

News
SpaceX private astronaut launch debut to reuse Crew-1 Dragon spacecraft
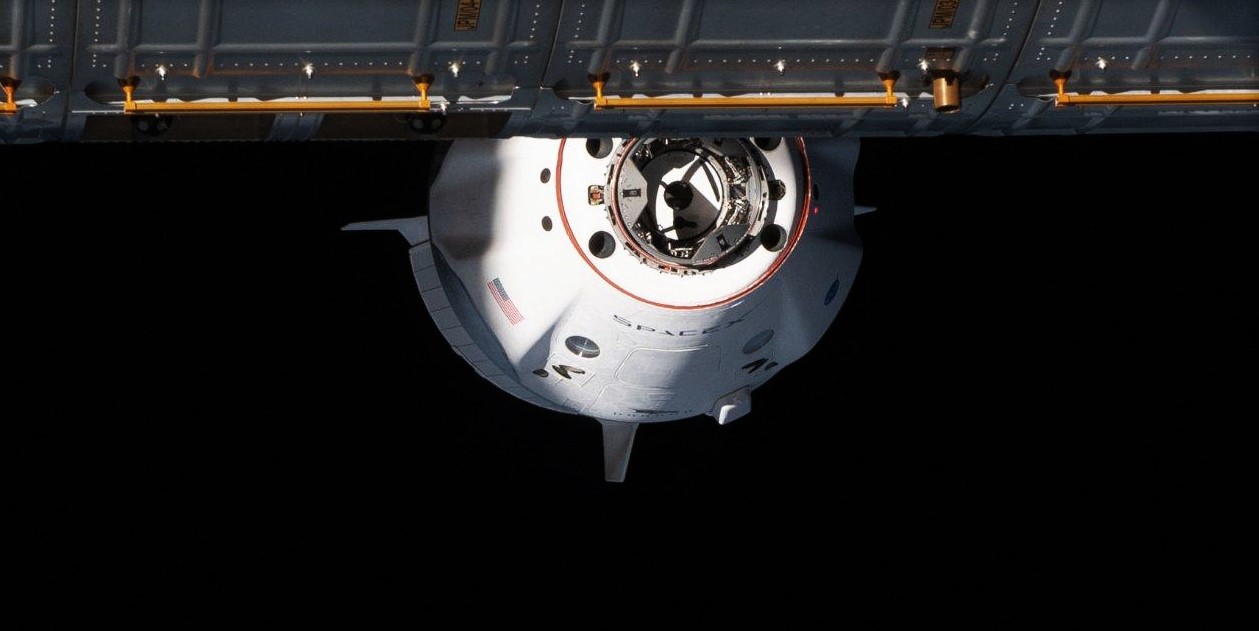
A former NASA astronaut now employed by Axiom Space says that SpaceX’s private astronaut launch debut will reuse the same Crew Dragon spacecraft currently supporting NASA’s Crew-1 mission in orbit.
Currently just a few weeks into a planned six-month stint in orbit, potentially marking the longest uninterrupted flight of an American spacecraft ever, Crew Dragon capsule C207 and an expendable trunk section arrived at the International Space Station (ISS) on November 16th. Known as Crew-1, the mission represents SpaceX and NASA’s commercial operational astronaut launch debut, carrying four astronauts to the ISS.
Crucially, the mission has been an almost flawless success so far and Falcon 9 has now completed four Crew Dragon launches without issue. On the Dragon side of things, the Crew-1 spacecraft performed a bit less perfectly than those tasked with flying Demo-1 and Demo-2, but SpaceX handled the minor issues that arose with the professionalism and composure of a team far more familiar with human spaceflight.

Early success aside, there is still some definite uncertainty ahead of Crew Dragon. While several Russian spacecraft have decades of experience spending at least several months at a time in orbit, a crewed US spacecraft has never spent more than 84 days in orbit. SpaceX itself actually beat out NASA to secure the second-place record with Crew Dragon’s 63-day Demo-2 astronaut launch debut, completed with a successful reentry and splashdown on August 2nd.
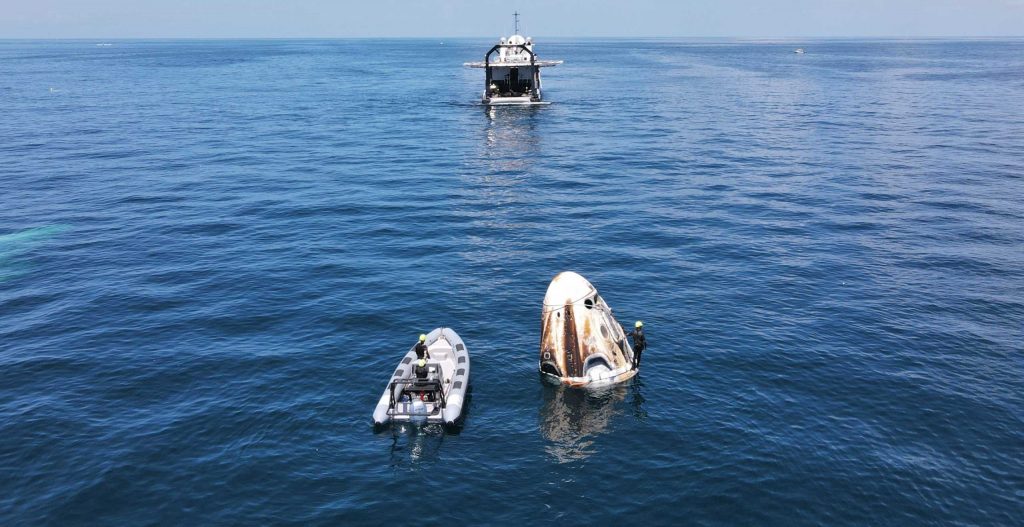

However, Crew-1 is expected to more than double that previous US record and almost triple SpaceX’s own second-place record, spending roughly 180 days (six months, give or take) in orbit. Barring an unprecedented space station or spacecraft emergency, Crew Dragon C207 will undock from ISS, reenter Earth’s atmosphere, and splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico or the Atlantic Ocean sometime in May 2021. Of course, as the first recoverable US spacecraft to spend anywhere close to that long in orbit, the Crew-1 Crew Dragon will be closely monitored to ensure the safety and reliability of its intricate reentry and recovery systems after some six months exposed to the extremes of space.
Still, success is by far the likeliest outcome. When Crew Dragon C207 splashes down, its four astronaut passengers will be carefully extricated and the inspection and refurbishment process will begin almost immediately thereafter. Crew-1 will technically be the second Crew Dragon spacecraft to be refurbished after an orbital spaceflight, following Demo-2 capsule C206’s inaugural Dragon 2 reuse perhaps just a month or two prior.
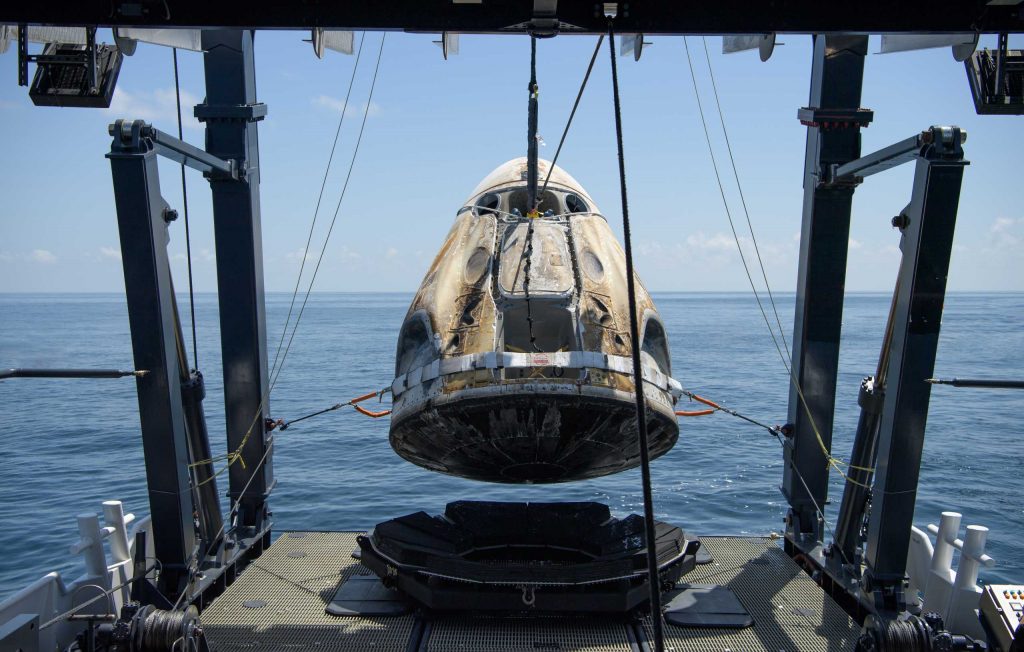

The Demo-2 Crew Dragon capsule is currently scheduled to fly a second time as early as March 31st, 2021 on SpaceX’s Crew-2 mission, ferrying another four astronauts to the ISS. If successful, Crew-2 will represent the first commercial astronaut launch ever to reuse both an orbital-class rocket booster and an orbital spacecraft, and the NASA-overseen process of refurbishment and re-flight will thus pave the way for future flight-proven astronaut launches. That includes private company Axiom Space’s first private AX-1 astronaut launch, which is currently scheduled to launch as early as Q4 2021.
AX-1 will be captained by former NASA astronaut Mike Lopez-Algeria and carry three other private astronauts, including Israeli multimillionaire Eytan Stibbe. SpaceX will thus be tasked with launching Israel’s second astronaut ever after Ilan Ramon was killed when a heat shield design flaw caused NASA Space Shuttle Columbia to break up during reentry in 2003.

News
Tesla VP explains latest updates in trade secret theft case
Tesla reportedly caught Matthews copying the tech into machines that were sold to competitors, claiming they lied about doing so for three years, and continued to ship it. That is when Tesla chose to sue Matthews in July 2024 in Federal court, demanding over $1 billion in damages due to trade secret theft.

Tesla Vice President Bonne Eggleston explained the latest updates in a trade secret theft case the company has against a former manufacturing equipment supplier, Matthews International.
Back in 2024, Tesla had filed a lawsuit against Matthews International, alleging that the firm stole trade secrets about battery manufacturing and shared those details with some of Tesla’s competitors.
Early last year, a U.S. District Court Judge denied Tesla’s request to block Matthews International from selling its dry battery electrode (DBE) technology across the world. The judge, Edward Davila, said that the patent for the tech was due to Matthews’ “extensive research and development.”
The two companies’ relationship began back in 2019, as Tesla hired Matthews to help build the equipment for its 4680 battery cell. Tesla shared confidential software, designs, and know-how under strict secrecy rules.
Fast forward a few years, and Tesla reportedly caught Matthews copying the tech into machines that were sold to competitors, claiming they lied about doing so for three years, and continued to ship it. That is when Tesla chose to sue Matthews in July 2024 in Federal court, demanding over $1 billion in damages due to trade secret theft.
Now, the latest twist, as this month, a Judge issued a permanent injunction—a court order banning Matthews from using certain stolen Tesla parts or designs in their machines. Matthews is also officially “liable” for damages. The exact amount would still to be calculated later.
Bonne Eggleston, a VP for Tesla, said on X today that Matthews is a supplier who “exploited customer IP through theft or deception,” and has no place in Tesla’s ecosystem:
Buyer beware: Matthews International stole Tesla’s DBE technology and is now subject to an injunction and liable for damages.
During our work with Matthews, we caught them red-handed copying our technology—including proprietary software and sensitive mechanical designs—into… https://t.co/Toc8ilakeM
— Bonne Eggleston (@BonneEggleston) March 10, 2026
Tesla calls this a big win and warns other companies: “Buyer beware—don’t buy from thieves.”
Matthews hit back with a press release claiming victory. They say an arbitrator ruled they can keep selling their own DBE equipment to anyone and rejected Tesla’s request for a total sales ban. They call Tesla’s claims “nonsense” and insist their 20-year-old tech is independent. Both sides are spinning the same narrow ruling: Matthews can sell their version, but they’re blocked from using Tesla’s specific secrets.
What are Tesla’s Current Legal Options
The case isn’t over—it’s moving to the damages phase. Tesla can:
- Push forward in court or arbitration to calculate and collect huge financial penalties (potentially $1 billion+ if willful theft is proven).
- Enforce the permanent injunction with contempt charges, fines, or even jail time if Matthews violates it.
- Challenge Matthews’ new patents that allegedly copy Tesla’s work, asking courts to invalidate them or add Tesla as co-inventor.
- Seek extra damages, lawyer fees, and possibly punitive awards under the federal Defend Trade Secrets Act and California law.
Tesla could also refer evidence to federal prosecutors for possible criminal trade-secret charges (rare but serious). Settlement is always possible, but Tesla’s fiery public response suggests they want full accountability.
This isn’t just corporate drama. It shows why trade secrets matter even when Tesla open-sources some patents, confidential know-how shared in trust must stay protected. For the EV industry, it’s a reminder: steal from your biggest customer, and you risk losing everything.
News
Tesla Cybercab includes this small but significant feature
The Cybercab is Tesla’s big plan to introduce fully autonomous ride-sharing in a seamless fashion. In fact, the Full Self-Driving suite was geared toward alleviating the need to manually drive vehicles.

Tesla Cybercab manufacturing is strikingly close, as the company is still aiming for an April start date. But small and significant features are still being identified for the first time as production units appear all over the country for testing and for regulatory events, like one yesterday in Washington, D.C.
The Cybercab is Tesla’s big plan to introduce fully autonomous ride-sharing in a seamless fashion. In fact, the Full Self-Driving suite was geared toward alleviating the need to manually drive vehicles.
This was for everyone, including the disabled, who are widely reliant on ride-sharing platforms, family members, and medical shuttles for transportation of any kind. Cybercab aims to change that, and Tesla evidently put a focus on those riders while developing the vehicle, evident in a small but significant feature revealed during its appearance in the Nation’s Capital.
Tesla Cybercab display highlights interior wizardry in the small two-seater
Tesla has implemented Braille within the Cybercab to make it easier for blind passengers to utilize the vehicle. On both the ‘Stop/Hazard Lights’ button and the Door Releases, Tesla has placed Braille so that blind passengers can navigate their way through the vehicle:
The hazard lights button will be used as an emergency stop. Smart pic.twitter.com/vkYBioqmKm
— Whole Mars Catalog (@wholemars) March 10, 2026
We have braille on the interior door releases as well
— Eric (@EricETesla) March 11, 2026
This is a great addition to the Cybercab, especially as Full Self-Driving has been partially pointed at as a solution for those with disabilities that would keep them from driving themselves from place to place.
It truly is a great addition and just another way that Tesla is showing they are making this massive product inclusive for everyone out there, including those who have not been able to drive due to not having vision.
The Cybercab is set to enter mass production sometime in April, and it will be responsible for launching Tesla’s massive plans for an autonomous ride-sharing program.
Elon Musk
Tesla and xAI team up on massive new project
It is the latest move by a Musk company to automate, streamline, and reduce the manual, monotonous, and tedious work currently performed by humans through AI and robotics development. Digital Optimus will be capable of processing and actioning the past five seconds of a real-time computer screen video and keyboard and mouse actions.
Elon Musk teased a massive new project, to be developed jointly by Tesla and xAI, called “Digital Optimus” or “Macrohard,” the first development under Tesla’s investment agreement with xAI.
Musk announced on X that Digital Optimus will “be capable of emulating the function of entire companies.”
Macrohard or Digital Optimus is a joint xAI-Tesla project, coming as part of Tesla’s investment agreement with xAI.
Grok is the master conductor/navigator with deep understanding of the world to direct digital Optimus, which is processing and actioning the past 5 secs of…
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 11, 2026
It is the latest move by a Musk company to automate, streamline, and reduce the manual, monotonous, and tedious work currently performed by humans through AI and robotics development. Digital Optimus will be capable of processing and actioning the past five seconds of a real-time computer screen video and keyboard and mouse actions.
Essentially, it will be an AI version of a desk worker in many capacities, including accounting, HR tasks, and others.
Musk said:
“Grok is the master conductor/navigator with deep understanding of the world to direct digital Optimus, which is processing and actioning the past 5 secs of real-time computer screen video and keyboard/mouse actions. Grok is like a much more advanced and sophisticated version of turn-by-turn navigation software. You can think of it as Digital Optimus AI being System 1 (instinctive part of the mind) and Grok being System 2. (thinking part of the mind).”
Its key applications would be used for enterprise automation, simulating entire companies, high-volume repetitive tasks, and potentially, future hybrid use with the Optimus robot, which would handle physical tasks, while Digital Optimus would handle the clerical work.
The creation of a digital AI suite like Digital Optimus would help companies save time and money, as well as become more efficient in their operations through massive scalability. However, there will undoubtedly be concerns from people who are skeptical of a fully-integrated AI workhorse like this one.
From an energy consumption perspective and just a general concern for the human workforce, these types of AI projects are polarizing in nature.
However, Digital Optimus would be a great digital counterpart to Tesla’s physical Optimus robot, as it would be a hyper-efficient addition to any company that is looking for more production for less cost.
Musk maintains that there is no other company on Earth that will be able to do this.








