SpaceX
SpaceX’s Starship hopper spotted with trio of dual-bell Raptor engines
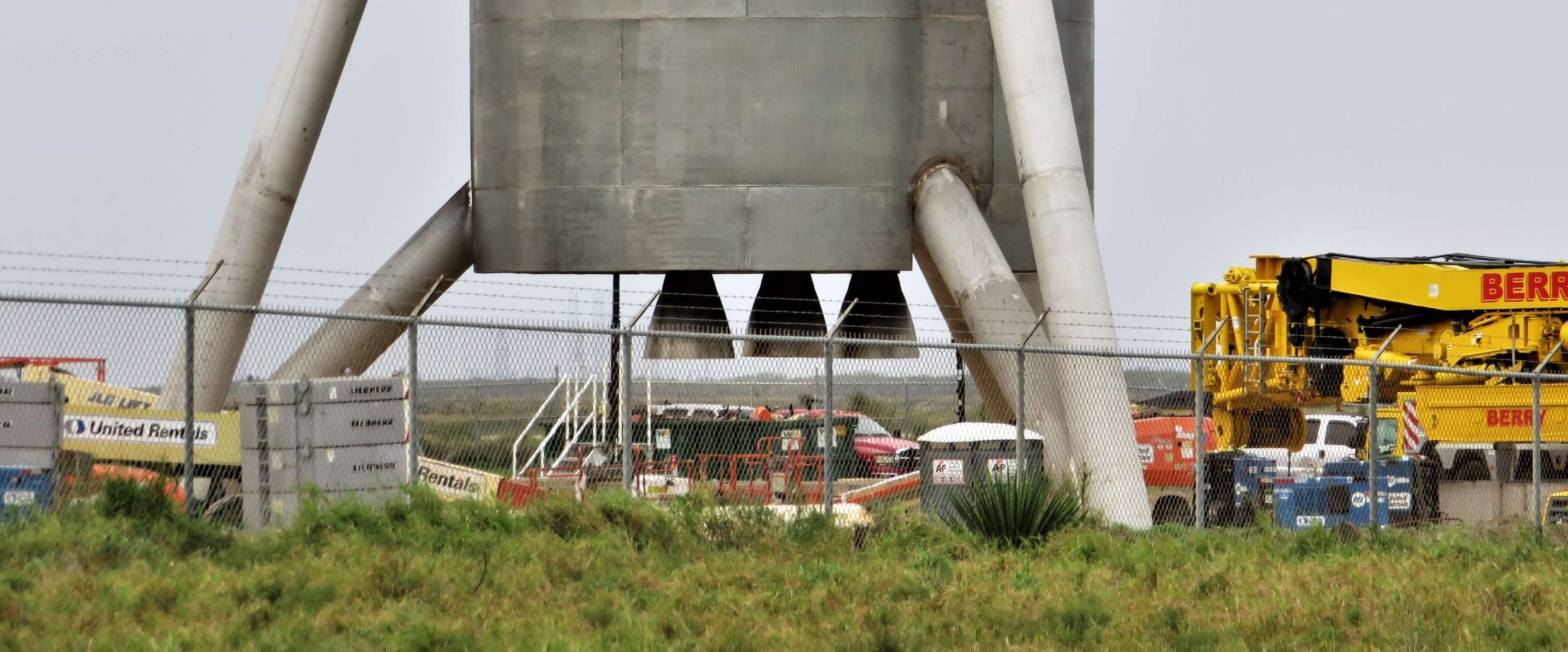
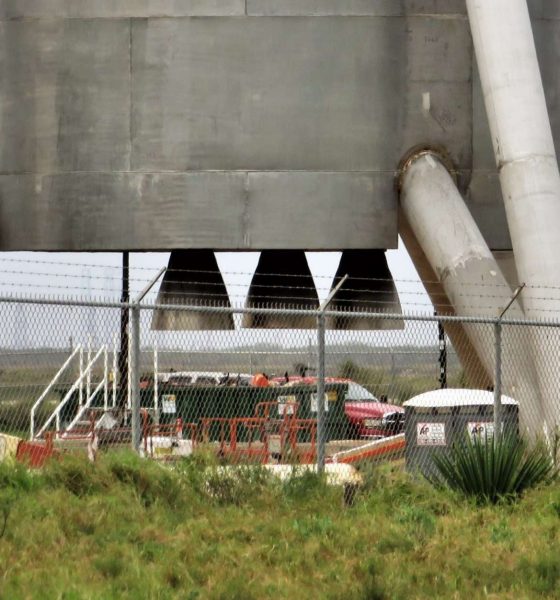
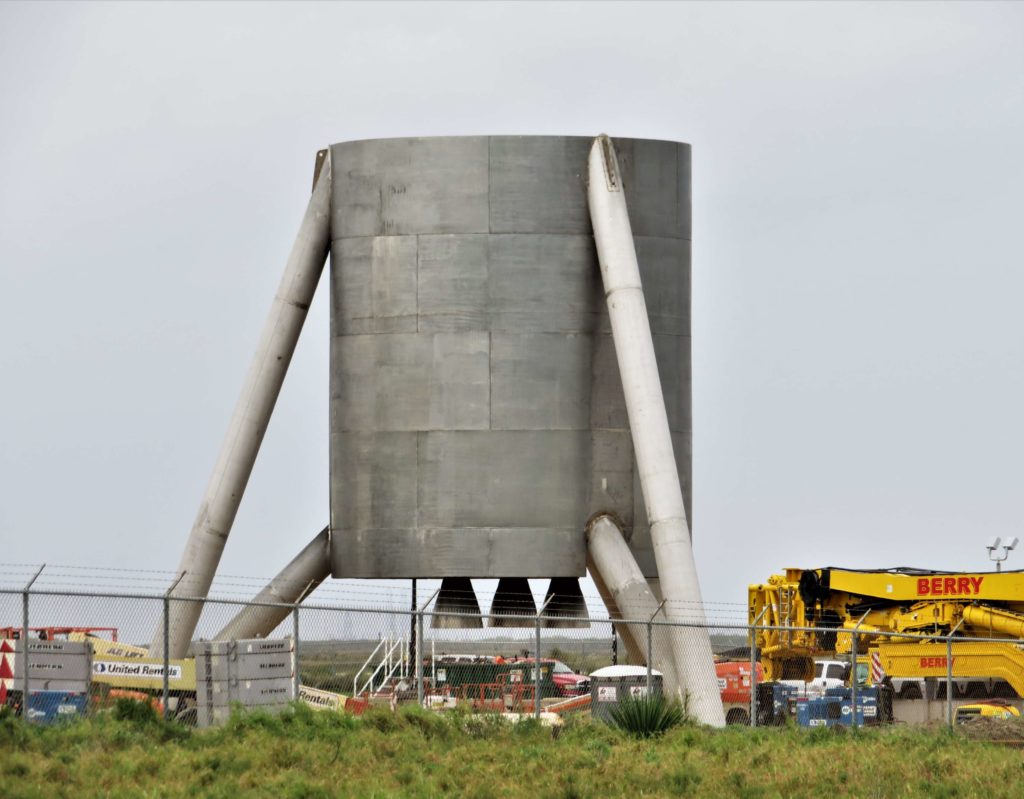
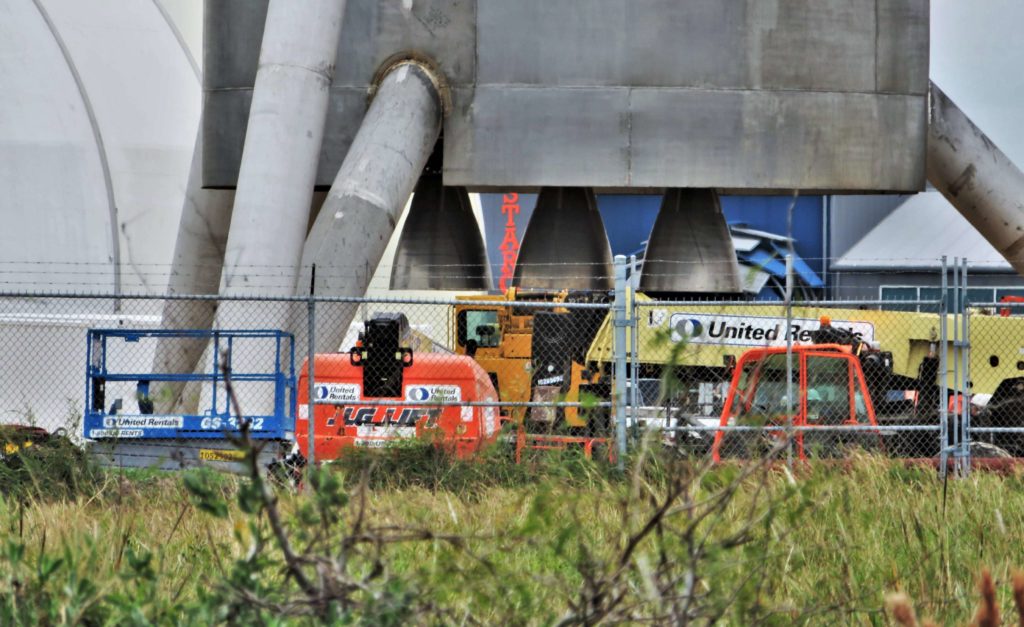
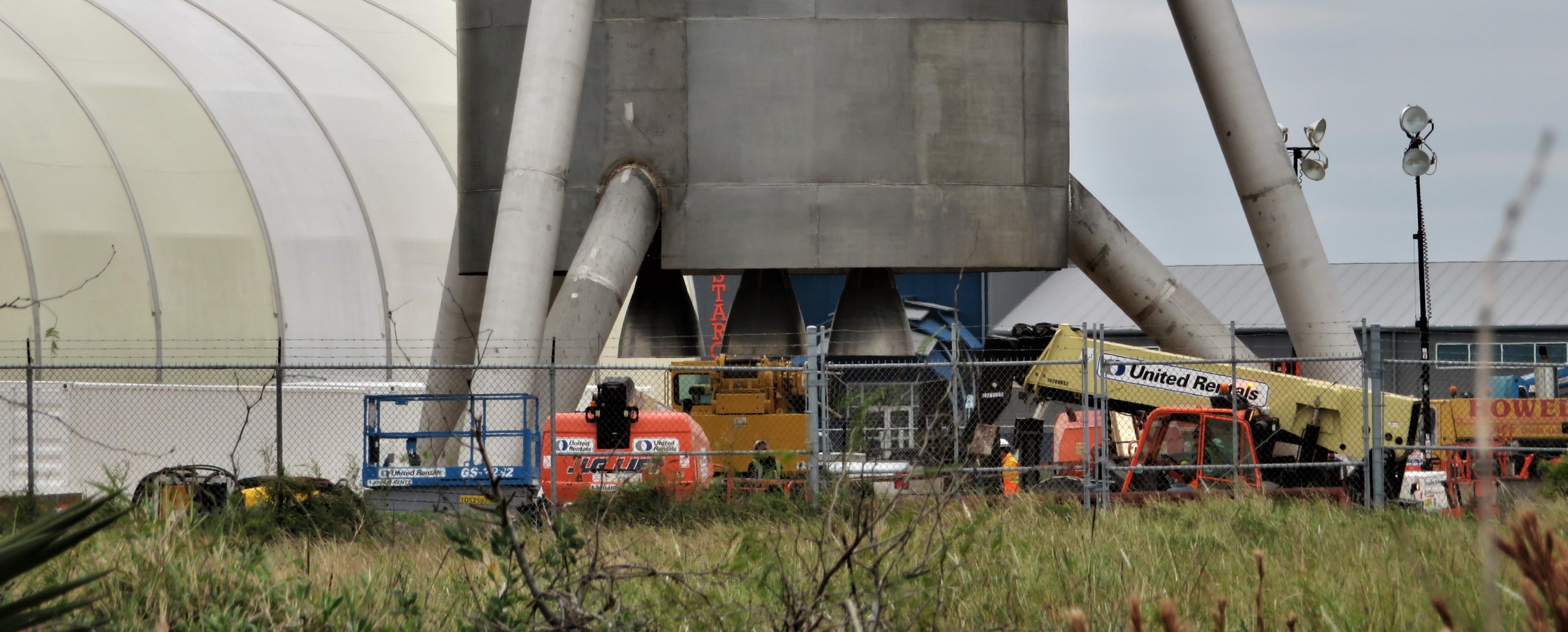
Following a brief ‘hop’ (via crane) off of a concrete build stand, the aft section of SpaceX’s first full-scale Starship hopper (Starhopper?) revealed that SpaceX technicians have already installed what appear to be three real Raptor engines, presumably the first time the propulsion system has ever been mounted to something that might eventually fly.
For a number of reasons, there is a strong chance that these Raptors are actually just boilerplate placeholders standing in as structural guides for the real deal some months down the line. On the other hand, there are also a number of reasons to assume that these apparent engines are indeed real Raptors.
Star ship hopper might be a bit bigger than we thought and with the crane placements over the nose end of the vehicle. This could suggest, @SpaceX are planning to move the segment elsewhere perhaps to the welding stand? We will have to wait and see. (Austin Barnard📸) #2019🚀 pic.twitter.com/kn8hhUPWCU
— Austin Barnard🚀 (@austinbarnard45) January 1, 2019
Despite an already shocking series of rapid-fire developments in the South Texas Starhopper saga, the abrupt appearance of what appears to be three Raptor engines – mirroring CEO Elon Musk’s recent statement that the test vehicle would sport three Raptors – is by far the most unexpected moment yet for the prototype Starship. Purportedly a full-scale prototype of BFR’s upper stage/spaceship (now known as Starship), Musk indicated over the last two weeks that the hopper has been designed to perform a number of hop tests in which the craft’s three Raptors would power it to a range of (relatively low) altitudes above Boca Chica, Texas.
According to a recent FCC filing related to this test program, SpaceX is currently seeking a license for Starship hop tests that will not exceed 5 km (3.1 mi) in altitude and/or 6 minutes in duration. There is admittedly nothing mentioned about the maximum allowed velocity during those tests, but – much like Blue Origin performs supersonic tests of New Shepard in Cape Horn, Texas – SpaceX will likely seek and be granted permission to break the sound barrier during those hypothetical tests. Nevertheless, a 5km ceiling is a fairly significant cap on the range of performance Starhopper will be able to test – accelerating vertically at 2Gs, Starhopper could travel from sea level to 5km in less than 30 seconds while reaching speeds no higher than Mach 1-1.5.
- SpaceX technicians and engineers are continuing to work at a breakneck pace on Starhopper. (NASASpaceflight – bocachicagal)
- At this rate, the hopper will likely wind up around 40m (130 feet) tall. (NASASpaceflight – bocachicagal)
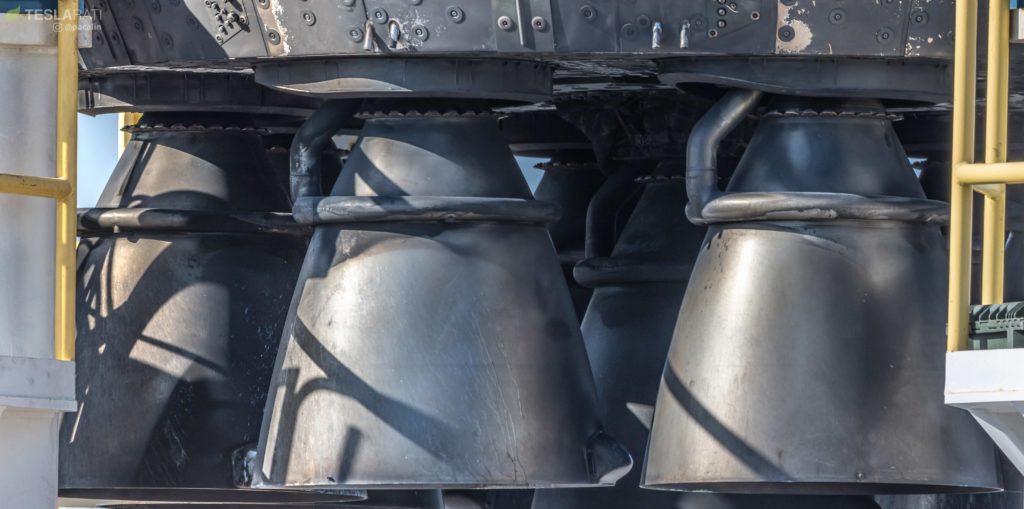
- A close examination of these three engine-like protrusions suggests a level of fit and finish far exceeding a boilerplate stand-in. (NASASpaceflight – bocachicagal)
Combined with the apparent fact that this Starhopper’s fins seem unlikely to ever actuate (i.e. no aerodynamic control surfaces), it’s probable that this ad hoc prototype is only meant to perform a very limited range of hop tests, perhaps as basic as ironing out the kinks of operating a trio of gimballed Raptors and ensuring that they can safely and reliably launch, hover, and land a very large Starship-shaped mass simulator. Falcon 9’s Grasshopper and F9R reusability testbeds performed a very similar task some five years ago, offering SpaceX engineers the opportunity to optimize software and hardware needed to reliably recover real orbital-class rockets after launch. Although Falcon 9 has nine gimballed Merlin 1D engines, SpaceX has long sided with the sole center Merlin as the dedicated landing engine and has only briefly experimented with triple-Merlin landing burns.
Dual-expansion whaaaaat?
According to Musk, Raptor – an advanced liquid methane and oxygen engine with a uniquely efficient propulsion cycle – was expected to produce an impressive ~2000 kN (200 ton, 450K lbf) of thrust in its finished form as of September 2018. However, Musk also mentioned in a late-2017 Reddit AMA that SpaceX engineers were modifying the ship’s design to ensure engine-out reliability during all regimes of flight, landing in particular. To accomplish this feat with an engine as powerful as Raptor, two or three Raptors – capable of producing as much as 600 tons of thrust total – would need to reliably throttle as low as 25%, assuming a landing mass of around 150t. To allow a nearly empty ship (~100t) to still reliably land with three Raptors ignited, the engines would need to be able to throttle to 20% or less.

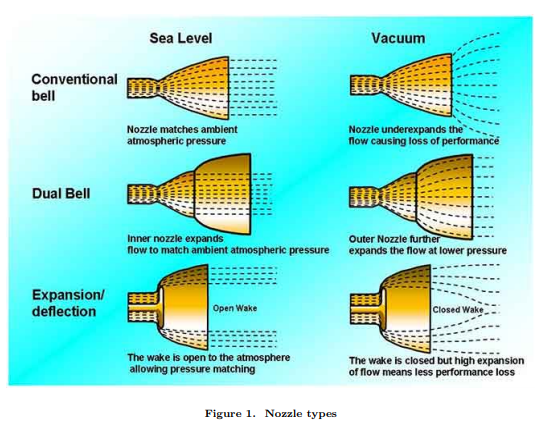
Known as deep throttling in rocketry, ensuring stable combustion and thrust at 20% (let alone 40%) throttle is an extraordinarily challenging feat, often subjecting engines to forces that can literally tear non-optimized hardware apart. To achieve such a deep throttle capability without excessively disrupting the engine’s design, SpaceX appears to have potentially sided with less efficient but extremely simple alternative, known as a dual-bell (or dual-expansion) rocket nozzle. A 1999 Rocketdyne paper concisely explained the primary draws of such a nozzle:
“The [altitude-compensating] dual-bell nozzle offers a unique combination of performance, simplicity, low weight, and ease of cooling” – Horn & Fisher, 1999
Exactly
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) December 27, 2018
Given that SpaceX has decided to delay the introduction and certification of a vacuum-optimized Raptor engine, choosing to instead use the same Raptor on both BFR stages, something like a dual-bell nozzle would be one of the best possible ways for the company to retain some of the efficiency benefits of a vacuum engine while also drastically improving design simplicity, ease of manufacturing, and cutting development time. Aside from offering efficiency gains by way of altitude compensation, a dual-bell nozzle also happens to enable a given engine to operate a much wider throttle range by mitigating problems with flow separation and instability.
- A gif of Raptor throttling over the course of a 90+ second static-fire test in McGregor, Texas. (SpaceX)
- Note that Merlin 1D and prior Raptor prototypes both feature traditional single nozzles. (Pauline Acalin)
- An overview of dual-bell and deflection nozzles. Raptor appears to have now graduated to the former style. (Johan Steelant, 2011)
- Starhopper’s Raptors feature a very distinct seam and second curve, indicative of a dual-bell nozzle. (NASASpaceflight /u/bocachicagal)
For Starhopper and Starship, both aspects are an undeniable net-gain and it’s entirely possible that these dual-bell nozzles – if successfully demonstrated – could find their way onto Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy to further boost their booster performance and efficiency.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!

News
SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell details xAI power pledge at White House event
The commitment was announced during an event with United States President Donald Trump.
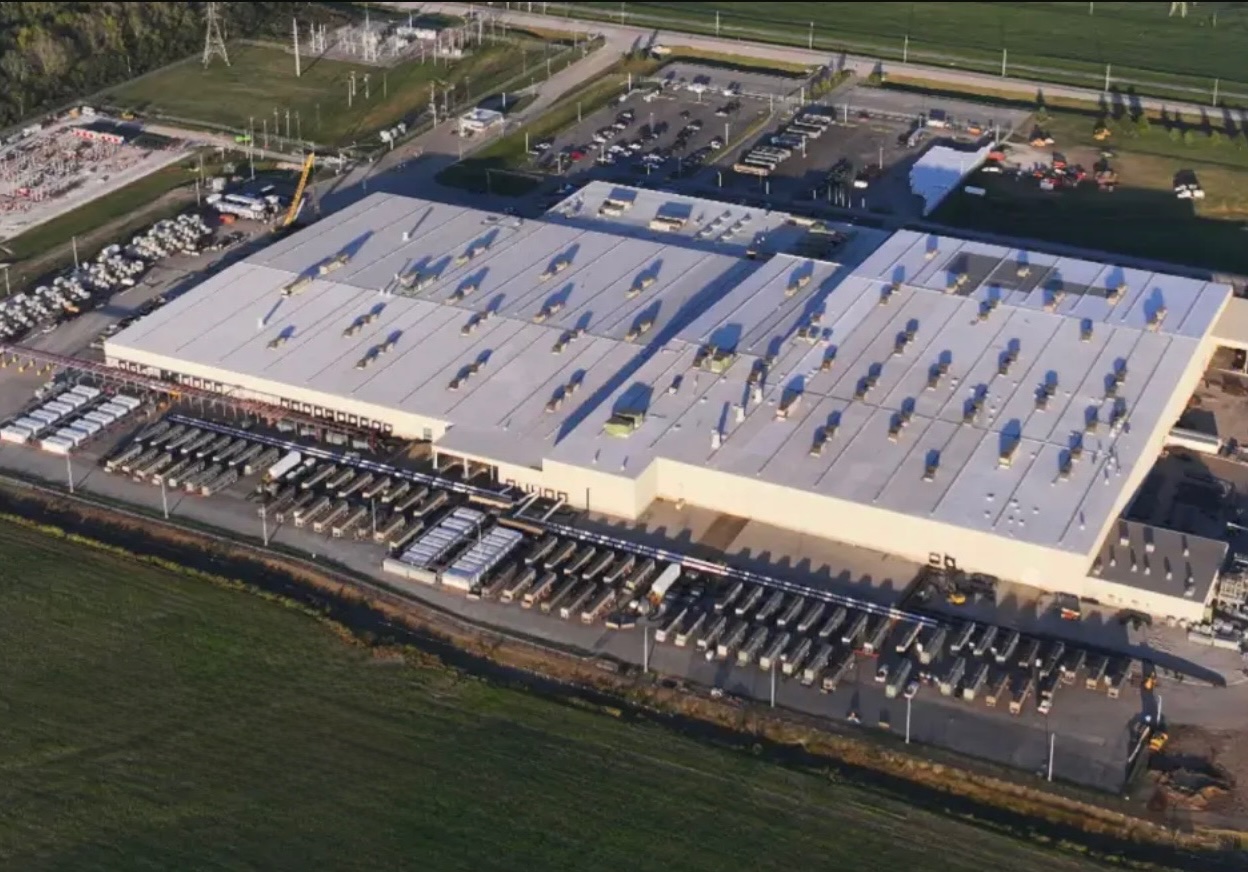

SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell stated that xAI will develop 1.2 gigawatts of power at its Memphis-area AI supercomputer site as part of the White House’s new “Ratepayer Protection Pledge.”
The commitment was announced during an event with United States President Donald Trump.
During the White House event, Shotwell stated that xAI’s AI data center near Memphis would include a major energy installation designed to support the facility’s power needs.
“As you know, xAI builds huge supercomputers and data centers and we build them fast. Currently, we’re building one on the Tennessee-Mississippi state line. As part of today’s commitment, we will take extensive additional steps to continue to reduce the costs of electricity for our neighbors…
“xAI will therefore commit to develop 1.2 GW of power as our supercomputer’s primary power source. That will be for every additional data center as well. We will expand what is already the largest global Megapack power installation in the world,” Shotwell said.
She added that the system would provide significant backup power capacity.
“The installation will provide enough backup power to power the city of Memphis, and more than sufficient energy to power the town of Southaven, Mississippi where the data center resides. We will build new substations and invest in electrical infrastructure to provide stability to the area’s grid.”
Shotwell also noted that xAI will be supporting the area’s water supply as well.
“We haven’t talked about it yet, but this is actually quite important. We will build state-of-the-art water recycling plants that will protect approximately 4.7 billion gallons of water from the Memphis aquifer each year. And we will employ thousands of American workers from around the city of Memphis on both sides of the TN-MS border,” she noted.
The Ratepayer Protection Pledge was introduced as part of the federal government’s effort to address concerns about rising electricity costs tied to large AI data centers, as noted in an Insider report. Under the agreement, companies developing major AI infrastructure projects committed to covering their own power generation needs and avoiding additional costs for local ratepayers.
Elon Musk
SpaceX to launch Starlink V2 satellites on Starship starting 2027
The update was shared by SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell and Starlink Vice President Mike Nicolls.
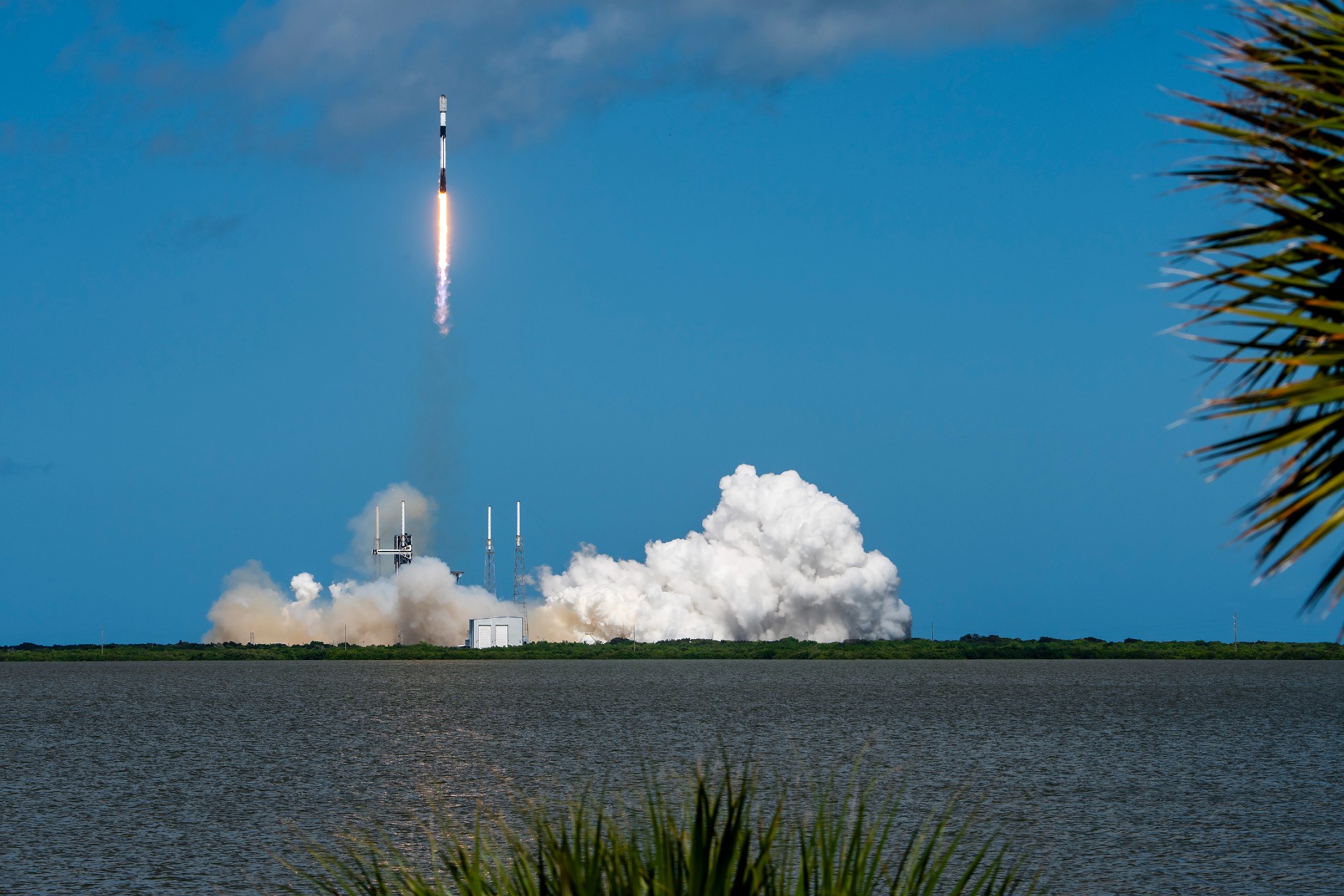

SpaceX is looking to start launching its next-generation Starlink V2 satellites in mid-2027 using Starship.
The update was shared by SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell and Starlink Vice President Mike Nicolls during remarks at Mobile World Congress (MWC) in Barcelona, Spain.
“With Starship, we’ll be able to deploy the constellation very quickly,” Nicolls stated. “Our goal is to deploy a constellation capable of providing global and contiguous coverage within six months, and that’s roughly 1,200 satellites.”
Nicolls added that once Starship is operational, it will be capable of launching approximately 50 of the larger, more powerful Starlink satellites at a time, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
The initial deployment of roughly 1,200 next-generation satellites is intended to establish global and contiguous coverage. After that phase, SpaceX plans to continue expanding the system to reach “truly global coverage, including the polar regions,” Nicolls said.
Currently, all Starlink satellites are launched on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket. The next-generation fleet will rely on Starship, which remains in development following a series of test flights in 2025. SpaceX is targeting its next Starship test flight, featuring an upgraded version of the rocket, as soon as this month.
Starlink is currently the largest satellite network in orbit, with nearly 10,000 satellites deployed. Bloomberg Intelligence estimates the business could generate approximately $9 billion in revenue for SpaceX in 2026.
Nicolls also confirmed that SpaceX is rebranding its direct-to-cell service as Starlink Mobile.
The service currently operates with 650 satellites capable of connecting directly to smartphones and has approximately 10 million monthly active users. SpaceX expects that figure to exceed 25 million monthly active users by the end of 2026.
Elon Musk
Starlink V2 to bring satellite-to-phone service to Deutsche Telekom in Europe
Starlink stated that the system is designed to deliver 5G speeds directly to compatible smartphones in remote areas.

Starlink is partnering with Deutsche Telekom to roll out satellite-to-mobile connectivity across Europe, extending coverage to more than 140 million subscribers across 10 countries.
The service, planned for launch in 2028 in several Telekom markets, including Germany, will use Starlink’s next-generation V2 satellites and Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) spectrum to enable direct-to-device connectivity.
In a post on X, the official Starlink account stated that the agreement will be the first in Europe to deploy its V2 next-generation satellite-to-mobile technology using new MSS spectrum. The company added that the system is designed to deliver 5G speeds directly to compatible smartphones in remote areas.
Abdu Mudesir, Board Member for Product and Technology at Deutsche Telekom, shared his excitement for the partnership in a press release. “We provide our customers with the best mobile network. And we continue to invest heavily in expanding our infrastructure. At the same time, there are regions where expansion is especially complex due to topographical conditions or official constraints,” he said.
“We want to ensure reliable connectivity for our customers in those areas as well. That is why we are strategically complementing our network with satellite-to-mobile connectivity. For us, it is clear: connectivity creates security and trust. And we deliver. Everywhere.”
Under the partnership, compatible smartphones will automatically switch to Starlink’s satellite network when terrestrial coverage is unavailable, enabling access to data, voice, video, and messaging services.
Telekom reports 5G geographic coverage approaching 90% in Germany, with LTE exceeding 92% and voice coverage reaching up to 99%. Starlink’s satellite layer is intended to extend connectivity beyond those terrestrial limits, particularly in topographically challenging or infrastructure-constrained areas.
Stephanie Bednarek, VP of Starlink Sales, also shared her thoughts on the partnership. “We’re so pleased to bring reliable satellite-to-mobile connectivity to millions of people across 10 countries in partnership with Deutsche Telekom. This agreement will be the first-of-its-kind in Europe to launch Starlink’s V2 next-generation technology that will expand on data, voice and messaging by providing broadband directly to mobile phones,” she said.
Starlink’s V2 constellation is designed to expand bandwidth and capacity compared to its predecessor. If implemented as outlined, the 2028 launch would mark one of the first large-scale European deployments of integrated satellite-to-phone connectivity by a major telecom operator.