SpaceX
SpaceX President talks BFR and Mars exploration in laid-back Madrid Q&A session
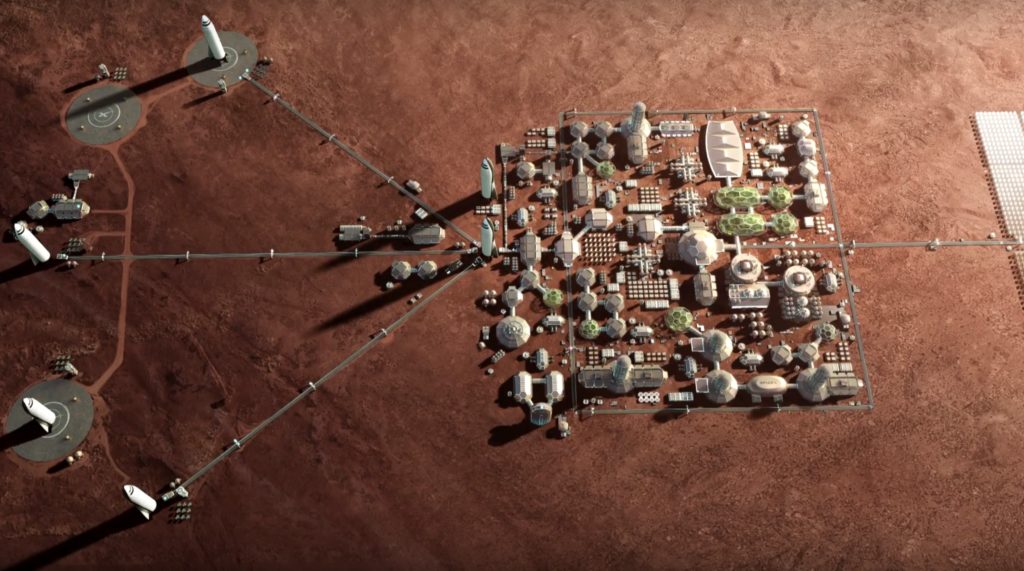
Speaking at a Q&A session hosted for a Madrid university’s Master’s of Business Administration students, SpaceX President and COO Gwynne Shotwell talked for nearly an hour about the launch company’s next-generation BFR rocket, the reality of long-term life on Mars, and more, revealing a number of interesting tidbits in the process.
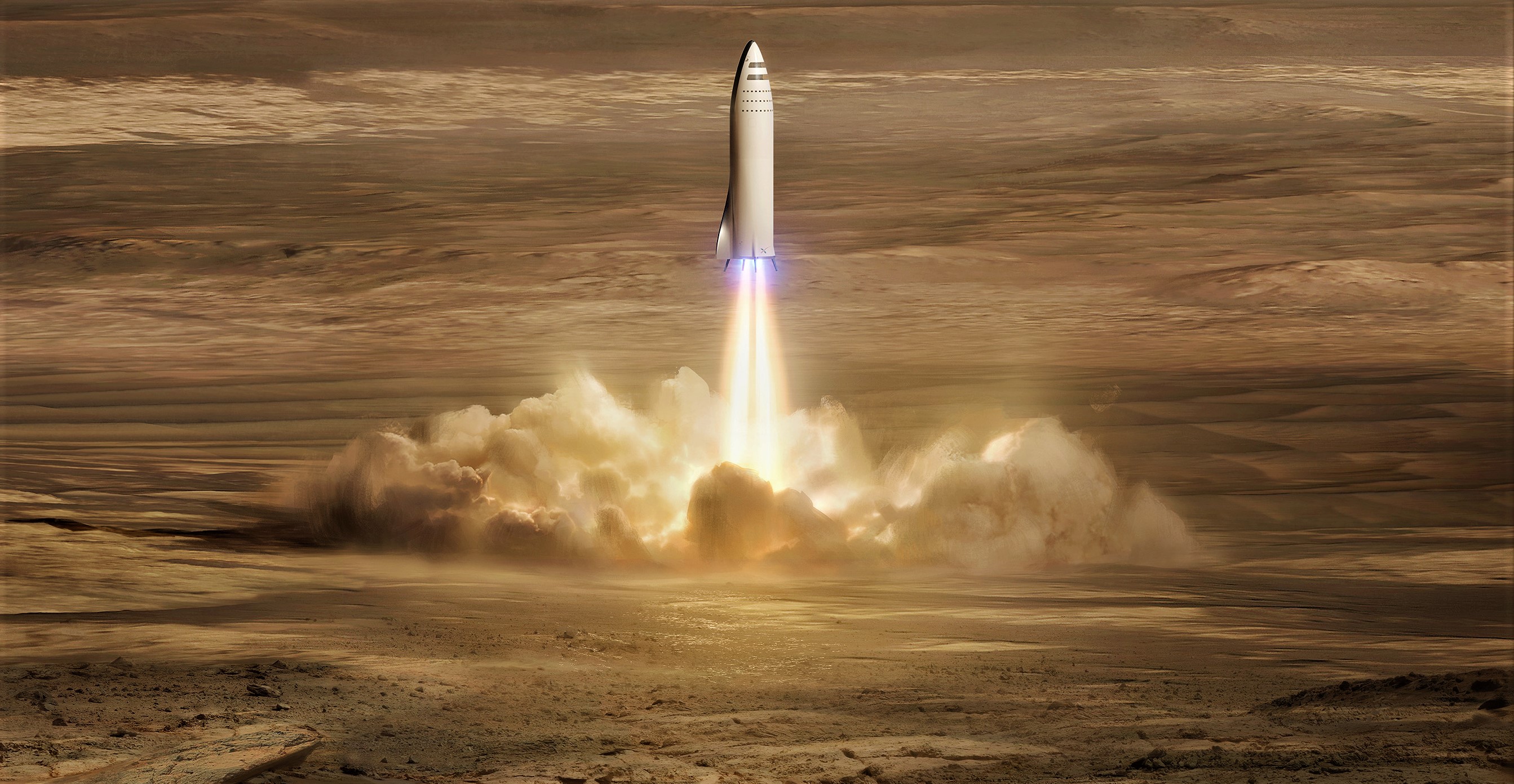

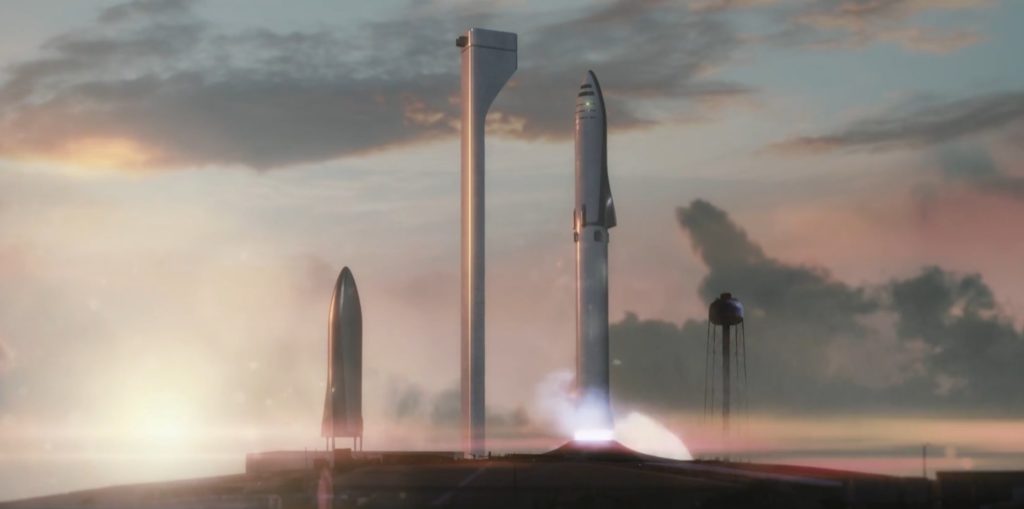
Almost entirely led by questions from the unusually well-informed audience, the graduate students and professors predominately kept the famous SpaceX exec more or less focused on the company’s future, delving into the reasoning behind BFR. Shotwell had only praise for the next-generation launch vehicle, which is targeting initial hop tests in late 2019 and its first full launches as early as 2021, a delay of several months from previous schedule estimates targeting hops in early 2019 and orbit by 2020.
Aside from schedule updates, Shotwell had more still to say about the rocket:
- “The flexibility that [BFR] offers will change how we do everything in space.”
- “BFR has the capability to open its payload bay, bring [a] satellite back in, close it, pressurize it, work on it (repair, upgrade, etc), and redeploy it”
- “BFR will basically allow people to work and live in space”
Although she offered some self-deprecating humor on SpaceX’s often-optimistic schedules for future projects, she was for the most part positive about the company’s ultimate aspirations of completing and perfecting BFR, stating without hesitation that “something terrible [would] have to happen at SpaceX for us to not be on our way to Mars and back in 10 years.”
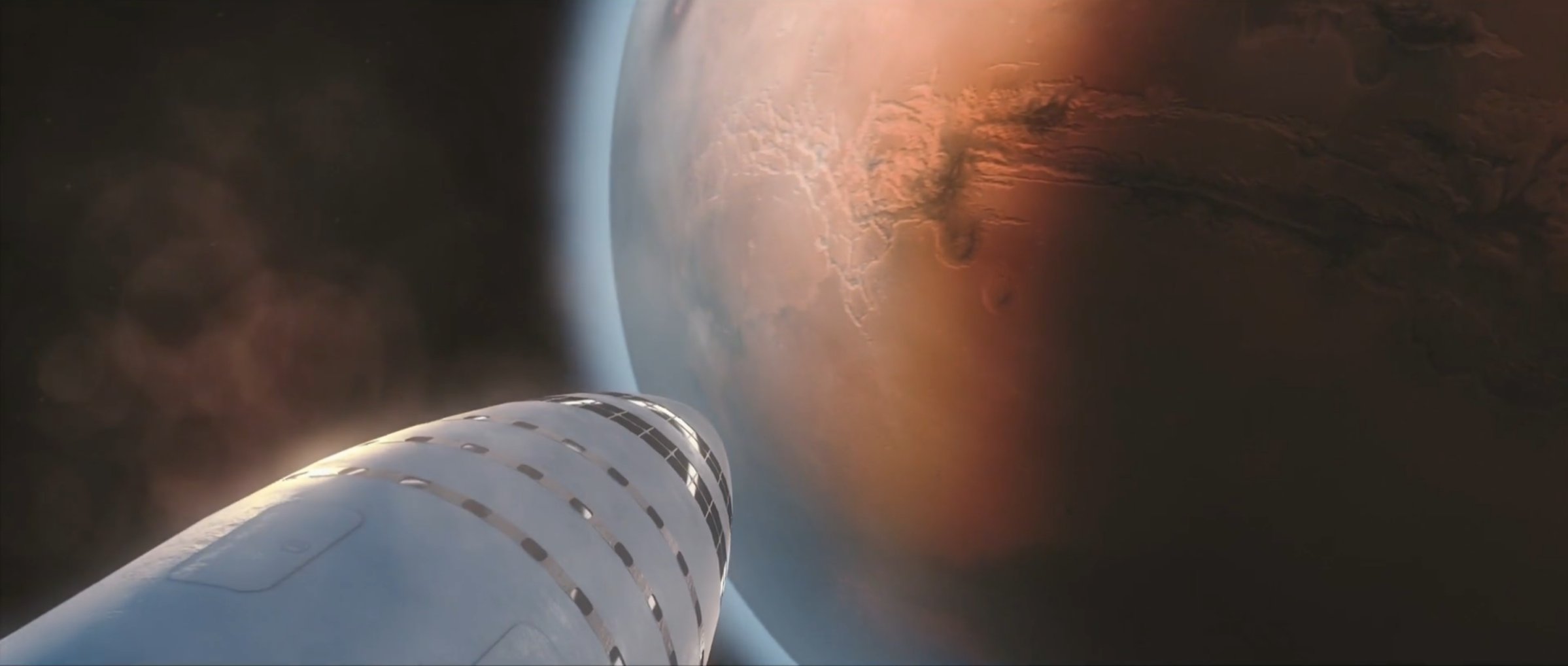
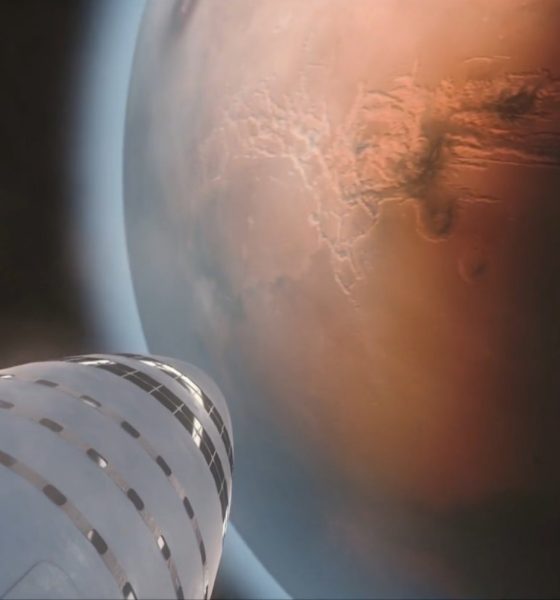
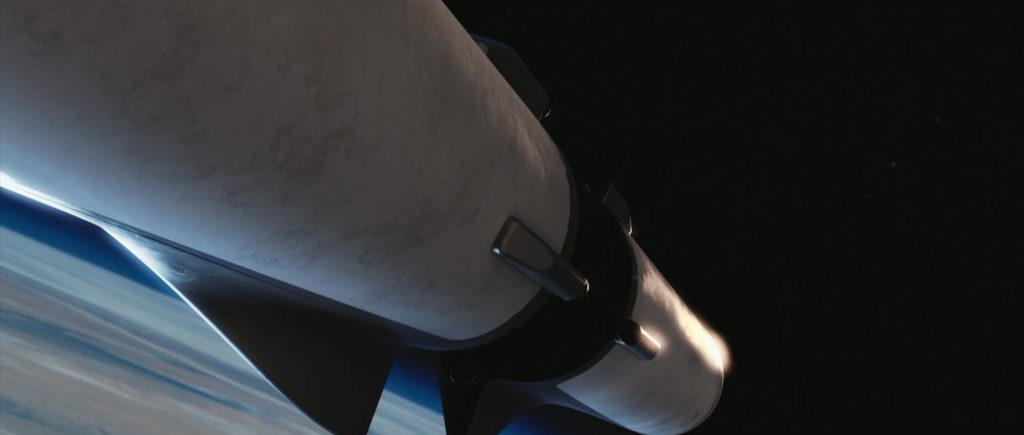
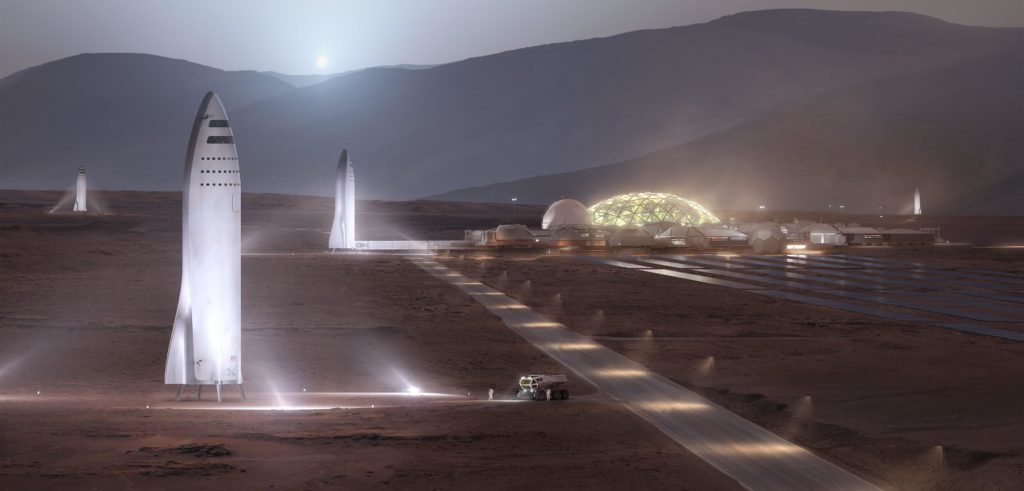
- SpaceX’s BFR visualized just before launch at a heavily-upgraded Pad 39A. (SpaceX)
- Note the 2017/early-2018 variant’s single delta-wing and extendable leg pods (silver). (SpaceX)
- We’re not here just yet, but SpaceX is pushing hard to build BFR and get humanity to Mars as quickly as practicable. (SpaceX)
Shotwell acknowledged that some of the hurdles in the way of those goals could become headaches, particularly the decision to build the rocket’s propellant tanks solely out of carbon fiber composites, but also expressed her belief that most of the difficulty of designing and building BFR’s advanced Raptor engine was already behind SpaceX. Roughly two times as powerful as Merlin 1D and dramatically more efficient, SpaceX’s Raptor development team has conducted extensive hot-fire testing (at least 1200 seconds) of the engine, optimizing it to the point that the company is already building (and maybe already hot-fire testing) flight-grade hardware.
Other miscellaneous comments showed Shotwell at her best, ad-libbing one-liners that were lucid, accurate, and entertaining.
- “We’ll be going to Mars … with NASA and with ESA. It’s gonna be like extreme camping… for 100 years. And then it might be okay.”
- “[Space] tourism is inevitable but [SpaceX] doesn’t want to do it too soon”, the goal is to launch “test pilots before families”
- “The first cars on Mars will be Teslas.”
Watch the full Shotwell Q&A – graciously recorded by the business student and SpaceX subreddit member LordsofDecay – at the link below.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!

Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
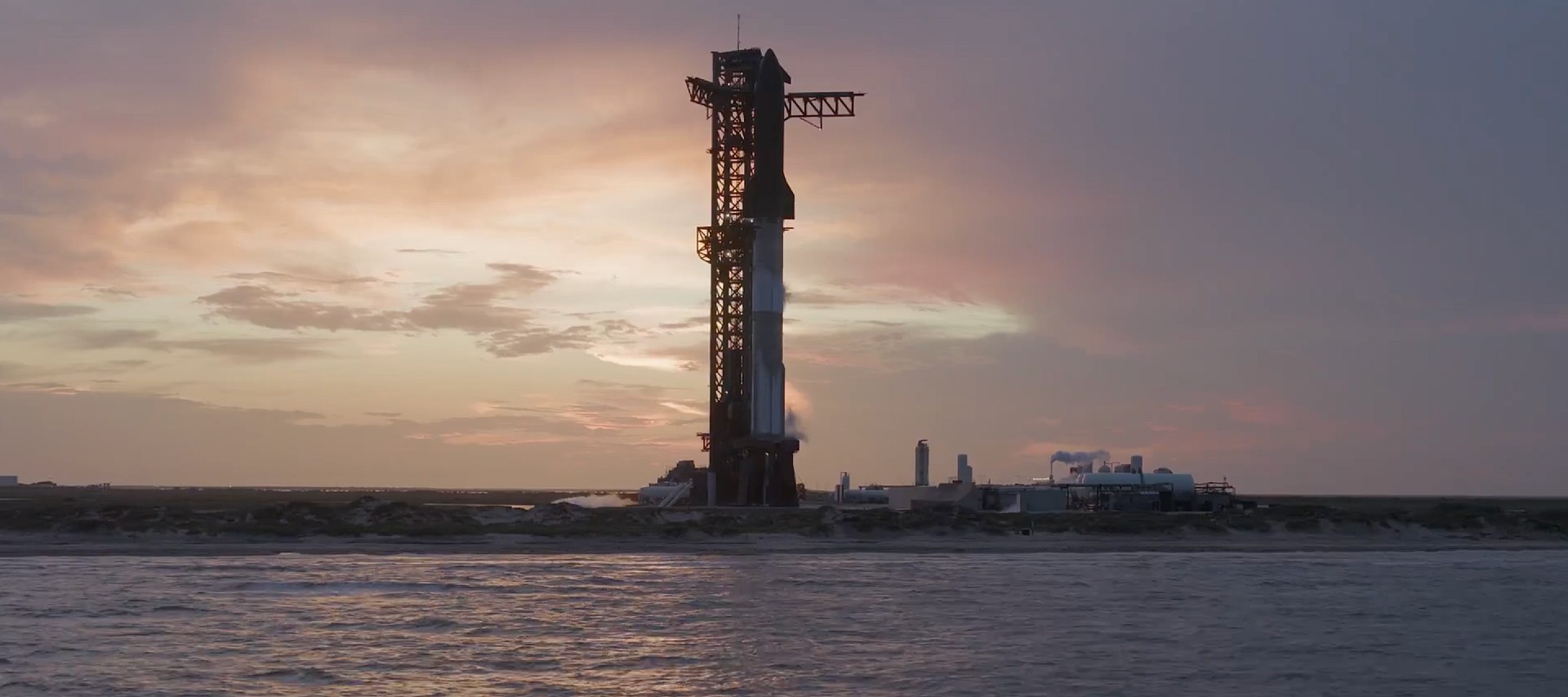

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.
Elon Musk
Starbase after dark: Musk’s latest photo captures a Spaceport on the brink of history
SpaceX’s Starbase city in Boca Chica, Texas is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
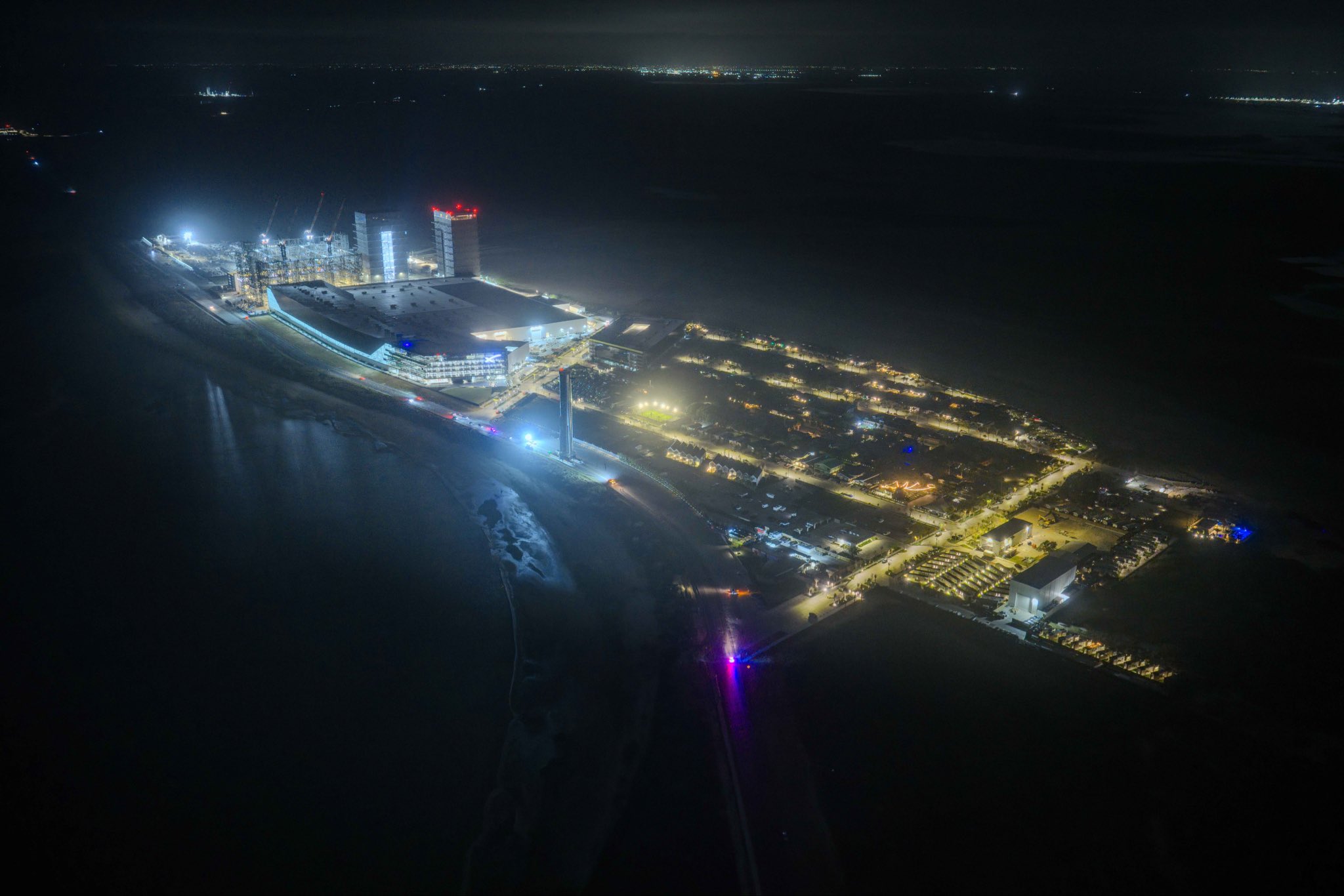

A striking nighttime photograph of SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, shared recently by Elon Musk on X, offers a dramatic glimpse of an operation that is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
The most immediately visible change in the photo is the presence of two fully erected Starship launch towers dominating the coastal skyline. The second orbital launch pad, known as Pad B, now features its fully erected tower, OLIT-3, which stands approximately 474 feet tall and incorporates an integrated water-cooled flame trench designed to minimize damage and reduce turnaround time between launches. The dual-tower silhouette against the night sky signals a decisive shift from experimental testing facility to high-cadence launch operations.
Grok Image concept of Elon Musk’s latest Starbase photo via X
Back at Starbase, Pad 2 is approaching hardware completion, with upgraded chopstick arms, a new chilldown vent system, and all 20 hold-down arms now fitted with protective doors to shield them from the intense exhaust of up to 33 Raptor 3 engines, according to a deeper dive by NASASpaceFlight.
SpaceX has also received approval to nearly double the footprint of the Starbase launch site, with groundwork already underway to add LNG liquefaction plants, expanded propellant storage, and additional ground support infrastructure.
The photo also carries a milestone civic dimension. Starbase officially became a Texas city in May 2025 after a community vote, with SpaceX employees elected as mayor and commissioners of the newly incorporated municipality. That legal status streamlines launch approvals and gives SpaceX direct control over local infrastructure decisions.
The FAA has approved an increase in launches from Starbase in Texas from five to twenty-five per year, clearing the runway for the kind of flight frequency needed to fulfill Starship’s ultimate mission of ferrying cargo and crew to the Moon, servicing the Department of Defense, deploying next-generation Starlink satellites, and eventually establishing Elon Musk’s long sought after goal of a self-sustaining human presence on Mars.
Seen from above in the dark, Starbase looks less like a test site and more like a spaceport.