
News
SpaceX nears big US govt. missions as ULA handwaves about risks of competition
Speaking at the 2018 Von Braun Symposium in Huntsville, Alabama, ULA COO John Elbon expressed worries that the US National Security Space (NSS) apparatus could be put at significant risk if it comes to rely too heavily on the commercial launch industry to assure access to space.
Given that the US military’s launch capabilities rest solely on SpaceX and ULA and will remain that way for at least three more years, Elbon’s comment was effectively an odd barb tossed in the direction of SpaceX and – to a lesser extent – Blue Origin, two disruptive and commercially-oriented launch providers.
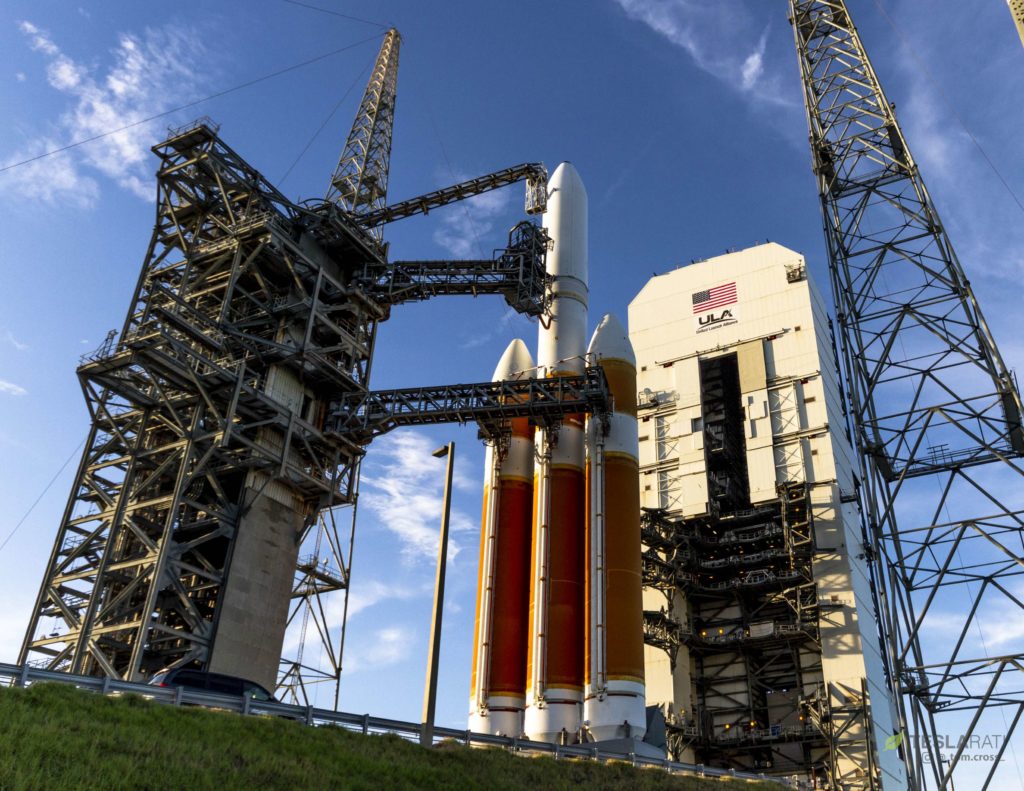
- The history of ULA and its Delta IV rocket is far wilder than most would expect. (Tom Cross)
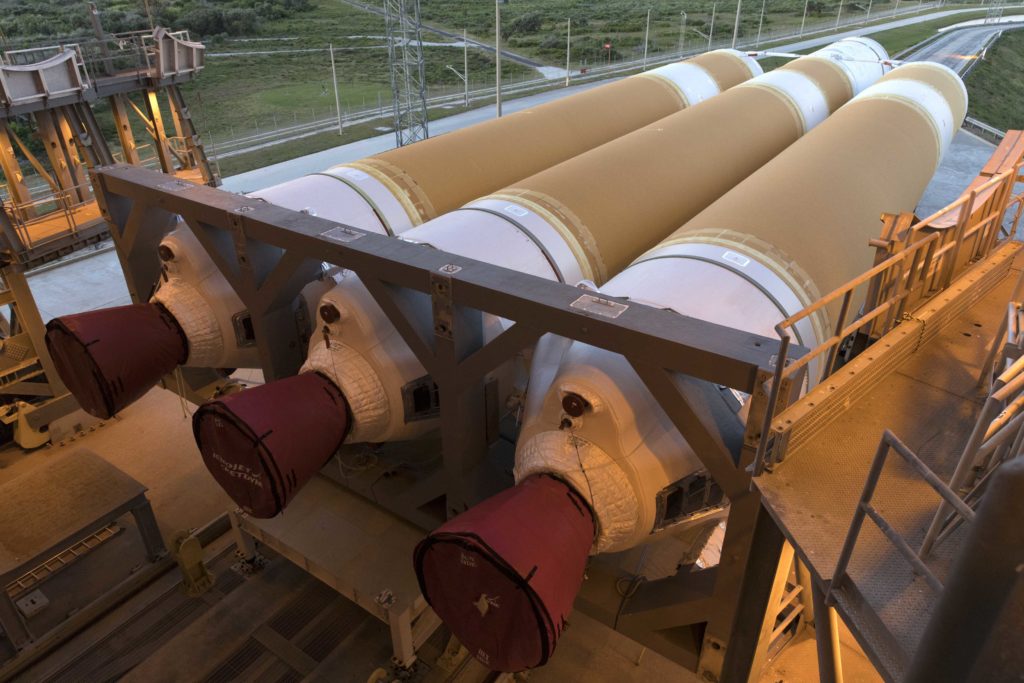
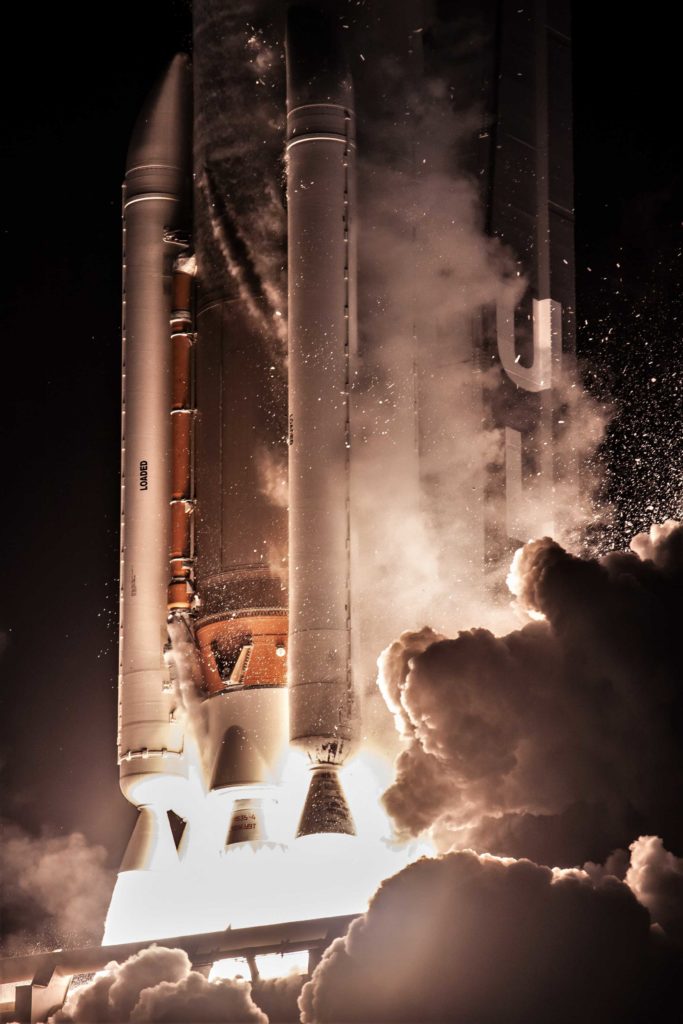
- The first stage of Parker Solar Probe’s Delta IV Heavy rocket prepares to be lifted vertical. (ULA)
Reading between the lines
For the most part, Elbon’s brief presentation centered around a reasonable discussion of ULA’s track record and future vehicle development, emphasizing the respectable reliability of its current Atlas V and Delta IV rockets and the ‘heritage’ they share with ULA’s next-generation Vulcan vehicle. However, the COO twice brought up an intriguing concern that the US military launch apparatus could suffer if it ends up relying too heavily on ‘commercially-sustained’ launch vehicles like Falcon 9/Heavy or New Glenn.
To provide historical context and evidence favorable to his position, Elbon brought up a now-obscure event in the history of the launch industry, where – 20 years ago – companies Lockheed Martin and Boeing reportedly “set out to develop … Atlas V and Delta IV” primarily to support the launch of several large satellite constellations. The reality and causes of the US launch industry’s instability in the late ’90s and early ’00s is almost indistinguishable from this narrative, however.
Despite the many veils of aerospace and military secrecy surrounding the events that occurred afterward, the facts show that – in 1999 – Boeing (per acquisition of McDonnell Douglas) and Lockheed Martin (LM) both received awards of $500M to develop the Delta IV and Atlas V rockets, and the military further committed to buying a full 28 launches for $2B between 2002 and 2006. Combined, the US military effectively placed $3B ($4.5B in 2018 dollars) on the table for its Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) program with the goal of ensuring uninterrupted access to space for national security purposes.
- Crew Dragon arrives at ISS. (SpaceX)
- Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft. (Boeing)
- A mockup of Boeing’s Starliner capsule is explored by one of NASA’s Commercial Crew astronauts, clad in a Boeing spacesuit. (Boeing)
- SpaceX’s Commercial Crew pressure suit seen on NASA astronauts during testing. (SpaceX)
Rocketing into corporate espionage
“The robust commercial market forecast led the Air Force to reconsider its acquisition strategy. The EELV acquisition strategy changed from a planned down-select to a single contractor and a standard Air Force development program [where the USAF funds vehicle development in its entirety] to a dual commercialized approach that leveraged commercial market share and contractor investment.” – USAF EELV Fact Sheet, March 2017
The above quote demonstrates that there is at least an inkling of truth in Elbon’s spin. However, perhaps the single biggest reason that the EELV program and its two awardees stumbled was gross, inexcusable conduct on the part of Boeing. In essence, the company’s space executives conspired to use corporate espionage to gain an upper-hand over Lockheed Martin, knowledge which ultimately allowed Boeing to severely low-ball the prices of its Delta IV rocket, securing 19 of 28 available USAF launch contracts.
Ultimately, Lockheed Martin caught wind of Boeing’s suspect behavior and filed a lawsuit that began several years of USAF investigations and highly unpleasant revelations, while Boeing also had at least 10 future launch contracts withdrawn to the tune of ~$1B (1999). USAF investigations discovered that Boeing had lied extensively to the Air Force for more than four years – the actual volume of information stolen would balloon wildly from Boeing’s initial reports of “seven pages of harmless data” to 10+ boxes containing more than 42,000 pages of extremely detailed technical and proprietary information about Lockheed Martin’s Atlas V rocket proposal.
“If you rewind the clock 20 years, there were folks on a panel like this having dialogue about commercial launch, and there were envisioned several constellations that were going to require significant commercial launch. Lockheed Martin and Boeing set out to develop launch vehicles that were focused on that very robust commercial market – in the case of McDonald Douglas at the time, which later became Boeing, the factory in Decatur was…sized to crank out 40 [rocket boosters] a year, a couple of ships were bought to transport those…significant infrastructure put in place to address that envisioned launch market.” – John Elbon, COO, United Launch Alliance (ULA)
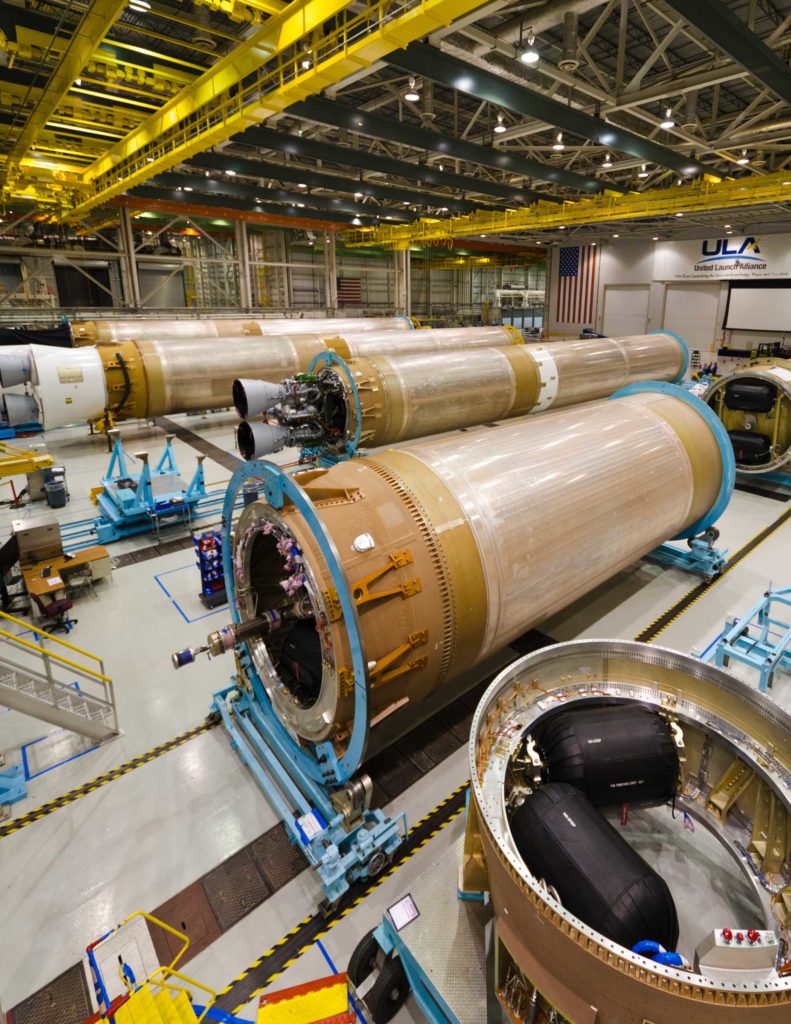
- ULA’s Decatur, Alabama factory now produces both Delta IV and Atlas 5. (ULA)
- ULA’s Atlas 5 launched AEHF-4 for the USAF earlier this month. (ULA)
In reality, Boeing was so desperate to secure USAF launches – despite the fact that it knew full well that Delta IV was too expensive to be sustainably competitive – that dozens of employees were eventually roped into a systematic, years-long, highly-illegal program of corporate espionage specifically designed to beat out government launch competitor Lockheed Martin. Humorously, Delta IV was not even Boeing’s design – rather, Boeing acquired designer McDonnell Douglas in late 1996, five days before the USAF announced the decision to reject Boeing and another company’s EELV proposals, narrowing down to two finalists (McDonnell Douglas and Lockheed Martin).
Seven years after the original lawsuit snowballed, Boeing settled with Lockheed Martin for a payment of more than $600M in 2006, accepting responsibility for its employees’ actions but admitting no corporate wrongdoing. Five years after that settlement, John Elbon became Vice President of Boeing’s Space Exploration division. This is by no means to suggest that Elbon is in any way complicit, having spent much of his 30+ years at Boeing managing the company’s involvement in the International Space Station, but more serves as an example of how recent these events are and why their consequences almost certainly continue to reverberate loudly within the US space industry.
SpaceX forces change
Worsened significantly by the consequences of Boeing’s lies about the actual operational costs of its Delta IV rocket (it had planned to secretly write off a loss on each rocket in order to steal USAF market share from LockMart), the commercial market for the extremely expensive rocket was and still is functionally nonexistent. 35 out of the family’s 36 launches have been contracted by the US military (30), NOAA (3), or NASA (2); the rocket’s first launch, likely sold at a major discount to Eutelsat, remains its one and only commercial mission.

Atlas V, typically priced around 30% less than comparable Delta IV variants, has had a far more productive career, albeit with very few commercial launches since the Dec. 2006 formation of the United Launch Alliance. Since 2007, just 5 of Atlas V’s 70 launches have been for commercial customers. Frankly, although Atlas V was appreciably more affordable than Delta IV, neither rocket was ever able to sustainably compete with Europe’s Ariane 5 workhorse – Ariane 5 cost more per launch, but superior payload performance often let Arianespace manifest two large satellites on a single launch, approximately halving the cost for each customer. Russia’s affordable (but only moderately reliable) Proton rockets also played an important role in the commercial launch industry prior to SpaceX’s arrival.
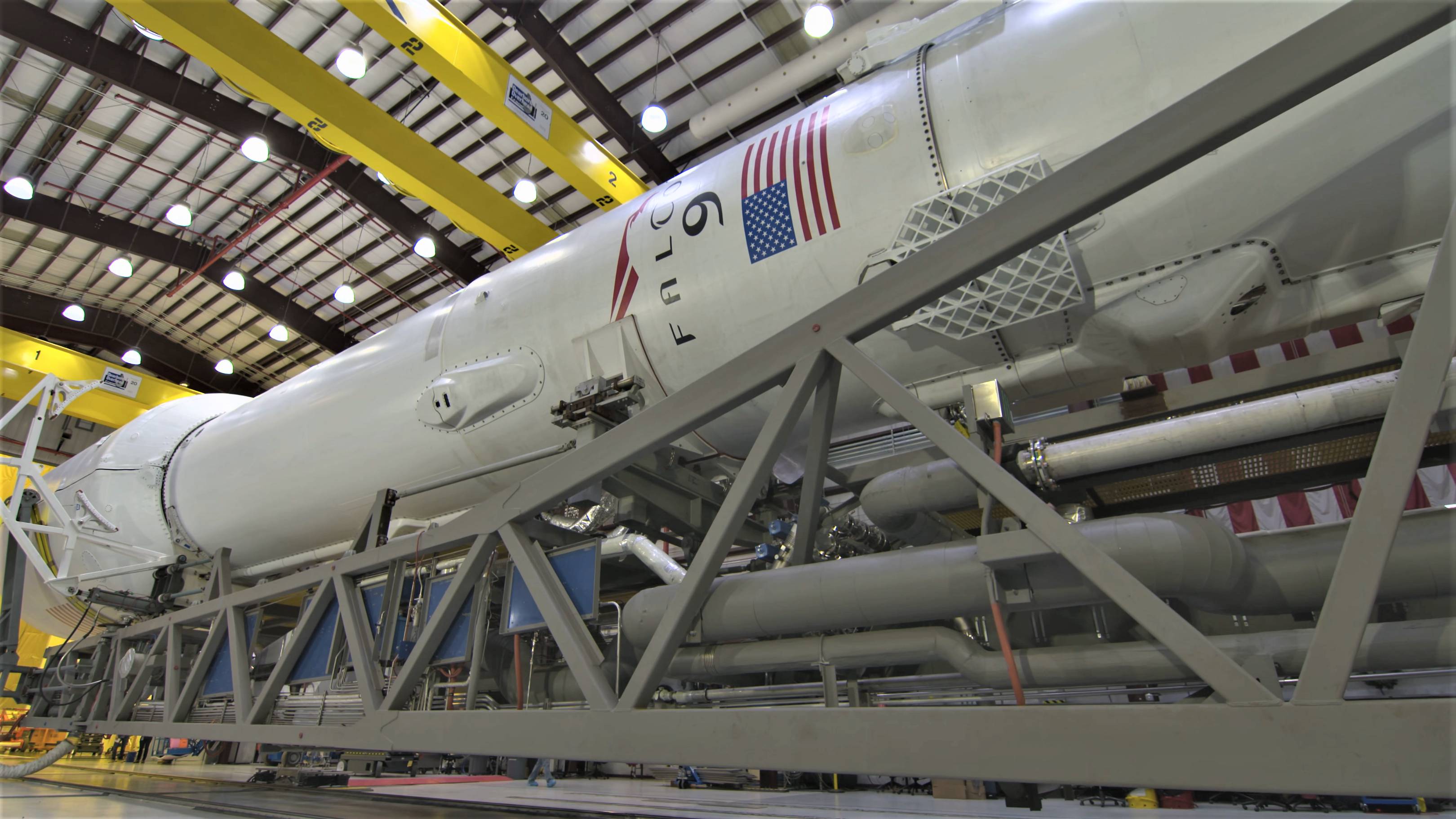
After fighting tooth and nail for years to break ULA’s US governmental launch monopoly, SpaceX’s first dedicated National Security Space launch finally occurred less than a year and a half ago, in May 2017. SpaceX has since placed a USAF spaceplane and a classified NSS-related satellite into orbit and been awarded launch contracts for critical USAF payloads, most notably winning five of five competed GPS III satellite launches, to begin as early as mid-December. Falcon 9 will cost the USAF roughly 30% less than a comparable Atlas 5 contract, $97M to ULA’s ~$135M.
- The aft connection mechanisms on Falcon Heavy Flight 1 and Flight 2 appear to be quite similar. It’s possible that SpaceX has chosen to reuse aspects of the hardware recovered on Flight 1’s two side boosters. (SpaceX)
- Falcon 9 Block 5 booster B1046 seen during both of its post-launch landings. (SpaceX/SpaceX)
A bit more than two decades after Boeing bought McDonnell Douglas and began a calculated effort to steal trade secrets from Lockheed Martin, Elbon – now COO of the Boeing/Lockheed Martin-cooperative ULA – seems to fervently believe that the most critical mistake made in the late 1990s and early 2000s was the USAF’s decision to partially support the development of two separate rockets. Elbon concluded his remarks on the topic with one impressively unambiguous summary of ULA’s position:
“We have to make sure that we don’t get too much supply and not enough demand so that the [launch] providers can’t survive in a robust business environment, and then we lose the capability as a country to do the launches we need to do … [That’s] the perspective we have at ULA and it’s based on the experience that we’ve been through in the past.”
In his sole Delta IV vs. Atlas V case-study, what ULA now seems to think might have been “too much supply” under the USAF’s EELV program appears to literally be the fundamental minimum conditions needed for competition to exist at all – two companies offering two competing products. Short of directly stating as much, it’s difficult to imagine a more concise method of revealing the apparent belief that competition – at all – is intrinsically undesirable or risky.
Elon Musk
Why Tesla’s Q3 could be one of its biggest quarters in history
Tesla could stand to benefit from the removal of the $7,500 EV tax credit at the end of Q3.

Tesla has gotten off to a slow start in 2025, as the first half of the year has not been one to remember from a delivery perspective.
However, Q3 could end up being one of the best the company has had in history, with the United States potentially being a major contributor to what might reverse a slow start to the year.
Earlier today, the United States’ House of Representatives officially passed President Trump’s “Big Beautiful Bill,” after it made its way through the Senate earlier this week. The bill will head to President Trump, as he looks to sign it before his July 4 deadline.
The Bill will effectively bring closure to the $7,500 EV tax credit, which will end on September 30, 2025. This means, over the next three months in the United States, those who are looking to buy an EV will have their last chance to take advantage of the credit. EVs will then be, for most people, $7,500 more expensive, in essence.
The tax credit is available to any single filer who makes under $150,000 per year, $225,000 a year to a head of household, and $300,000 to couples filing jointly.
Ending the tax credit was expected with the Trump administration, as his policies have leaned significantly toward reliance on fossil fuels, ending what he calls an “EV mandate.” He has used this phrase several times in disagreements with Tesla CEO Elon Musk.
Nevertheless, those who have been on the fence about buying a Tesla, or any EV, for that matter, will have some decisions to make in the next three months. While all companies will stand to benefit from this time crunch, Tesla could be the true winner because of its sheer volume.
If things are done correctly, meaning if Tesla can also offer incentives like 0% APR, special pricing on leasing or financing, or other advantages (like free Red, White, and Blue for a short period of time in celebration of Independence Day), it could see some real volume in sales this quarter.
You can now buy a Tesla in Red, White, and Blue for free until July 14 https://t.co/iAwhaRFOH0
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 3, 2025
Tesla is just a shade under 721,000 deliveries for the year, so it’s on pace for roughly 1.4 million for 2025. This would be a decrease from the 1.8 million cars it delivered in each of the last two years. Traditionally, the second half of the year has produced Tesla’s strongest quarters. Its top three quarters in terms of deliveries are Q4 2024 with 495,570 vehicles, Q4 2023 with 484,507 vehicles, and Q3 2024 with 462,890 vehicles.
Elon Musk
Tesla Full Self-Driving testing continues European expansion: here’s where
Tesla has launched Full Self-Driving testing in a fifth European country ahead of its launch.
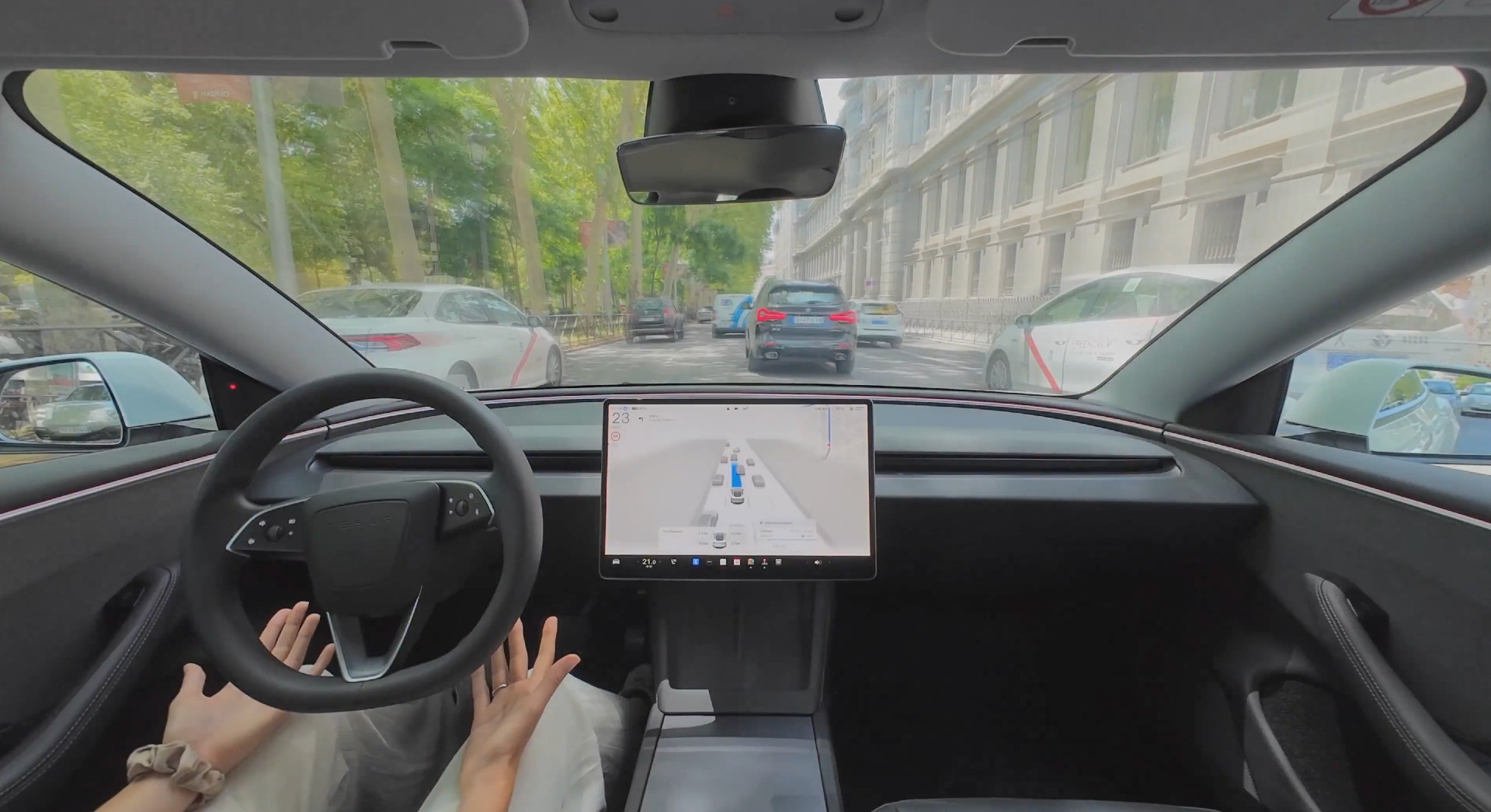

Tesla Full Self-Driving is being tested in several countries across Europe as the company prepares to launch its driver assistance suite on the continent.
The company is still working through the regulatory hurdles with the European Union. They are plentiful and difficult to navigate, but Tesla is still making progress as its testing of FSD continues to expand.
Today, it officially began testing in a new country, as more regions open their doors to Tesla. Many owners and potential customers in Europe are awaiting its launch.
On Thursday, Tesla officially confirmed that Full Self-Driving testing is underway in Spain, as the company shared an extensive video of a trip through the streets of Madrid:
Como pez en el agua …
FSD Supervised testing in Madrid, Spain
Pending regulatory approval pic.twitter.com/txTgoWseuA
— Tesla Europe & Middle East (@teslaeurope) July 3, 2025
The launch of Full Self-Driving testing in Spain marks the fifth country in which Tesla has started assessing the suite’s performance in the European market.
Across the past several months, Tesla has been expanding the scope of countries where Full Self-Driving is being tested. It has already made it to Italy, France, the Netherlands, and Germany previously.
Tesla has already filed applications to have Full Self-Driving (Supervised) launched across the European Union, but CEO Elon Musk has indicated that this particular step has been the delay in the official launch of the suite thus far.
In mid-June, Musk revealed the frustrations Tesla has felt during its efforts to launch its Full Self-Driving (Supervised) suite in Europe, stating that the holdup can be attributed to authorities in various countries, as well as the EU as a whole:
Tesla Full Self-Driving’s European launch frustrations revealed by Elon Musk
“Waiting for Dutch authorities and then the EU to approve. Very frustrating and hurts the safety of people in Europe, as driving with advanced Autopilot on results in four times fewer injuries! Please ask your governing authorities to accelerate making Tesla safer in Europe.”
Waiting for Dutch authorities and then the EU to approve.
Very frustrating and hurts the safety of people in Europe, as driving with advanced Autopilot on results in four times fewer injuries!
Please ask your governing authorities to accelerate making Tesla safer in Europe. https://t.co/QIYCXhhaQp
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) June 11, 2025
Tesla said last year that it planned to launch Full Self-Driving in Europe in 2025.
Elon Musk
xAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
xAI welcomed the development in a post on its official xAI Memphis account on X.
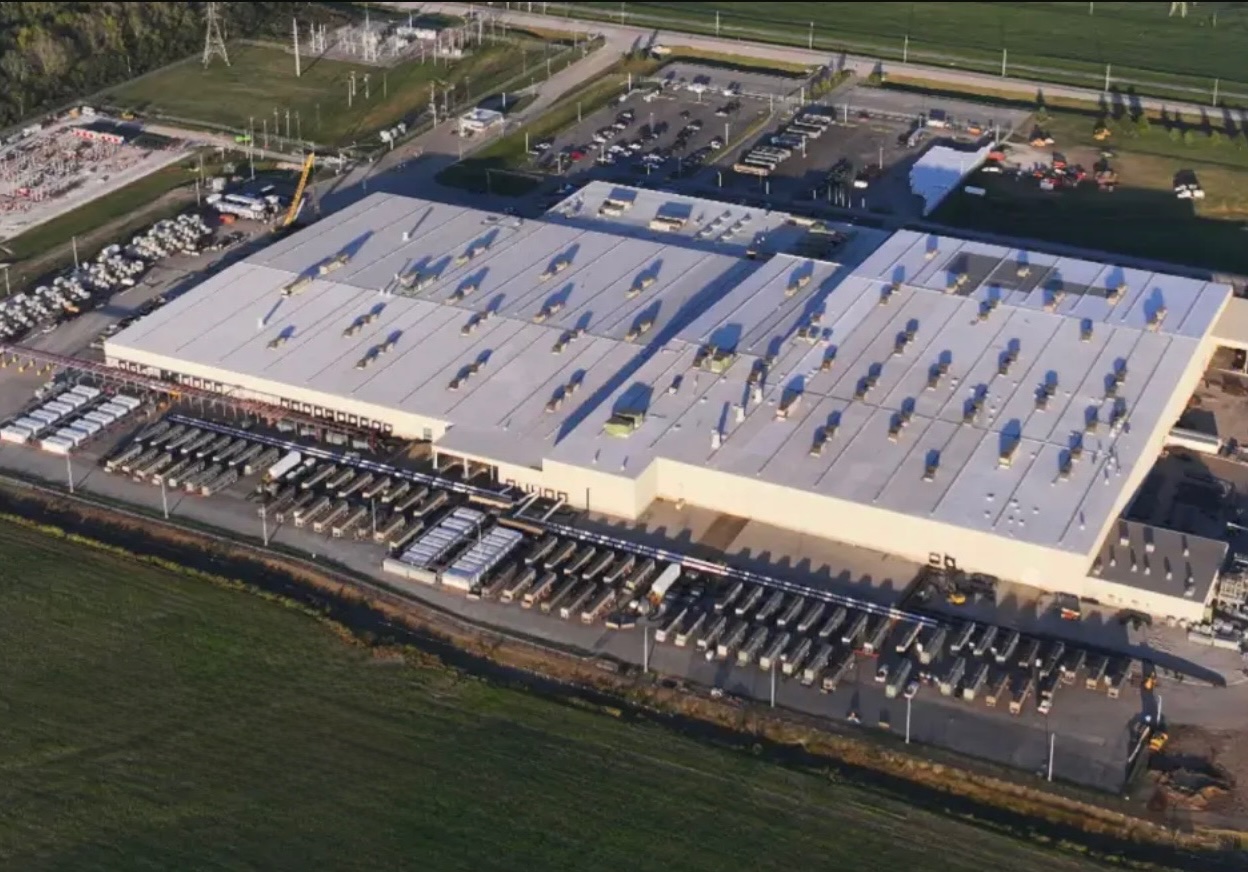

Elon Musk’s artificial intelligence startup xAI has secured an air permit from Memphis health officials for its data center project, despite critics’ opposition and pending legal action. The Shelby County Health Department approved the permit this week, allowing xAI to operate 15 mobile gas turbines at its facility.
Air permit granted
The air permit comes after months of protests from Memphis residents and environmental justice advocates, who alleged that xAI violated the Clean Air Act by operating gas turbines without prior approval, as per a report from WIRED.
The Southern Environmental Law Center (SELC) and the NAACP has claimed that xAI installed dozens of gas turbines at its new data campus without acquiring the mandatory Prevention of Significant Deterioration (PSD) permit required for large-scale emission sources.
Local officials previously stated the turbines were considered “temporary” and thus not subject to stricter permitting. xAI applied for an air permit in January 2025, and in June, Memphis Mayor Paul Young acknowledged that the company was operating 21 turbines. SELC, however, has claimed that aerial footage shows the number may be as high as 35.
Critics are not giving up
Civil rights groups have stated that they intend to move forward with legal action. “xAI’s decision to install and operate dozens of polluting gas turbines without any permits or public oversight is a clear violation of the Clean Air Act,” said Patrick Anderson, senior attorney at SELC.
“Over the last year, these turbines have pumped out pollution that threatens the health of Memphis families. This notice paves the way for a lawsuit that can hold xAI accountable for its unlawful refusal to get permits for its gas turbines,” he added.
Sharon Wilson, a certified optical gas imaging thermographer, also described the emissions cloud in Memphis as notable. “I expected to see the typical power plant type of pollution that I see. What I saw was way worse than what I expected,” she said.
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
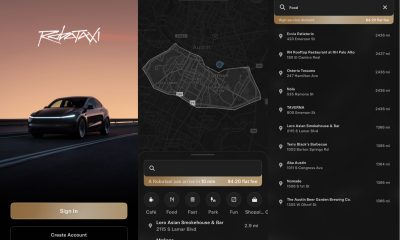
Elon Musk2 weeks agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Grok 3 partners with Oracle Cloud for corporate AI innovation
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoWatch Tesla’s first driverless public Robotaxi rides in Texas
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoSpaceX and Elon Musk share insights on Starship Ship 36’s RUD
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla has started rolling out initial round of Robotaxi invites



























