SpaceX
SpaceX’s first Starship engine suffers “expected” damage during Raptor test fire
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk says that the first full-scale Starship engine to be tested has already been pushed to the point of damage less than three weeks after the campaign began, setting the stage for the second full-scale Raptor to take over in the near future.
According to Musk, while most of the damaged pathfinder Raptor’s components should still be easily reusable, the assembly of the second finalized engine is “almost done” and that Raptor will take over near-term testing rather than waiting for repairs to the first engine. This is undoubtedly an extraordinarily aggressive test program, particularly for such a new and cutting-edge rocket propulsion system, but these latest developments are ultimately far more encouraging than they are concerning.
Merlins. The max chamber pressure run damaged Raptor SN 1 (as expected). A lot of the parts are fine for reuse, but next tests will be with SN 2, which is almost done.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 21, 2019
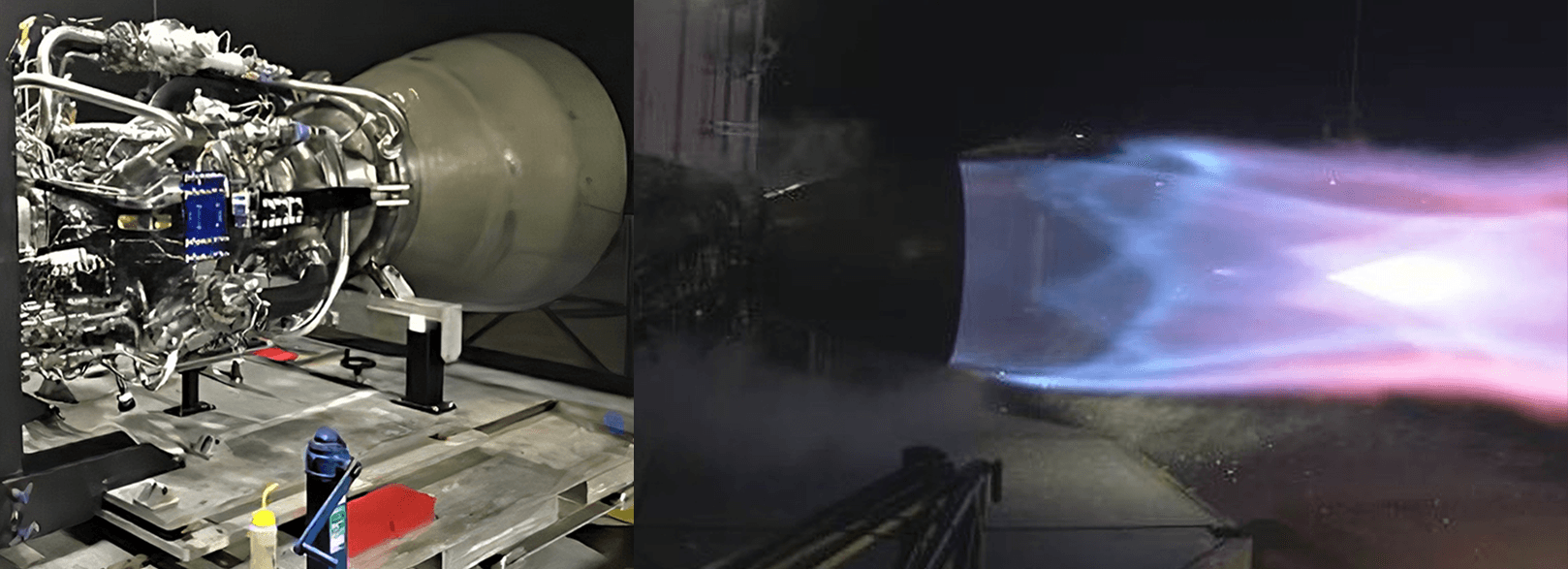
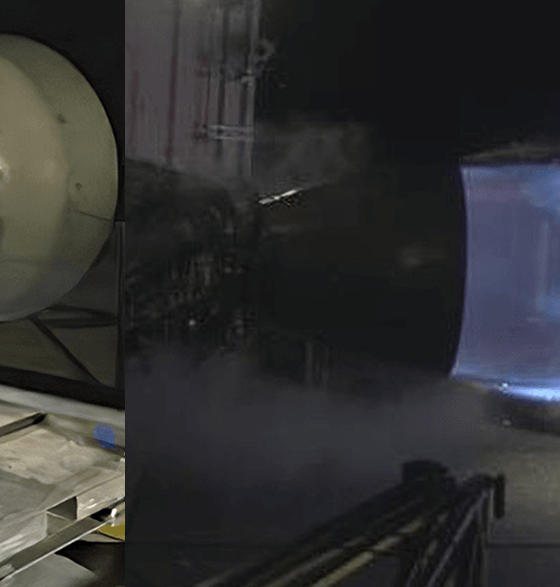
Although the Raptor engine family began integrated subscale static fires way back in September 2016, SpaceX’s propulsion team finalized Raptor’s baseline design and completed assembly, shipment, and an integrated static fire of the first full-scale engine on February 3rd, considerably less than three weeks before Musk took to Twitter. Aside from confirming that the new Raptor had been damaged during its most recent static fire several days prior, Musk indicated that the failure (unsurprisingly) was primarily attributed to the engine reaching the highest chamber pressures yet.
Raptor’s main combustion chamber (the bit directly above the nozzle) has been designed to nominally operate at and reliably withstand extraordinary pressures of 250+ bar (3600+ psi), performance that demands even higher pressures in the components that feed hot methane and oxygen gas into Raptor’s combustion chamber. One prime example hinted at by Musk in a 2018 tweet is its oxygen preburner, used to convert liquid propellant into a high-velocity gas that can then feed a dedicated oxygen turbopump. Aside from the absurdly corrosive environment created by extremely hot gaseous oxygen, the preburner must also survive pressures that could peak as high as 800+ bar, or 12,000 psi.
- SpaceX’s world-class rocket propulsion team has been progressing through early full-scale Raptor tests at an incredible speed. (SpaceX)
- Full-scale Raptor’s first static fire test, February 3rd. (SpaceX)
- Raptor’s business end with a Musk-for-scale. (Elon Musk)
- Starship revealed a trio of Raptor mockups when SpaceX technicians moved the assembly from stand to ground. (NSF – bocachicagal)
- A September 2018 render of Starship (then BFS) shows one of the vehicle’s two hinged wings/fins/legs. (SpaceX)
- BFR (2018) breaks through a cloud layer shortly after launch. (SpaceX)
A lack of technical detail means that it’s hard to know what thrust or main chamber pressure Musk had in mind when referring to exotic alloys that would be needed to survive those pressures, but the performance statistics of a Raptor with a preburner operating at 800+ bar would probably outstrip anything Musk has thus far described. In other words, it’s safe to assume that Raptor has probably not been pushed to those performance levels just yet, although it’s still a distant possibility. More likely is that 800+ bar in the oxygen preburner is an extreme stretch-goal that will take concerted research, development, and optimization to achieve, with Raptor having suffered damage somewhere below those levels while still reaching eye-watering performance figures.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 4, 2019
For an engine as complex as Raptor, there are countless dozens of potential failure modes the appearance of which would come as little surprise for an engine just days into full-scale testing. Above all else, the Raptor test schedule held by SpaceX’s world-class propulsion team – be it self-motivated or driven by reckless management-by-spreadsheet – has been fast-paced in the extreme, taking the first high-performance Raptor ever built from standstill to more than 90% thrust and chamber pressures of almost 270 bar (3900 psi) in – quite literally – less than one week. In the same period of time, more than half a dozen static fire tests (ranging from 1-10 seconds) were performed.
Within a few days of that February 10th milestone, in which Raptor reached chamber pressures comparable with the most advanced modern engines (namely RD-180/190/191), the engine was apparently pushed dramatically higher still, reaching a chamber pressure (and thus thrust) that wrought damage on some of the more sensitive parts of the engine’s plumbing. Despite the fact that the second production Raptor is apparently already “almost done”, Musk suggested that it would already feature changes (of unknown gravity) to mitigate the failure modes experienced by Raptor SN01.
SN2 has changes that should help
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 21, 2019
In an industry where NASA and contractors like Aerojet-Rocketdyne will spend months between static fire tests of Space Shuttle engines that have each literally flown multiple (if not) dozens of missions to orbit and have a demonstrated performance and reliability record that is measured in the hundreds of thousands of seconds, the speed and agility of SpaceX’s Raptor development and test program is breathtaking. What remains to be seen is just how comparably reliable and successful the end results (i.e. operational Raptor) will be, but an attitude that actively accepts and even pursues testing to destruction can ultimately only serve to benefit the finished product at the cost of destroyed hardware and many on-ground lessons learned the hard ways.
Given the immense success of SpaceX’s Merlin family of engines and the aggressive strategy of development and continuous improvement that brought it from Merlin 1A to 1D and MVacD, SpaceX is clearly not fumbling around in the dark when it comes to Raptor R&D.
Check out Teslarati’s newsletters for prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket launch and recovery processes!

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
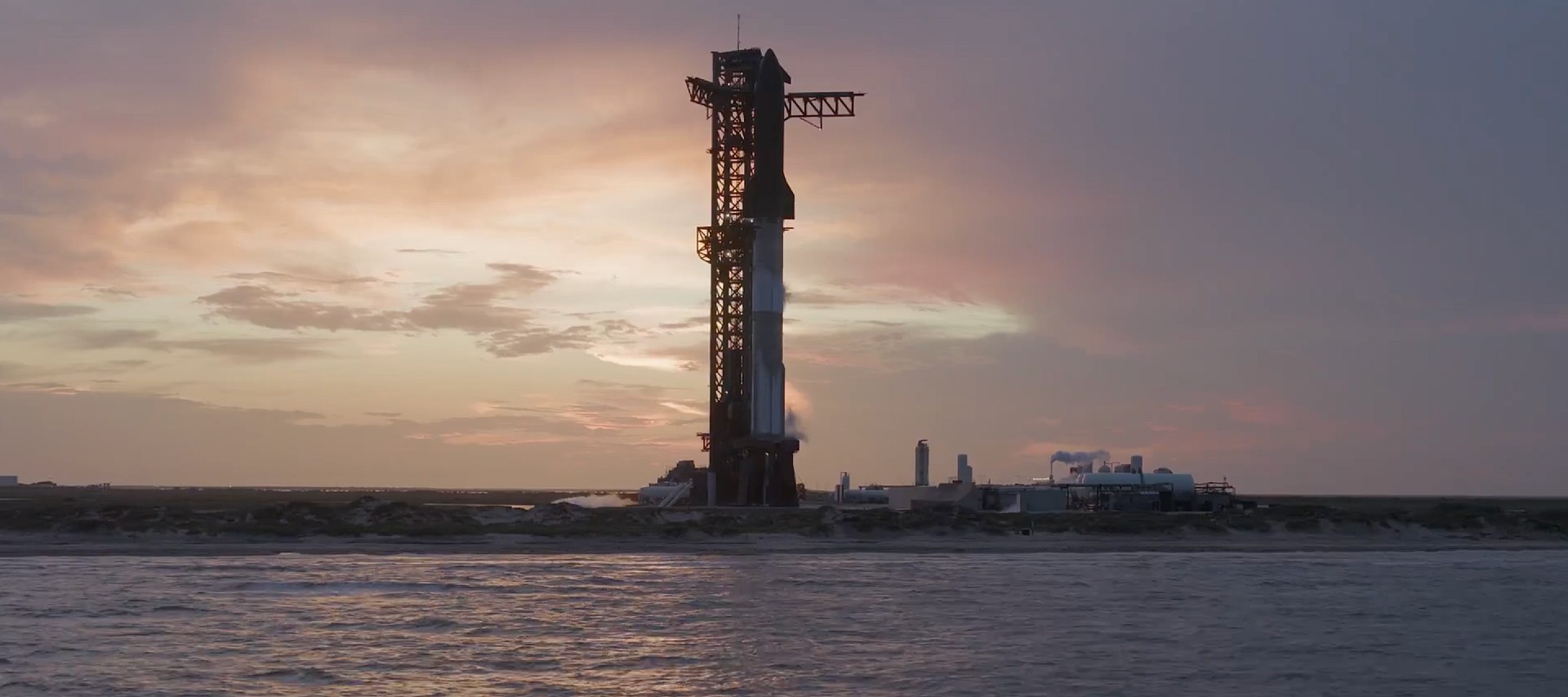

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.







![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





