News
SpaceX’s internet satellite strategy faces possible setback (Correction: It’s actually in great shape)
Correction: Upon further analysis of FCC filings and proposed updates to ITU regulations, SpaceX’s Internet constellation is on much steadier ground than it initially appeared to be, and the FCC decision made on September 26 2017 to update its NGSO FSS regulations is likely to help SpaceX far more than it might harm the company.
The ITU has since 2015 taken a stance that aligns more with the FCC’s cooperative spectrum sharing policy and did not intend for Part 5 of its Radio Regulations to be interpreted as a “first come, first serve” attitude. Specifically, the ITU’s 2017 Rules of Procedure pointedly state in Article 9.6 (Word document download) that those rules were not intended “to state an order of priorities for rights to a particular orbital position” and that “the [interference] coordination process is a two way process”. An ex parte filed with the FCC (PDF download) by SpaceX on September 15 stated SpaceX’s support for these international and domestic policy adoptions, as well as the FCC International Bureau’s responsive consideration of SpaceX’s own suggestions.
The company’s first two test satellites could still launch later this year
The U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) responded September 7th to requests for modification to existing satellite communications regulations and FCC practices from a number of prospective constellation operators, including OneWeb, Telesat, and SpaceX.
The FCC ultimately decided to avoid one major rule change that could force SpaceX to completely reconsider its strategic approach to its proposed Low Earth Orbit broadband constellation.
To grossly oversimplify, SpaceX had requested that the FCC apply their non-interference rules for lower orbit communications satellites to internet constellations operating both inside and outside the physical United States. These rules require that communication satellites operating in non-geostationary orbits (NGSO) share the available wireless spectrum equally among themselves when two or more satellites pass within a certain distance of each other relative to ground stations. In simpler terms, consider your smartphone’s cellular connectivity. The FCC’s rule for satellites in lower orbits can be thought of like multiple smartphones using the same cell tower to access the internet: the cell tower simply acknowledges the multiple devices it needs to serve and allows each device a certain amount of bandwidth.
However, the FCC is admittedly a domestic Commission focused on administering communications rules and regulations in the United States, and an agency already exists for coordinating global communications needs, called the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The ITU’s Radio Regulations are considerably more simplistic. Rather than the FCC’s more nuanced and reasonable methods of spectrum sharing, the ITU allows the first satellite operator actively using a certain orbit or spectrum to become the primary coordinator for all interference issues. Put more simply, it gives those who launch communications satellites first a “first come, first serve” advantage that lets those entities then set the rules for interference with their constellation.
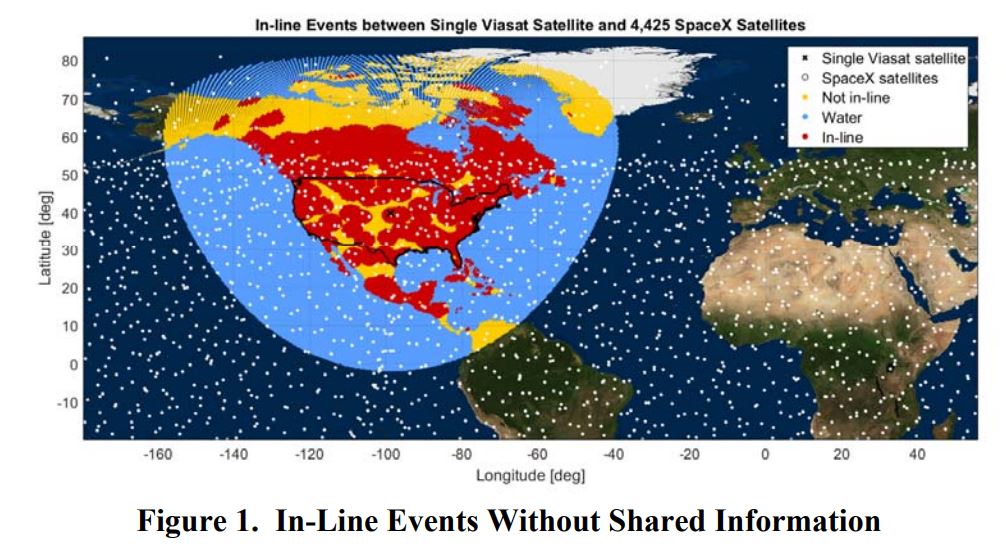
- In these figures, SpaceX attempts to demonstrate the significance of cooperation between different satellite constellation operators. (SpaceX/FCC)
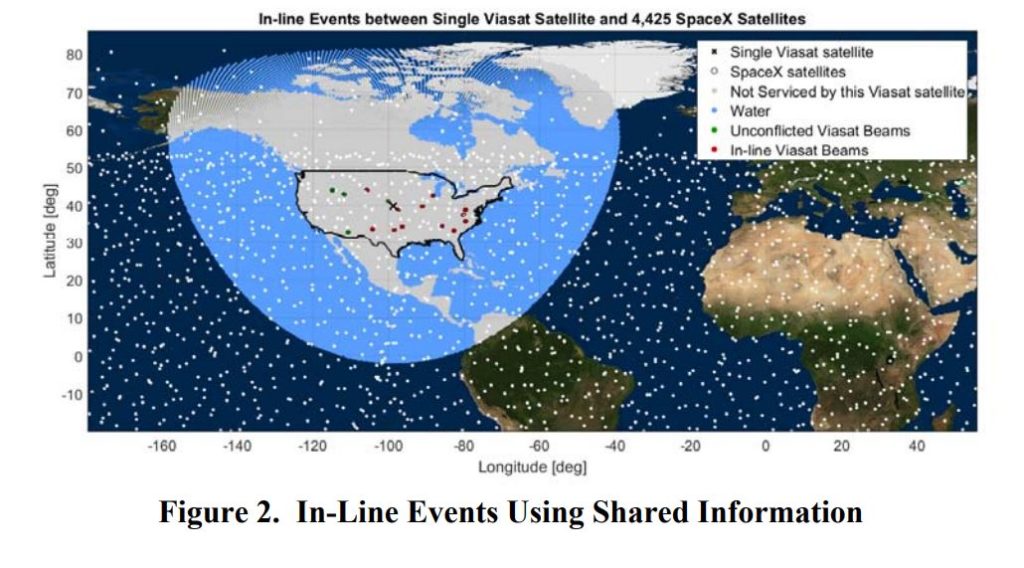
- Compared to the first figure, interference events while sharing data on satellite locations is almost nonexistent. (SpaceX/FCC)
Both OneWeb and Telesat, companies also interested in launching global broadband constellations, are licensed in countries other than the United States, meaning that the FCC has given the ITU precedent in deciding how to deal with SpaceX’s potential constellation interference. SpaceX’s proposed constellation of at least several thousand satellites ends up being at a distinct disadvantage simply because it would take far longer for SpaceX to even partially complete its constellation when compared with competitors like OneWeb, who expect to finish launching the first phase of their constellation several hundred satellites by the end of 2020. Under the ITU’s regulations, SpaceX could be forced by competitors to effectively step on eggshells around their constellations by avoiding interference to the furthest extent possible, rather than simply sharing spectrum in the brief periods where different satellites temporarily interfere with each other.
While the FCC’s choice to cede international interference coordination to the ITU is a huge blow to SpaceX’s proposed internet constellation efforts, the same September 7th report also eased a handful of other requirements that would have proven difficult for SpaceX’s massive constellation. For geostationary constellations, the FCC previously required that all satellites be launched within a period of six years, with failure to do so resulting in a revoked license for the company in question. In a small concession to SES, O3b, and SpaceX, the FCC now plans to require that 50% of lower orbit satellite constellations be launched within six years of receiving an FCC license. This would still be a massive challenge for SpaceX’s plan of 4,425 initial satellites and a follow-up constellation of more than 7,000 additional satellites (PDF download).
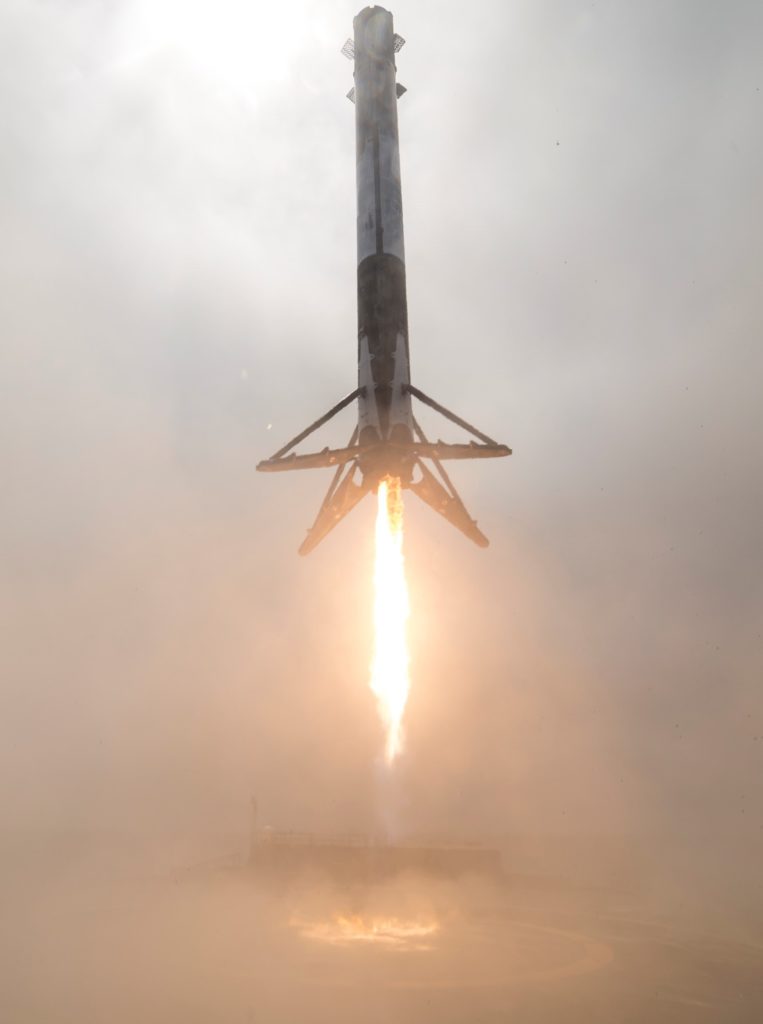
- Falcon 9 lands on drone ship JRTI after launching Formosat-5, August 2017. (SpaceX)
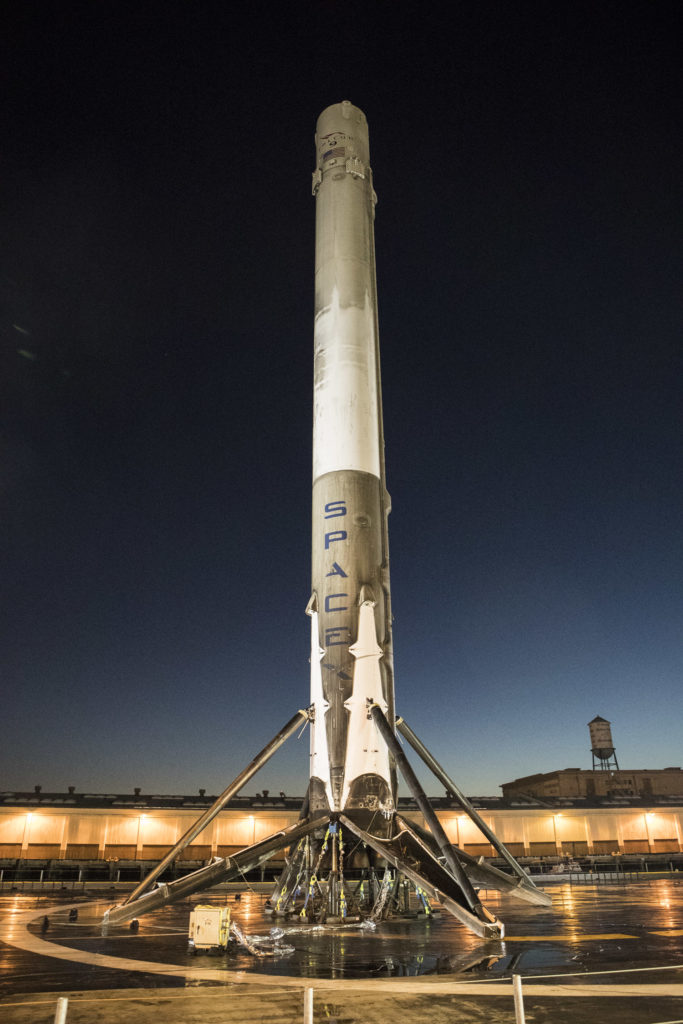
- 2017 saw SpaceX recovery 10 Falcon 9 first stages, 5 by sea. (SpaceX)
- Falcon 9 B1040 returns to LZ-1 after the launch of the USAF’s X-37B spaceplane. (SpaceX)
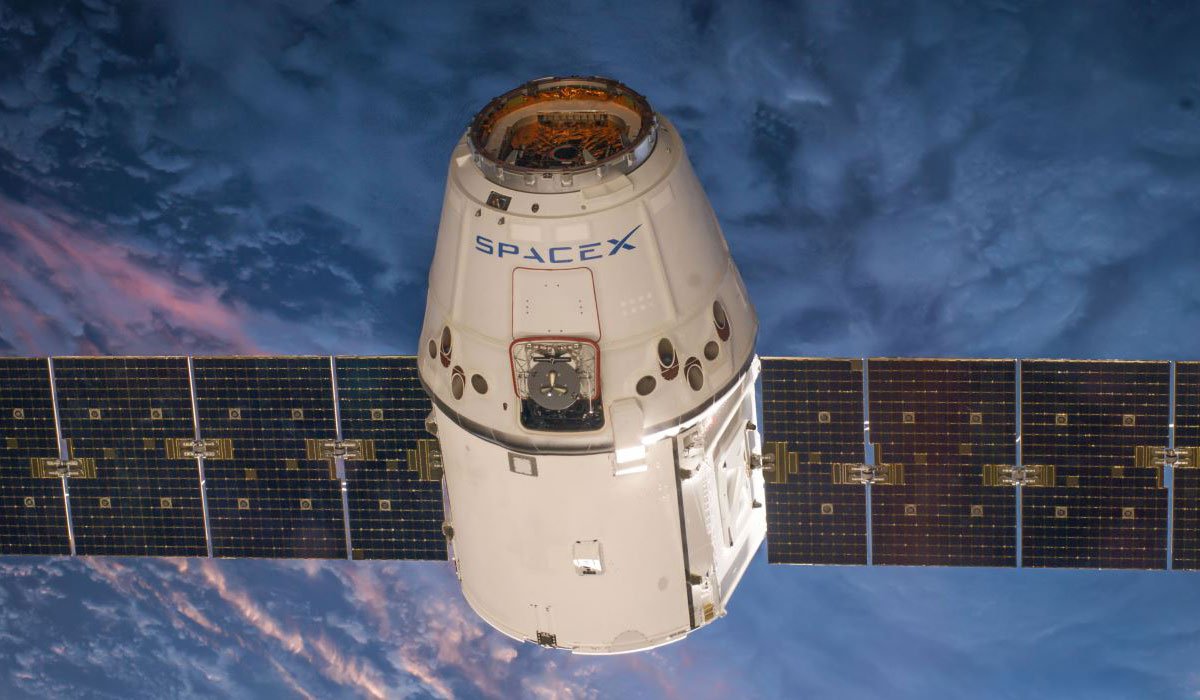
The FCC’s September 7th report will not become final unless it is passed by vote in a September 26th Open Commission Meeting. It is possible that SpaceX council will make a statement protesting the FCC’s decision, but it is nevertheless likely that the FCC’s report will be accepted and become official. While the LEO internet constellation has remained a low priority for SpaceX since it was revealed in 2015, the company has steadily continued work on the project and SpaceX has every reason to continue pursuing it given the potential profit margins it could produce. In spite of the now expanded difficulties lying ahead, SpaceX appears to be preparing for the first launch of two test satellites related to its internet constellation efforts. The move is seen as a likely attempt to tag along as passengers during SpaceX’s launch of PAZ, a Spanish earth imaging satellite, during the final three months of 2017.
Elon Musk is scheduled to reveal more details on SpaceX’s Mars exploration and colonization efforts on September 29th. He has stated that this presentation will focus more on the “how” of colonizing Mars, revealing how exactly SpaceX thinks it can fund the development of its Interplanetary Transport System. Musk also confirmed several weeks ago that SpaceX had reduced the size of the ITS rocket to a still-massive diameter of 9 meters, and sources inside the company have also indicated that the company is thinking about modifying its LC-39A Florida launch pad to support both Falcon and ITS vehicles. SpaceX recruiters revealed earlier this week that SpaceX also intends to have their Boca Chica, Texas launch pad, which is currently under construction, be capable of eventually launching ITS-sized vehicles once it comes online in 2019 or later.

Elon Musk
Brazil Supreme Court orders Elon Musk and X investigation closed
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.

Brazil’s Supreme Federal Court has ordered the closure of an investigation involving Elon Musk and social media platform X. The inquiry had been pending for about two years and examined whether the platform was used to coordinate attacks against members of the judiciary.
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.
According to a report from Agencia Brasil, the investigation conducted by the Federal Police did not find evidence that X deliberately attempted to attack the judiciary or circumvent court orders.
Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet concluded that the irregularities identified during the probe did not indicate fraudulent intent.
Justice Moraes accepted the prosecutor’s recommendation and ruled that the investigation should be closed. Under the ruling, the case will remain closed unless new evidence emerges.
The inquiry stemmed from concerns that content on X may have enabled online attacks against Supreme Court justices or violated rulings requiring the suspension of certain accounts under investigation.
Justice Moraes had previously taken several enforcement actions related to the platform during the broader dispute involving social media regulation in Brazil.
These included ordering a nationwide block of the platform, freezing Starlink accounts, and imposing fines on X totaling about $5.2 million. Authorities also froze financial assets linked to X and SpaceX through Starlink to collect unpaid penalties and seized roughly $3.3 million from the companies’ accounts.
Moraes also imposed daily fines of up to R$5 million, about $920,000, for alleged evasion of the X ban and established penalties of R$50,000 per day for VPN users who attempted to bypass the restriction.
Brazil remains an important market for X, with roughly 17 million users, making it one of the platform’s larger user bases globally.
The country is also a major market for Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet service, which has surpassed one million subscribers in Brazil.
Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Energy
Tesla Energy gains UK license to sell electricity to homes and businesses
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.

Tesla Energy has received a license to supply electricity in the United Kingdom, opening the door for the company to serve homes and businesses in the country.
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.
According to Ofgem, the license took effect at 6 p.m. local time on Wednesday and applies to Great Britain.
The approval allows Tesla’s energy business to sell electricity directly to customers in the region, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
Tesla has already expanded similar services in the United States. In Texas, the company offers electricity plans that allow Tesla owners to charge their vehicles at a lower cost while also feeding excess electricity back into the grid.
Tesla already has a sizable presence in the UK market. According to price comparison website U-switch, there are more than 250,000 Tesla electric vehicles in the country and thousands of Tesla home energy storage systems.
Ofgem also noted that Tesla Motors Ltd., a separate entity incorporated in England and Wales, received an electricity generation license in June 2020.
The new UK license arrives as Tesla continues expanding its global energy business.
Last year, Tesla Energy retained the top position in the global battery energy storage system (BESS) integrator market for the second consecutive year. According to Wood Mackenzie’s latest rankings, Tesla held about 15% of global market share in 2024.
The company also maintained a dominant position in North America, where it captured roughly 39% market share in the region.
At the same time, competition in the energy storage sector is increasing. Chinese companies such as Sungrow have been expanding their presence globally, particularly in Europe.