
SpaceX
SpaceX’s Starlink satellite lawyers refute latest “flawed” OneWeb critique
After years of relentless legal badgering from internet satellite constellation competitor OneWeb, SpaceX’s regulatory and legal affairs team appears to have begun to (in a professional manner) lose patience with the constant barrage.
On February 21st, SpaceX published a withering refutation of 
SpaceX’s Starlink modification request
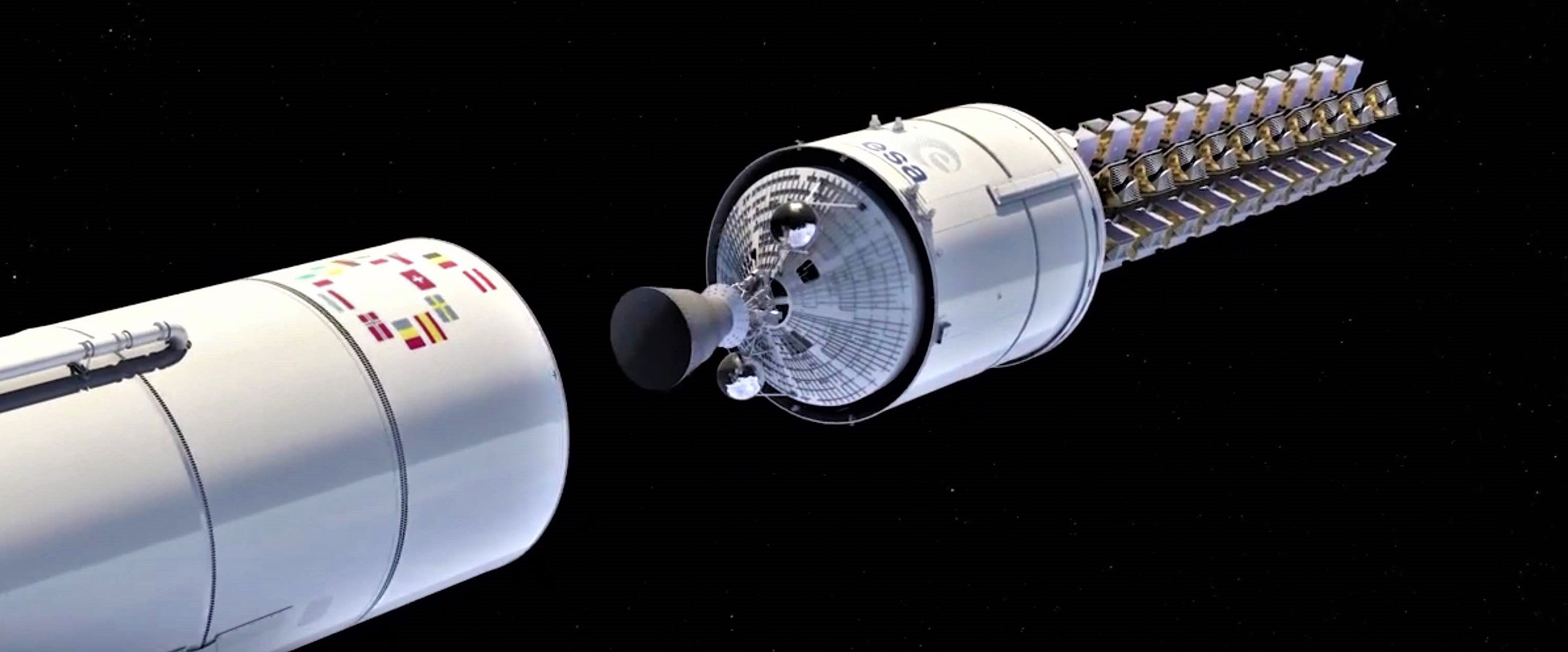
In late 2018, SpaceX filed a request with the FCC (Federal Communications Commission) that would allow the company to significantly modify parts of its Starlink satellite constellation license, cutting 16 spacecraft from the original total of 4425 and moving Phase 1’s now-1584 satellites from an operating altitude of ~1100-1300 km (680-810 mi) to just 550 km (340 mi). Aside from further reducing the latency of communications, SpaceX also argues that “the principal reason” behind lowering the operational altitude of the first ~37% of Starlink satellites was “to [further] enhance the already considerable space safety attributes of [the] constellation.”

The safety benefits of a significantly lower orbit come into play when the potential dangers of space debris come into play. Put simply, satellites in lower orbits – particularly orbits below ~1000 km – end up experiencing far more drag from the upper vestiges of the Earth’s atmosphere, drag that acts like an automatic switch in the event that a given LEO satellite loses control. At 500 km and below, even small spacecraft with enough surface area will automatically reenter Earth’s atmosphere within just a few years (~5), while orbits around 1000-1500 km can stretch the time to reentry by a factor of 5-10, often taking decades. In other words, SpaceX’s desire to lower the initial operating orbit of ~1600 Starlink satellites would end up dramatically reducing the consequences the failure of one or several satellites would have on other spacecraft operating in the same orbital regions
“Rather than base its critiques on facts in SpaceX’s application or evidence in the record, OneWeb relies entirely on a collection of flawed assumptions cobbled together into an equally-flawed fictional scenario.
Overall, OneWeb rested its interference analysis entirely on incorrect assumptions and overlooked basic operational distinctions in the actual effect of the proposed SpaceX modification.”
A step further, there is a great deal more irony to be found in
SpaceX never explicitly says as much but it becomes eminently clear that the authors behind this latest response are rapidly losing patience with OneWeb’s years of shoddy attempts at legally suppressing competition. Given that lowering the orbits of almost 40% of SpaceX’s first round of Starlink satellites would end up working in
“OneWeb is now challenging SpaceX’s plan to reduce altitude to further enhance the space safety attributes of its system. Considering OneWeb’s frequent request that SpaceX take this exact step of moving farther away from OneWeb’s proposed constellation, one is left to wonder whether OneWeb would be satisfied with SpaceX operating at any altitude whatsoever.“
SpaceX, 02/21/2019

SpaceX takes a different approach
Aside from seemingly hollow concerns about the “safety” of SpaceX’s request to lower Starlink satellite orbits, OneWeb further criticized SpaceX for what it perceived to be “operational setbacks” after launching a duo of prototype Starlink spacecraft, known as Tintin A and B. In essence, it appears that OneWeb made the bizarre decision to cite officially-unconfirmed and often-disputed reports that SpaceX’s prototypes were unable to reach their originally planned operational orbits of ~1125 km, effectively trapped at the ~515 km orbit they were dropped off in as a result of their shared launch.
“SpaceX originally expected to operate these satellites at approximately 515 km and then raise them to an altitude of 1,125 km for further testing, but chose not to do so. From this, OneWeb leaps to an unsupported conclusion that SpaceX’s experimental satellites faced “operational setbacks.” To the contrary, SpaceX made a conscious decision to remain at this optimal altitude for further experimentation.
Far from facing setbacks, the experimental program has validated SpaceX technology – including the Hall-effect thruster propulsion system and the capabilities of the communications payload. Thus, unlike OneWeb, SpaceX has successfully tested its spacecraft design in advance of initiating deployment of its commercial constellation.”
SpaceX, 02/21/2019
While there was, in fact, some plausible evidence in mid-2018 that at least tentatively suggested that the spacecraft may have had issues with their first-generation ion thruster prototypes, it soon became clear that SpaceX and several major investors were sticking to the narrative that the Tintin twins were operating in fine health in orbit. It’s possible that SpaceX’s legal team and government relations executives are trying to aggressively spin on-orbit difficulties with the prototypes into good news, and the fact that SpaceX is requesting a modification to 550 km instead of Tintin A and B’s ~520 km orbits remains more than a little odd. However, including such brazen and open-faced lies in official legal/regulatory documents would be a deathwish SpaceX’s Starlink license in its entirety, while also begging for major SpaceX-aimed lawsuits and a general black cloud forming over the company.
If the FCC ultimately chooses to permit SpaceX’s Starlink license modification, the company’s first more or less operational Starlink launch – likely carrying anywhere from 10 to 30 satellites – could occur as early as late April or early May.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.
News
SpaceX’s Crew-11 mission targets July 31 launch amid tight ISS schedule
The flight will lift off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
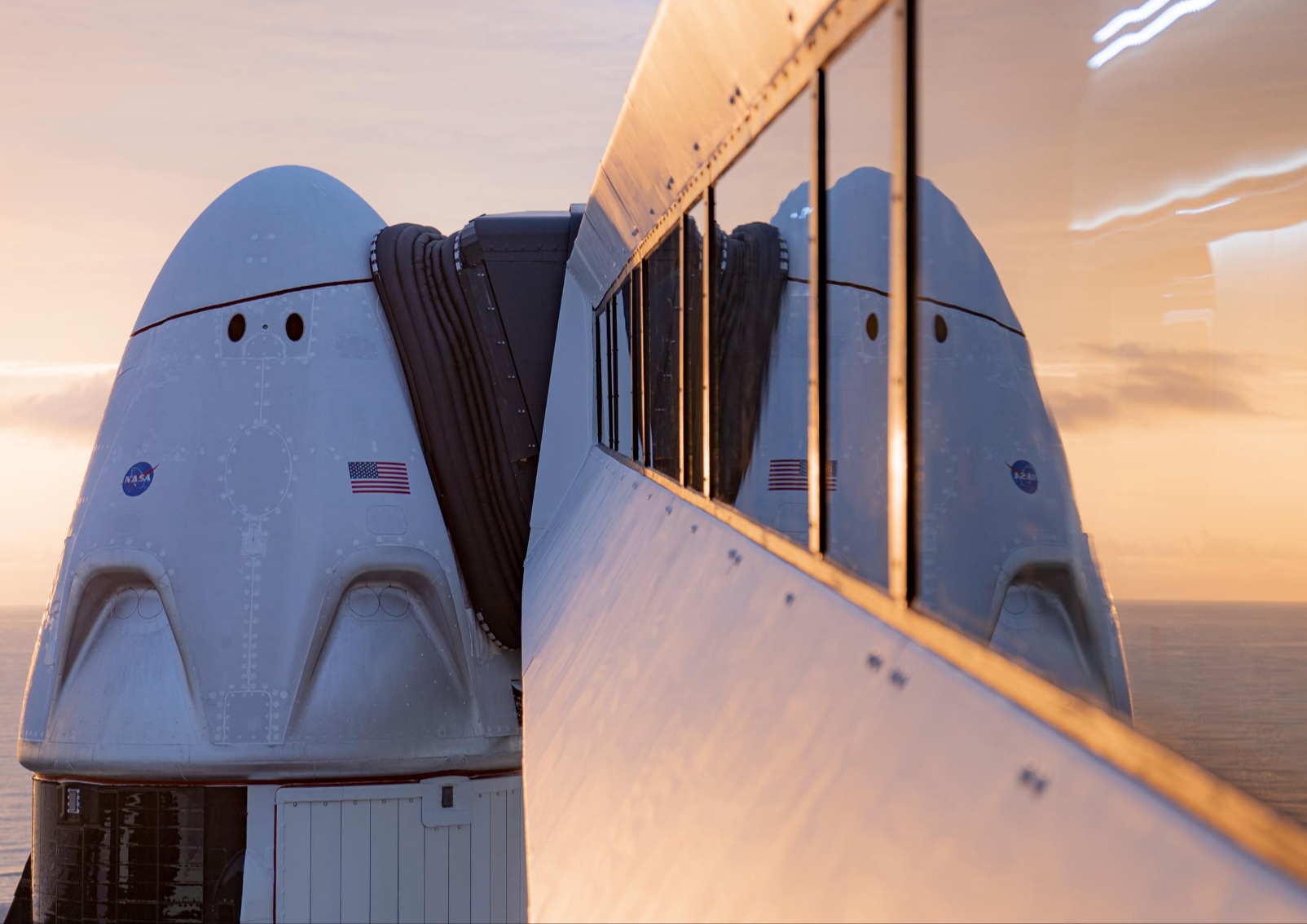

NASA and SpaceX are targeting July 31 for the launch of Crew-11, the next crewed mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The flight will lift off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using the Crew Dragon Endeavour and a Falcon 9 booster.
Crew Dragon Endeavour returns
Crew-11 will be the sixth flight for Endeavour, making it SpaceX’s most experienced crew vehicle to date. According to SpaceX’s director of Dragon mission management, Sarah Walker, Endeavour has already carried 18 astronauts representing eight countries since its first mission with NASA’s Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley in 2020, as noted in an MSN report.
“This Dragon spacecraft has successfully flown 18 crew members representing eight countries to space already, starting with (NASA astronauts) Bob (Behnken) and Doug (Hurley) in 2020, when it returned human spaceflight capabilities to the United States for the first time since the shuttle retired in July of 2011,” Walker said.
For this mission, Endeavour will debut SpaceX’s upgraded drogue 3.1 parachutes, designed to further enhance reentry safety. The parachutes are part of SpaceX’s ongoing improvements to its human-rated spacecraft, and Crew-11 will serve as their first operational test.
The Falcon 9 booster supporting this launch is core B1094, which has launched in two previous Starlink missions, as well as the private Ax-4 mission on June 25, as noted in a Space.com report.
The four-members of Crew-11 are NASA astronauts Zena Cardman and Mike Fincke, as well as Japan’s Kimiya Yui and Russia’s Oleg Platonov.
Tight launch timing
Crew-11 is slated to arrive at the ISS just as NASA coordinates a sequence of missions, including the departure of Crew-10 and the arrival of SpaceX’s CRS-33 mission. NASA’s Bill Spetch emphasized the need for careful planning amid limited launch resources, noting the importance of maintaining station altitude and resupply cadence.
“Providing multiple methods for us to maintain the station altitude is critically important as we continue to operate and get the most use out of our limited launch resources that we do have. We’re really looking forward to demonstrating that capability with (CRS-33) showing up after we get through the Crew-11 and Crew-10 handover,” Spetch stated.
News
SpaceX launches Ax-4 mission to the ISS with international crew
The SpaceX Falcon 9 launched Axiom’s Ax-4 mission to ISS. Ax-4 crew will conduct 60+ science experiments during a 14-day stay on the ISS.
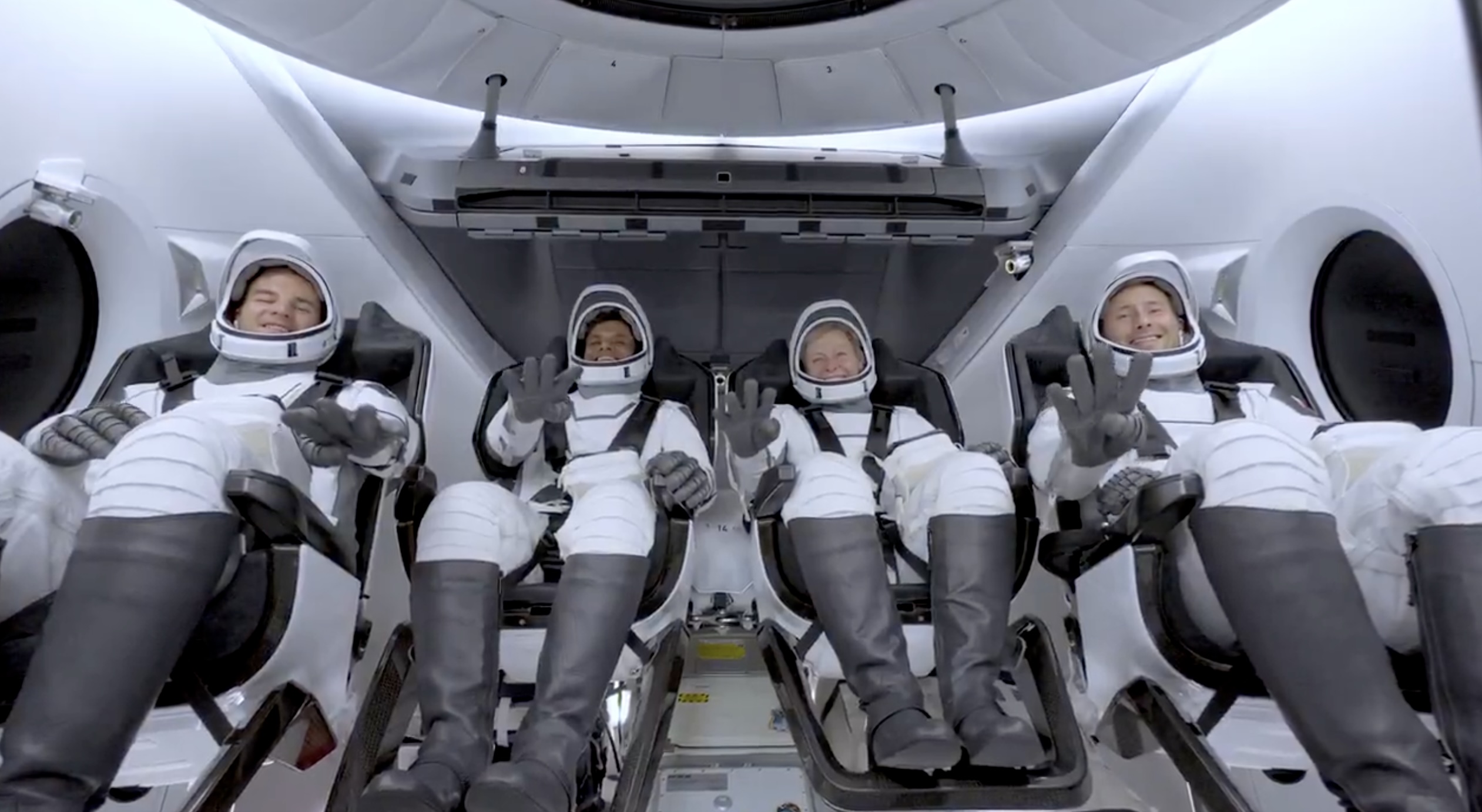

SpaceX launched the Falcon 9 rocket kickstarting Axiom Space’s Ax-4 mission to the International Space Station (ISS). Axiom’s Ax-4 mission is led by a historic international crew and lifted off from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A at 2:31 a.m. ET on June 25, 2025.
The Ax-4 crew is set to dock with the ISS around 7 a.m. ET on Thursday, June 26, 2025. Axiom Space, a Houston-based commercial space company, coordinated the mission with SpaceX for transportation and NASA for ISS access, with support from the European Space Agency and the astronauts’ governments.
The Ax-4 mission marks a milestone in global space collaboration. The Ax-4 crew, commanded by U.S. astronaut Peggy Whitson, includes Shubhanshu Shukla from India as the pilot, alongside mission specialists Sławosz Uznański-Wiśniewski from Poland and Tibor Kapu from Hungary.
“The trip marks the return to human spaceflight for those countries — their first government-sponsored flights in more than 40 years,” Axiom noted.
Shukla’s participation aligns with India’s Gaganyaan program planned for 2027. He is the first Indian astronaut to visit the ISS since Rakesh Sharma in 1984.
Axiom’s Ax-4 mission marks SpaceX’s 18th human spaceflight. The mission employs a Crew Dragon capsule atop a Falcon 9 rocket, designed with a launch escape system and “two-fault tolerant” for enhanced safety. The Axiom mission faced a few delays due to weather, a Falcon 9 leak, and an ISS Zvezda module leak investigation by NASA and Roscosmos before the recent successful launch.
As the crew prepares to execute its scientific objectives, SpaceX’s Ax-4 mission paves the way for a new era of inclusive space research, inspiring future generations and solidifying collaborative ties in the cosmos. During the Ax-4 crew’s 14-day stay in the ISS, the astronauts will conduct nearly 60 experiments.
“We’ll be conducting research that spans biology, material, and physical sciences as well as technology demonstrations,” said Whitson. “We’ll also be engaging with students around the world, sharing our experience and inspiring the next generation of explorers.”
SpaceX’s Ax-4 mission highlights Axiom’s role in advancing commercial spaceflight and fostering international partnerships. The mission strengthens global space exploration efforts by enabling historic spaceflight returns for India, Poland, and Hungary.
News
Starlink Cellular’s T-Mobile service to grow with third-party app data
From Oct 2025, T-Satellite will enable third-party apps in dead zones! WhatsApp, X, AccuWeather + more coming soon.

Starlink Cellular’s T-Mobile service will expand with third-party app data support starting in October, enhancing connectivity in cellular dead zones.
T-Mobile’s T-Satellite, supported by Starlink, launches officially on July 23. Following its launch, T-Mobile’s Starlink Cellular service will enable data access for third-party apps like WhatsApp, X, Google, Apple, AccuWeather, and AllTrails on October 1, 2025.
T-Mobile’s Starlink Cellular is currently in free beta. T-Satellite will add MMS support for Android phones on July 23, with iPhone support to follow. MMS support allows users to send images and audio clips alongside texts. By October, T-Mobile will extend emergency texting to all mobile users with compatible phones, beyond just T-Mobile customers, building on its existing 911 texting capability. The carrier also provides developer tools to help app makers integrate their software with T-Satellite’s data service, with plans to grow the supported app list.
T-Mobile announced these updates during an event celebrating an Ookla award naming it the best U.S. phone network, a remarkable turnaround from its last-place ranking a decade ago.
“We not only dream about going from worst to best, we actually do it. We’re a good two years ahead of Verizon and AT&T, and I believe that lead is going to grow,” said T-Mobile’s Chief Operating Officer Srini Gopalan.
T-Mobile unveiled two promotions for its Starlink Cellular services to attract new subscribers. A free DoorDash DashPass membership, valued at $10/month, will be included with popular plans like Experience Beyond and Experience More, offering reduced delivery and service fees. Meanwhile, the Easy Upgrade promotion targets Verizon customers by paying off their phone balances and providing flagship devices like the iPhone 16, Galaxy S25, or Pixel 9.
T-Mobile’s collaboration with SpaceX’s Starlink Cellular leverages orbiting satellites to deliver connectivity where traditional networks fail, particularly in remote areas. Supporting third-party apps underscores T-Mobile’s commitment to enhancing user experiences through innovative partnerships. As T-Satellite’s capabilities grow, including broader app integration and emergency access, T-Mobile is poised to strengthen its lead in the U.S. wireless market.
By combining Starlink’s satellite technology with strategic promotions, T-Mobile is redefining mobile connectivity. The upcoming third-party app data support and official T-Satellite launch mark a significant step toward seamless communication, positioning T-Mobile as a trailblazer in next-generation wireless services.
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoTesla debuts hands-free Grok AI with update 2025.26: What you need to know
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 Elon Musk5 days ago
Elon Musk5 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla reveals it is using AI to make factories more sustainable: here’s how
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales






















