SpaceX
SpaceX’s first orbital Starship begins assembly as steel heat shield passes tests
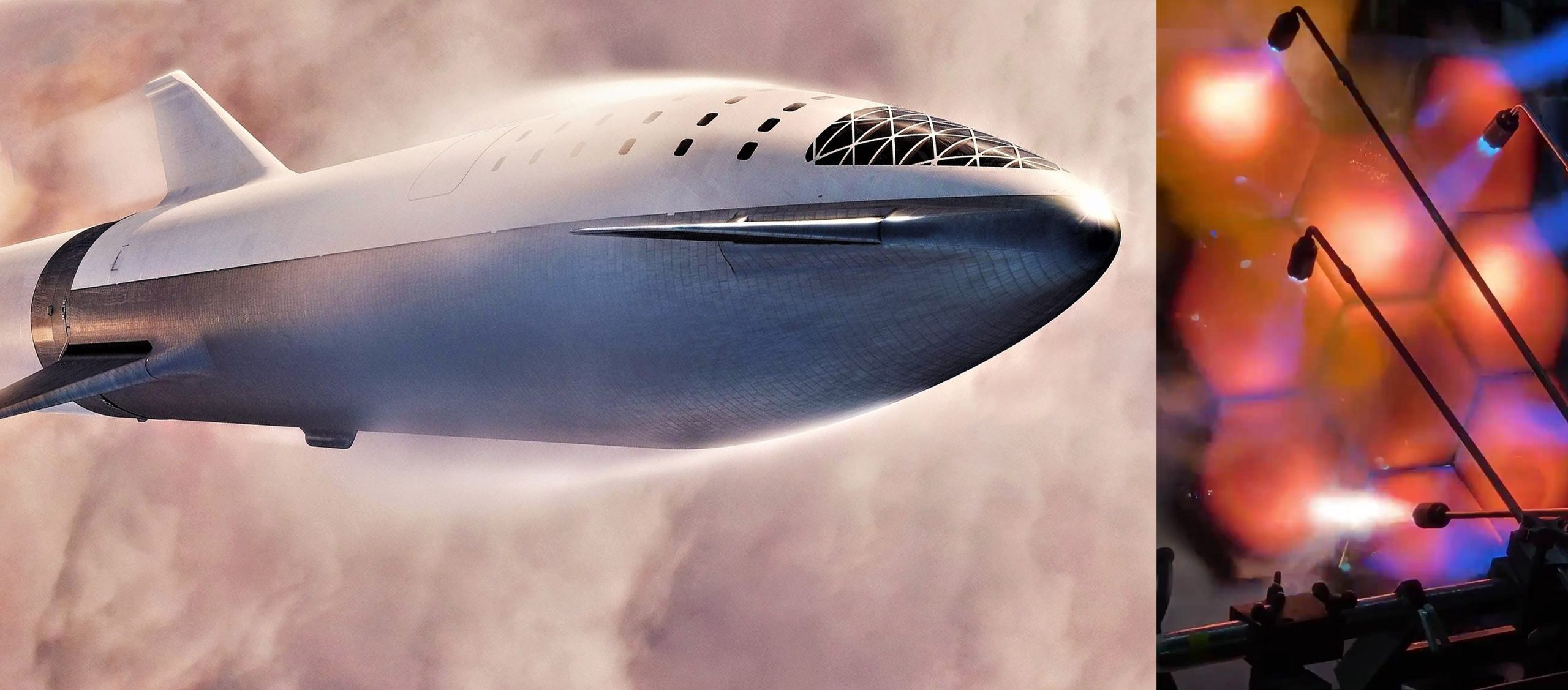
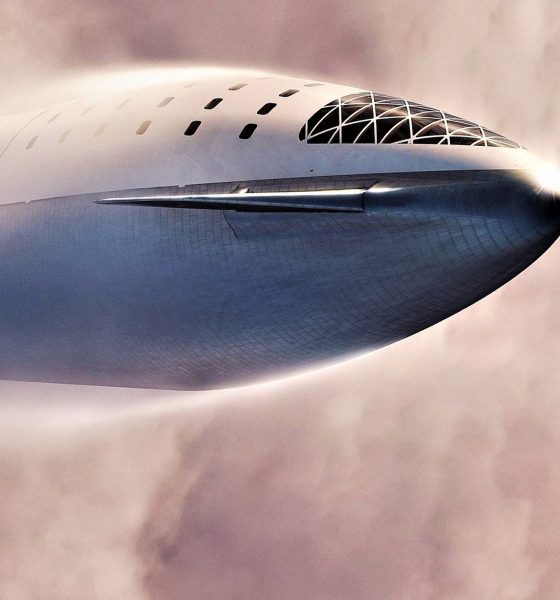
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk says that the company’s South Texas workforce has already begun to fabricate the first orbital-class Starship prototype, while Hawthorne engineers and technicians are in the midst of performing small-scale testing of the vehicle’s unprecedented stainless steel heat shield.
To be assembled out of hexagonal tiles of (presumably) stainless steel, Starship’s metallic heat shield will be one of the most crucial aspects of the orbital spacecraft, particularly with respect to ensuring that it’s extraordinarily easy to reuse. To survive extreme interplanetary-velocity reentry conditions at Mars, Earth, and beyond and remain in a functional, flight-ready condition after landing, SpaceX will need to implement the world’s first orbital-class, large-scale metallic heat shield with an immature technology known as transpirational cooling.
By quite literally drilling tiny holes (pores) into heat shield plates at the hottest parts of Starship’s hull, transpirational cooling effectively allows a large portion of the heat of reentry to be wicked away by the flash evaporation of a liquid, typically water. For SpaceX’s Starship, it’s likely that the coolant of choice would be either liquid water or liquid methane, the former of which offers better cooling per unit of mass at the cost of added plumbing complexity and spaceship mass, while the latter would make use of the same propellant fueling the ship at the cost of worse cooling per unit of mass. Either way, SpaceX will be heading into unproven territory, demanding extensive ground and flight testing to first ensure that the concept is truly viable and then to verify that it can be made as reliable and reusable as it simply has to be.
Tests like those shown on March 17th by Musk indicate that SpaceX is indeed deep into the process of extensive and often destructive testing, something the company has proven to be exceptionally good at. It’s unclear if the above test of Starship’s hexagonal heat shield tiles – likely made out of a variant of 300-series stainless steel – involved tiles with active or passive cooling, but Musk suggested that the hot-spots created with spin-forming torches reached temperatures as high as 1650 Kelvin (2500ºF/1400ºC. Unlike the ablative heat shields SpaceX is familiar with building and operating through its Crew and Cargo Dragon spacecraft, a stainless steel heat shield would be expected to almost entirely resist erosion (i.e. ablation) during extremely high-velocity reentries of at least 12-14 km/s (~31,000 mph, Mach 40+).
Update on the fairing and the unknown “2nd fairing” pic.twitter.com/5PMBYyBDAi— Austin Barnard? (@austinbarnard45) March 16, 2019
Meanwhile, Musk also confirmed that SpaceX has decided to skip constructing a replacement nosecone/fairing for Starhopper, a functional Starship prototype that will be used to conduct extremely short hop tests like Falcon 9’s development-era Grasshopper and F9R test articles. Over the last several weeks, SpaceX technicians have been rapidly assembling what was initially assumed to be the replacement fairing Musk had previously suggested would be built. Instead, the duo of stainless steel barrel sections – relying on steel much thinner than the heavy-duty stuff used to build Starhopper – are apparently the beginnings of the first orbital-class Starship prototype, said by Musk to be aiming for flight-readiness as early as June 2019 around two months ago.
While still an extraordinarily ambitious target for a vehicle that has yet to conduct any integrated hops or flight-tests in any form, the fact that SpaceX is began the process of building the first orbital Starship in late February could actually give the company’s engineers and technicians a fighting chance to complete Starhopper testing and Starship assembly over the next 90-100 days.
If stacked atop each other, the two new steel sections in work would likely stretch a solid 20-30 meters (65-100 ft) tall. Meanwhile, the first orbital-grade tank domes and/or conical nose section is also in the process of being welded together out of smaller segments, already fast approaching something ready to be installed inside the steel barrel sections.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.


![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





