News
Tesla Model 3’s body structure is a strategic blend of aluminum and ultra high-strength steel
New photos from Tesla Model 3’s Body Repair Tech Note reveal a metal composition for the vehicle’s structure that strikes a perfect balance between world class safety and cost effectiveness.
One might recall Tesla CEO Elon Musk giving a tonque-in-cheek response about Model 3’s 5-star safety rating during a speech in Fremont, California. “The Volvo [S60] is arguably the second safest car in the world”, said Musk while alluding to the fact that Model 3 takes top honors for being the safest car in the world.
Photos posted to Twitter and shared on Reddit illustrate just how Tesla has been able to achieve a Model 3 body structure design that’s lightweight and has unparalleled strength at an entry level price point.
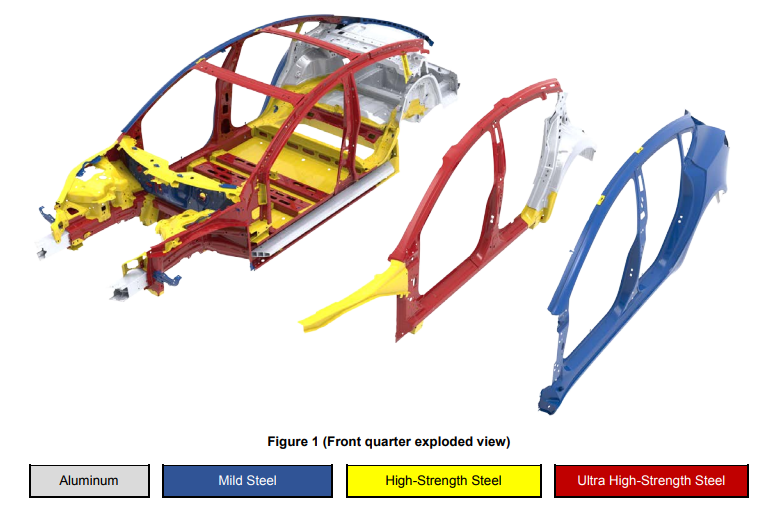
Looking at a front quarter exploded view of the Model 3 body, one can see the various compositions of steel the Tesla engineers used across the machine-stamped, multi-layer structure.
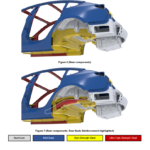
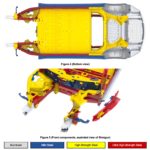
Tesla uses three different grades of steel, from mild steel used on the outer body structure where it’s designed to absorb initial impacts, and high-strength, to ultra high-strength used in the vehicle’s core. For instance, the A-pillar and B-pillar (noted in red on the graphic) is fabricated from ultra high-strength steel in order to provide maximum rollover protection. Model 3’s front frame rail is a composition between high-strength and ultra high-strength steel, and serves as the main support for the front “crumple zone”.
Tesla Model 3’s body repair manual notes that “Structural Pulling” is not allowed, meaning that any structural component that’s welded, weld-bonded, riveted, or rivet-bonded to the vehicle can not undergo a process wherein the straightening of structural parts are facilitated through a hydraulic pulling machine. Doing so would compromise the yield strength of the metals being used.
Also noted in the Model 3 structural diagram is the “underbelly” that serves as the main support for Model 3’s skateboard style battery pack, similar to what’s used in its older Model S and Model X siblings. The entire underside of the vehicle is fabricated from high-strength steel.
Side impact safety on the Model 3 is bolstered by a fully fortified closed steel structure in ultra high-strength steel. Looking at the crash test video showing a side-pole impact test performed on Tesla’s Model 3 and Volvo’s S60, one can easily see the level of deformity the Volvo has over the Model 3.
Watch a Tesla Model 3 vs. Volvo S60 side-pole impact test pic.twitter.com/dXBQkstrdo
— Tesla (@Tesla) July 29, 2017
Lastly, lightweight aluminum is introduced in areas of the body structure that are less susceptible to accidental impact such as the trunk floor and wheel wells. Using aluminum helps Model 3 maintain a relatively light curb weight of 3,549 lbs. for the standard version and 3,814 lbs. for the Long Range Model 3 with larger (and heavier) battery pack.
All in all, Tesla’s use of various steels and aluminum in Model 3’s body structure can be seen as a learning experience and first iteration towards even more affordable and higher volume production down the road – Model Y.
News
Tesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
Tesla seems serious about expanding its Robotaxi service to several states in the coming months.

Tesla has initiated discussions with Arizona transportation regulators to certify its driverless Robotaxi service in the state, as per a recent report from Bloomberg News. The move follows Tesla’s launch of its Robotaxi pilot program in Austin, Texas, as well as CEO Elon Musk’s recent comments about the service’s expansion in the Bay Area.
The Arizona Department of Transportation confirmed to Bloomberg that Tesla has reached out to begin the certification process for autonomous ride-sharing operations in the state. While details remain limited, the outreach suggests that Tesla is serious about expanding its driverless Robotaxi service to several territories in the coming months.
The Arizona development comes as Tesla prepares to expand its service area in Austin this weekend, as per CEO Elon Musk in a post on X. Musk also stated that Tesla is targeting the San Francisco Bay Area as its next major market, with a potential launch “in a month or two,” pending regulatory approvals.
Tesla first launched its autonomous ride-hailing program on June 22 in Austin with a small fleet of Model Y vehicles, accompanied by a Tesla employee in the passenger seat to monitor safety. While still classified as a test, Musk has said the program will expand to about 1,000 vehicles in the coming months. Tesla will later upgrade its Robotaxi fleet with the Cyercab, a two-seater that is designed without a steering wheel.
Sightings of Cybercab castings around the Giga Texas complex suggests that Tesla may be ramping the initial trial production of the self-driving two-seater. Tesla, for its part, has noted in the past that volume production of the Cybercab is expected to start sometime next year.
In California, Tesla has already applied for a transportation charter-party carrier permit from the state’s Public Utilities Commission. The company is reportedly taking a phased approach to operating in California, with the Robotaxi service starting with pre-arranged rides for employees in vehicles with safety drivers.
News
Tesla sets November 6 date for 2025 Annual Shareholder Meeting
The automaker announced the date on Thursday in a Form 8-K.

Tesla has scheduled its 2025 annual shareholder meeting for November 6, addressing investor concerns that the company was nearing a legal deadline to hold the event.
The automaker announced the date on Thursday in a Form 8-K submitted to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The company also listed a new proposal submission deadline of July 31 for items to be included in the proxy statement.
Tesla’s announcement followed calls from a group of 27 shareholders, including the leaders of large public pension funds, which urged Tesla’s board to formally set the meeting date, as noted in a report from The Wall Street Journal.
The group noted that under Texas law, where Tesla is now incorporated, companies must hold annual meetings within 13 months of the last one if requested by shareholders. Tesla’s previous annual shareholder meeting was held on June 13, 2024, which placed the July 13 deadline in focus.
Tesla originally stated in its 2024 annual report that it would file its proxy statement by the end of April. However, an amended filing on April 30 indicated that the Board of Directors had not yet finalized a meeting date, at least at the time.
The April filing also confirmed that Tesla’s board had formed a special committee to evaluate certain matters related to CEO Elon Musk’s compensation plan. Musk’s CEO performance award remains at the center of a lengthy legal dispute in Delaware, Tesla’s former state of incorporation.
Due to the aftermath of Musk’s legal dispute about his compensation plan in Delaware, he has not been paid for his work at Tesla for several years. Musk, for his part, has noted that he is more concerned about his voting stake in Tesla than his actual salary.
At last year’s annual meeting, TSLA shareholders voted to reapprove Elon Musk’s compensation plan and ratified Tesla’s decision to relocate its legal domicile from Delaware to Texas.
Elon Musk
Grok coming to Tesla vehicles next week “at the latest:” Elon Musk
Grok’s rollout to Tesla vehicles is expected to begin next week at the latest.

Elon Musk announced on Thursday that Grok, the large language model developed by his startup xAI, will soon be available in Tesla vehicles. Grok’s rollout to Tesla vehicles is expected to begin next week at the latest, further deepening the ties between the two Elon Musk-led companies.
Tesla–xAI synergy
Musk confirmed the news on X shortly after livestreaming the release of Grok 4, xAI’s latest large language model. “Grok is coming to Tesla vehicles very soon. Next week at the latest,” Musk wrote in a post on social media platform X.
During the livestream, Musk and several members of the xAI team highlighted several upgrades to Grok 4’s voice capabilities and performance metrics, positioning the LLM as competitive with top-tier models from OpenAI and Google.
The in-vehicle integration of Grok marks a new chapter in Tesla’s AI development. While Tesla has long relied on in-house systems for autonomous driving and energy optimization, Grok’s integration would introduce conversational AI directly into its vehicles’ user experience. This integration could potentially improve customer interaction inside Tesla vehicles.
xAI and Tesla’s collaborative footprint
Grok’s upcoming rollout to Tesla vehicles adds to a growing business relationship between Tesla and xAI. Earlier this year, Tesla disclosed that it generated $198.3 million in revenue from commercial, consulting, and support agreements with xAI, as noted in a report from Bloomberg News. A large portion of that amount, however, came from the sale of Megapack energy storage systems to the artificial intelligence startup.
In July 2023, Musk polled X users about whether Tesla should invest $5 billion in xAI. While no formal investment has been made so far, 68% of poll participants voted yes, and Musk has since stated that the idea would be discussed with Tesla’s board.
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 Elon Musk15 hours ago
Elon Musk15 hours agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla’s Omead Afshar, known as Elon Musk’s right-hand man, leaves company: reports
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”