
News
Of Mice And Musk: A SpaceX Odyssey
Elon Musk has dreamed of a human colony on Mars since he was a young man. Today, his SpaceX company is taking the first steps toward achieving that dream.
As Ashlee Vance tells it, one wall of Elon Musk’s office at SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, contains two posters of Mars. On the left is Mars as it exists today – a frozen, lifeless orb. On the right is Musk’s vision of Mars as it could be — a happy place inhabited by humans who frolic on verdant continents surrounded by oceans.
“I would like to die thinking that humanity has a bright future,” he tells Vance while eating cookies and cream with sprinkles on top. “If we can solve sustainable energy and be well on our way to becoming a multi-planetary species with a self-sustaining civilization on another planet—to cope with a worst-case scenario happening and extinguishing human consciousness— then I think that would be really good.” No one has ever accused Elon Musk of thinking too small.
At the turn of the 21st century, Musk had two Martian fantasies. One was to send a colony of mice to the Red Planet and bring them back again, along with their interplanetary babies. The other involved building a greenhouse on Mars and letting Earthlings see the plants inside grow over the internet. Each venture required at least one if not two rocket ships.
He and a coterie of friends traveled twice to Moscow, once in 2001 and again in 2002, trying to purchase surplus Russian rockets that could be refurbished for the Martian missions. The first time did not go well. Recalls Jim Cantrell, one of the team that traveled to Moscow with Musk, “One of their chief designers spit on me and Elon because he thought we were full of shit.” On the second excursion, Musk became convinced the Russians he was meeting with were only interested in fleecing a gullible American with too much money and too few brains.
On the way home from the second failed mission, Musk astonished his team by announcing, “Hey, guys, I think we can build this rocket ourselves.” In June 2002, Space Exploration Technologies, popularly known as SpaceX, was formed to build a cheaper rocket that could carry small payloads into space for paying clients on an average of once a month. The only problem? It had no rocket.
Such trifles were never matters to hold Elon Musk back. He assembled a team of committed rocket engineers and set about accomplishing, with millions, what NASA spent billions doing. Musk’s principle talent, apart from concocting outrageously impossible dreams, is finding people to work for him who are ready, willing and eager to give up all semblance of a normal life in exchange for insane working hours in remote locations. One test launching area was set up in the middle of Texas and another on far away Kwajalein Island, the largest island in an atoll between Guam and Hawaii that is part of the Marshall Islands.
“I would like to die thinking that humanity has a bright future”
SpaceX CEO, Elon Musk
Musk is not a man without a sense of humor. He dubbed his new rocket Falcon 1, paying homage to the Millennium Falcon of Star Wars fame. On its first flight on March 24, 2006, it crashed back to Earth after only 25 seconds. SpaceX employees dutifully donned scuba gear to retrieve some of the pieces from the ocean and set about rebuilding for another attempt.
Musk responded by hiring more engineers and starting work on a brand new rocket, the Falcon 9, that featured one large central rocket surrounded by 8 smaller rockets. Despite the failure of Falcon 1, Musk was already busy positioning the company to bid on NASA contracts to resupply the International Space Station.
On September 1, 2008, Falcon 1 flew its first successful mission. SpaceX was a viable commercial company at last but one that was rapidly going broke. At the end of 2008, Musk knew he would have to choose between SpaceX and Tesla. Alone, one of them might survive. Together? The odds were, both would fail. Musk worried that Tesla would be bought out by one of the Big Three automakers and become just a small part of a giant company.
Later in 2008, Tesla was within hours of defaulting on its payroll obligations. If that happened, Musk’s personal fortune would be gone, along with Tesla and SpaceX. He asked for help from venture capital group VantagePoint but was rebuffed. That’s when Musk put all his chips on red and let them ride.
With all of his dreams and aspirations on the line, Musk executed a colossal bluff. He told investors he would put in $40,000,000 of his own fortune to keep the business going — $40,000,000 he didn’t have. Based on his assurances, other investors agreed to put up $20,000,000 more in financing and the crisis passed. A few weeks later, NASA awarded SpaceX a $1.6 billion contract to do twleve ISS re-supply missions.
Antonio Gracias, a Tesla and SpaceX investor and one of Musk’s closest friends, watched all of this at close hand. He says 2008 told him everything he would ever need to know about Musk’s character. “He has the ability to work harder and endure more stress than anyone I’ve ever met,” Gracias says. “What he went through in 2008 would have broken anyone else. Most people who are under that sort of pressure fray. Their decisions go bad. Elon gets hyperrational. He’s still able to make very clear, long-term decisions. The harder it gets, the better he gets.”
Today, SpaceX launches an average of one rocket a month, carrying payloads for many companies and several nations. Its prices undercut those of Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Orbital Science by a wide margin. Many of its competitors rely on Russian and other foreign suppliers but SpaceX makes its machines from scratch in the U.S.
Its clientele includes Canadian, European, and Asian customers and it has more than 50 flights planned over the coming years worth more than $5 billion. The company remains privately owned, with Musk as the largest shareholder. SpaceX is profitable and is estimated to be worth $12 billion.
The Falcon 9 has gone from a fantasy to SpaceX’s workhorse. Painted pure white with only an American flag and the SpaceX logo adorning its sides, there’s nothing particularly flashy looking about the Falcon 9. It’s just an elegant, purposeful machine. And to think that for a period of weeks just a few years ago, it’s ability to lead mankind into the dawn of commercial space travel almost died before it was ever born, thanks to a bluff so bold and so daring, it would leave most of us breathless.
Jimmy Buffett once sang, “Read dozens of books about heroes and crooks, and I learned much from both of their styles.” Which one is Elon Musk? Read Ashlee Vance’s book and make up your own mind.
Source: Bloomberg

News
Tesla Cybercab spotted with interesting charging solution, stimulating discussion
The port is located in the rear of the vehicle and features a manual door and latch for plug-in, and the video shows an employee connecting to a Tesla Supercharger.
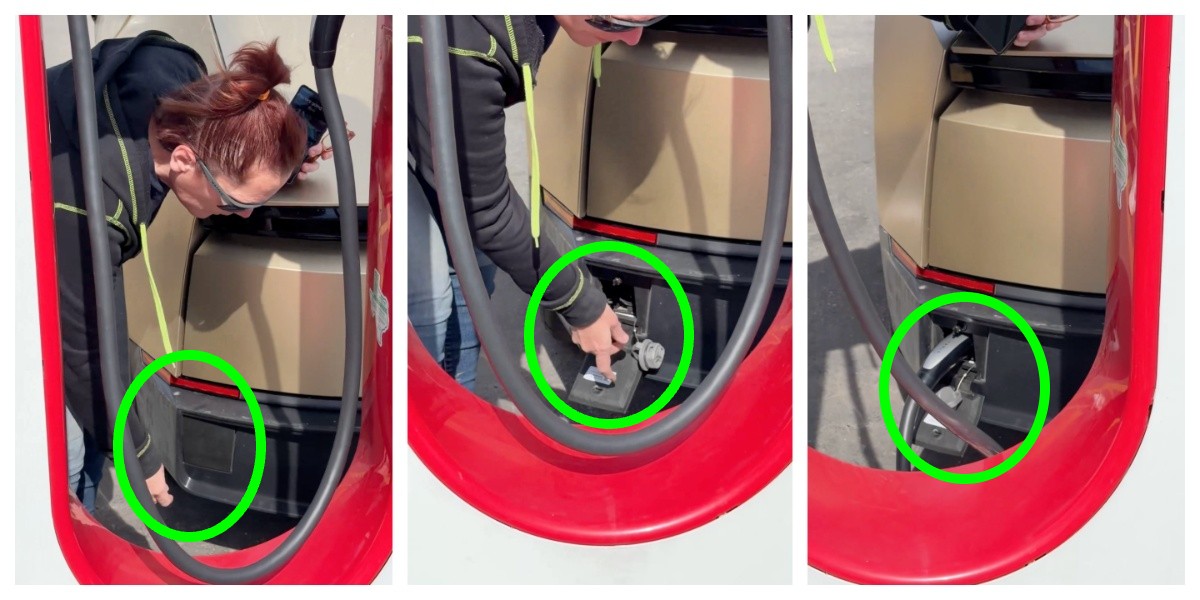
Tesla Cybercab units are being tested publicly on roads throughout various areas of the United States, and a recent sighting of the vehicle’s charging port has certainly stimulated some discussions throughout the community.
The Cybercab is geared toward being a fully-autonomous vehicle, void of a steering wheel or pedals, only operating with the use of the Full Self-Driving suite. Everything from the driving itself to the charging to the cleaning is intended to be operated autonomously.
But a recent sighting of the vehicle has incited some speculation as to whether the vehicle might have some manual features, which would make sense, but let’s take a look:
🚨 Tesla Cybercab charging port is in the rear of the vehicle!
Here’s a great look at plugging it in!!
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 29, 2026
The port is located in the rear of the vehicle and features a manual door and latch for plug-in, and the video shows an employee connecting to a Tesla Supercharger.
Now, it is important to remember these are prototype vehicles, and not the final product. Additionally, Tesla has said it plans to introduce wireless induction charging in the future, but it is not currently available, so these units need to have some ability to charge.
However, there are some arguments for a charging system like this, especially as the operation of the Cybercab begins after production starts, which is scheduled for April.
Wireless for Operation, Wired for Downtime
It seems ideal to use induction charging when the Cybercab is in operation. As it is for most Tesla owners taking roadtrips, Supercharging stops are only a few minutes long for the most part.
The Cybercab would benefit from more frequent Supercharging stops in between rides while it is operating a ride-sharing program.
Tesla wireless charging patent revealed ahead of Robotaxi unveiling event
However, when the vehicle rolls back to its hub for cleaning and maintenance, standard charging, where it is plugged into a charger of some kind, seems more ideal.
In the 45-minutes that the car is being cleaned and is having maintenance, it could be fully charged and ready for another full shift of rides, grabbing a few miles of range with induction charging when it’s out and about.
Induction Charging Challenges
Induction charging is still something that presents many challenges for companies that use it for anything, including things as trivial as charging cell phones.
While it is convenient, a lot of the charge is lost during heat transfer, which is something that is common with wireless charging solutions. Even in Teslas, the wireless charging mat present in its vehicles has been a common complaint among owners, so much so that the company recently included a feature to turn them off.
Production Timing and Potential Challenges
With Tesla planning to begin Cybercab production in April, the real challenge with the induction charging is whether the company can develop an effective wireless apparatus in that short time frame.
It has been in development for several years, but solving the issue with heat and energy loss is something that is not an easy task.
In the short-term, Tesla could utilize this port for normal Supercharging operation on the Cybercab. Eventually, it could be phased out as induction charging proves to be a more effective and convenient option.
News
Tesla confirms that it finally solved its 4680 battery’s dry cathode process
The suggests the company has finally resolved one of the most challenging aspects of its next-generation battery cells.
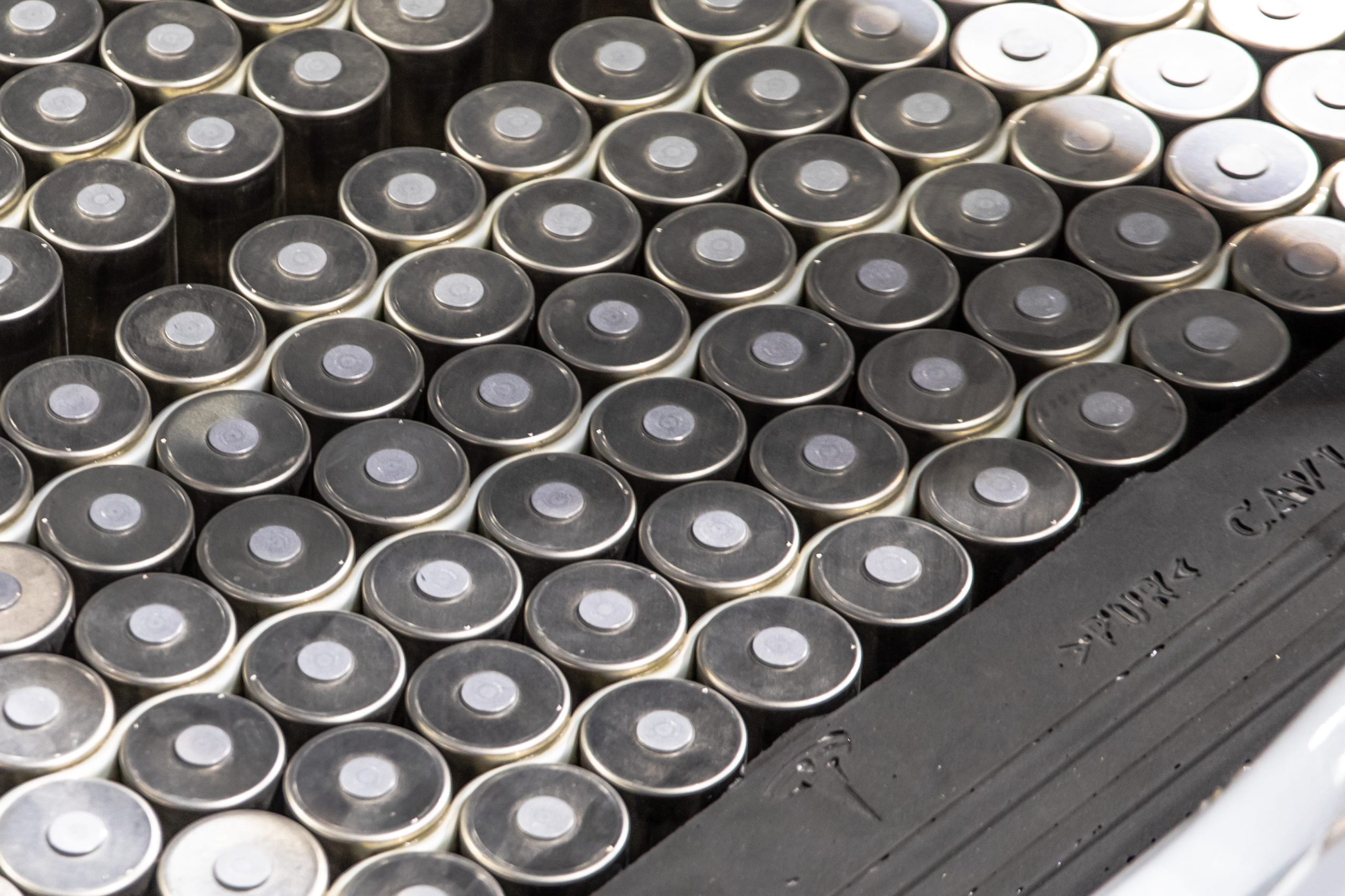

Tesla has confirmed that it is now producing both the anode and cathode of its 4680 battery cells using a dry-electrode process, marking a key breakthrough in a technology the company has been working to industrialize for years.
The update, disclosed in Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 update letter, suggests the company has finally resolved one of the most challenging aspects of its next-generation battery cells.
Dry cathode 4680 cells
In its Q4 and FY 2025 update letter, Tesla stated that it is now producing 4680 cells whose anode and cathode were produced during the dry electrode process. The confirmation addresses long-standing questions around whether Tesla could bring its dry cathode process into sustained production.
The disclosure was highlighted on X by Bonne Eggleston, Tesla’s Vice President of 4680 batteries, who wrote that “both electrodes use our dry process.”
Tesla first introduced the dry-electrode concept during its Battery Day presentation in 2020, pitching it as a way to simplify production, reduce factory footprint, lower costs, and improve energy density. While Tesla has been producing 4680 cells for some time, the company had previously relied on more conventional approaches for parts of the process, leading to questions about whether a full dry-electrode process could even be achieved.
4680 packs for Model Y
Tesla also revealed in its Q4 and FY 2025 Update Letter that it has begun producing battery packs for certain Model Y vehicles using its in-house 4680 cells. As per Tesla:
“We have begun to produce battery packs for certain Model Ys with our 4680 cells, unlocking an additional vector of supply to help navigate increasingly complex supply chain challenges caused by trade barriers and tariff risks.”
The timing is notable. With Tesla preparing to wind down Model S and Model X production, the Model Y and Model 3 are expected to account for an even larger share of the company’s vehicle output. Ensuring that the Model Y can be equipped with domestically produced 4680 battery packs gives Tesla greater flexibility to maintain production volumes in the United States, even as global battery supply chains face increasing complexity.
Elon Musk
Tesla Giga Texas to feature massive Optimus V4 production line
This suggests that while the first Optimus line will be set up in the Fremont Factory, the real ramp of Optimus’ production will happen in Giga Texas.

Tesla will build Optimus 4 in Giga Texas, and its production line will be massive. This was, at least, as per recent comments by CEO Elon Musk on social media platform X.
Optimus 4 production
In response to a post on X which expressed surprise that Optimus will be produced in California, Musk stated that “Optimus 4 will be built in Texas at much higher volume.” This suggests that while the first Optimus line will be set up in the Fremont Factory, and while the line itself will be capable of producing 1 million humanoid robots per year, the real ramp of Optimus’ production will happen in Giga Texas.
This was not the first time that Elon Musk shared his plans for Optimus’ production at Gigafactory Texas. During the 2025 Annual Shareholder Meeting, he stated that Giga Texas’ Optimus line will produce 10 million units of the humanoid robot per year. He did not, however, state at the time that Giga Texas would produce Optimus V4.
“So we’re going to launch on the fastest production ramp of any product of any large complex manufactured product ever, starting with building a one-million-unit production line in Fremont. And that’s Line one. And then a ten million unit per year production line here,” Musk stated.
How big Optimus could become
During Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call, Musk offered additional context on the potential of Optimus. While he stated that the ramp of Optimus’ production will be deliberate at first, the humanoid robot itself will have the potential to change the world.
“Optimus really will be a general-purpose robot that can learn by observing human behavior. You can demonstrate a task or verbally describe a task or show it a task. Even show it a video, it will be able to do that task. It’s going to be a very capable robot. I think long-term Optimus will have a very significant impact on the US GDP.
“It will actually move the needle on US GDP significantly. In conclusion, there are still many who doubt our ambitions for creating amazing abundance. We are confident it can be done, and we are making the right moves technologically to ensure that it does. Tesla, Inc. has never been a company to shy away from solving the hardest problems,” Musk stated.











