
News
Boeing Starliner joins SpaceX’s Crew Dragon at the International Space Station
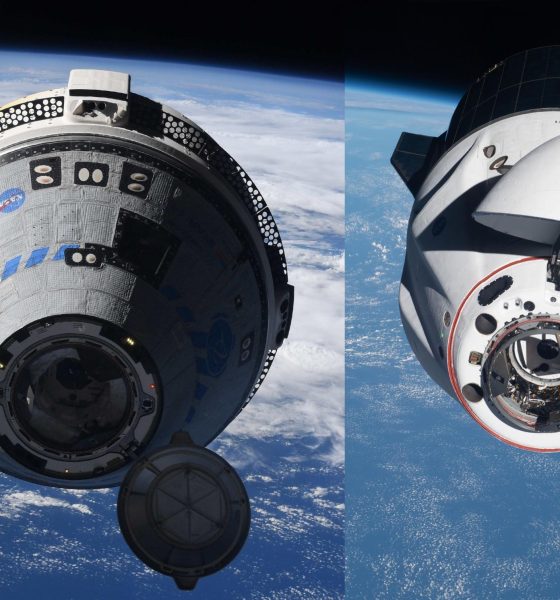
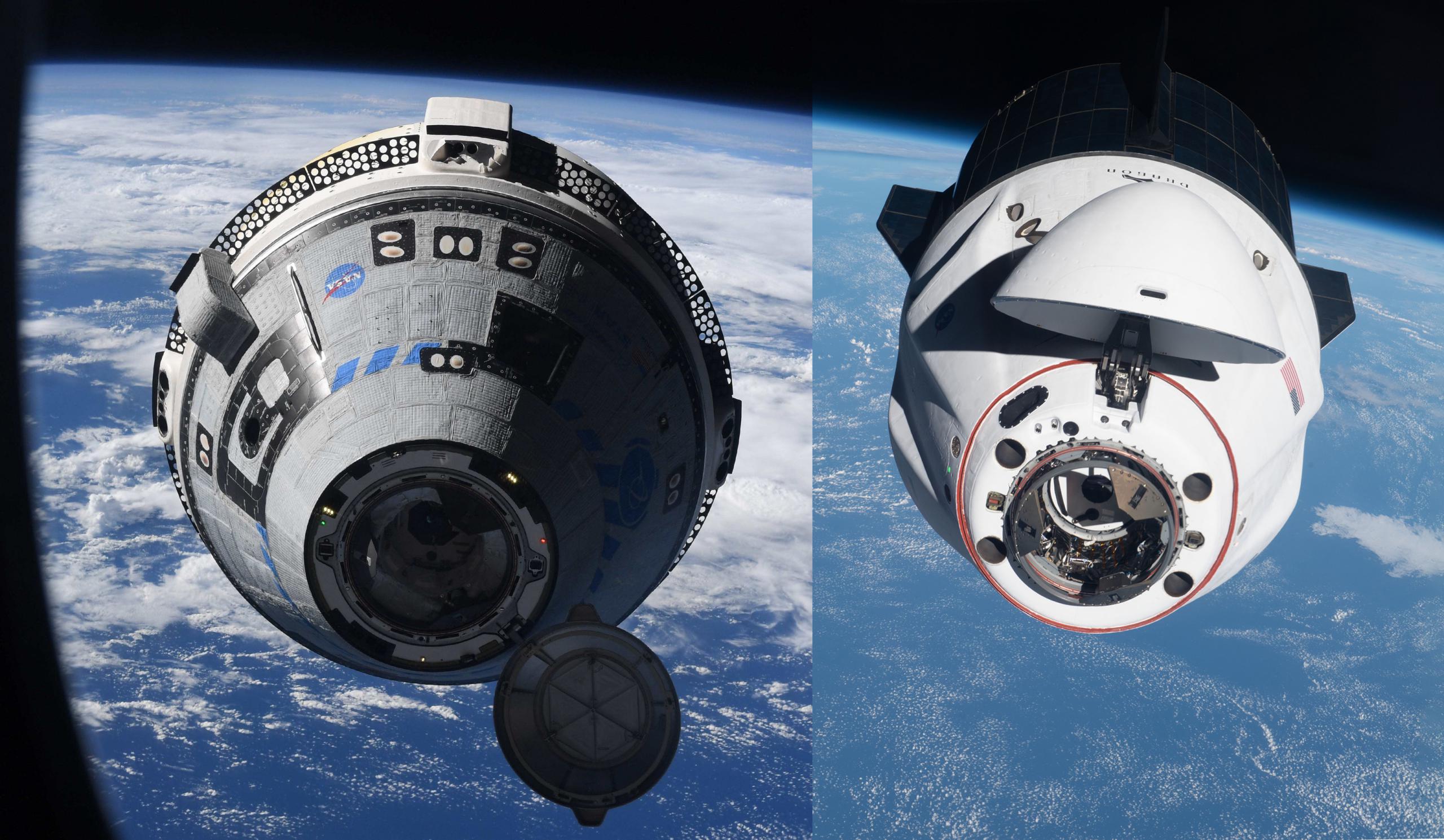
Boeing’s Starliner crew capsule has successfully rendezvoused, approached, and docked with the International Space Station for the first time, marking major several major milestones for NASA and its second Commercial Crew partner.
Starliner’s second orbital flight test (OFT-2) began as expected with a near-flawless May 19th launch on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket. As thousands of employees and stakeholders held their collective breath, the uncrewed prototype safely detached from Atlas V’s Centaur upper stage and propelled itself the rest of the to a stable parking orbit. Two and a half years after their first attempt, Boeing and NASA were then finally able to send Starliner on its way to the International Space Station (ISS) and prepare for proximity operations.
Welcome #Starliner ! pic.twitter.com/F7KVIRO24c— Samantha Cristoforetti (@AstroSamantha) May 21, 2022
As previously discussed on Teslarati, Starliner making it through the first hour or so of flight without running into a catastrophic problem was already a huge milestone for Boeing and a massive improvement over the company’s last two orbital flight test attempts.
“The story of Starliner’s tortured orbital flight test (OFT) campaign began in earnest on December 20th, 2019, when an uncrewed prototype first attempted to launch to the International Space Station (ISS) atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket. A major software bug that could have been easily detected with even the most basic integrated hardware-in-the-loop prelaunch testing caused Starliner to lose control the moment it separated from Atlas V. After hundreds of seconds of unplanned burns of its many attitude control thrusters, Boeing finally regained control but Starliner no longer had enough propellant to safely reach the ISS.
Boeing would later catch and correct another unrelated software bug mere hours before Starliner’s planned reentry and recovery that, if undetected, could have caused the spacecraft’s capsule and service sections to crash into each other shortly after separation.
On July 30th, 2021, shortly before a different uncrewed Starliner was scheduled to reattempt the first Orbital Flight Test, the launch was aborted. Boeing and NASA later reported that 13 of Starliner’s 24 main oxidizer valves failed to open during a prelaunch test just a few hours before liftoff. It was eventually concluded that faulty Aerojet Rocketdyne-supplied valves and poor Boeing integration enabled water intrusion and extensive corrosion. The next OFT-2 launch attempt was delayed by almost ten months, as a result.”
Teslarati.com – May 19th, 2022
Instead of calamity, Starliner’s second OFT and third OFT attempt was mainly greeted with success. After reaching orbit, the spacecraft began raising and ‘phasing’ its orbit to rendezvous with the ISS and completed all the burns and navigation required without major issues. Finally, after several intentional test maneuvers and about an hour of unplanned troubleshooting, Starliner began its final approach and successfully docked with the ISS – joining a SpaceX Crew Dragon – at 8:28 pm EDT on May 20th (00:28 UTC 21 May).
Starliner’s successful docking made it the fourth, fifth, or sixth US spacecraft to reach the ISS, joining the Space Shuttle, three main variants of SpaceX’s Dragon, and Orbital ATK’s (now Northrop Grumman) Cygnus cargo vehicle. It also marked the first time that both NASA Commercial Crew Program vehicles have been simultaneously docked at the space station – a reassuring sign of a future with redundant access after years of Boeing delays forced SpaceX to temporarily become NASA’s sole source of astronaut transportation. While odds are good that SpaceX will ultimately be required to singlehandedly maintain NASA access to the ISS for seven six-month ‘expeditions’ (>3 years), Starliner’s thus-far-successful OFT2 mission significantly improves the odds that the Boeing spacecraft will be fully ready within a year or two.
Nonetheless, Starliner must still safely depart the ISS, lower its orbit, reenter Earth’s atmosphere, and safely touch down for recovery and reuse. Starliner has already accomplished all of those tasks during OFT1, but tensions will still be high. Additionally, Starliner’s performance during OFT2 has been far from perfect. Aside from a few minor issues with coolers and radiators, Boeing and NASA revealed that four of the spacecraft’s several dozen thrusters (two larger maneuvering/control thrusters and two smaller attitude control thrusters) – had failed by the time it was docked. During OFT1, as many as 13 thrusters failed as a result of minutes of unplanned burns, but Boeing was able to recover all but one before reentry.
Technically, that means that both missions have demonstrated the solid redundancy of Starliner’s propulsion systems, but NASA will undoubtedly demand that Boeing determine probable root causes and qualify fixes before greenlighting Starliner’s first Crewed Flight Test (CFT). For SpaceX, it took 14 months after Crew Dragon’s first near-flawless uncrewed debut for NASA to agree to proceed with a crewed flight test. However, during post-flight testing, the capsule that support Demo-1 catastrophically exploded, triggering a several-month investigation. The effect of a few failed thrusters is decidedly less severe, so Starliner might not have to wait as long for CFT. With any luck, that means that NASA will have two fully-redundant astronaut transport spacecraft available and operational by the end of 2023, if not earlier.

Elon Musk
Tesla to increase Full Self-Driving subscription price: here’s when

Tesla will increase its Full Self-Driving subscription price, meaning it will eventually be more than the current $99 per month price tag it has right now.
Already stating that the ability to purchase the suite outright will be removed, Tesla CEO Elon Musk said earlier this week that the Full Self-Driving subscription price would increase when its capabilities improve:
“I should also mention that the $99/month for supervised FSD will rise as FSD’s capabilities improve. The massive value jump is when you can be on your phone or sleeping for the entire ride (unsupervised FSD).”
This was an expected change, especially as Tesla has been hinting for some time that it is approaching a feature-complete version of Full Self-Driving that will no longer require driver supervision. However, with the increase, some are concerned that they may be priced out.
$99 per month is already a tough ask for some. While Full Self-Driving is definitely worth it just due to the capabilities, not every driver is ready to add potentially 50 percent to their car payment each month to have it.
While Tesla has not revealed any target price for FSD, it does seem that it will go up to at least $150.
I should also mention that the $99/month for supervised FSD will rise as FSD’s capabilities improve.
The massive value jump is when you can be on your phone or sleeping for the entire ride (unsupervised FSD). https://t.co/YDKhXN3aaG
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 23, 2026
Additionally, the ability to purchase the suite outright is also being eliminated on February 14, which gives owners another reason to be slightly concerned about whether they will be able to afford to continue paying for Full Self-Driving in any capacity.
Some owners have requested a tiered program, which would allow people to pay for the capabilities they want at a discounted price.
Unsupervised FSD would be the most expensive, and although the company started removing Autopilot from some vehicles, it seems a Supervised FSD suite would still attract people to pay between $49 and $99 per month, as it is very useful.
Tesla will likely release pricing for the Unsupervised suite when it is available, but price increases could still come to the Supervised version as things improve.
This is not the first time Musk has hinted that the price would change with capability improvements, either. He’s been saying it for some time. In 2020, he even said the value of FSD would “probably be somewhere in excess of $100,000.”
The FSD price will continue to rise as the software gets closer to full self-driving capability with regulatory approval. It that point, the value of FSD is probably somewhere in excess of $100,000.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) May 18, 2020
News
Tesla starts removing outright Full Self-Driving purchase option at time of order

Tesla has chosen to axe the ability to purchase Full Self-Driving outright from a select group of cars just days after CEO Elon Musk announced the company had plans to eliminate that option in February.
The company is making a clear-cut stand that it will fully transition away from the ability to purchase the Full Self-Driving suite outright, a move that has brought differing opinions throughout the Tesla community.
Earlier this week, the company also announced that it will no longer allow buyers to purchase Full Self-Driving outright when ordering a pre-owned vehicle from inventory. Instead, that will be available for $99 per month, the same price that it costs for everyone else.
The ability to buy the suite for $8,000 for a one-time fee at the time of order has been removed:
NEWS: Tesla no longer allows buyers to purchase FSD outright in the U.S. when ordering a pre-owned vehicle directly from inventory. Tesla now gives you the option to either subscribe for $99/month, or purchase FSD outright after taking delivery (available until February 14th). pic.twitter.com/1xZ0BVG4JB
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) January 23, 2026
This is a major move because it is the first time Tesla is eliminating the ability to purchase FSD outright for one flat fee to any of its vehicles, at least at the time of purchase.
It is trying to phase out the outright purchase option as much as it can, preparing people for the subscription-based service it will exclusively offer starting on February 14.
In less than a month, it won’t be available on any vehicle, which has truly driven some serious conversation from Tesla owners throughout the community.
There’s a conflict, because many believe that they will now lose the ability to buy FSD and not pay for it monthly, which is an attractive offer. However, others believe, despite paying $8,000 for FSD, that they will have to pay more money on top of that cost to get the unsupervised suite.
Additionally, CEO Elon Musk said that the FSD suite’s subscription price would increase over time as capabilities increase, which is understandable, but is also quite a conflict for those who spent thousands to have what was once promised to them, and now they may have to pay even more money.
News
Tesla Robotaxi has a highly-requested hardware feature not available on typical Model Ys
These camera washers are crucial for keeping the operation going, as they are the sole way Teslas operate autonomously. The cameras act as eyes for the car to drive, recognize speed limit and traffic signs, and travel safely.
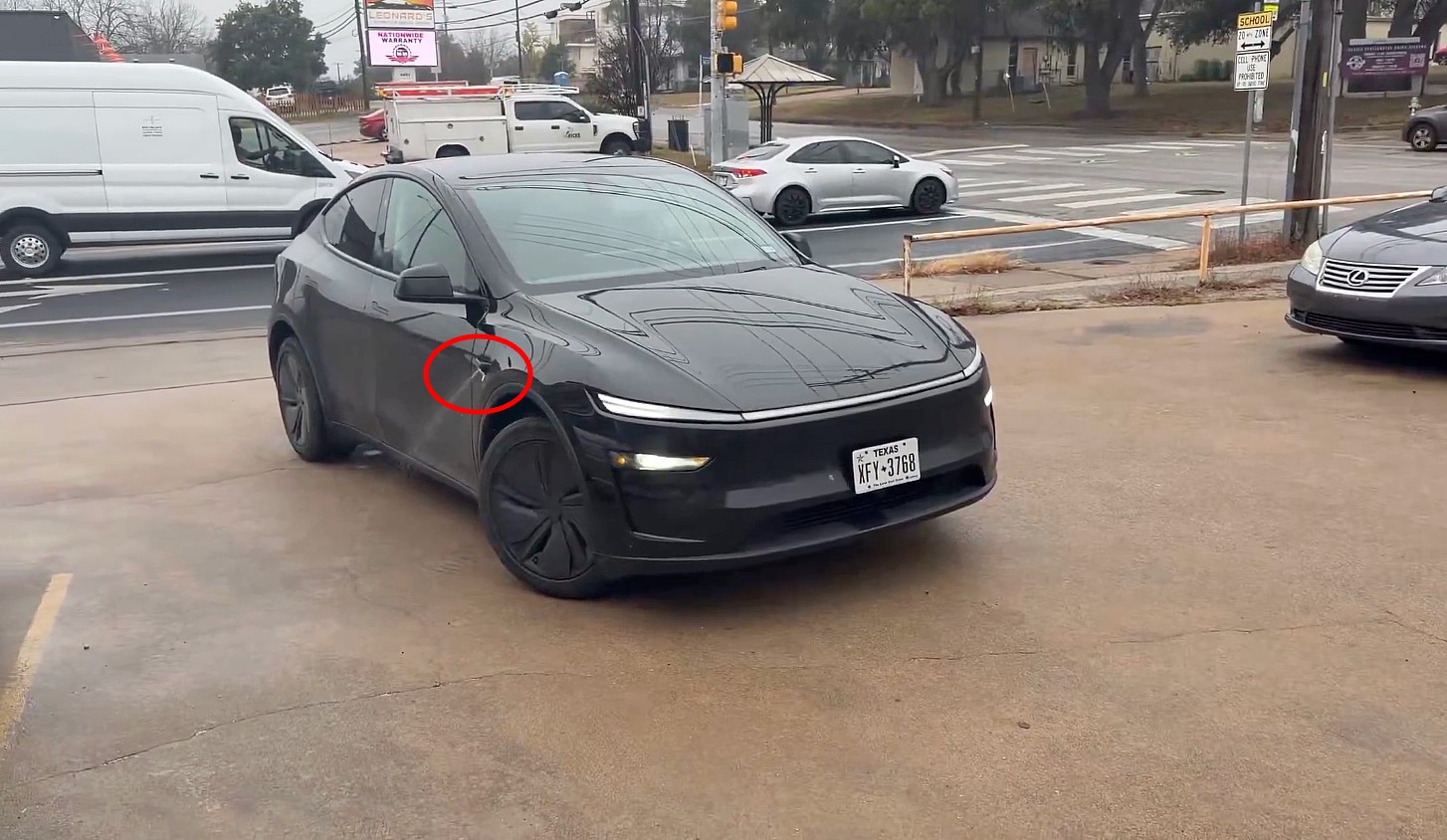

Tesla Robotaxi has a highly-requested hardware feature that is not available on typical Model Ys that people like you and me bring home after we buy them. The feature is something that many have been wanting for years, especially after the company adopted a vision-only approach to self-driving.
After Tesla launched driverless Robotaxi rides to the public earlier this week in Austin, people have been traveling to the Lone Star State in an effort to hopefully snag a ride from one of the few vehicles in the fleet that are now no longer required to have Safety Monitors present.
BREAKING: Tesla launches public Robotaxi rides in Austin with no Safety Monitor
Although only a few of those completely driverless rides are available, there have been some new things seen on these cars that are additions from regular Model Ys, including the presence of one new feature: camera washers.
With the Model Y, there has been a front camera washer, but the other exterior “eyes” have been void of any solution for this. For now, owners are required to clean them manually.
In Austin, Tesla is doing things differently. It is now utilizing camera washers on the side repeater and rear bumper cameras, which will keep the cameras clean and keep operation as smooth and as uninterrupted as possible:
🚨 Tesla looks to have installed Camera Washers on the side repeater cameras on Robotaxis in Austin
pic.twitter.com/xemRtDtlRR— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 23, 2026
Rear Camera Washer on Tesla Robotaxi pic.twitter.com/P9hgGStHmV
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 24, 2026
These camera washers are crucial for keeping the operation going, as they are the sole way Teslas operate autonomously. The cameras act as eyes for the car to drive, recognize speed limit and traffic signs, and travel safely.
This is the first time we are seeing them, so it seems as if Safety Monitors might have been responsible for keeping the lenses clean and unobstructed previously.
However, as Tesla transitions to a fully autonomous self-driving suite and Robotaxi expands to more vehicles in the Robotaxi fleet, it needed to find a way to clean the cameras without any manual intervention, at least for a short period, until they can return for interior and exterior washing.









