Ahead of the United Nations COP28 climate summit in Dubai later this year, the International Energy Agency (IEA) has once again released its yearly report on energy generation and renewables.
The IEA shared the 2023 World Energy Outlook earlier this month, offering a comprehensive look at how energy is generated today and where energy industries are headed. The report is lengthy and includes a handful of insights, notably including that the agency expects there to be almost ten times as many electric vehicles (EVs) on the road by 2030 with the current path of global policies.
The report looked at inputs for three potential scenarios based on the Global Energy Climate (GEC) model: the Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS), looking at currently in-place policies sector by sector and country by country; the Announced Pledges Scenario (APS), which assumes that government and industry climate commitments are met in full and on time; and the Net-Zero Emissions (NZE) by 2050 Scenario, which looks at a specific emissions trajectory set to keep the temperature increases below 1.5 degrees Celsius.
You can see the IEA’s definitions and objectives for looking at each model scenario below.
Credit: IEA | World Energy Outlook 2023
According to the report’s STEPS scenario, EVs comprise roughly 15 percent of car sales globally and are expected to increase to 40 percent by 2030. In addition to the increase in EVs, the agency expects renewable energy to make up 50 percent of the global electricity mix by 2030, jumping from around 30 percent today.
The agency also says that, for the first time ever, it can see a path to peak demand for coal, oil and natural gas within this decade, and it expects global energy-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions to peak by 2025.
Fossil fuel market share is also expected to drop to 73 percent by 2030 after floating at about 80 percent for the past few decades.
The agency is also seeing growth in investments in renewable energy, including the adoption of EVs, solar PV generation, and heat pumps and other electric heating equipment being sold more than fossil fuel boilers on a global scale.
Interestingly, the IEA notes that, for every $1 invested in fossil fuels five years ago, $1 also went to clean energy. In 2023, however, for every $1 invested into fossil fuels, there is $1.80 going toward renewable energy, depicting the continued investment increases in clean energy.
You can see the IEA’s chart on investment flows below, showing a decrease in oil demand and increases to low-emissions power sources.
Credit: IEA | World Energy Outlook 2023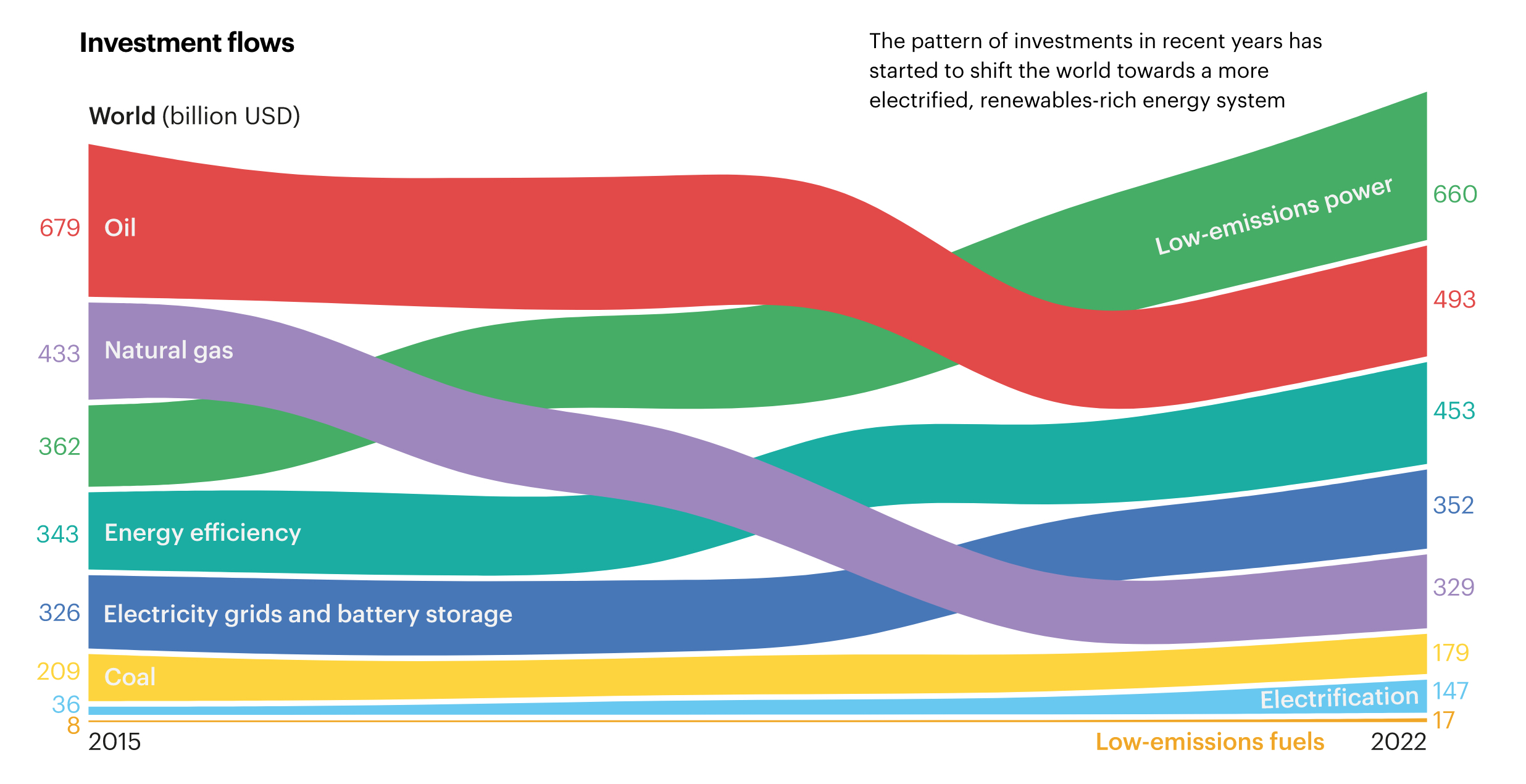
Although the report also shows a continued increase in renewable energy investments, the IEA says that stronger policies are still needed if the world hopes to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius. At the current rate, the IEA says global emissions are high enough to push global average temperatures upward by roughly 2.4 degrees Celsius within this century.
In response to a post with the investment flow chart on X, Tesla Senior Vice President of Powertrain and Energy Drew Baglino also weighed in, emphasizing that there is still more to be done to help transition the world to renewables.
Super interesting charts. Great to see investment shifting to sustainble energy, but we need to do more to accelerate.
— Drew Baglino (@baglino) October 30, 2023
The report touches on several other renewable energy topics, including current geopolitical conflicts going on in the Middle East that could be poised to threaten the security of world energy systems.
You can watch the full live stream of the World Energy Outlook below,
You can also read the IEA’s full press release on this year’s World Energy Outlook here or watch the agency’s full live stream detailing the report below, complete with a Q&A with the agency’s directors.
What are your thoughts? Let me know at zach@teslarati.com, find me on X at @zacharyvisconti, or send your tips to us at tips@teslarati.com.
News
Tesla launches in India with Model Y, showing pricing will be biggest challenge
Tesla finally got its Model Y launched in India, but it will surely come at a price for consumers.

Tesla has officially launched in India following years of delays, as it brought its Model Y to the market for the first time on Tuesday.
However, the launch showed that pricing is going to be its biggest challenge. The all-electric Model Y is priced significantly higher than in other major markets in which Tesla operates.
On Tuesday, Tesla’s Model Y went up for sale for 59,89,000 rupees for the Rear-Wheel Drive configuration, while the Long Range Rear-Wheel Drive was priced at 67,89,000.
This equates to $69,686 for the RWD and $78,994 for the Long Range RWD, a substantial markup compared to what these cars sell for in the United States.
🚨 Here’s the difference in price for the Tesla Model Y in the U.S. compared to India.
🚨 59,89,000 is $69,686
🚨 67,89,000 is $78,994 pic.twitter.com/7EUzyWLcED— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 15, 2025
Deliveries are currently scheduled for the third quarter, and it will be interesting to see how many units they can sell in the market at this price point.
The price includes tariffs and additional fees that are applied by the Indian government, which has aimed to work with foreign automakers to come to terms on lower duties that increase vehicle cost.
Tesla Model Y seen testing under wraps in India ahead of launch
There is a chance that these duties will be removed, which would create a more stable and affordable pricing model for Tesla in the future. President Trump and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi continue to iron out those details.
Maharashtra Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis said to reporters outside the company’s new outlet in the region (via Reuters):
“In the future, we wish to see R&D and manufacturing done in India, and I am sure at an appropriate stage, Tesla will think about it.”
It appears to be eerily similar to the same “game of chicken” Tesla played with Indian government officials for the past few years. Tesla has always wanted to enter India, but was unable to do so due to these import duties.
India wanted Tesla to commit to building a Gigafactory in the country, but Tesla wanted to test demand first.
It seems this could be that demand test, and the duties are going to have a significant impact on what demand will actually be.
Elon Musk
Tesla ups Robotaxi fare price to another comical figure with service area expansion
Tesla upped its fare price for a Robotaxi ride from $4.20 to, you guessed it, $6.90.

Tesla has upped its fare price for the Robotaxi platform in Austin for the first time since its launch on June 22. The increase came on the same day that Tesla expanded its Service Area for the Robotaxi ride-hailing service, offering rides to a broader portion of the city.
The price is up from $4.20, a figure that many Tesla fans will find amusing, considering CEO Elon Musk has used that number, as well as ’69,’ as a light-hearted attempt at comedy over the past several years.
Musk confirmed yesterday that Tesla would up the price per ride from that $4.20 point to $6.90. Are we really surprised that is what the company decided on, as the expansion of the Service Area also took effect on Monday?
But the price is now a princely $6.90, as foretold in the prophecy 😂
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) July 14, 2025
The Service Area expansion was also somewhat of a joke too, especially considering the shape of the new region where the driverless service can travel.
I wrote yesterday about how it might be funny, but in reality, it is more of a message to competitors that Tesla can expand in Austin wherever it wants at any time.
Tesla’s Robotaxi expansion wasn’t a joke, it was a warning to competitors
It was only a matter of time before the Robotaxi platform would subject riders to a higher, flat fee for a ride. This is primarily due to two reasons: the size of the access program is increasing, and, more importantly, the service area is expanding in size.
Tesla has already surpassed Waymo in Austin in terms of its service area, which is roughly five square miles larger. Waymo launched driverless rides to the public back in March, while Tesla’s just became available to a small group in June. Tesla has already expanded it, allowing new members to hail a ride from a driverless Model Y nearly every day.
The Robotaxi app is also becoming more robust as Tesla is adding new features with updates. It has already been updated on two occasions, with the most recent improvements being rolled out yesterday.
Tesla updates Robotaxi app with several big changes, including wider service area
News
Tesla Model Y and Model 3 dominate U.S. EV sales despite headwinds
Tesla’s two mainstream vehicles accounted for more than 40% of all EVs sold in the United States in Q2 2025.

Tesla’s Model Y and Model 3 remained the top-selling electric vehicles in the U.S. during Q2 2025, even as the broader EV market dipped 6.3% year-over-year.
The Model Y logged 86,120 units sold, followed by the Model 3 at 48,803. This means that Tesla’s two mainstream vehicles accounted for 43% of all EVs sold in the United States during the second quarter, as per data from Cox Automotive.
Tesla leads amid tax credit uncertainty and a tough first half
Tesla’s performance in Q2 is notable given a series of hurdles earlier in the year. The company temporarily paused Model Y deliveries in Q1 as it transitioned to the production of the new Model Y, and its retail presence was hit by protests and vandalism tied to political backlash against CEO Elon Musk. The fallout carried into Q2, yet Tesla’s two mass-market vehicles still outsold the next eight EVs combined.
Q2 marked just the third-ever YoY decline in quarterly EV sales, totaling 310,839 units. Electric vehicle sales, however, were still up 4.9% from Q1 and reached a record 607,089 units in the first half of 2025. Analysts also expect a surge in Q3 as buyers rush to qualify for federal EV tax credits before they expire on October 1, Cox Automotive noted in a post.
Legacy rivals gain ground, but Tesla holds its commanding lead
General Motors more than doubled its EV volume in the first half of 2025, selling over 78,000 units and boosting its EV market share to 12.9%. Chevrolet became the second-best-selling EV brand, pushing GM past Ford and Hyundai. Tesla, however, still retained a commanding 44.7% electric vehicle market share despite a 12% drop in in Q2 revenue, following a decline of almost 9% in Q1.
Incentives reached record highs in Q2, averaging 14.8% of transaction prices, roughly $8,500 per vehicle. As government support winds down, the used EV market is also gaining momentum, with over 100,000 used EVs sold in Q2.
Q2 2025 Kelley Blue Book EV Sales Report by Simon Alvarez on Scribd
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoTesla debuts hands-free Grok AI with update 2025.26: What you need to know
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 Elon Musk5 days ago
Elon Musk5 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla reveals it is using AI to make factories more sustainable: here’s how
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales

















