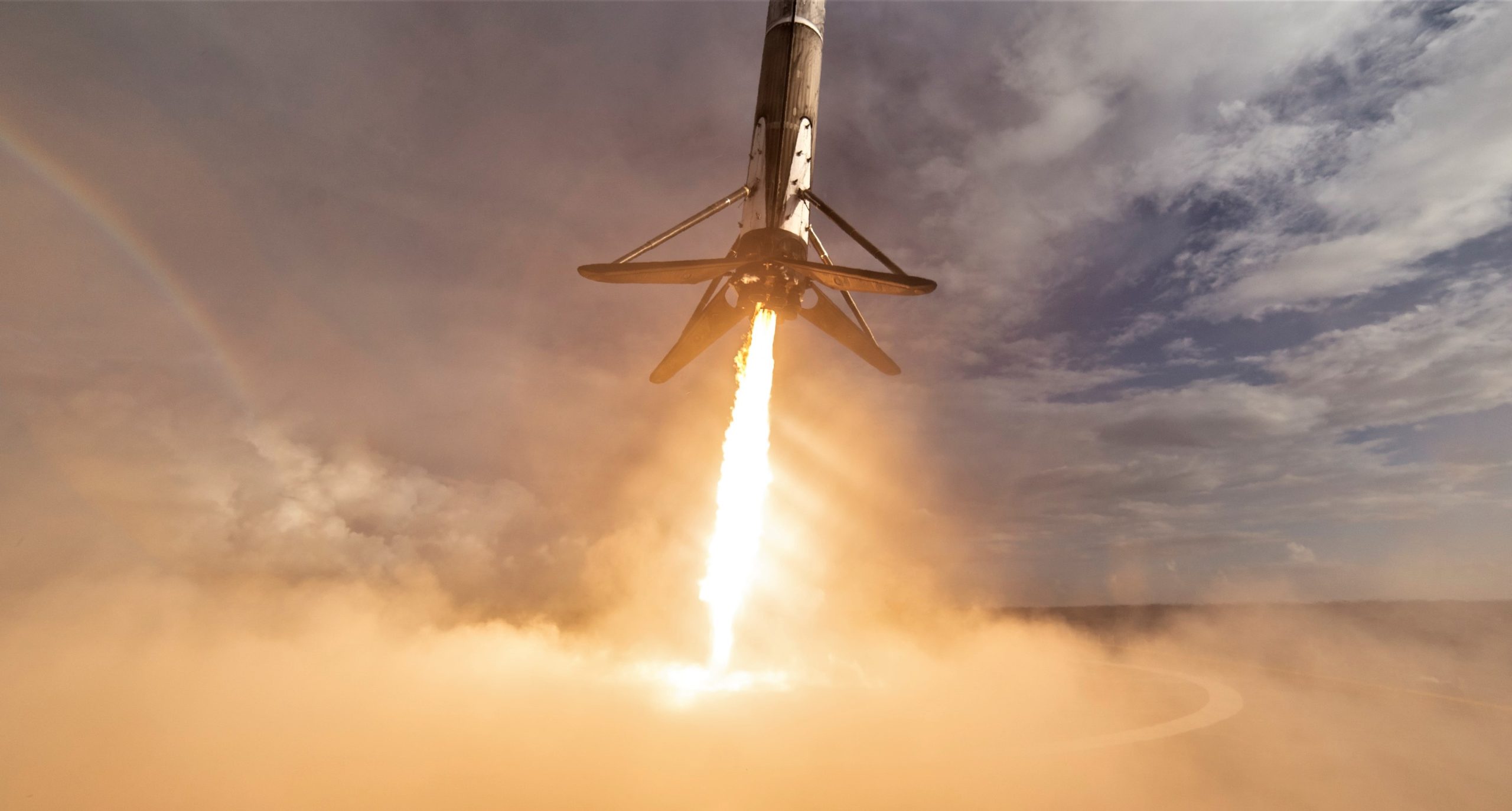
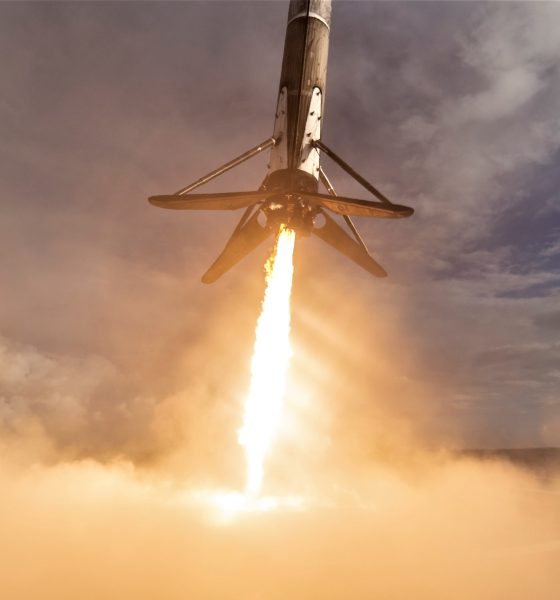
Set to launch on an unspecified Falcon 9, process of elimination (i.e. which boosters are in Florida) implies that PSN-6/GTO-1 will feature either Falcon 9 booster B1047 or B1048, two flight-proven boosters with no know missions assigned that are also known to be in Cape Canaveral. B1047 last launched the Es’hail-2 satellite in mid-November, while B1048 completed its second launch (from California) in early October before shipping to Florida for unknown reasons. With B1048 situated in 39A’s hangar, the lack of any reports of a booster moving from 39A to 40 suggest that B1047 was the Falcon 9 that successfully conducted its third on-pad static fire last night.
Shortly after launch, the Falcon 9 booster will make its way to drone ship Of Course I Still Love You (OCISLY) – located ~650 km (400 mi) off the coast of Florida – for what will be the second time ever that SpaceX has successfully launched and landed the same Falcon 9 booster three times, following on the heels of B1046’s third launch last December. SpaceX fairing recovery vessel Mr. Steven also arrived at Port Canaveral last week after a nearly 8000 km (5000 mi) journey from Port of Los Angeles, raising the possibility of his first attempt at a fairing catch on the East Coast.

Check out Teslarati’s newsletters for prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket launch and recovery processes!

Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.
Elon Musk
Starbase after dark: Musk’s latest photo captures a Spaceport on the brink of history
SpaceX’s Starbase city in Boca Chica, Texas is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
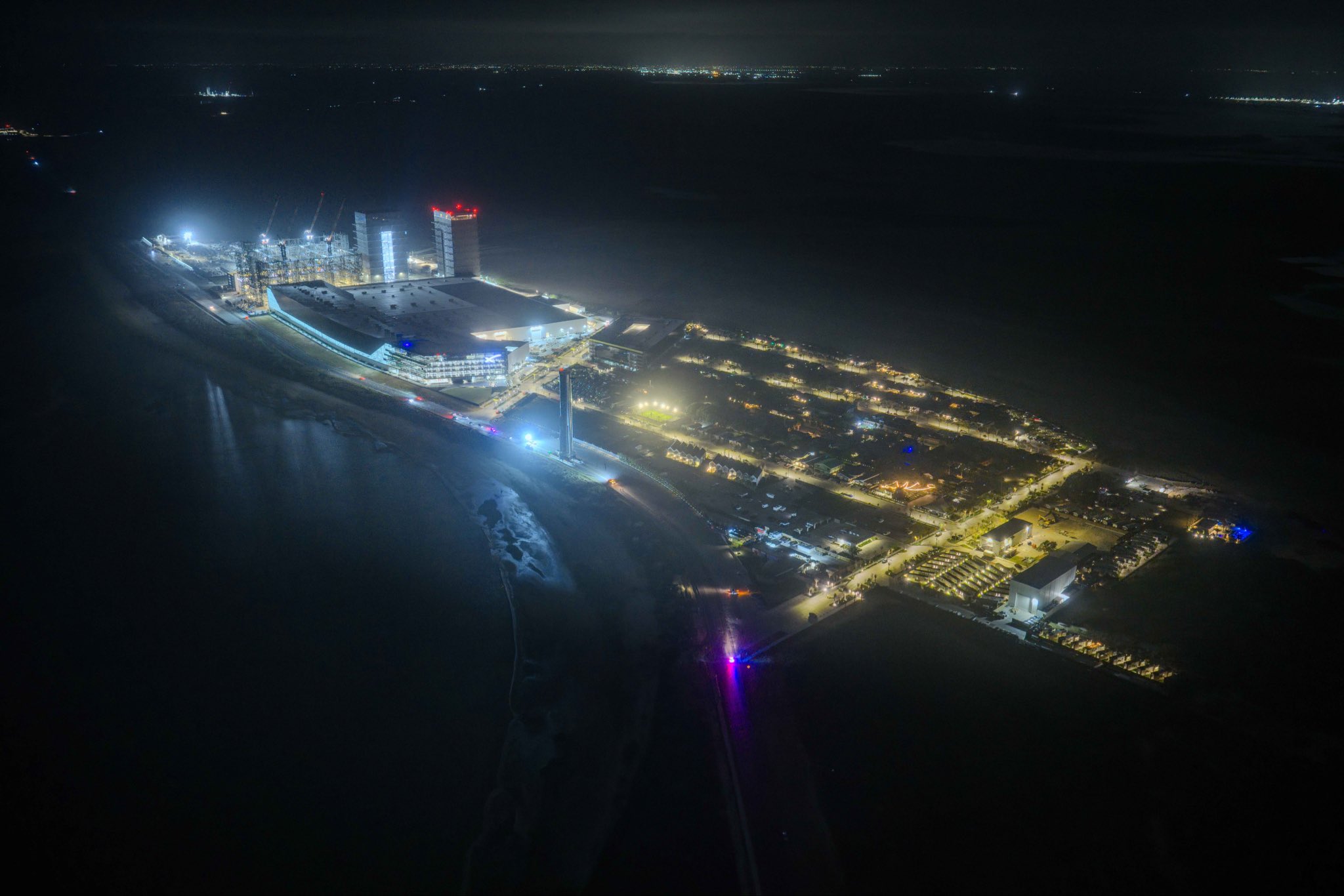

A striking nighttime photograph of SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, shared recently by Elon Musk on X, offers a dramatic glimpse of an operation that is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
The most immediately visible change in the photo is the presence of two fully erected Starship launch towers dominating the coastal skyline. The second orbital launch pad, known as Pad B, now features its fully erected tower, OLIT-3, which stands approximately 474 feet tall and incorporates an integrated water-cooled flame trench designed to minimize damage and reduce turnaround time between launches. The dual-tower silhouette against the night sky signals a decisive shift from experimental testing facility to high-cadence launch operations.
Grok Image concept of Elon Musk’s latest Starbase photo via X
Back at Starbase, Pad 2 is approaching hardware completion, with upgraded chopstick arms, a new chilldown vent system, and all 20 hold-down arms now fitted with protective doors to shield them from the intense exhaust of up to 33 Raptor 3 engines, according to a deeper dive by NASASpaceFlight.
SpaceX has also received approval to nearly double the footprint of the Starbase launch site, with groundwork already underway to add LNG liquefaction plants, expanded propellant storage, and additional ground support infrastructure.
The photo also carries a milestone civic dimension. Starbase officially became a Texas city in May 2025 after a community vote, with SpaceX employees elected as mayor and commissioners of the newly incorporated municipality. That legal status streamlines launch approvals and gives SpaceX direct control over local infrastructure decisions.
The FAA has approved an increase in launches from Starbase in Texas from five to twenty-five per year, clearing the runway for the kind of flight frequency needed to fulfill Starship’s ultimate mission of ferrying cargo and crew to the Moon, servicing the Department of Defense, deploying next-generation Starlink satellites, and eventually establishing Elon Musk’s long sought after goal of a self-sustaining human presence on Mars.
Seen from above in the dark, Starbase looks less like a test site and more like a spaceport.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk shares updated Starship V3 maiden launch target date
The comment was posted on Musk’s official account on social media platform X.

SpaceX CEO Elon Musk shared a brief Starship V3 update in a post on social media platform X, stating the next launch attempt of the spacecraft could take place in about four weeks.
The comment was posted on Musk’s official account on social media platform X.
Musk’s update suggests that Starship Flight 12 could target a launch around early April, though the schedule will depend on several remaining milestones at SpaceX’s Starbase launch facility in Texas.
Among the key steps is testing and certification of the site’s new launch tower, launch mount, and tank farm systems. These upgrades will support the next generation of Starship vehicles.
Booster 19 is expected to roll to the launch site and be placed on the launch mount before returning to the production facility to receive its 33 Raptor engines. The booster would then return for a static fire test, which could mark the first time a Super Heavy booster equipped with Raptor V3 engines is fired on the pad.
Ship 39 is expected to undergo a similar preparation process. The vehicle will likely return to the production site to receive its six engines before heading to Massey’s test site for static fire testing.
Once both stages are prepared, the booster and ship will roll out to the launch site for the first full stack of a V3 Super Heavy and V3 Starship. A full wet dress rehearsal is expected to follow before any launch attempt.
Elon Musk has previously shared how SpaceX plans to eventually recover Starship’s upper stage using the launch tower’s robotic arms. Musk noted that the company will only attempt to catch the Starship spacecraft after two successful soft landings in the ocean. The approach is intended to reduce risk before attempting a recovery over land.
“Should note that SpaceX will only try to catch the ship with the tower after two perfect soft landings in the ocean. The risk of the ship breaking up over land needs to be very low,” Musk wrote in a post on X.
Such a milestone would represent a major step toward the full reuse of the Starship system, which remains a central goal for SpaceX’s long-term launch strategy.