

News
SpaceX to replicate Starbase, build multiple Starship launch pads in Florida
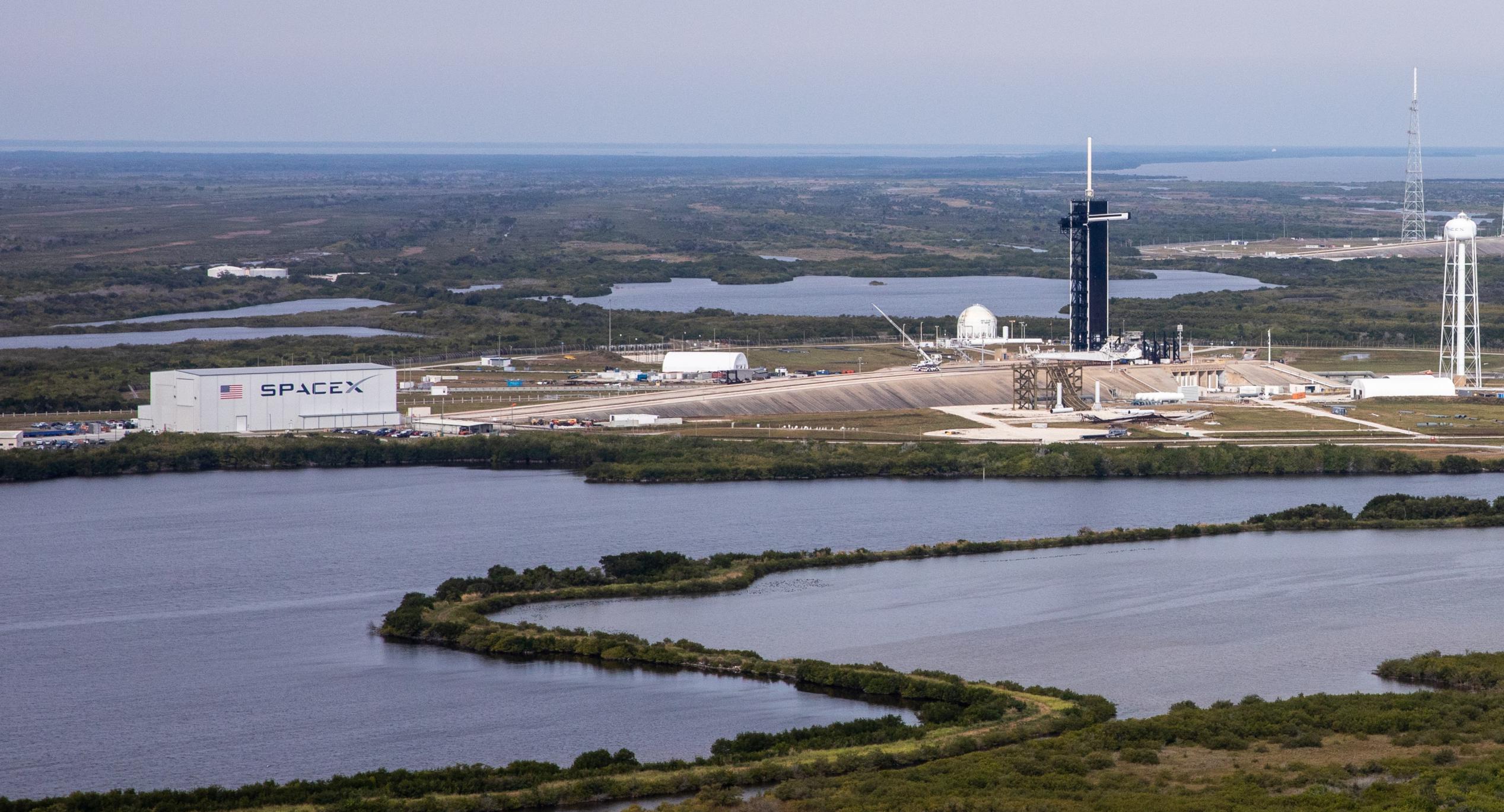
Less than two weeks after CEO Elon Musk revealed that SpaceX has restarted construction of a Starship launch site at Kennedy Space Center’s existing LC-39A pad, NASA has revealed the company’s plans for an entirely different Starship launch site just a few miles to the north.
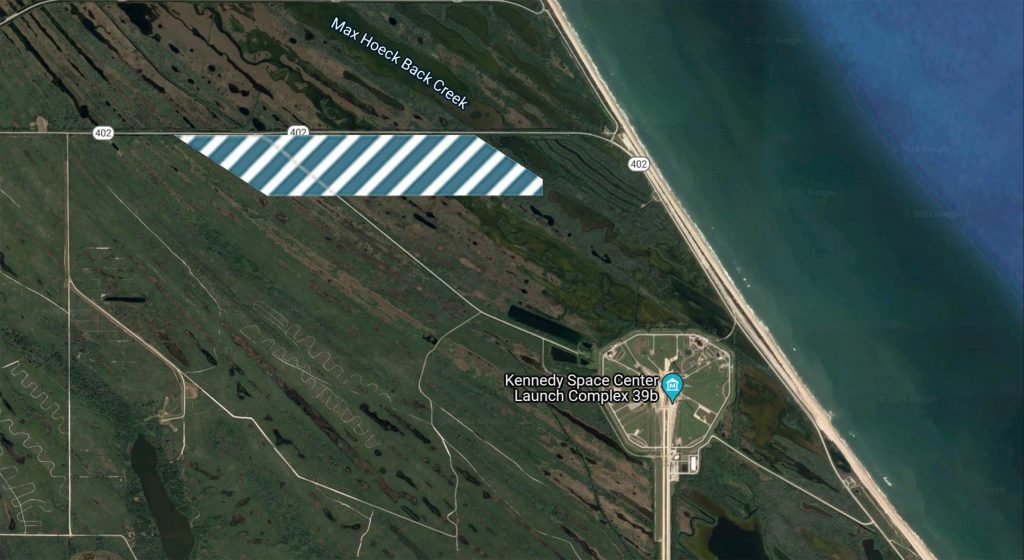
Known as Launch Complex 49 (LC-49) and located where NASA once considered building LC-39C, a third Saturn-class pad to match 39A and 39B, NASA now says that SpaceX aims to develop the site into a dedicated Starship launch pad. The plot of land NASA deemed LC-49 as recently as 2017 sits about 1 mile (1.6 km) northwest of NASA’s LC-39B Space Launch System (SLS) pad and 3 miles (5 km) northwest of LC-39A, which SpaceX has leased since 2014 and launched out of since 2017. Unlike 39A, though, SpaceX has a huge amount of work – and major environmental reviews – ahead of it to turn LC-49 into a site capable of launching a rocket more than twice as powerful as Saturn V.
As of today, “LC-49” amounts to a mostly arbitrary dotted line on a map. Situated a few thousand feet south of the lovingly named Mosquito Lagoon Aquatic Preserve and Canaveral Seashore National Park, the site encompasses a variety of wild wetlands and is fully undeveloped. While substantially wetter, the land SpaceX hopes to develop is actually quite similar to the site that now hosts Starbase’s Starship launch facilities in Boca Chica, Texas. Prior to SpaceX’s arrival, the area was empty coastal mudflats.
To turn such a fragile and unstable area into an orbital launch site, SpaceX trucked in thousands of tons of soil, which then sat in a pile for three years ‘surcharging’ or compressing the ground beneath it. Ironically, while SpaceX did build a relatively small suborbital launch site where it surcharged, the company has built the site’s first orbital Starship launch pad a bit to the east, where no such preparations were made. That bodes well for the speed with which SpaceX could potentially build LC-49 from nothing, though it will likely be significantly more of a challenge.
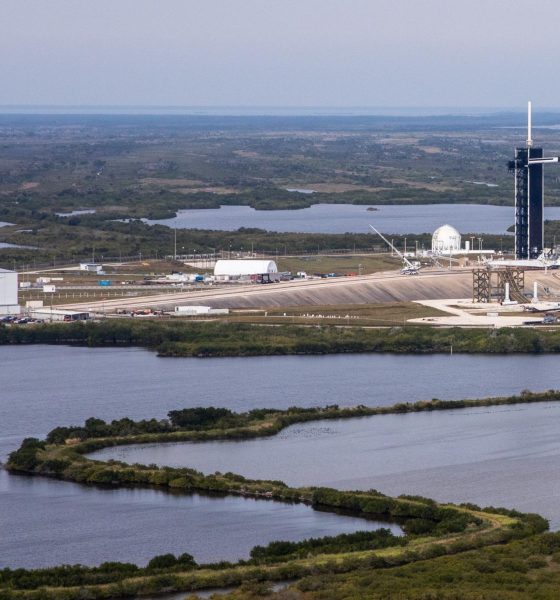
Because NASA’s proposed LC-49 site is effectively swamp and marshland, SpaceX will have to create the ground any planned Starship launch site will stand on. It’s possible that soil surcharging will be required – and potentially on an even larger scale than what SpaceX did in Boca Chica. However, given that SpaceX ultimately didn’t even use that surcharged land to construct the orbital half of the pad, it’s possible that SpaceX will again be able to make do with less time-consuming construction methods. If SpaceX does more or less replicate an orbital launch site similar to Starbase’s, the pad could be ready to launch just 12-18 months later. NASA and SpaceX will have to complete environmental reviews along the way but given planning work that NASA’s already done over the decades, it’s possible that SpaceX will be able to start building LC-49 well before that process – which could take one or several years – is complete.
No less intriguing is NASA’s implication that SpaceX is simultaneously preparing to expand a facility it leases elsewhere at Kennedy Space Center. Currently used to process and store Falcon boosters, fairings, and upper stages, SpaceX has been clearing a lot beside that hangar that’s about the same size as the entirety of Starbase’s South Texas Starship factory. The obvious implication: SpaceX intends to both build and launch Starships out of multiple Florida launch pads.
Just a few miles south, CEO Elon Musk says that SpaceX has restarted work on a separate Starship launch pad situated on Pad 39A grounds after halting construction last year to focus on South Texas. SpaceX chose to entirely scrap the unfinished launch mount it had built, clearing the site for the construction of a new and improved version of Starbase’s orbital launch site. Altogether, SpaceX is now simultaneously constructing two orbital Starship launch pads (one at Starbase and one at 39A) and planning for the construction of two or three more (a second at Starbase and at least one or two at LC-49).

News
Tesla opens Supercharging Network to other EVs in new country
Tesla’s Supercharging infrastructure is the most robust in the world, and it has done a wonderful job of keeping things up and running for the millions of owners out there. As it expanded access to non-Tesla EVs a couple years back, it has still managed to keep things pretty steady, although the need for more charging is apparent.

Tesla has started opening its Supercharging Network, which is the most expansive in the world, to other EVs in a new country for the first time.
After expanding its Supercharging offerings to other car companies in the United States a few years ago, Tesla is still making the move in other markets, as it aims to make EV ownership easier for everyone, regardless of what manufacturer a consumer chose to purchase from.
Tesla’s Supercharging infrastructure is the most robust in the world, and it has done a wonderful job of keeping things up and running for the millions of owners out there. As it expanded access to non-Tesla EVs a couple years back, it has still managed to keep things pretty steady, although the need for more charging is apparent.
Tesla just added a cool new feature for leaving your charger at home or even leaving the Supercharger pic.twitter.com/iw0SDrWuX6
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 10, 2026
Now, Tesla is expanding access to the Supercharger Network to non-Tesla EVs in Malaysia. The automaker just opened up a charging stie at the Pavilion KL Mall in Kuala Lumpur to non-Tesla owners, giving them eight additional Superchargers to utilize with a charging speed of up to 250 kW.
Tesla is also opening up the four-Supercharger site in Shah Alam, a four-Supercharger site at the IOI City Mall, and a six-Supercharger site in Gamuda Cove Township.
Electrive first reported the opening of these Superchargers in Malaysia.
The initiative from Tesla helps make EV ownership much simpler for those who only have access to third-party charging solutions or at-home charging. While at-home charging is the most advantageous, it is not an end-all solution as every driver will eventually need to grab some range on the road.
Tesla has been offering its Superchargers to non-Tesla EVs in the United States since 2024, as Ford became the first company to gain access to the massive network early that year when CEO Elon Musk and Ford frontman Jim Farley announced it together. Since then, Tesla has offered its chargers to nearly every EV maker, as companies like Rivian and Lucid, and even legacy car companies like General Motors have gained access.
It’s best for everyone to have the ability to use Tesla Superchargers, but there are of course some growing pains.
Charging cables are built to cater to Tesla owners, so pull-in Superchargers are most advantageous for non-Tesla EVs currently, but the company’s V4 Superchargers, which are not as plentiful in the U.S. quite yet, do enable easier reach for those vehicles.
News
Tesla Semi expands pilot program to Texas logistics firm: here’s what they said
Mone said the Tesla Semi it put into its fleet for this test recorded 1.64 kWh per mile efficiency, beating Tesla’s official 1.7 kWh per mile target and delivering a massive leap over conventional diesel trucks.
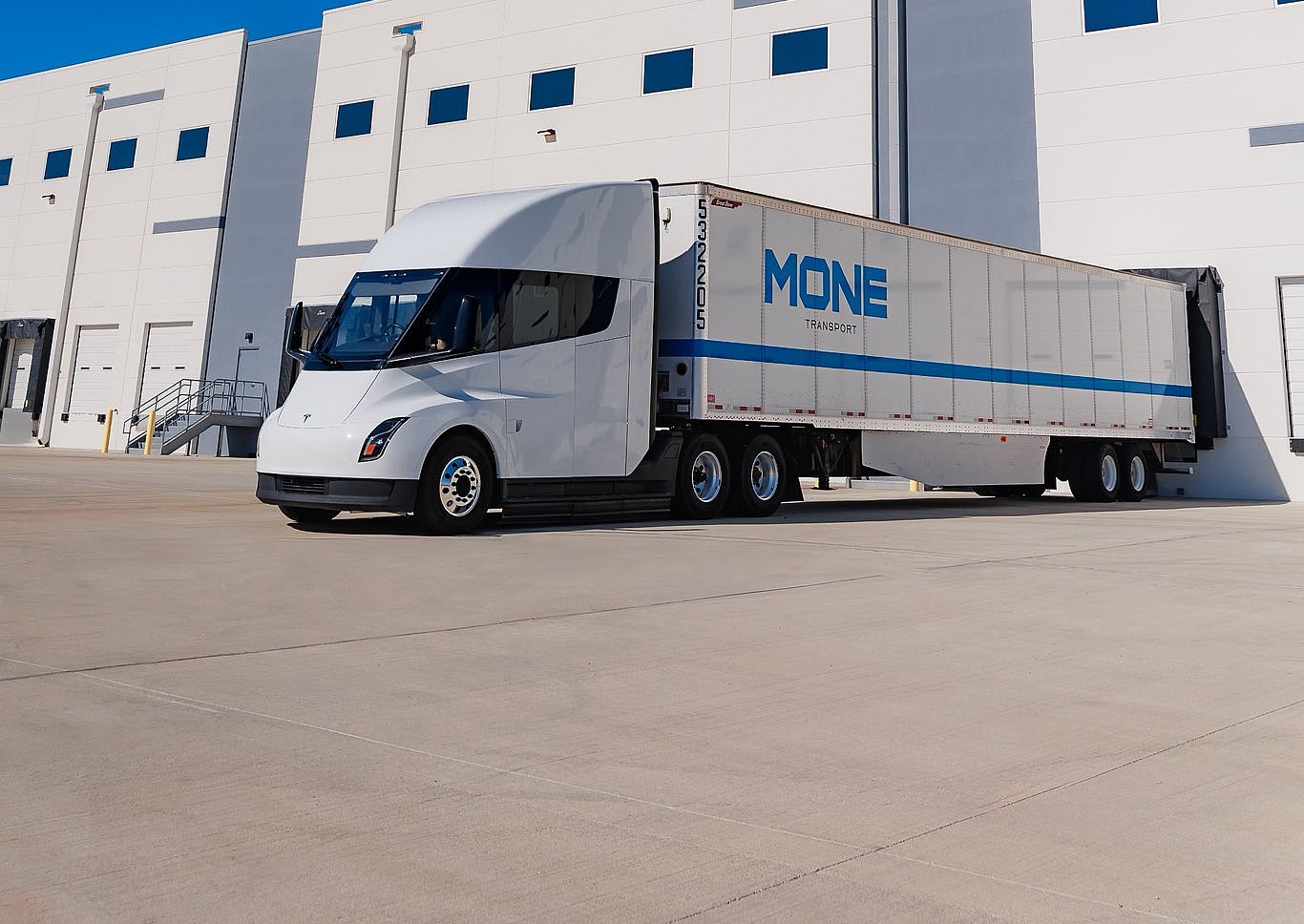

Tesla has expanded its Semi pilot program to a new region, as it has made it to Texas to be tested by logistics from Mone Transport. With the Semi entering production this year, Tesla is getting even more valuable data regarding the vehicle and its efficiency, which will help companies cut expenditures.
Mone Transport operates in Texas and on the Southern border, and it specializes in cross-border U.S.-Mexico freight operations. After completing some rigorous testing, Mone shared public results, which stand out when compared to efficiency metrics offered by diesel vehicles.
“Mone Transport recently had the opportunity to put the Tesla Semi to the test, and we’re thrilled with the results! Over 4,700 miles of operations at 1.64 kWh/mile in our Texas operation. We’re committed to providing zero-emission transportation to our customers!” the company said in a post on X.
🚨 Mone Transport just recorded an extremely impressive Tesla Semi test:
1.64 kWh per mile over 4,700 miles! https://t.co/xwS2dDeomP pic.twitter.com/oLZHoQgXsu
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 10, 2026
Mone said the Tesla Semi it put into its fleet for this test recorded 1.64 kWh per mile efficiency, beating Tesla’s official 1.7 kWh per mile target and delivering a massive leap over conventional diesel trucks.
Comparable Class 8 diesel semis, typically achieving 6-7 miles per gallon, consume roughly 5.5 kWh per mile in energy-equivalent terms, meaning the Semi uses three to four times less energy while also producing zero tailpipe emissions.
Tesla Semi undergoes major redesign as dedicated factory preps for deliveries
The performance of the Tesla Semi in Mone Transport’s testing aligns with data from other participants in the pilot program. ArcBest’s ABF Freight Division logged 4,494 miles over three weeks in 2025, averaging 1.55 kWh per mile across varied routes, including a grueling 7,200-foot Donner Pass climb. The truck “generally matched the performance of its diesel counterparts,” the carrier said.
PepsiCo, which operates the largest known Semi fleet, recorded 1.7 kWh per mile in North American Council for Freight Efficiency testing. Additional pilots showed similar gains: DHL hit 1.72 kWh per mile, and Saia achieved 1.73 kWh per mile.
These metrics underscore the Semi’s ability to slash operating costs through superior efficiency, lower maintenance, and zero-emission operation. As charging infrastructure scales and production ramps toward 2026 targets, participants like Mone Transport are proving electric semis can seamlessly integrate into freight networks, accelerating the industry’s shift to sustainable, high-performance trucking.
Tesla continues to prep for a more widespread presence of the Semi in the coming months as it recently launched the first public Semi Megacharger site in Los Angeles. It is working on building out infrastructure for regional runs on the West Coast initially, with plans to expand this to the other end of the country in the coming years.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.








