

News
Astra ‘Rocket 3’ nosecone dooms first Florida launch attempt
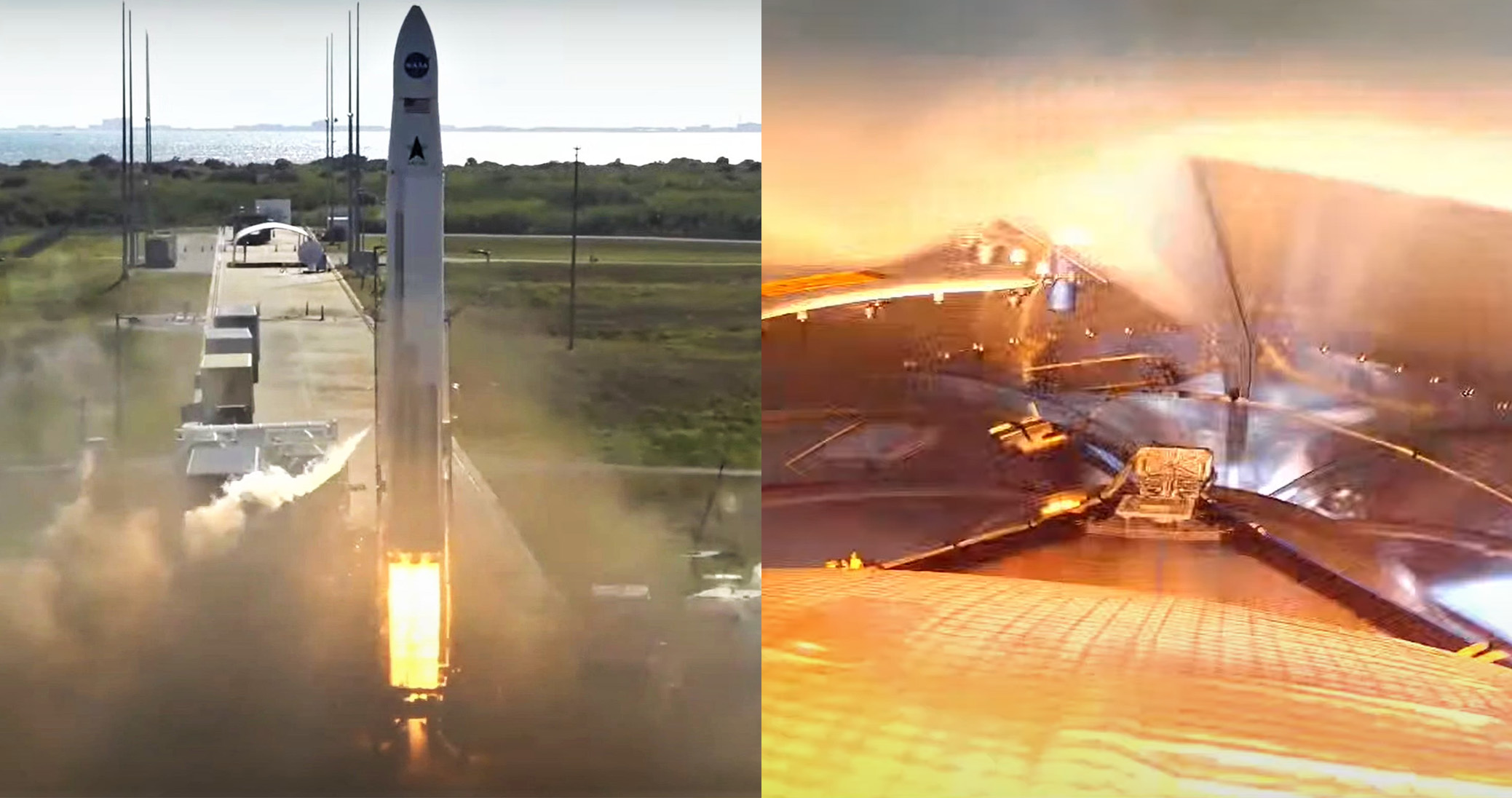
On Thursday, February 10th, Astra Space’s Rocket 3.3 launch vehicle took off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) Launch Complex 46 (LC-46).
Unfortunately, while liftoff and booster ascent appeared to be more or less perfect, Rocket 3’s payload fairing failed to separate, triggering a series of events that caused its upper stage to enter an uncontrolled and unrecoverable spin after burning for just a few seconds. Astra was unable to salvage the spinning rocket, resulting in a mission failure well short of orbit.
“Unfortunately we heard that an issue has been experienced during flight that prevented the delivery of our customer payloads to orbit today. We are deeply sorry to our customers NASA, University of Alabama, the University of Mexico and the University of California Berkeley,” said Astra Space Director of Product Management Carolina Grossman. “More information will be provided as we complete the data review.”
Today’s launch comes after two previous aborted launch attempts. The first attempt on February 5th was delayed due to a CCSFS radar system malfunction. The second launch delay came on February 7th, after the rocket aborted briefly after ignition because of a minor telemetry issue.
The Mission
NASA’s first mission under the agency’s Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) Demonstration 2 contract hoped to launch four CubeSats to space as early as February 5th, 2022. The satellites, which made up the agency’s 41st Educational Launch of Nano-satellites (ELaNa) mission, were the first VCLS payloads launched – albeit unsuccessfully – from Cape Canaveral’s LC-46 pad, which last supported NASA’s Orion spacecraft Ascent Abort 2 (AA-2) test flight in July 2019.
The satellites onboard the flight were developed by three universities and one NASA center:
- BAMA 1 (University of Alabama, Tusscolusa)
- INCA (New Mexico State University, Las Cruces)
- QubeSat (University of California, Berkeley)
- R5-S1 (NASA’s Johnson Space Center, Houston)
The ELaNa 41 mission CubeSats were selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) and were assigned to the mission by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy. CSLI provides launch opportunities for small satellite payloads built by universities, high schools, NASA Centers, and non-profit organizations.
About Astra
Founded in 2016, Astra Space is an American launch vehicle company based in Alameda, California. Astra’s official vision “is to Improve Life on Earth from Space by creating a healthier and more connected planet.” The company hopes to secure a large portion of the small satellite launch market, stating that it “offers the lowest cost-per-launch dedicated orbital launch service of any operational launch provider in the world.”
As of November 2021, Astra charges around $2.5-3.5M for a dedicated Rocket 3 launch, which can deliver up to 150 kg (330 lb) to low Earth orbit (LEO). In comparison, for a dedicated Electron launch, Rocket Lab charges about $7.5M for 300 kg (660 lb) to LEO. For customers willing to accept a one-size-fits-all rideshare solution, SpaceX charges $1M for 200 kg (440 lb) to LEO or higher sun-synchronous orbits (SSOs).
While the aerospace company is based out of California, its frequent orbital and suborbital test flights have all been conducted at the Pacific Spaceport Complex in Kodiak, Alaska. Prior test flights used Rocket 1, Rocket 2, and Rocket 3 prototypes as Astra refined its design and embraced a hardware-rich development style that didn’t shy away from failure.
Rocket 3.3 reached orbit for the first time – carrying an instrumented boilerplate payload for the United States Space Force – on November 21st, 2021. Less than two months later, Rocket 3.3 (serial number LV08) attempted to carry several NASA-sponsored cubesats into orbit on February 10th, 2022 – also the rocket’s first East Coast launch. Like Rocket 3.3’s predecessors, the two-stage vehicle was fueled with liquid oxygen (LOx) and refined kerosene (RP-1). Powered by five Delphin engines, the first stage produces up to ~145 kilonewtons (32,500 lbf) of thrust at liftoff. The second stage is powered by one pressure-fed Aether engine that delivers about 3.3 kN (740 lbf) of thrust in the vacuum of space.
The unsuccessful launch attempt occurred just three months after Astra applied for their Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) launch license and less than one day after receiving that license.
Elon Musk
Why Tesla’s Q3 could be one of its biggest quarters in history
Tesla could stand to benefit from the removal of the $7,500 EV tax credit at the end of Q3.

Tesla has gotten off to a slow start in 2025, as the first half of the year has not been one to remember from a delivery perspective.
However, Q3 could end up being one of the best the company has had in history, with the United States potentially being a major contributor to what might reverse a slow start to the year.
Earlier today, the United States’ House of Representatives officially passed President Trump’s “Big Beautiful Bill,” after it made its way through the Senate earlier this week. The bill will head to President Trump, as he looks to sign it before his July 4 deadline.
The Bill will effectively bring closure to the $7,500 EV tax credit, which will end on September 30, 2025. This means, over the next three months in the United States, those who are looking to buy an EV will have their last chance to take advantage of the credit. EVs will then be, for most people, $7,500 more expensive, in essence.
The tax credit is available to any single filer who makes under $150,000 per year, $225,000 a year to a head of household, and $300,000 to couples filing jointly.
Ending the tax credit was expected with the Trump administration, as his policies have leaned significantly toward reliance on fossil fuels, ending what he calls an “EV mandate.” He has used this phrase several times in disagreements with Tesla CEO Elon Musk.
Nevertheless, those who have been on the fence about buying a Tesla, or any EV, for that matter, will have some decisions to make in the next three months. While all companies will stand to benefit from this time crunch, Tesla could be the true winner because of its sheer volume.
If things are done correctly, meaning if Tesla can also offer incentives like 0% APR, special pricing on leasing or financing, or other advantages (like free Red, White, and Blue for a short period of time in celebration of Independence Day), it could see some real volume in sales this quarter.
You can now buy a Tesla in Red, White, and Blue for free until July 14 https://t.co/iAwhaRFOH0
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 3, 2025
Tesla is just a shade under 721,000 deliveries for the year, so it’s on pace for roughly 1.4 million for 2025. This would be a decrease from the 1.8 million cars it delivered in each of the last two years. Traditionally, the second half of the year has produced Tesla’s strongest quarters. Its top three quarters in terms of deliveries are Q4 2024 with 495,570 vehicles, Q4 2023 with 484,507 vehicles, and Q3 2024 with 462,890 vehicles.
Elon Musk
Tesla Full Self-Driving testing continues European expansion: here’s where
Tesla has launched Full Self-Driving testing in a fifth European country ahead of its launch.
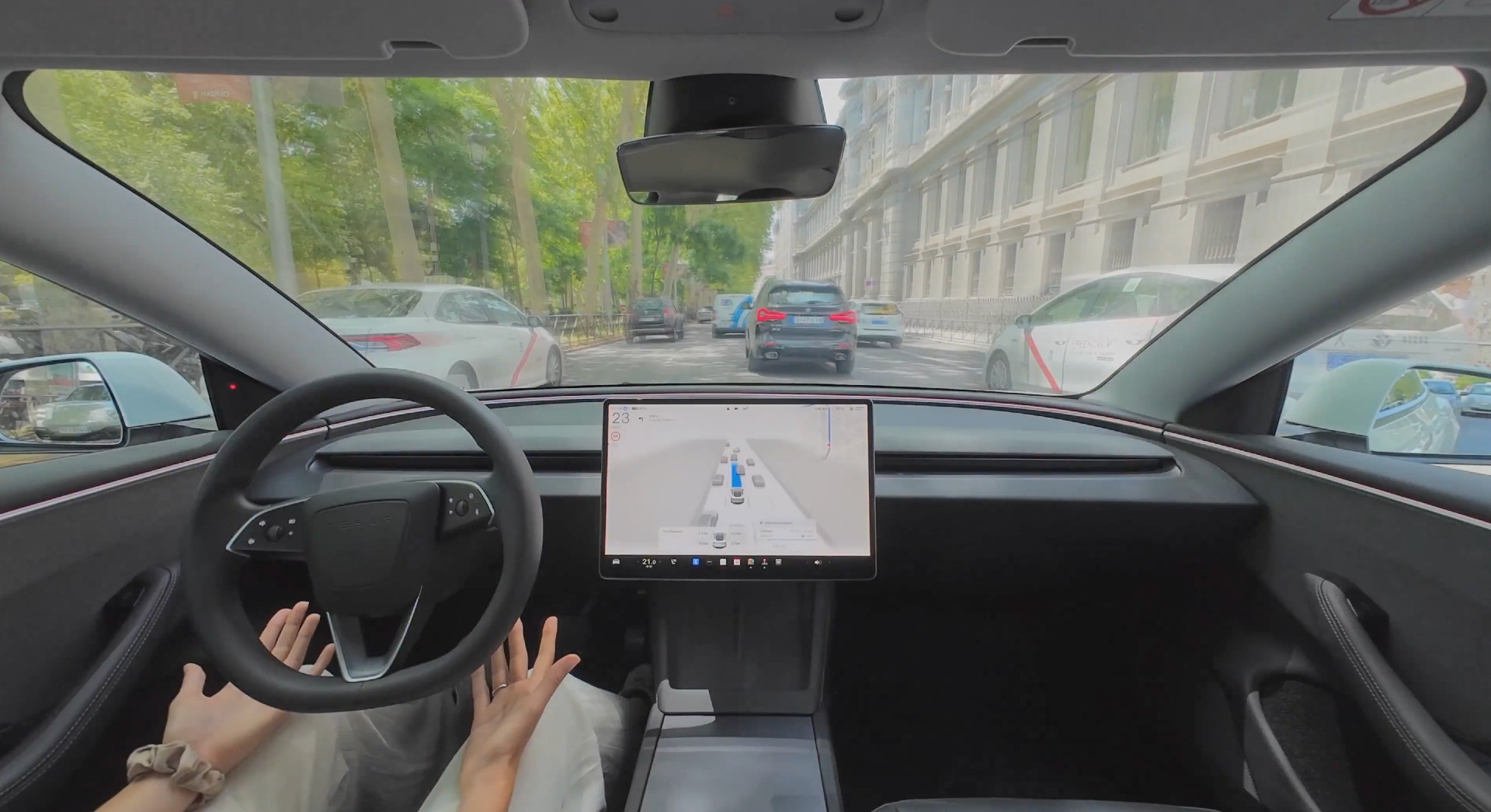

Tesla Full Self-Driving is being tested in several countries across Europe as the company prepares to launch its driver assistance suite on the continent.
The company is still working through the regulatory hurdles with the European Union. They are plentiful and difficult to navigate, but Tesla is still making progress as its testing of FSD continues to expand.
Today, it officially began testing in a new country, as more regions open their doors to Tesla. Many owners and potential customers in Europe are awaiting its launch.
On Thursday, Tesla officially confirmed that Full Self-Driving testing is underway in Spain, as the company shared an extensive video of a trip through the streets of Madrid:
Como pez en el agua …
FSD Supervised testing in Madrid, Spain
Pending regulatory approval pic.twitter.com/txTgoWseuA
— Tesla Europe & Middle East (@teslaeurope) July 3, 2025
The launch of Full Self-Driving testing in Spain marks the fifth country in which Tesla has started assessing the suite’s performance in the European market.
Across the past several months, Tesla has been expanding the scope of countries where Full Self-Driving is being tested. It has already made it to Italy, France, the Netherlands, and Germany previously.
Tesla has already filed applications to have Full Self-Driving (Supervised) launched across the European Union, but CEO Elon Musk has indicated that this particular step has been the delay in the official launch of the suite thus far.
In mid-June, Musk revealed the frustrations Tesla has felt during its efforts to launch its Full Self-Driving (Supervised) suite in Europe, stating that the holdup can be attributed to authorities in various countries, as well as the EU as a whole:
Tesla Full Self-Driving’s European launch frustrations revealed by Elon Musk
“Waiting for Dutch authorities and then the EU to approve. Very frustrating and hurts the safety of people in Europe, as driving with advanced Autopilot on results in four times fewer injuries! Please ask your governing authorities to accelerate making Tesla safer in Europe.”
Waiting for Dutch authorities and then the EU to approve.
Very frustrating and hurts the safety of people in Europe, as driving with advanced Autopilot on results in four times fewer injuries!
Please ask your governing authorities to accelerate making Tesla safer in Europe. https://t.co/QIYCXhhaQp
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) June 11, 2025
Tesla said last year that it planned to launch Full Self-Driving in Europe in 2025.
Elon Musk
xAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
xAI welcomed the development in a post on its official xAI Memphis account on X.
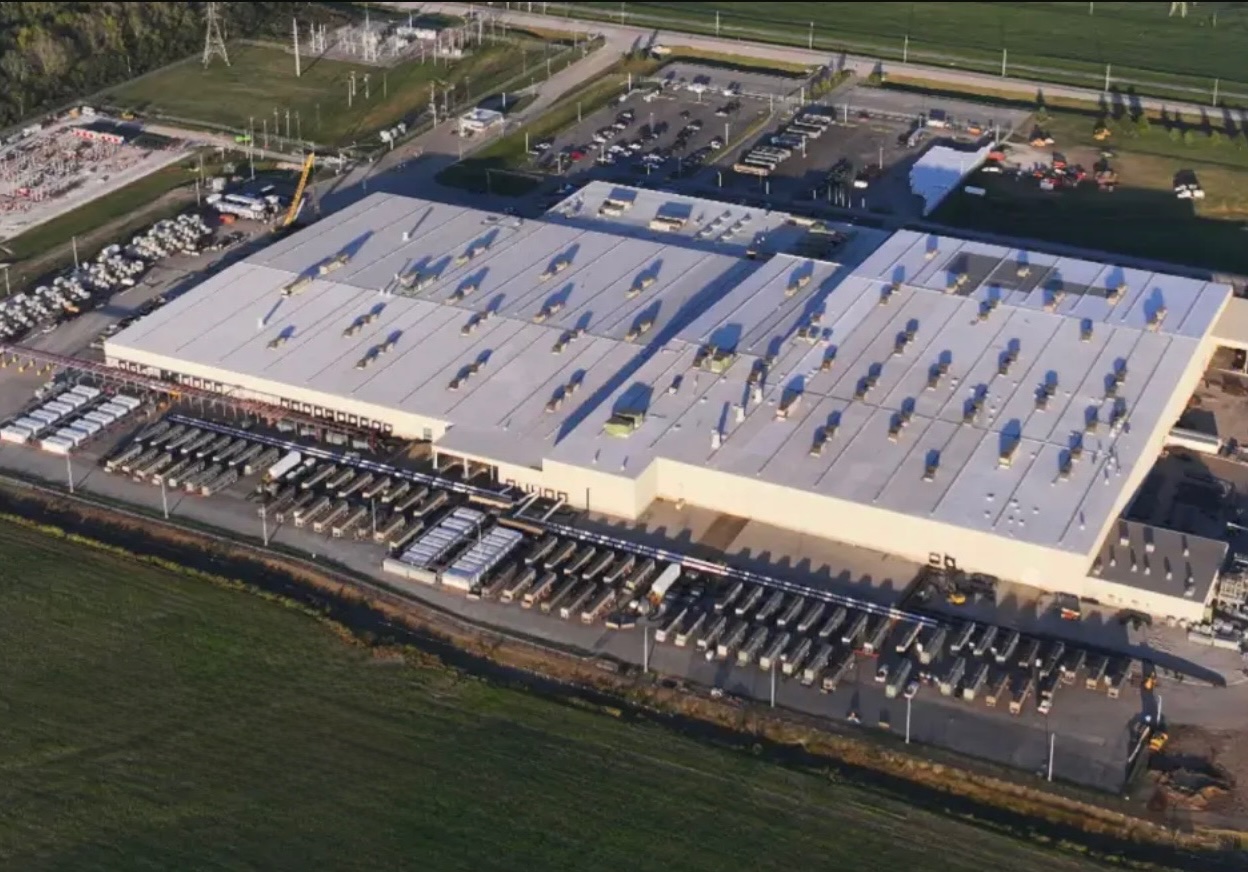

Elon Musk’s artificial intelligence startup xAI has secured an air permit from Memphis health officials for its data center project, despite critics’ opposition and pending legal action. The Shelby County Health Department approved the permit this week, allowing xAI to operate 15 mobile gas turbines at its facility.
Air permit granted
The air permit comes after months of protests from Memphis residents and environmental justice advocates, who alleged that xAI violated the Clean Air Act by operating gas turbines without prior approval, as per a report from WIRED.
The Southern Environmental Law Center (SELC) and the NAACP has claimed that xAI installed dozens of gas turbines at its new data campus without acquiring the mandatory Prevention of Significant Deterioration (PSD) permit required for large-scale emission sources.
Local officials previously stated the turbines were considered “temporary” and thus not subject to stricter permitting. xAI applied for an air permit in January 2025, and in June, Memphis Mayor Paul Young acknowledged that the company was operating 21 turbines. SELC, however, has claimed that aerial footage shows the number may be as high as 35.
Critics are not giving up
Civil rights groups have stated that they intend to move forward with legal action. “xAI’s decision to install and operate dozens of polluting gas turbines without any permits or public oversight is a clear violation of the Clean Air Act,” said Patrick Anderson, senior attorney at SELC.
“Over the last year, these turbines have pumped out pollution that threatens the health of Memphis families. This notice paves the way for a lawsuit that can hold xAI accountable for its unlawful refusal to get permits for its gas turbines,” he added.
Sharon Wilson, a certified optical gas imaging thermographer, also described the emissions cloud in Memphis as notable. “I expected to see the typical power plant type of pollution that I see. What I saw was way worse than what I expected,” she said.
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-
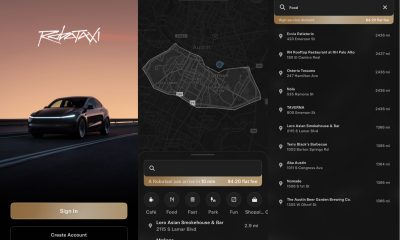
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Grok 3 partners with Oracle Cloud for corporate AI innovation
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoSpaceX and Elon Musk share insights on Starship Ship 36’s RUD
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoWatch Tesla’s first driverless public Robotaxi rides in Texas
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla has started rolling out initial round of Robotaxi invites



















