News
SpaceX sends “radically redesigned” Starship engine to Texas for hot-fire tests
SpaceX has shipped one of the first of a group of Starship engines known as Raptor, described last month by CEO Elon Musk as “radically redesigned”. A culmination of more than 24 months of prototype testing, the first flight-worthy Raptor could be ignited for the first time as early as February.
According to Musk, three of these redesigned Raptors will power the first full-scale BFR prototype, a Starship (upper stage) test article meant to conduct relatively low-altitude, low-velocity hop tests over the southern tip of Texas. Those tests could also begin next month, although a debut sometime in March or April is increasingly likely.
Engines currently on Starship hopper are a blend of Raptor development & operational parts. First hopper engine to be fired is almost finished assembly in California. Probably fires next month.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 5, 2019
Effectively designed on a blank slate, Raptor began full-scale component-level tests in 2014 at NASA’s Mississippi-based Stennis Space Center, evolving from main injector development to oxygen preburner hot-fires in 2015. Soon after Raptor’s prototype preburner design was validated at Stennis, SpaceX moved testing to its privately-owned and operated facilities in McGregor, Texas, where Raptor static fire testing has remained since.
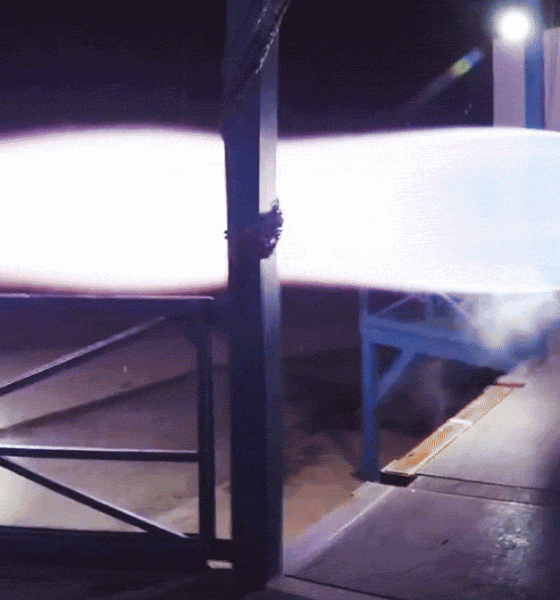
Mach diamonds pic.twitter.com/TCX7ZGFnN0
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) September 26, 2016
Just days before CEO Elon Musk was scheduled to reveal SpaceX’s next-generation rocket (BFR, formerly known as the Interplanetary Transport System or ITS) in September 2016, he announced in a tweet that propulsion engineers and technicians had successful hot-fired an integrated Raptor prototype – albeit subscale – for the first time ever. Just 12 months later, Musk once again took to the stage to announce an update to BFR’s design, while also revealing that prototype Raptor engines had already completed more than 1200 seconds (20 minutes) of cumulative hot-fire tests, an extremely aggressive and encouraging rate of progress for such a new engine.
SpaceX has completed over 1,200 seconds of firing across 42 main Raptor engine tests. pic.twitter.com/EhxbPjd8Cj
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) September 29, 2017
Although Raptor undoubtedly borrows heavily from much of the same expertise that designed Merlin 1 and operated and improved it for years, that is roughly where the similarities between Raptor and M1D end. M1D, powered by refined kerosene (RP-1) and liquid oxygen, uses a combustion cycle (gas-generator) that is relatively simple and reliable at the cost of engine efficiency, although SpaceX propulsion expertise still managed to give M1D the highest thrust-to-weight ratio of any liquid rocket engine ever flown. Still, measured by ISP (instantaneous specific impulse), M1D’s inefficient kerolox gas-generator cycle ultimately means that the engine simply can’t compete with the performance of engines with more efficient propellants and combustion cycles.
While SpaceX’s Falcon 9 and Heavy rockets – powered by Merlin 1D and Merlin Vacuum – are more than adequate in and around Earth orbit, a far more efficient engine was needed for the company to enable the sort of interplanetary colonization Musk had in mind when he created SpaceX. Raptor was the answer. Ultimately settling on liquid methane and oxygen (methalox) as the propellant and a full-flow staged-combustion (FFSC) cycle, Raptor was designed to be extraordinarily reliable and efficient in order to safely power a spacecraft (BFS/Starship) meant to ferry dozens or hundreds of people to and from Mars.
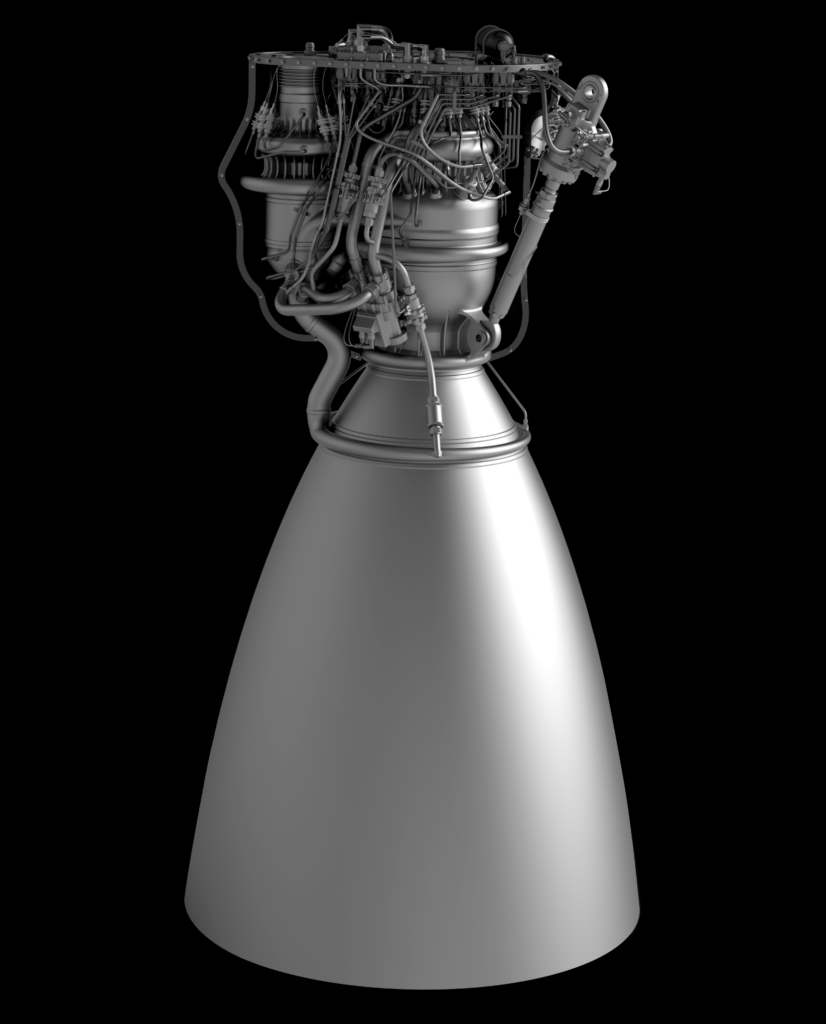
- The only official render of Raptor, published by SpaceX in September 2016. The Raptor departing Hawthorne in Jan ’19 looked reasonably similar. (SpaceX)
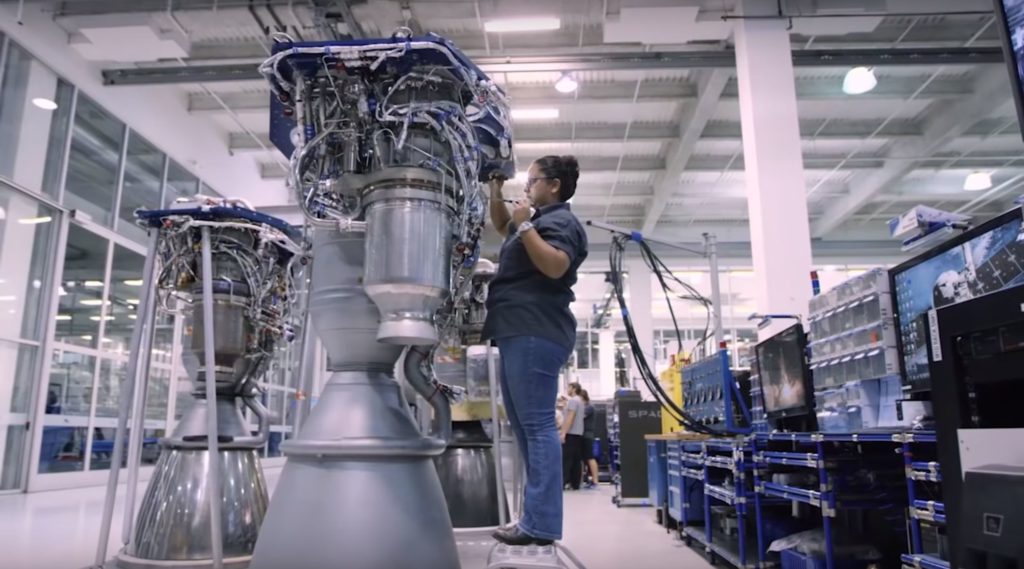
- SpaceX technicians wrench on Merlin 1D and Merlin Vacuum engines. Raptor was apparently dramatically larger in person. (SpaceX)
- Starhopper’s Raptors feature a very distinct seam and second curve, indicative of a dual-bell nozzle. (NASASpaceflight /u/bocachicagal)
Raptor enters a new era
For all the extensive and invaluable testing SpaceX has done with a series of prototype Raptor engines, the engines tested were subscale versions with around 30% the thrust of the c. 2016 Raptor and around 40-50% of the updated c. 2017 iteration, producing almost the same amount of thrust as Merlin 1D (914 kN to Raptor’s ~1000 kN). In September 2018, Musk described Raptor as an “approximately…200-ton (~2000 kN) thrust engine” that would eventually operate with a chamber pressure as high as 300 bar (an extraordinary ~4400 psi), requiring at least one of the FFSC engine’s two preburners (used to power separate turbopumps) to operate at a truly terrifying ~810 bar (nearly 12,000 psi).
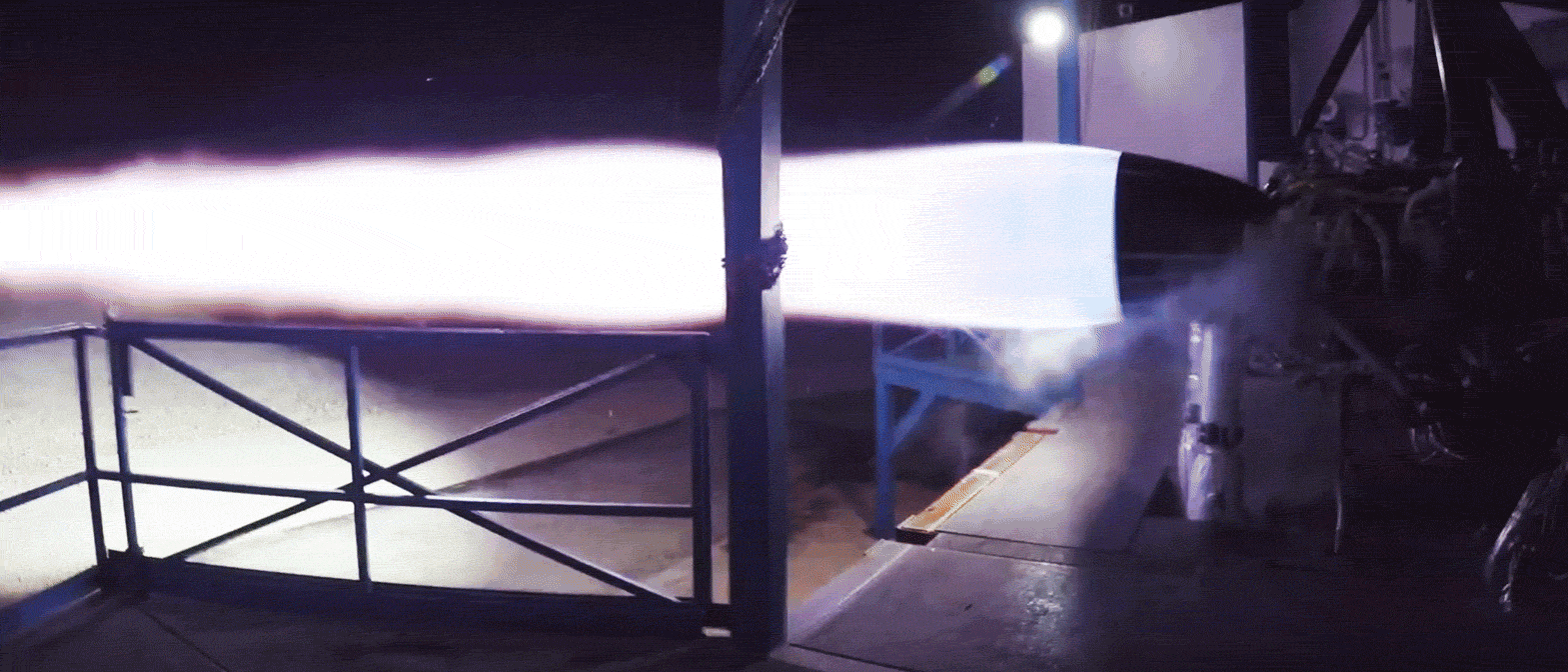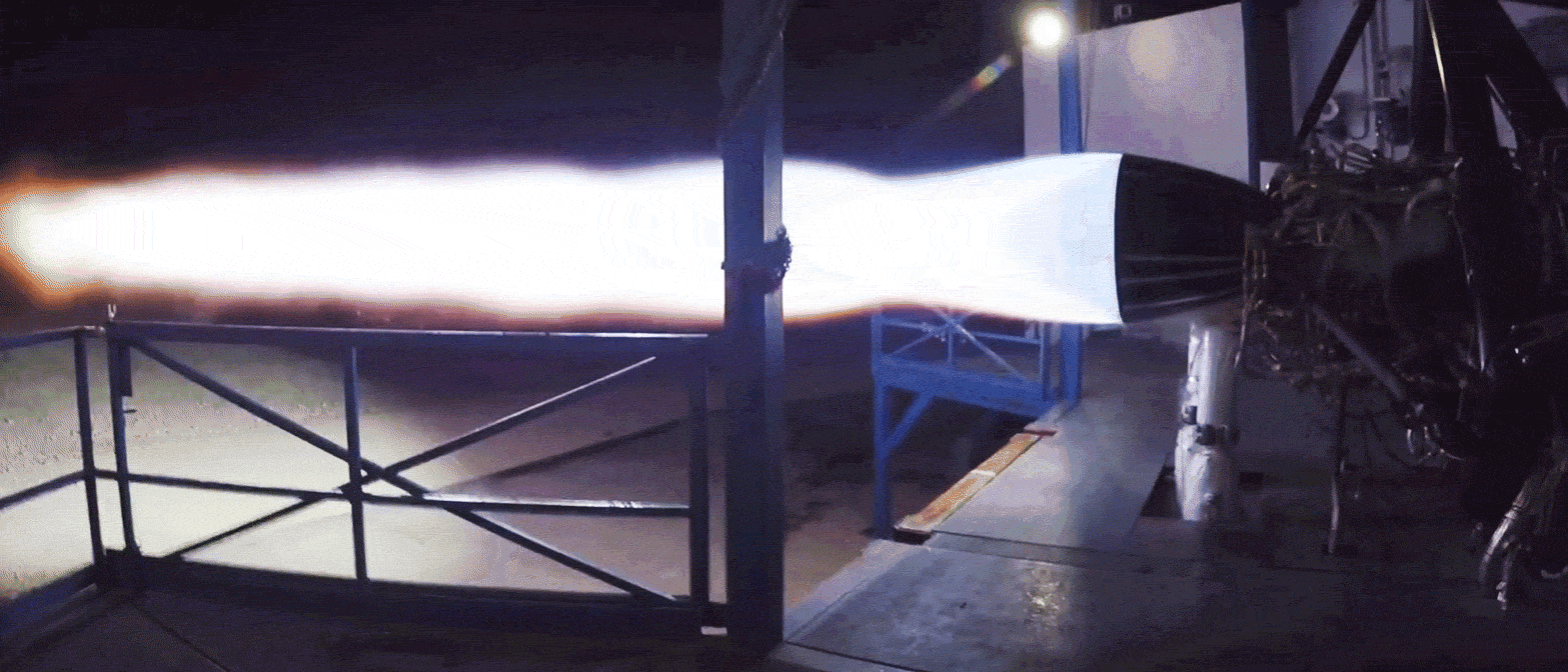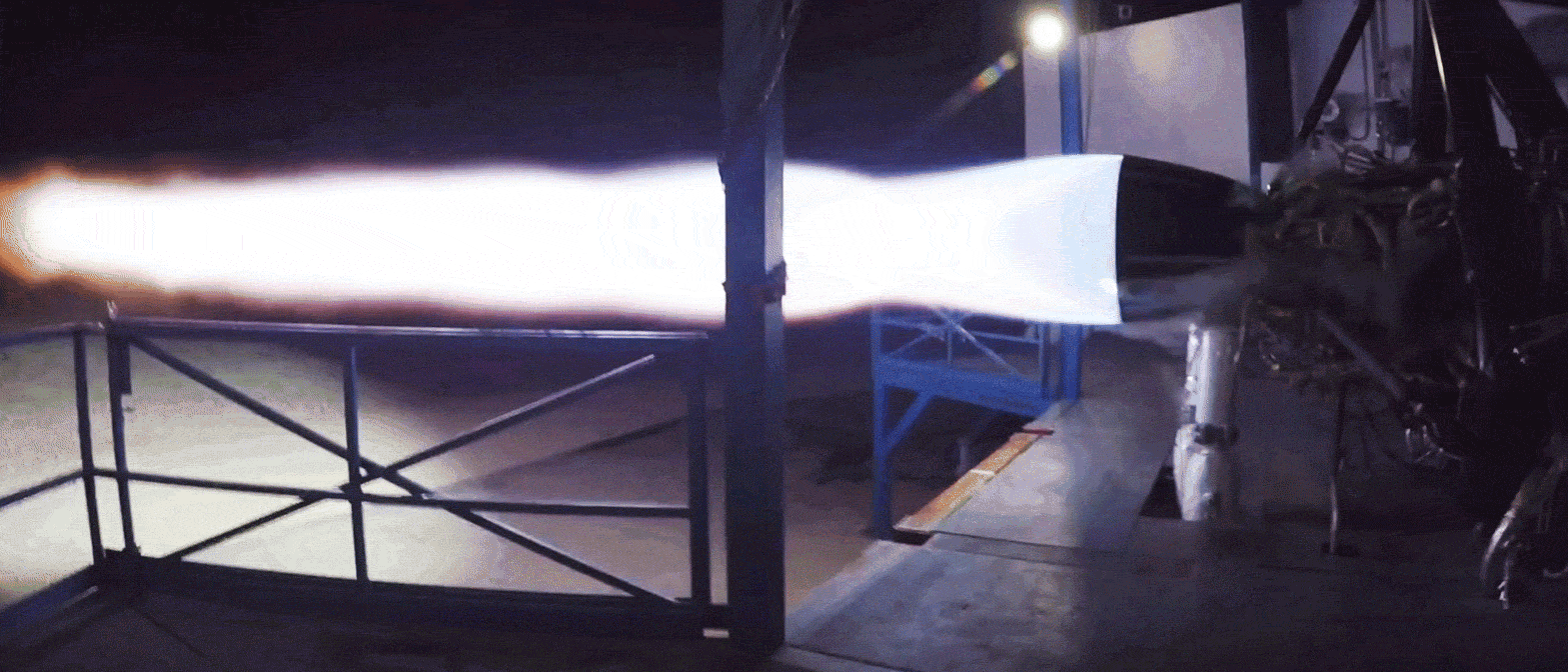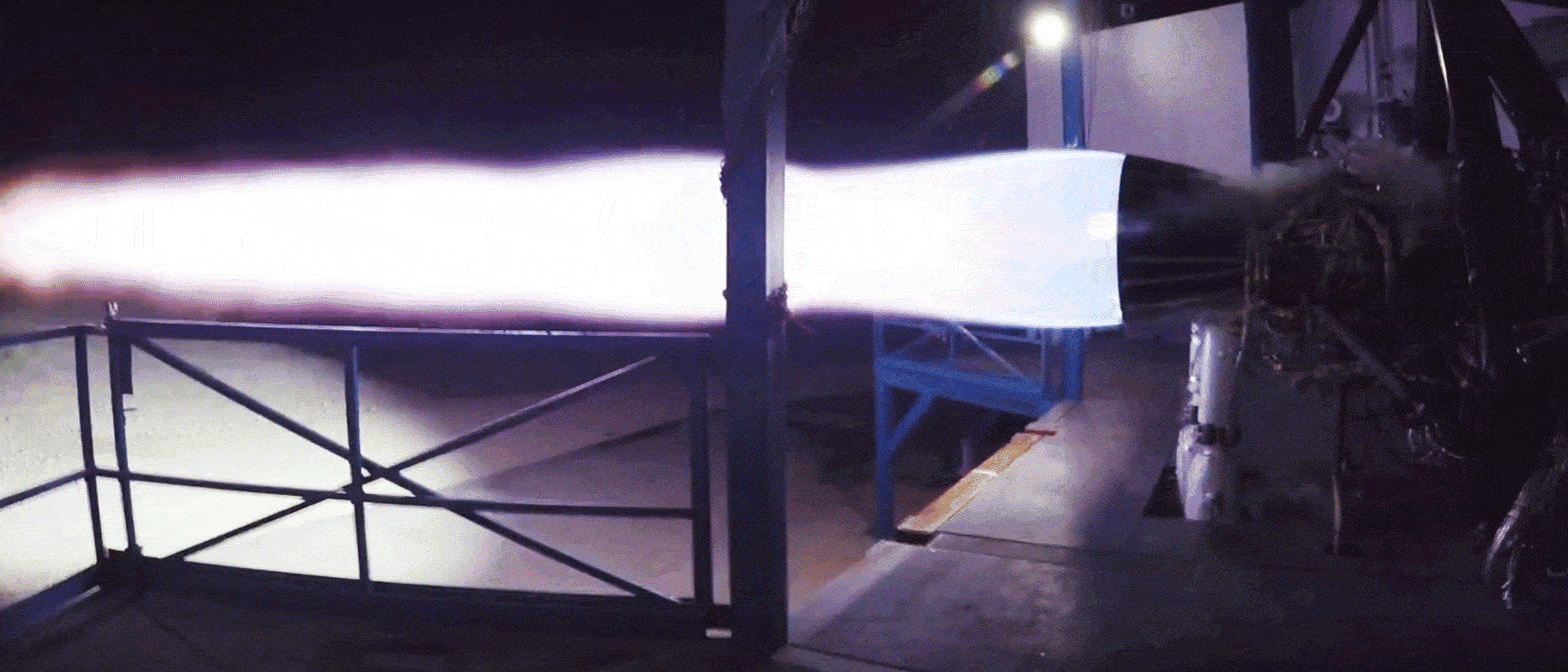
Conveniently stood beside a Merlin 1D engine also ready for hot-fire acceptance testing, the Raptor engine spotted departing SpaceX’s Hawthorne, CA factory last week was reportedly immense in person, towering over an M1D engine. Raptor also featured a mass of spaghetti-like plumbing (complexity necessary for its advanced combustion cycle), with a significant fraction of the metallic pipes and tubes displaying mirror-like finishes. Most notable was an obvious secondary preburner/turbopump stack and the lack of any exhaust port, whereas M1D relies on a single turbopump and exhausts the gases used to power it. Raptor’s full-flow staged-combustion cycle uses separate oxygen and methane preburners to power separate turbopumps, significantly improving mass flow rate and smoothing out combustion mixing.
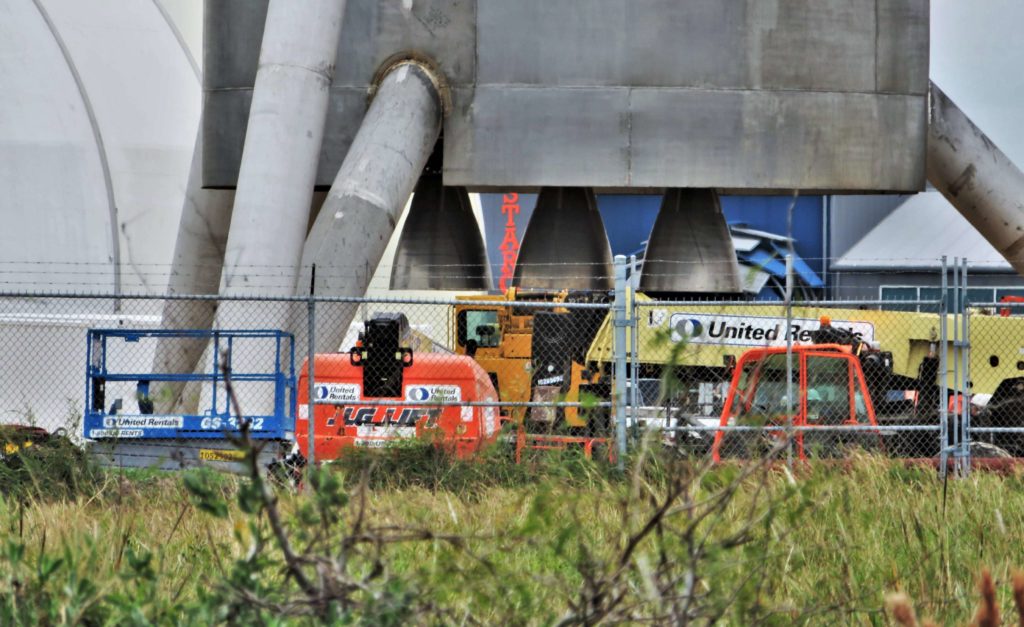
- SpaceX’s current Texas facilities feature a test stand for Raptor, the engine intended to power BFR and BFS to Mars. (SpaceX)
- SpaceX’s subscale Raptor engine has completed more than 1200 seconds of testing in less than two years. (SpaceX)
- A gif of Raptor throttling over the course of a 90+ second static-fire test in McGregor, Texas. (SpaceX)
- A September 2018 render of Starship (then BFS) shows one of the vehicle’s two hinged wings/fins/legs. (SpaceX)
Unlike all previous hot-fired Raptors, those shipping now to McGregor, Texas are expected to be the first completed engines with a finalized design, arrived at only after a period of extensive testing and iterative improvement. They also appear to be full-scale, meaning that the test bays dedicated to Raptor will likely need to be upgraded (if they haven’t been already) to support a two- or threefold increase in maximum thrust.
Yes. Radically redesigned Raptor ready to fire next month.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) December 22, 2018
SpaceX’s Starship hopper will need three finalized engines, meaning that the Raptor now in McGregor, Texas may not have been the first to arrive. Nevertheless, the shipment of full-scale hardware is always an extremely encouraging milestone for any advanced technology development program, while also foreshadowing the first imminent static-fires of the “radcally redesigned” rocket engine. With hardware now at the test site before January is out, a February test debut – one month behind a January debut teased by Elon Musk last December – is not out of the question.

News
Tesla Cybercab ramps Robotaxi public street testing as vehicle enters mass production queue
Recent sightings on public roads and growing fleet activity at Giga Texas signal Tesla’s accelerating push toward the Cybercab’s commercial launch.

Tesla Cybercab is being spotted with increasing frequency both on public roads and across the grounds of Gigafactory Texas, suggesting that the company’s road testing and validation program is ramping meaningfully ahead of mass production.
A total of 25 Cybercab units were recently observed across three separate locations at Giga Texas by drone observer Joe Tegtmeyer — with 14 metallic gold units parked in a tight formation outside the factory exit, nine more at the crash testing facility undergoing structural and safety validations, and two additional units at the west end-of-line area for final checks.
The activity on public roads is just as telling. The Cybercab was spotted testing on public roads for the first time last October, near Tesla’s Engineering Headquarters in Los Altos, California, marking a significant development in the vehicle’s progression toward commercial readiness. As expected at that early stage, a safety driver was present in the seat.
Since then, sightings have only become more frequent. Community observers on X have posted fresh footage of Cybercabs navigating public streets in Silicon Valley, with each new clip adding to a growing body of evidence that Tesla’s validation efforts are well underway. The production backdrop supports the momentum. Tesla’s production line at Giga Texas moved into a higher volume early in March, representing what observers are calling the largest single-day grouping of Cybercabs seen to date.
- Tesla Cybercab spotted in San Jose, CA testing on public roads with Robotaxi validation equipment [Credit: Nic Cruz Patane via X]

Tesla Cybercab spotted testing on public roads in Los Gatos, CA – March 10, 2026 [Credit: Osman Sarood via X]
Tesla ramps Cybercab test manufacturing ahead of mass production
Musk has also stated that Tesla is aiming for at least 2 million Cybercab units per year across more than one factory, with a potential ceiling of 4 million annually.
With testing activity on public roads accelerating and factory output visibly increasing week over week, the coming months at Giga Texas are set to be pivotal in determining how quickly Tesla can bring the Cybercab from validation to volume.
News
Tesla opens Supercharging Network to other EVs in new country
Tesla’s Supercharging infrastructure is the most robust in the world, and it has done a wonderful job of keeping things up and running for the millions of owners out there. As it expanded access to non-Tesla EVs a couple years back, it has still managed to keep things pretty steady, although the need for more charging is apparent.
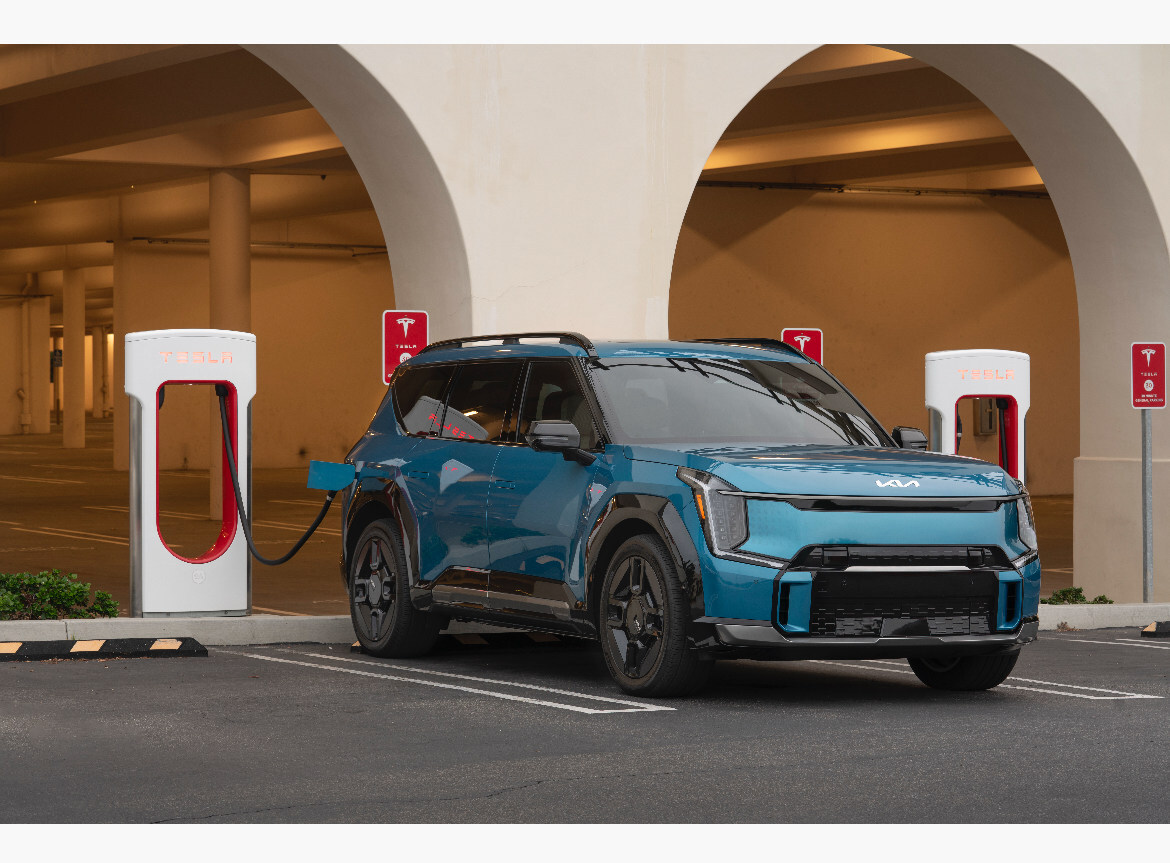

Tesla has started opening its Supercharging Network, which is the most expansive in the world, to other EVs in a new country for the first time.
After expanding its Supercharging offerings to other car companies in the United States a few years ago, Tesla is still making the move in other markets, as it aims to make EV ownership easier for everyone, regardless of what manufacturer a consumer chose to purchase from.
Tesla’s Supercharging infrastructure is the most robust in the world, and it has done a wonderful job of keeping things up and running for the millions of owners out there. As it expanded access to non-Tesla EVs a couple years back, it has still managed to keep things pretty steady, although the need for more charging is apparent.
Tesla just added a cool new feature for leaving your charger at home or even leaving the Supercharger pic.twitter.com/iw0SDrWuX6
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 10, 2026
Now, Tesla is expanding access to the Supercharger Network to non-Tesla EVs in Malaysia. The automaker just opened up a charging stie at the Pavilion KL Mall in Kuala Lumpur to non-Tesla owners, giving them eight additional Superchargers to utilize with a charging speed of up to 250 kW.
Tesla is also opening up the four-Supercharger site in Shah Alam, a four-Supercharger site at the IOI City Mall, and a six-Supercharger site in Gamuda Cove Township.
Electrive first reported the opening of these Superchargers in Malaysia.
The initiative from Tesla helps make EV ownership much simpler for those who only have access to third-party charging solutions or at-home charging. While at-home charging is the most advantageous, it is not an end-all solution as every driver will eventually need to grab some range on the road.
Tesla has been offering its Superchargers to non-Tesla EVs in the United States since 2024, as Ford became the first company to gain access to the massive network early that year when CEO Elon Musk and Ford frontman Jim Farley announced it together. Since then, Tesla has offered its chargers to nearly every EV maker, as companies like Rivian and Lucid, and even legacy car companies like General Motors have gained access.
It’s best for everyone to have the ability to use Tesla Superchargers, but there are of course some growing pains.
Charging cables are built to cater to Tesla owners, so pull-in Superchargers are most advantageous for non-Tesla EVs currently, but the company’s V4 Superchargers, which are not as plentiful in the U.S. quite yet, do enable easier reach for those vehicles.
News
Tesla Semi expands pilot program to Texas logistics firm: here’s what they said
Mone said the Tesla Semi it put into its fleet for this test recorded 1.64 kWh per mile efficiency, beating Tesla’s official 1.7 kWh per mile target and delivering a massive leap over conventional diesel trucks.
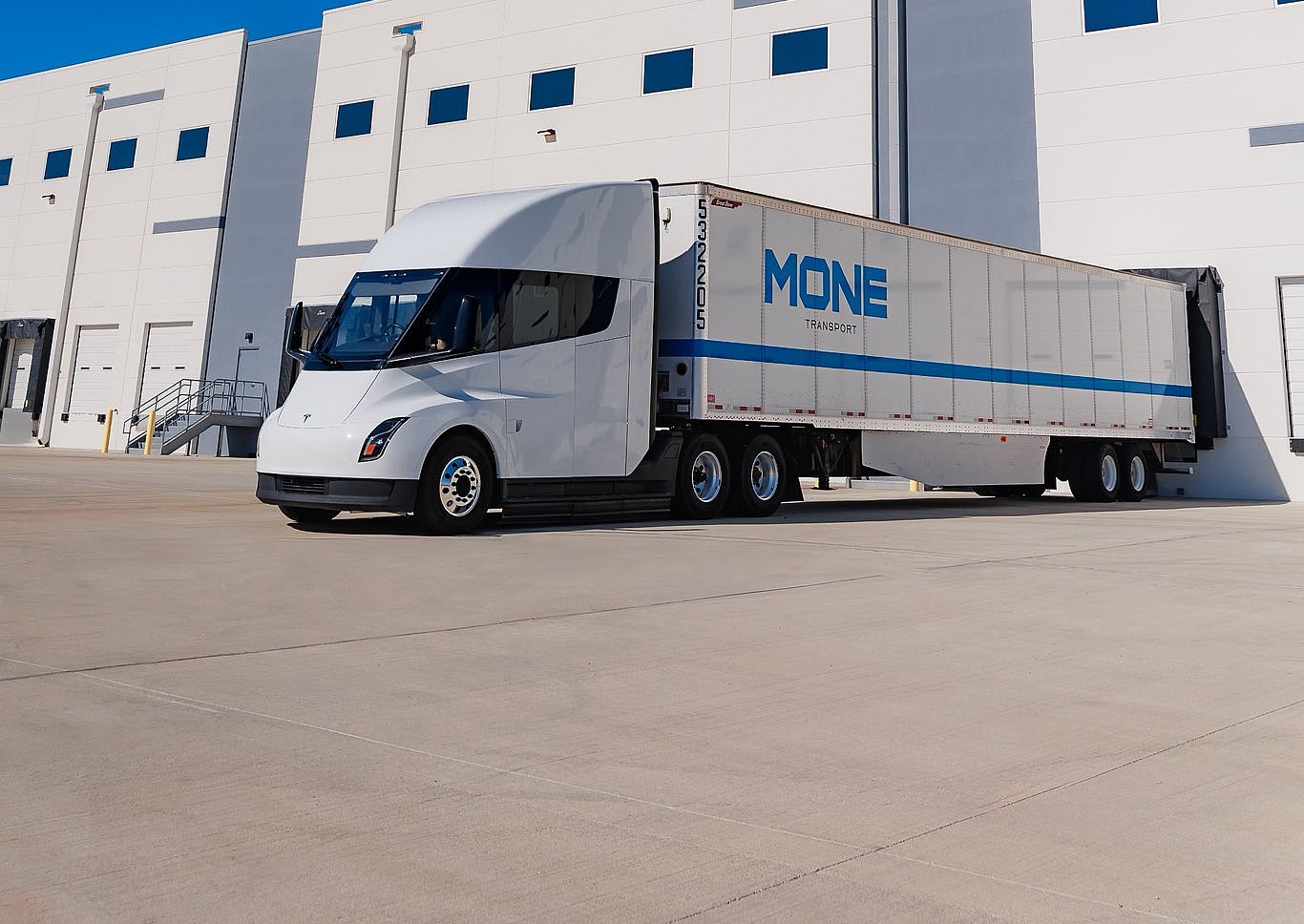

Tesla has expanded its Semi pilot program to a new region, as it has made it to Texas to be tested by logistics from Mone Transport. With the Semi entering production this year, Tesla is getting even more valuable data regarding the vehicle and its efficiency, which will help companies cut expenditures.
Mone Transport operates in Texas and on the Southern border, and it specializes in cross-border U.S.-Mexico freight operations. After completing some rigorous testing, Mone shared public results, which stand out when compared to efficiency metrics offered by diesel vehicles.
“Mone Transport recently had the opportunity to put the Tesla Semi to the test, and we’re thrilled with the results! Over 4,700 miles of operations at 1.64 kWh/mile in our Texas operation. We’re committed to providing zero-emission transportation to our customers!” the company said in a post on X.
🚨 Mone Transport just recorded an extremely impressive Tesla Semi test:
1.64 kWh per mile over 4,700 miles! https://t.co/xwS2dDeomP pic.twitter.com/oLZHoQgXsu
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 10, 2026
Mone said the Tesla Semi it put into its fleet for this test recorded 1.64 kWh per mile efficiency, beating Tesla’s official 1.7 kWh per mile target and delivering a massive leap over conventional diesel trucks.
Comparable Class 8 diesel semis, typically achieving 6-7 miles per gallon, consume roughly 5.5 kWh per mile in energy-equivalent terms, meaning the Semi uses three to four times less energy while also producing zero tailpipe emissions.
Tesla Semi undergoes major redesign as dedicated factory preps for deliveries
The performance of the Tesla Semi in Mone Transport’s testing aligns with data from other participants in the pilot program. ArcBest’s ABF Freight Division logged 4,494 miles over three weeks in 2025, averaging 1.55 kWh per mile across varied routes, including a grueling 7,200-foot Donner Pass climb. The truck “generally matched the performance of its diesel counterparts,” the carrier said.
PepsiCo, which operates the largest known Semi fleet, recorded 1.7 kWh per mile in North American Council for Freight Efficiency testing. Additional pilots showed similar gains: DHL hit 1.72 kWh per mile, and Saia achieved 1.73 kWh per mile.
These metrics underscore the Semi’s ability to slash operating costs through superior efficiency, lower maintenance, and zero-emission operation. As charging infrastructure scales and production ramps toward 2026 targets, participants like Mone Transport are proving electric semis can seamlessly integrate into freight networks, accelerating the industry’s shift to sustainable, high-performance trucking.
Tesla continues to prep for a more widespread presence of the Semi in the coming months as it recently launched the first public Semi Megacharger site in Los Angeles. It is working on building out infrastructure for regional runs on the West Coast initially, with plans to expand this to the other end of the country in the coming years.








![Tesla Cybercab spotted testing on public roads in Los Gatos, CA - March 10, 2026 [Credit: Osmad Sarood via X]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/tesla-cybercab-public-road-testing-823x1024.jpg)








