News
Installing Solar Panels through SolarCity
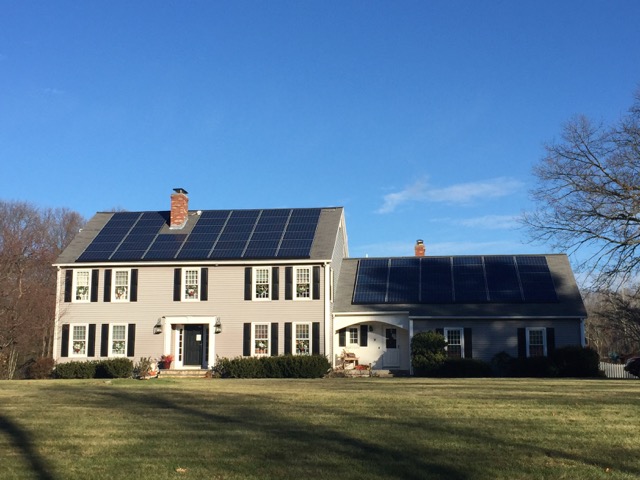
 Shortly after placing my order for my Tesla Model S I started looking into installing a solar panel system at home as a way to offset the soon-to-be increased electricity bill. My research turned me to a SolarCity system which I ended up signing up with in April of 2014.
Shortly after placing my order for my Tesla Model S I started looking into installing a solar panel system at home as a way to offset the soon-to-be increased electricity bill. My research turned me to a SolarCity system which I ended up signing up with in April of 2014.
After a number of scoping, design, and utility company challenges the day finally came for installation.
Sizing the Job
While I had originally hoped for a much larger system, the system that was installed was still large by most people’s standards. The final design called for 70 panels, each capable of generating 255W for a total of 17.8 kW and an annual expected output of 18,611 kWh.
To put that into perspective, my Model S uses an average of 775 kWh (as measured through a digital submeter) or approximately 2,400 miles. That usage will climb a bit for the winter months, but I still intend to use about 9,300 kWh per year for my Model S which equates to 50% of my expected solar generation capacity.
What this means is that I’ll be driving my Model S on 100% solar generated energy and still have solar energy to spare to offset my normal electric costs.
Many installations are half this size or smaller due to a number of constraints. Because of the size of this job, SolarCity booked 2 days for the install and sent a crew of about 8 to do the work.
Scheduling
 It was a bit nerve wracking waiting for the project to begin 8 months after my April sign up date. This put us smack dab in the middle of winter for a December 8th install in New England. We’ve had snow and ice storms along the way which made me more skeptical that the install would ever take place.
It was a bit nerve wracking waiting for the project to begin 8 months after my April sign up date. This put us smack dab in the middle of winter for a December 8th install in New England. We’ve had snow and ice storms along the way which made me more skeptical that the install would ever take place.
I’m happy to report that the entire SolarCity team in charge of the project arrived on the scheduled date. They were late due to leftover work at a different site, but they turned up despite the wet weather, 30 degree temperature and got right to work. It was immediately evident that this crew knew what they were doing and it was just another day on the job despite the magnitude of the install.
Solar Panel Installation
 The first order of business was to tape off and secure the area from foot traffic. Anchors are attached to the roof which the crew secured their safety harnesses to.
The first order of business was to tape off and secure the area from foot traffic. Anchors are attached to the roof which the crew secured their safety harnesses to.
Once the precautionary safety measures were in place, the crew began setting up dozens of anchor points across the roof surfaces later to be used as mounting points for the solar panels. That part took most of the first day.
By the end of the first day they had managed to install solar panels on the smaller of the 2 roof lines and had most of the anchors ready on the larger roof line.
Weather Proof Guarantee
A Noreaster hit right in the middle of the week so installation was postponed. To make matter worse, all of the heavy rain and cold weather ended up icing over the roof. I crawled into both attics below each roof to ensure that all of the nails and anchors on the roof didn’t create a leak and was relieved to find that everything was totally dry.
SolarCity guarantees a leak-free installation so it was great to be able to validate that even after torrential rains.
The crew returned on the third day despite the rain and proceeded to work a full day in extremely cold weather and light rain.
Uh oh, Design Challenges
 Two different design issues were uncovered during the solar panel installation. The first of which was related to a misjudgment on the number of solar panels that would fit. Designers back at corporate had mapped out 70 panels for the roof, but one of the panels would not fit behind the chimney. The crew offered to stick it somewhere else, but we declined as it would have been asymmetrical anywhere else and the aesthetics would not have been good. So we ended up with a total of 69 panels and a slight decrease in target generation capacity.
Two different design issues were uncovered during the solar panel installation. The first of which was related to a misjudgment on the number of solar panels that would fit. Designers back at corporate had mapped out 70 panels for the roof, but one of the panels would not fit behind the chimney. The crew offered to stick it somewhere else, but we declined as it would have been asymmetrical anywhere else and the aesthetics would not have been good. So we ended up with a total of 69 panels and a slight decrease in target generation capacity.
The second issue was identified on the third day. While the entire install was on the front of the house (thanks to National Grid), they had a pipe running in the middle of the roof on the rear of the house which looked stupid and unnecessary.
I spoke to them about it and they cheerfully redesigned and relocated the entire pipe. In the rain. In 30 degree weather. On top of the house. The install team took our concerns seriously and took care of the problem.
The Final Touches
 After lugging the panels up all day (each panel weighs about 45 pounds) and mounting them, they took the time to level each of them so they were completely flat.
After lugging the panels up all day (each panel weighs about 45 pounds) and mounting them, they took the time to level each of them so they were completely flat.
At one point a single panel in the middle of the lot was a bit out of place (not perfect) so one of the guys had to slide down the wet, cold, glass on his knees (getting soaked in the process), 30 feet above ground with just a line to keep him safe just to adjust the angle slightly. Those installers are hard core!
Electric Connection
 I was surprised that SolarCity needed no access to the house (other than for bathroom breaks) to do the job. The entire connection for my house was on the outside. They needed to cut the power for about 45 minutes to connect into the mains but otherwise there was very little disruption.
I was surprised that SolarCity needed no access to the house (other than for bathroom breaks) to do the job. The entire connection for my house was on the outside. They needed to cut the power for about 45 minutes to connect into the mains but otherwise there was very little disruption.
The size of the installation required 3 inverters which they placed on the side of the house.
Next Steps
The process leading up to the install (3 part series) was frustrating and error-prone between the reluctant power company and the mistakes made by the out-of-touch engineers back at SolarCity corporate. But SolarCity’s installation team was nothing but first class, all the way. They knew their stuff, were very safety conscious and worked through some harsh conditions to get the job done, and done well. They restored my confidence in the decision I made and I’m confident again that things are going to work out well.
Now that the system is installed and ready to go we need to have the inspections done. SolarCity coordinates it all, but there’s a building inspection, an electrical inspection and then an inspection by the power company. Once all passes (in about 3-4 weeks) we’re given the green light to flip the switches and start putting that free energy from the sun to good use.

Elon Musk
Brazil Supreme Court orders Elon Musk and X investigation closed
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.

Brazil’s Supreme Federal Court has ordered the closure of an investigation involving Elon Musk and social media platform X. The inquiry had been pending for about two years and examined whether the platform was used to coordinate attacks against members of the judiciary.
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.
According to a report from Agencia Brasil, the investigation conducted by the Federal Police did not find evidence that X deliberately attempted to attack the judiciary or circumvent court orders.
Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet concluded that the irregularities identified during the probe did not indicate fraudulent intent.
Justice Moraes accepted the prosecutor’s recommendation and ruled that the investigation should be closed. Under the ruling, the case will remain closed unless new evidence emerges.
The inquiry stemmed from concerns that content on X may have enabled online attacks against Supreme Court justices or violated rulings requiring the suspension of certain accounts under investigation.
Justice Moraes had previously taken several enforcement actions related to the platform during the broader dispute involving social media regulation in Brazil.
These included ordering a nationwide block of the platform, freezing Starlink accounts, and imposing fines on X totaling about $5.2 million. Authorities also froze financial assets linked to X and SpaceX through Starlink to collect unpaid penalties and seized roughly $3.3 million from the companies’ accounts.
Moraes also imposed daily fines of up to R$5 million, about $920,000, for alleged evasion of the X ban and established penalties of R$50,000 per day for VPN users who attempted to bypass the restriction.
Brazil remains an important market for X, with roughly 17 million users, making it one of the platform’s larger user bases globally.
The country is also a major market for Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet service, which has surpassed one million subscribers in Brazil.
Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Energy
Tesla Energy gains UK license to sell electricity to homes and businesses
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.

Tesla Energy has received a license to supply electricity in the United Kingdom, opening the door for the company to serve homes and businesses in the country.
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.
According to Ofgem, the license took effect at 6 p.m. local time on Wednesday and applies to Great Britain.
The approval allows Tesla’s energy business to sell electricity directly to customers in the region, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
Tesla has already expanded similar services in the United States. In Texas, the company offers electricity plans that allow Tesla owners to charge their vehicles at a lower cost while also feeding excess electricity back into the grid.
Tesla already has a sizable presence in the UK market. According to price comparison website U-switch, there are more than 250,000 Tesla electric vehicles in the country and thousands of Tesla home energy storage systems.
Ofgem also noted that Tesla Motors Ltd., a separate entity incorporated in England and Wales, received an electricity generation license in June 2020.
The new UK license arrives as Tesla continues expanding its global energy business.
Last year, Tesla Energy retained the top position in the global battery energy storage system (BESS) integrator market for the second consecutive year. According to Wood Mackenzie’s latest rankings, Tesla held about 15% of global market share in 2024.
The company also maintained a dominant position in North America, where it captured roughly 39% market share in the region.
At the same time, competition in the energy storage sector is increasing. Chinese companies such as Sungrow have been expanding their presence globally, particularly in Europe.








