

News
SpaceX Starlink Gen2 constellation weakened by “partial” FCC grant
More than two and a half years after SpaceX began the process of securing regulatory approval for its next-generation Starlink constellation, the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has finally granted the company a license – but only after drastically decreasing its scope.
In May 2020, SpaceX filed its first FCC license application for Starlink Gen2, an upgraded constellation of 30,000 satellites. In the second half of 2021, SpaceX amended its Starlink Gen2 application to take full advantage of the company’s more powerful Starship rocket and further improve the constellation’s potential utility. Only in December 2021 did the FCC finally accept SpaceX’s Gen2 application for filing, kicking off the final review process.
On November 29th, 2022, the FCC completed that review and granted SpaceX permission to launch just 7,500 of the ~30,000 Starlink Gen2 satellites it had requested permission for more than 30 months prior. The FCC offered no explanation of how it arrived at its arbitrary 75% reduction, nor why the resulting number is slightly lower than a different 7,518-satellite Starlink Gen1 constellation SpaceX had already received a license to deploy in late 2018. Adding insult to injury, the FCC repeatedly acknowledges that “the total number of satellites SpaceX is authorized to deploy is not increased by our action today, and in fact is slightly reduced.”
The update that's rolling out to the fleet makes full use of the front and rear steering travel to minimize turning circle. In this case a reduction of 1.6 feet just over the air— Wes (@wmorrill3) April 16, 2024
That claimed reduction is thanks to the fact that shortly before this decision, SpaceX told the FCC in good faith that it would voluntarily avoid launching the dedicated V-band Starlink constellation it already received a license for in order “to significantly reduce the total number of satellites ultimately on orbit.” Instead, once Starlink Gen2 was approved, it would request permission to add V-band payloads to a subset of the 29,988 planned Gen2 satellites, achieving a similar result without the need for another 7,518 satellites.
In response, the FCC slashed the total number of Starlink Gen2 satellites permitted to less than the number of satellites approved by the FCC’s November 2018 Starlink V-band authorization; limited those satellites to middle-ground orbits, entirely precluding Gen2 launches to higher or lower orbits; and didn’t even structure its compromise in a way that would at least allow SpaceX to fully complete three Starlink Gen2 ‘shells.’ Worse, the FCC’s partial grant barely mentioned SpaceX’s detailed plans to use new E-band antennas on Starlink Gen2 satellites and next-generation ground stations, simply stating that it will “defer acting on” the request until “further review and coordination with Federal users.”
Throughout the partial grant, the FCC couches its decision to drastically downscale SpaceX’s Starlink Gen2 constellation in terms of needing more time “to evaluate the complex and novel issues on the record before [the Commission],” raising the question of what exactly the Commission was doing instead in the 30 months since SpaceX’s first Gen2 application and 15 months since its Gen2 modification. In comparison, SpaceX received a full license for its 7,518-satellite V-band constellation less than five months after applying. SpaceX’s 4,408-satellite Starlink Gen1 constellation – the first megaconstellation ever reviewed by the modern FCC – was licensed 16 months after its first application and eight months after a modified application was submitted.
Adding to the oddity of the unusual and inconsistent decision-making in this FCC ruling, the Commission openly acknowledges that the idea to grant SpaceX permission to launch a fraction of its Starlink Gen2 constellation came from Amazon’s Project Kuiper [PDF], a major prospective Starlink competitor. The FCC says it agreed with Amazon’s argument, stating that “the public interest would be served by taking this approach in order to permit monitoring of developments involving this large-scale deployment and permit additional consideration of issues unique to the other orbits SpaceX requests.”
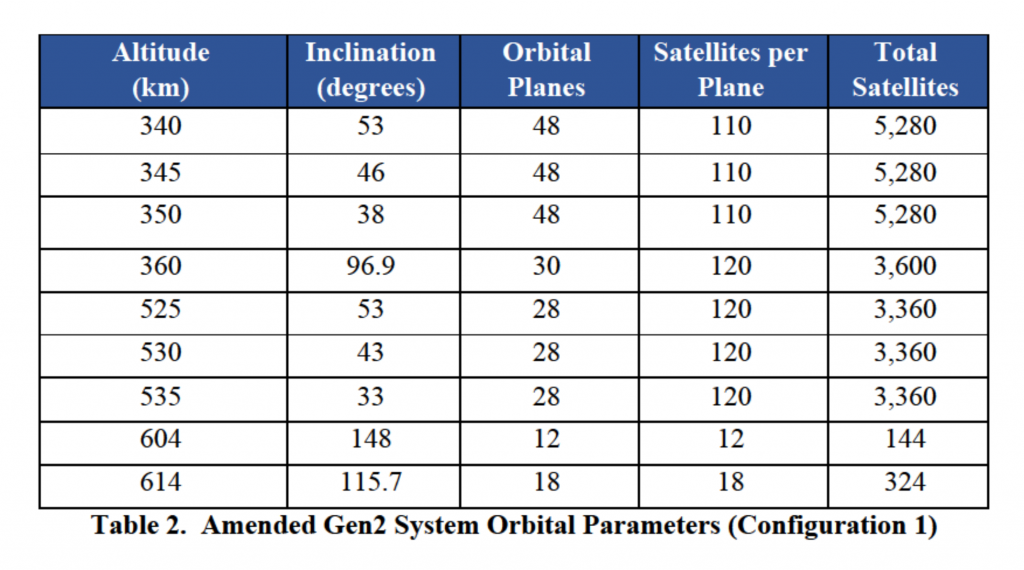
The V-band Starlink constellation already approved by the FCC was for 7,518 satellites in very low Earth orbits (~340 km). In the first 4,425-satellite Starlink constellation licensed by the FCC, the Commission gave SpaceX permission to operate 2,814 satellites at orbits between 1100 and 1300 kilometers. Increasingly conscious of the consequences of space debris, which would last hundreds of years at 1000+ kilometers, SpaceX later requested permission in 2019 and 2020 to launch those 2,814 satellites to around 550 kilometers, where failed satellites would reenter in just five years. For unknown reasons, the FCC only fully approved the change two years later, in April 2021.
The “other orbits [requested by SpaceX]” that the FCC says create unique issues that demand “additional consideration” of Starlink Gen2 are for 19,400 satellites between 340 and 360 kilometers and 468 satellites between 604 and 614 kilometers. Starlink satellites are expected to be around four times heavier and feature a magnitude more surface area, but the fact remains that the FCC has already granted SpaceX permission to launch almost 3000 smaller satellites to orbits much higher than 604 kilometers and more than 7500 satellites to orbits lower than 360 kilometers. It’s thus hard not to conclude that the Commission’s claims that a partial license denial was warranted by “concerns about orbital debris and space safety,” and “issues unique to…other orbits” are incoherent at best.
Perhaps the strangest inclusion in the partial grant is a decision by the FCC to subject SpaceX to an arbitrary metric devised by another third-party, for-profit company LeoLabs. In a March 2022 letter, LeoLabs reportedly proposed that “SpaceX’s authorization to continue deploying satellites” be directly linked to an arbitrary metric measuring “the number of years each failed satellite remains in orbit, summed across all failed satellites.” The FCC apparently loved the suggestion and made it an explicit condition of its already harsh Starlink Gen2 authorization, even adopting the arbitrary limit of “100 object years” proposed by LeoLabs.
In other words, once the sum of the time required for all failed Starlink Gen2 satellites to naturally deorbit reaches 100 years, the FCC will force SpaceX to “cease satellite deployment” while it “[reviews] sources of satellite failure” and “determine[s] whether there are any adequate and reliable mitigation measures going forward.” The FCC acknowledges that the arbitrary 100-year limit means that the failure of just 20 Starlink satellites at operational orbits would force the company to halt launches. The Commission does not explain how it will decide when SpaceX can restart Starlink launches after a launch halt. SpaceX must simultaneously follow the FCC’s deployment schedule, which could see the company’s license revoked if it doesn’t deploy 3,750 Starlink Gen2 satellites by November 2028 and all 7,500 satellites by November 2031.
Based on the unofficial observations of astrophysicist Jonathan McDowell, SpaceX currently has more 30 failed Starlink Gen1 satellites at or close to their operational altitudes of 500+ kilometers, meaning that SpaceX would almost certainly be forced to stop launching Gen1 satellites if this arbitrary new rule were applied to other constellations. The same is true for competitor OneWeb, which had a single satellite fail at around 1200 kilometers in 2021. At that altitude, it will likely take hundreds of “object years” to naturally deorbit, easily surpassing LeoLabs’ draconian 100-year limit.
In theory, the FCC does make it clear that it will consider changing those restrictions and allowing SpaceX to launch more of its proposed Starlink Gen2 constellation in the future. But the Commission has also repeatedly demonstrated to SpaceX that it will happily take years to modify existing licenses or approve new ones – not a particularly reassuring foundation for investments as large and precarious as megaconstellations.
Ultimately, short of shady handshake deals in back rooms, the FCC’s partial grant leaves SpaceX’s Starlink Gen2 constellation in an undesirable position. For the company to proceed under the current license, it could be forced to redesign its satellites and ground stations to avoid the E-band, or gamble by continuing to build and deploy satellites and ground stations with E-band antennas without a guarantee that it’ll ever be able to use that hardware. There is also no guarantee that the FCC will permit SpaceX to launch any of the ~22,500 satellites left on the table by the partial grant, which will drastically change the financial calculus that determines whether the constellation is economically viable and how expansive associated infrastructure needs to be.
Additionally, if SpaceX accepts the gambit and launches all 7,500 approved Gen2 satellites only for the FCC to fail to approve expansions, Starlink Gen2 would be stuck with zero polar coverage, significantly reducing the constellation’s overall utility. Starlink Gen2 likely represents an investment of at least $30-60 billion (assuming an unprecedentedly low $1-2M to build and launch each 50-150 Gbps satellite). With its partial license denial and the addition of several new and arbitrary conditions, the FCC is effectively forcing SpaceX to take an even riskier gamble with the billions of dollars of brand new infrastructure it will need to build to manufacture, launch, operate, and utilize its Starlink Gen2 constellation.

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Energy
Tesla Energy gains UK license to sell electricity to homes and businesses
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.

Tesla Energy has received a license to supply electricity in the United Kingdom, opening the door for the company to serve homes and businesses in the country.
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.
According to Ofgem, the license took effect at 6 p.m. local time on Wednesday and applies to Great Britain.
The approval allows Tesla’s energy business to sell electricity directly to customers in the region, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
Tesla has already expanded similar services in the United States. In Texas, the company offers electricity plans that allow Tesla owners to charge their vehicles at a lower cost while also feeding excess electricity back into the grid.
Tesla already has a sizable presence in the UK market. According to price comparison website U-switch, there are more than 250,000 Tesla electric vehicles in the country and thousands of Tesla home energy storage systems.
Ofgem also noted that Tesla Motors Ltd., a separate entity incorporated in England and Wales, received an electricity generation license in June 2020.
The new UK license arrives as Tesla continues expanding its global energy business.
Last year, Tesla Energy retained the top position in the global battery energy storage system (BESS) integrator market for the second consecutive year. According to Wood Mackenzie’s latest rankings, Tesla held about 15% of global market share in 2024.
The company also maintained a dominant position in North America, where it captured roughly 39% market share in the region.
At the same time, competition in the energy storage sector is increasing. Chinese companies such as Sungrow have been expanding their presence globally, particularly in Europe.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk shares big Tesla Optimus 3 production update
According to Musk, Tesla is in the final stages of completing Optimus 3, which he described as one of the world’s most advanced humanoid robots.

Tesla CEO Elon Musk has stated that production of Optimus 3 could begin this summer. Musk shared the update in his interview at the Abundance Summit.
According to Musk, Tesla is in the final stages of completing Optimus 3, which he described as one of the world’s most advanced humanoid robots.
“We’re in the final stages of completion of Optimus 3, which is really going to be by far the most advanced robot in the world. Nothing’s even close. In fact, I haven’t even seen demos of robots that are as good as Optimus 3,” Musk said.
He also set expectations on the pace of Optimus 3’s production ramp, stating that the initial volumes of the humanoid robot will likely be very low. Musk did, however, also state that high production rates for Optimus 3 should be possible in 2027.
“I think we’ll start production on Optimus 3 this summer, but very slow at first, like sort of this classic S-curve ramp of manufacturing units versus time. And then, probably reach high volume production around summer next year,” he said.
Interestingly enough, the CEO hinted that Tesla is looking to iterate on the robot quickly, potentially releasing a new Optimus design every year.
“We’ll have Optimus 4 design complete next year. We’ll try to release a new robot design every year,” Musk stated.
Tesla has already outlined broader plans for scaling Optimus production beyond its first manufacturing line. Musk previously stated that Optimus 4 will be built at Gigafactory Texas at significantly higher production volumes.
Initial production lines for the robot are expected to be located at Tesla’s Fremont Factory, where the company plans to establish a line capable of producing up to 1 million robots per year.
A larger production ramp is expected to occur at Gigafactory Texas, where Musk has previously suggested could eventually support production of up to 10 million robots per year.
“We’re going to launch on the fastest production ramp of any product of any large complex manufactured product ever, starting with building a one-million-unit production line in Fremont. And that’s Line one. And then a ten million unit per year production line here,” Musk said previously.
The comments suggest that while Optimus 3 will likely begin production at Fremont, Tesla’s larger-scale manufacturing push could arrive with Optimus 4 at Gigafactory Texas.








