News
Inside Rivian’s California battery lab: 180 kWh ‘megapacks’, carbon fiber, and ballistic shields
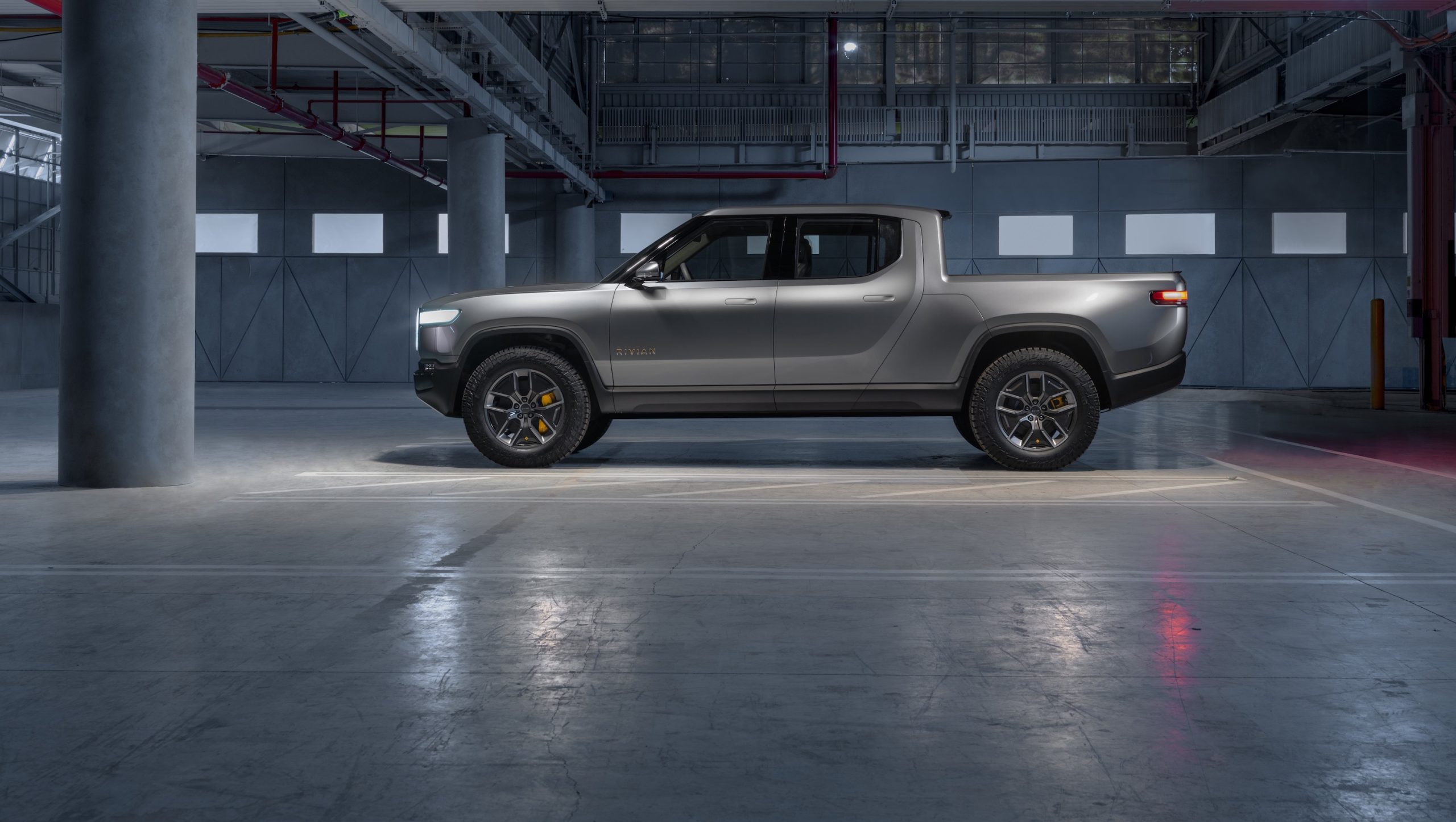
I found myself perplexed when I heard about Rivian’s plan to unveil an all-electric pickup truck with a battery pack nearly double the size of any other electric vehicle. Packing 80% more energy than Tesla’s flagship Model S and Model X, Rivian’s 180 kWh battery pack enables their full-size, adventure vehicles to travel 400+ miles (643 km) on a single charge. Rivian’s response? We actually call it the “megapack.”
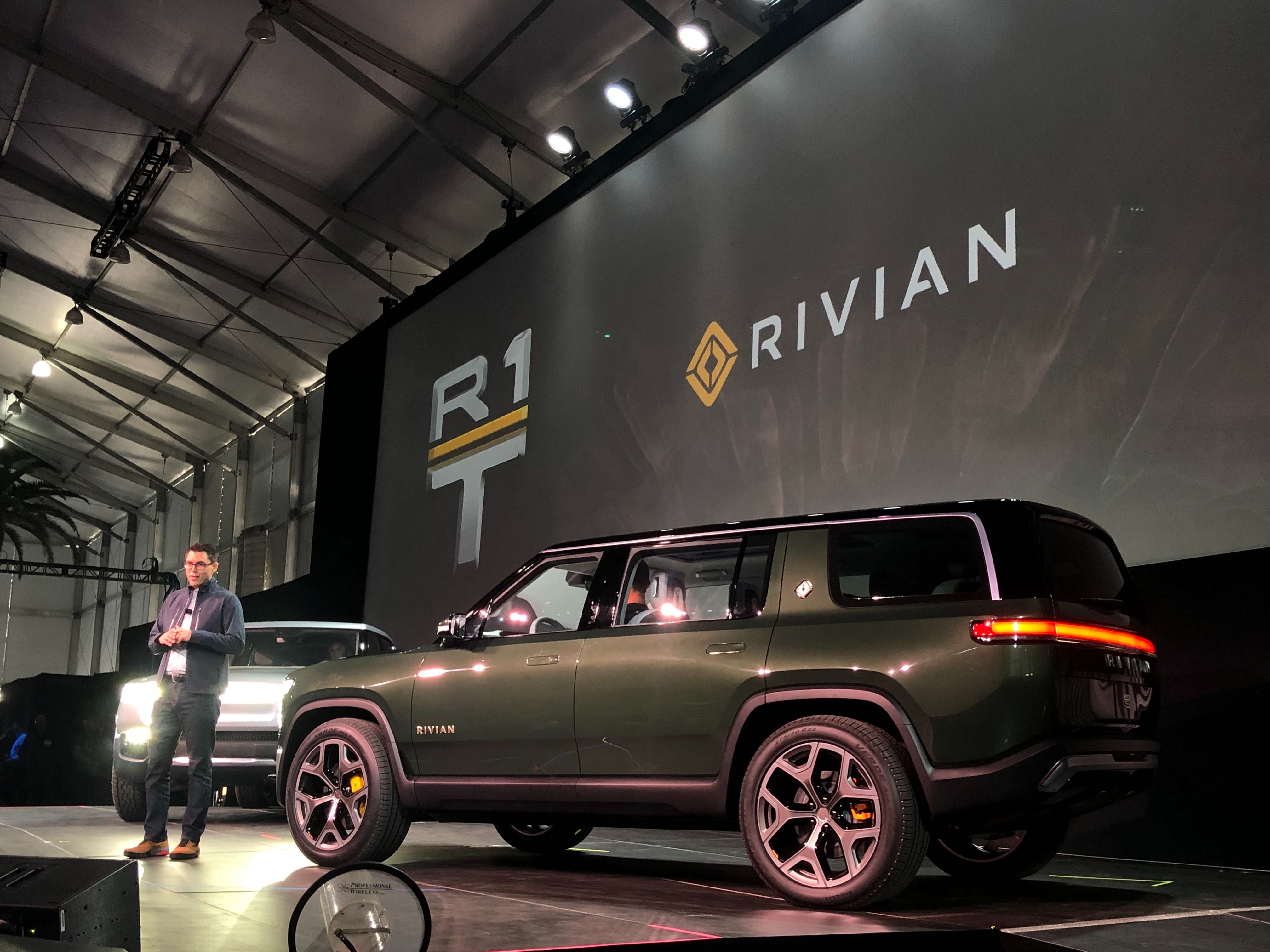
At a flashy unveiling event in Los Angeles, the Michigan-based electric car company exited stealth mode and debuted their first two production vehicles: an all-electric pickup truck dubbed the R1T and an R1S luxury SUV. Capable of towing 11,000 lbs from its all-electric powertrain, the R1T is set to disrupt a $95-billion-dollar US truck market that’s largely dominated by Ford and GM. Rivian’s seven-seater, R1S SUV takes aim directly at gas guzzlers that are competing in the premium sports utility segment like Land Rover and Porsche’s Cayenne.
Powering the R1T Truck and R1S SUV is a quad-motor electric drivetrain that’s paired with one of Rivian’s three battery pack configurations, in 105 kWh, 135 kWh, and 180 kWh (the “megapack”). Rivian’s 180 kWh megapack holds enough energy to power a typical US household for more than two weeks. To learn more about the engineering that goes into each of Rivian’s battery packs, and the company’s plan to bring their ultra-long-range battery packs to market, I visited their research and development facility in Southern California.

The Battery Lab
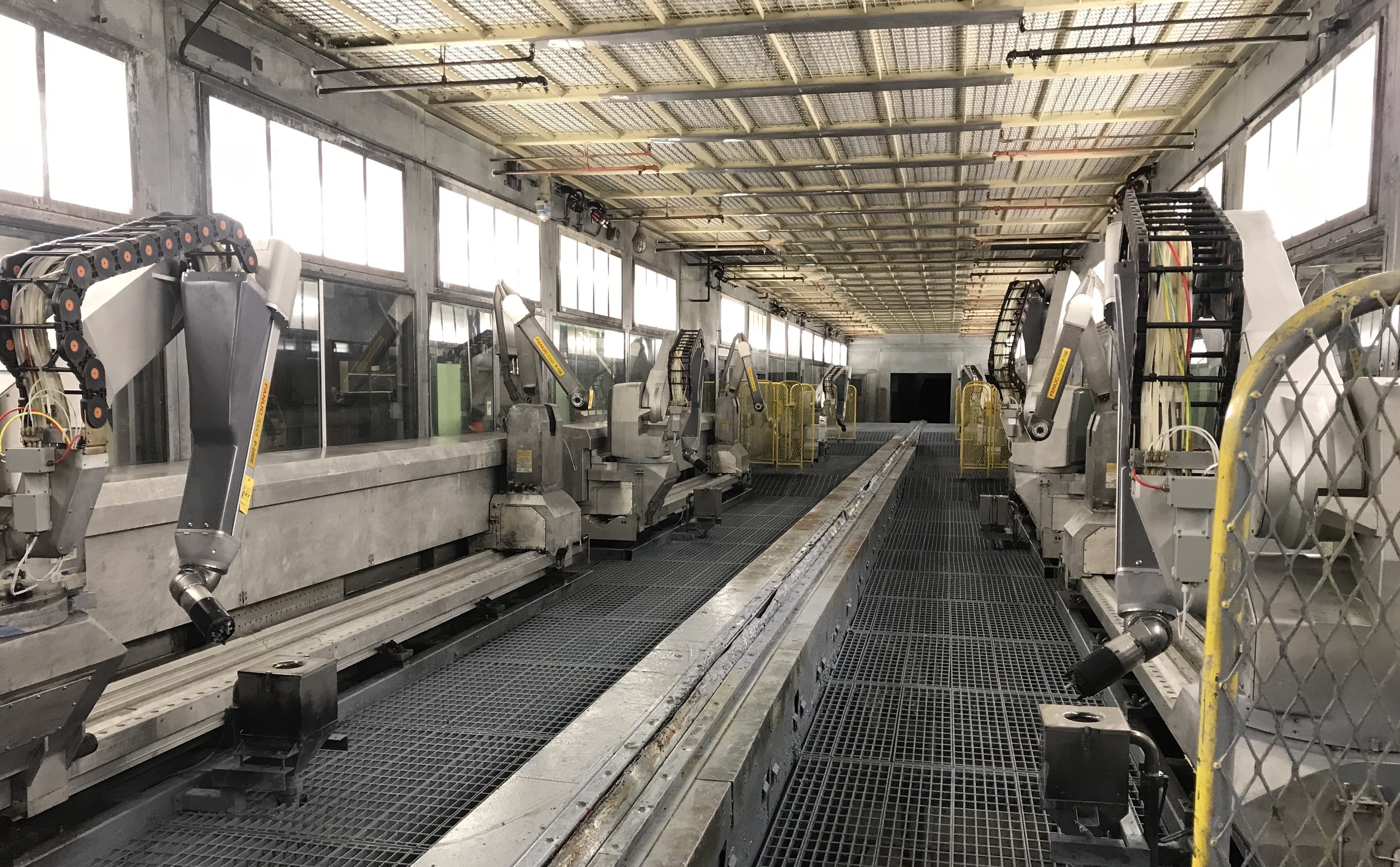
Rivian’s battery lab is located in an unassuming industrial business park in Irvine, California. Still working its way out of nine-years in stealth mode, the 19,000 sq ft facility lacks any signage on its doors, yet has played a major role since mid-2017 when the company moved in to begin its research and development.
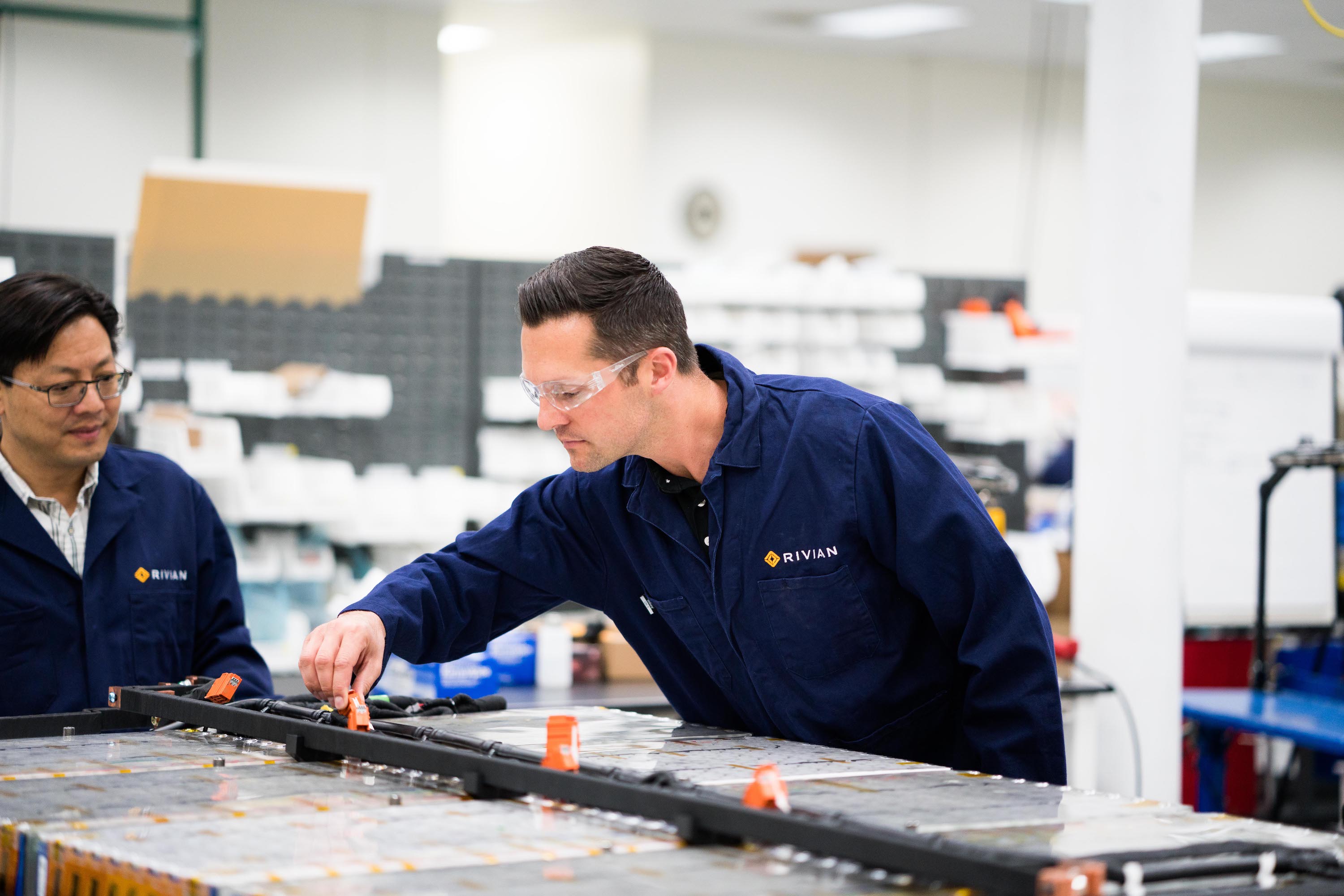
Upon entering the battery lab, I was greeted by the faint hum of testing equipment around me. Bright white lights illuminate a team of engineers in blue Rivian lab coats. I was told that the lab is where Rivian performs tests on the lithium-ion battery cells being used in its vehicles. The lab is also where battery module production is currently taking place, albeit mostly for prototype battery packs.
Leading Rivian’s battery and powertrain development is former hypercar engineer Richard Farquhar, who enjoys an insanely fun-sounding title: VP of Propulsion. Farquhar is one of the many members to recently join Rivian from renowned supercar brand McLaren. Rivian has brought on seven executives from the British company since late 2017, including Executive Director of Engineering and Programs, Mark Vinnels.
 (Photo: Rivian)
(Photo: Rivian)
Rivian’s Battery Cells and Supplier
As Farquhar and I walk past a long row of glass cabinets, seen packed with hundreds of cylindrical battery cells in their testing phase, his eyes lit up with excitement while discussing the most intricate elements of the lithium-ion cells. “We want to understand the battery cells even better than their manufacturer,” Farquhar tells me.
It was the perfect segue I was looking for. “So, where is Rivian getting these battery cells from?” I ask. Farquhar wasn’t able to share the name of their battery partner but emphasized that Rivian wasn’t worried about their supply of cells. “I have no concern whatsoever,” Farquhar emphatically stated.
While Rivian isn’t ready to announce a battery supplier (yet), U.S. customs import records suggest that the company could be partnering with LG Chem to procure their cylindrical 2170 form factor lithium-ion cells. Rivian imported nearly 12,933 kg (28,500 lbs) of the 2170 cells from LG Chem in 2018 thus far — enough to support a test production run of ~195 Rivian battery modules at 15 kWh each.
Designed for extreme conditions
Inside the cabinets were cells being cycled through various charge and discharge states, and at various temperatures. Rivian wants to be the leading experts on battery technology, and in lieu of having numerous vehicles on the road, the company is testing its batteries using real-world simulations.
In the office area next to the lab, engineers analyze the testing data in real-time while adjusting computer-generated models. These tests aren’t just being done for a few hours or days, Farquhar tells me. One battery test has been ongoing for 11 months and counting. Rivian plans to analyze battery cell behavior over time and collect as much data as possible before making adjustments to it and entering production.
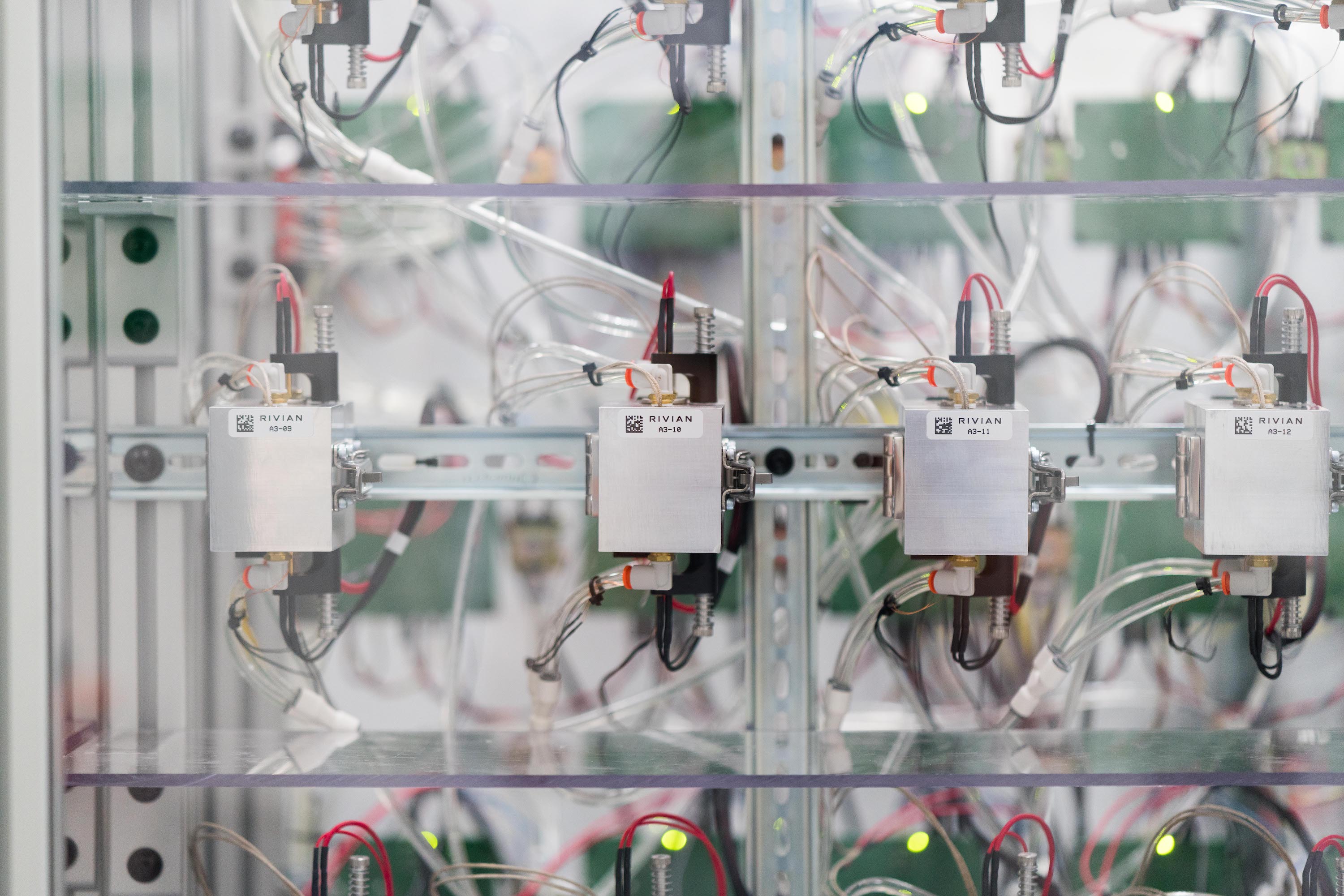

While standing the test of time is incredibly important for all battery cells, standing up to extreme conditions is just as critical. On one side of the lab, special climate-controlled containers simulate extreme temperature scenarios and test how the cells, modules, and full-sized battery packs react to these conditions. Rivian expects their adventure-ready vehicles to be capable of handling extreme temperatures and climates. Pushing their batteries to the limit isn’t just a precaution, but a necessity.
From Battery Cells to Modules
Farquhar tells me that Rivian engineers have worked on battery algorithms that leverage a driver’s profile, including their location and navigation data, and real-time weather conditions, to preemptively optimize a battery. For example, when a vehicle is on its way to a DC-charging station, the battery modules will be cooled ahead of time and prepared to accept the fastest charging rate. In essence, Rivian’s battery algorithms are adjusting battery cell settings, constantly, on the fly. By using machine-learning to build predictive models of various conditions, Rivian is able to tune battery cells, with high confidence, on conditions it may encounter.
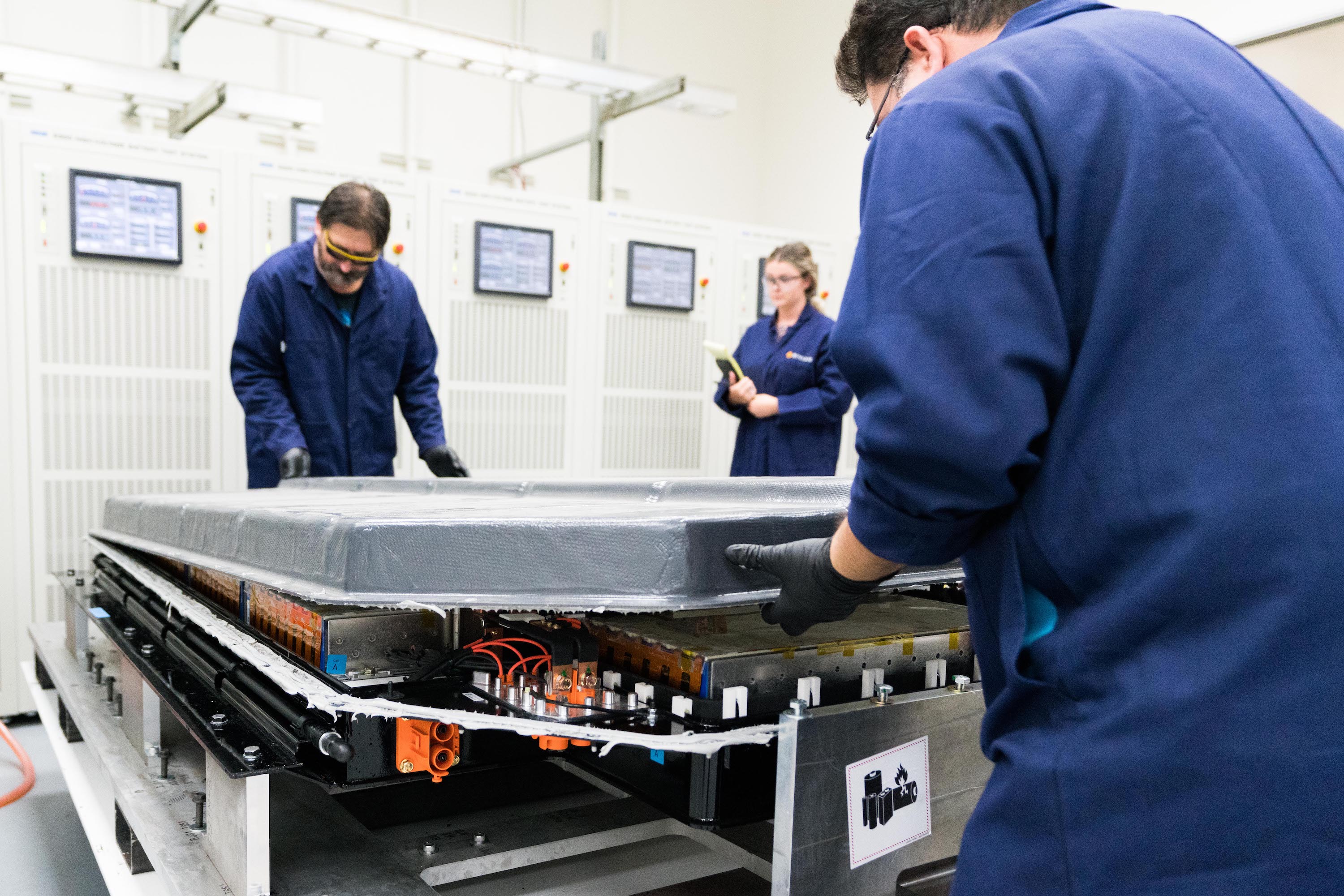
Rivian’s R1T pickup truck and R1S adventure SUV will use the exact same battery modules. Battery capacity will vary based on the number of modules inside a skateboard-style battery pack design. Each Rivian module holds 864 cells, with 432 on the bottom and the other half stacked on top. In between the cells is a thin 7mm aluminum plate with liquid coolant. The unique structure isn’t known to be used by any other manufacturer.
- A side view of Rivian’s battery module. Between the two layers of battery cells lies a proprietary cooling plate, allowing cells to be packed in tightly, while cooling the module efficiently. (Photo: Rivian)
- Rivian Battery modules being tested in Rivian’s Irvine, CA Development Center (Photo: Rivian)
A battery’s cooling system is one of the most important components within an electric car. If the batteries get too hot from fast charging or extended periods of high output, they could degrade in energy capacity and face permanent damage. If the batteries get too cold, they lose range. Keeping the batteries at their optimum temperature is a constant battle and is what truly differentiates any electric vehicle manufacturer.
Rivian’s solution to battery thermal management is the use of a cold plate that’s placed between two battery cells. A single cooling system chills both layers of cells at the same time. According to Rivian, this reduces the amount of energy needed to power the system, thereby allowing the car to have better range in all types of conditions. In addition to saving power, the cooling system’s design allows for tighter packaging of cells within the modules. According to Farquhar, Rivian’s unique packaging allows the module to be 25% denser than any other battery module on the market.
Rivian’s Battery Pack: Carbon Fiber and Ballistic Shields
I saw it from afar. Carbon fiber. Walking toward a station that was outfitted with Rivian’s line of 135 kWh and 180 kWh battery packs, my eyes were immediately drawn to a fibrous-looking cover plate.
Securing Rivian’s battery modules and high-voltage cabling in place is a carbon-fiber composite shell. Engineers were able to create a unique, high-strength geometric shape out of the carbon fiber while keeping weight to a minimum. Rivian seals the battery pack to be completely watertight. The pack is bolted into the frame of the vehicle and then covered by a smooth ‘ballistic shield’, which prevents damage to the underside of the battery pack and protects occupants within the vehicle’s cabin. The ballistic shield is fitted to the entire underbody of the vehicle.

Having a watertight battery pack that’s armored by a ballistic shield bodes well for a company whose mission is to build extreme off-road vehicles. That’s the messaging Rivian wants consumers to see. The vehicles are designed to be adventure-ready, being able to wade through 1 meter of water, climb 45-degree inclines, and drive over boulders.
Rivian’s Executive Director of Engineering and Programs, Mark Vinnels, told Teslarati that they dropped the vehicle on a boulder from 2 ft in the air, just to be able to verify the battery pack’s integrity in extreme off-road situations.
What about Production?
With the design of its battery module completed, a significant portion of the team’s focus has turned to module production — specifically, designing methods to quickly and efficiently manufacture modules by using automation. Rivian has set up a pilot production line at the Irvine facility, ahead of its anticipated summer 2020 production.

Rivian is actively developing automation processes for the entire battery module assembly. In a corner of the battery facility were two Japan-made robots that were brought in from the company’s massive factory in Normal, Illinois. A robotics technician was actively working on the robots, while I watched a module come together on the line.
The entirety of Rivian’s module and battery pack production is slated to be installed in a 300,000 sq-ft section of Rivian’s 2.6M sq ft factory in Normal, IL. The plant was acquired by Rivian in 2017 for $16M and originally part of an expansion made by Mitsubishi that the Japanese automaker never occupied. Farquhar stated that the area is virtually a “clean slate.”
ALSO SEE: Rivian R1T and R1S: Top 10 hidden features that make an electric off-road vehicle
Rivian expects to start deliveries of the R1S and R1T in the second half of 2020, with the largest battery packs entering production first. The R1S SUV starts at $72,500 (before tax credits) and has a range that varies between 240 to 410+ miles (385 to 660 km). Rivian’s R1T pickup truck has a starting price of $69,000 and similar range as the R1S at 230 to 400+ miles (370 to 643 km), depending on battery pack size. Both vehicles will support CCS DC-fast charging up to 160 kW and are capable of accelerating from 0-60 mph in 3 seconds.
Rivian is accepting preorders at its website.


News
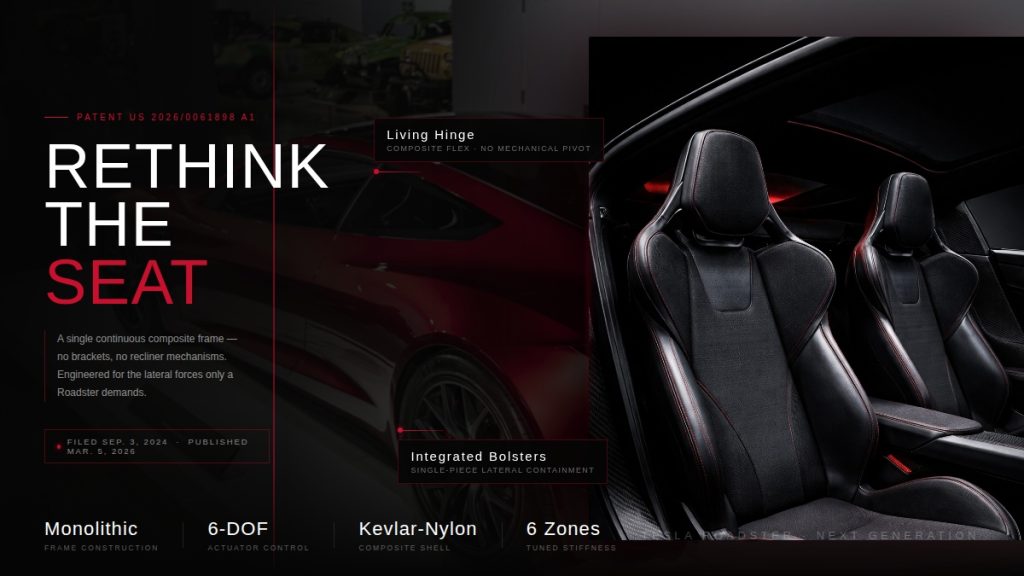
Tesla Roadster patent hints at radical seat redesign ahead of reveal
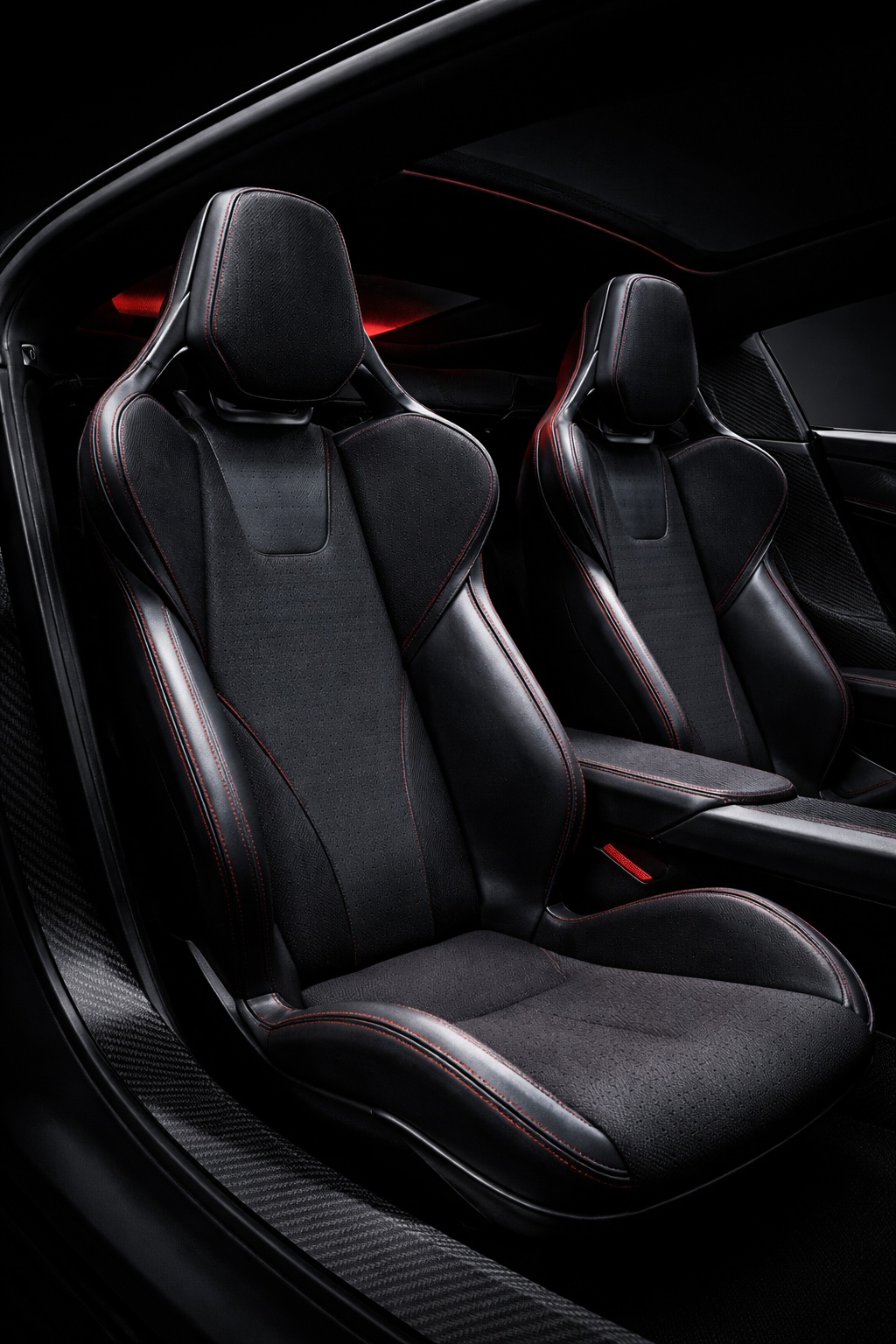

A newly published Tesla patent could offer one of the clearest signals yet that the long-awaited next-generation Roadster is nearly ready for its public debut.
Patent No. US 20260061898 A1, published on March 5, 2026, describes a “vehicle seat system” built around a single continuous composite frame – a dramatic departure from the dozens of metal brackets, recliner mechanisms, and rivets that make up a traditional car seat. Tesla is calling it a monolithic structure, with the seat portion, backrest, headrest, and bolsters all thermoformed as one unified piece.
The approach mirrors Tesla’s broader manufacturing philosophy. The same company that pioneered massive aluminum castings to eliminate hundreds of body components is now applying that logic to the cabin. Fewer parts means fewer potential failure points, less weight, and a cleaner assembly process overall.
Tesla ramps hiring for Roadster as latest unveiling approaches
The timing of the filing is difficult to ignore. Elon Musk has publicly targeted April 1, 2026 as the date for an “unforgettable” Roadster design reveal, and two new Roadster trademarks were filed just last month. A patent describing a seat architecture suited for a hypercar, and one that Tesla has promised will hit 60 mph in under two seconds.
The Roadster, originally unveiled in 2017, has been one of Tesla’s most anticipated yet most delayed products. With a target price around $200,000 and engineering ambitions to match, it is being positioned as the ultimate showcase for what Tesla’s technology can do.
The patent was first flagged by @seti_park on X.
Tesla Roadster Monolithic Seat: Feature Highlights via US Patent 20260061898 A1
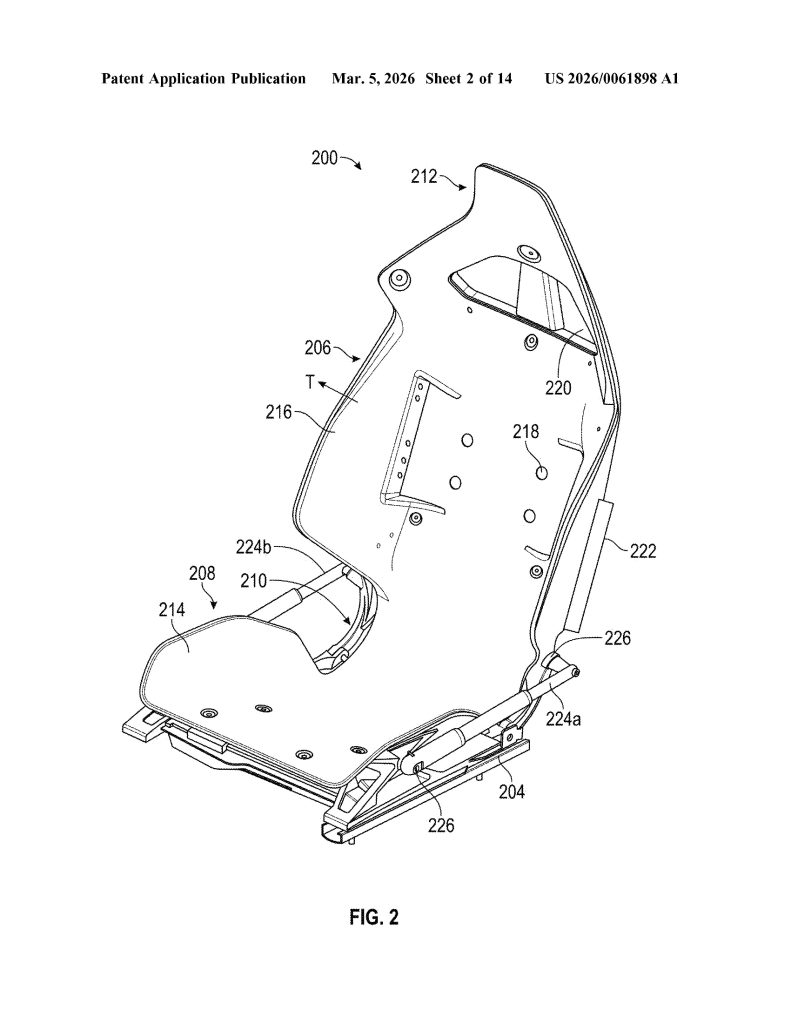
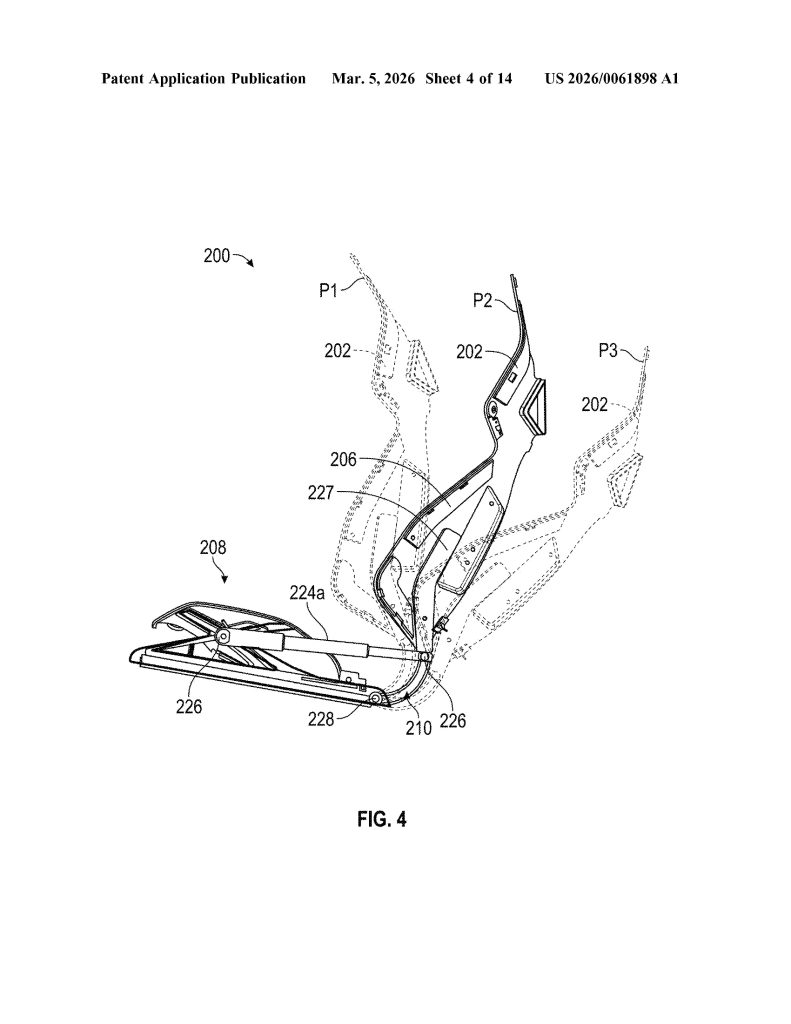
- Single Continuous Frame (Monolithic Construction). The core invention is a seat assembly built from one continuous frame that integrates the seat portion, backrest portion, and hinge into a single component — eliminating the need for separate structural parts and mechanical joints typical in conventional seats.
- Integrated Flexible Hinge. Rather than a traditional mechanical recliner, the hinge is built directly into the continuous frame and is designed to flex, and allowing the backrest to move relative to the seat portion. The hinge can be implemented as a fiber composite leaf spring or an assembly of rigid linkages.
- Thermoformed Anisotropic Composite Material. The continuous frame is manufactured via thermoforming from anisotropic composite materials, including fiberglass-nylon, fiberglass-polymer, nylon carbon composite, Kevlar-nylon, or Kevlar-polymer composites, enabling a molded-to-shape monolithic structure.
- Regionally Tuned Stiffness Zones. The frame is engineered with up to six distinct stiffness regions (R1–R6) across the seat, backrest, hinge, headrest, and bolsters. Each zone can have a different stiffness, allowing precise ergonomic and structural tuning without adding separate components.
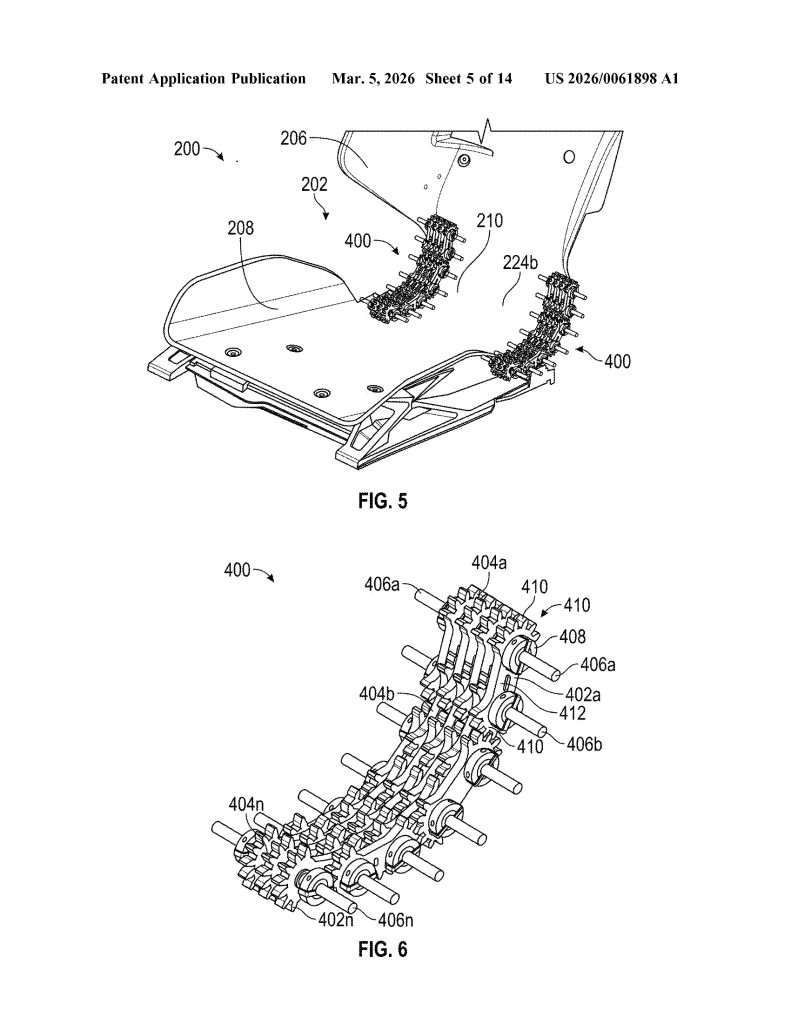
- Linkage Assembly Hinge Mechanism. The hinge incorporates one or more linkage assemblies consisting of multiple interlocking links with gears, connected by rods. When driven by motors or actuators, these linkages act as a flexible member to control backrest movement along a precise, ergonomically optimized trajectory.
- Multi-Actuator Six-Degree-of-Freedom Positioning System. The seat uses four distinct actuator pairs, all controlled by a central controller. These actuators work in coordinated combinations to achieve fore/aft, height, cushion tilt, and backrest rotation adjustments simultaneously.
- ECU-Based Controller Architecture. An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) and programmable controller manage all seat actuators, receive user input via a user interface (touchscreen, buttons, or switches), and incorporate sensor feedback to confirm and maintain desired seat positions, essentially making this a software-driven seat system.
- Airbag-Integrated Bolster Deployment System. The backrest bolsters (216) are geometrically shaped and sized to guide airbag deployment along a specific, pre-configured trajectory. Left and right bolsters can have different shapes so that each guides its respective airbag along a distinct trajectory, improving occupant protection.
- Ventilation Holes Formed into the Backrest. The continuous frame includes one or more ventilation holes formed directly into the backrest portion, configured to either receive airflow into or deliver airflow from the seat frame — enabling passive or active thermal comfort without requiring separate ventilation components.
- Soft Trim Recess for Tool-Free Integration. The headrest and backrest portions together define a molded recess, specifically designed to receive and secure a soft trim component (foam, fabric, or cushioning) directly into the continuous frame, eliminating the need for separate attachment hardware and simplifying final assembly.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk’s xAI plans $659M expansion at Memphis supercomputer site
The new building is planned for a 79-acre parcel located at 5414 Tulane Road, next to xAI’s Colossus 2 data center site.

Elon Musk’s artificial intelligence company xAI has filed a permit to construct a new building at its growing data center complex outside Memphis, Tennessee.
As per a report from Data Center Dynamics, xAI plans to spend about $659 million on a new facility adjacent to its Colossus 2 data center. Permit documents submitted to the Memphis and Shelby County Division of Planning and Development show the proposed structure would be a four-story building totaling about 312,000 square feet.
The new building is planned for a 79-acre parcel located at 5414 Tulane Road, next to xAI’s Colossus 2 data center site. Permit filings indicate the structure would reach roughly 75 feet high, though the specific function of the building has not been disclosed.
The filing was first reported by the Memphis Business Journal.
xAI uses its Memphis data centers to power Grok, the company’s flagship large language model. The company entered the Memphis area in 2024, launching its Colossus supercomputer in a repurposed Electrolux factory located in the Boxtown district.
The company later acquired land for the Colossus 2 data center in March last year. That facility came online in January.
A third data center is also planned for the cluster across the Tennessee–Mississippi border. Musk has stated that the broader campus could eventually provide access to about 2 gigawatts of compute power.
The Memphis cluster is also tied to new power infrastructure commitments announced by SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell. During a White House event with United States President Donald Trump, Shotwell stated that xAI would develop 1.2 gigawatts of power for its supercomputer facility as part of the administration’s “Ratepayer Protection Pledge.”
“As you know, xAI builds huge supercomputers and data centers and we build them fast. Currently, we’re building one on the Tennessee-Mississippi state line… xAI will therefore commit to develop 1.2 GW of power as our supercomputer’s primary power source. That will be for every additional data center as well…
“The installation will provide enough backup power to power the city of Memphis, and more than sufficient energy to power the town of Southaven, Mississippi where the data center resides. We will build new substations and invest in electrical infrastructure to provide stability to the area’s grid,” Shotwell said.
Shotwell also stated that xAI plans to support the region’s water supply through new infrastructure tied to the project. “We will build state-of-the-art water recycling plants that will protect approximately 4.7 billion gallons of water from the Memphis aquifer each year. And we will employ thousands of American workers from around the city of Memphis on both sides of the TN-MS border,” she said.
News
Tesla wins another award critics will absolutely despise
Tesla earned an overall score of 49 percent, up 6 percentage points from the previous year, widening its lead over second-place Ford (45 percent, up 2 points) to a commanding 4-percentage-point gap. The company also excelled in the Fossil Free & Environment category with a 50 percent score, reflecting strong progress in reducing emissions and decarbonizing operations.

Tesla just won another award that critics will absolutely despise, as it has been recognized once again as the company with the most sustainable supply chain.
Tesla has once again proven its critics wrong, securing the number one spot on the 2026 Lead the Charge Auto Supply Chain Leaderboard for the second consecutive year, Lead the Charge rankings show.
NEWS: Tesla ranked 1st on supply chain sustainability in the 2026 Lead the Charge auto/EV supply chain scorecard.
“@Tesla remains the top performing automaker of the Leaderboard for the second year running, and increased its overall score by 6 percentage points, while Ford only… pic.twitter.com/nAgGOIrGFS
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) March 4, 2026
This independent ranking, produced by a coalition of environmental, human rights, and investor groups including the Sierra Club, Transport & Environment, and others, evaluates 18 major automakers on their efforts to build equitable, sustainable, and fossil-free supply chains for electric vehicles.
Tesla earned an overall score of 49 percent, up 6 percentage points from the previous year, widening its lead over second-place Ford (45 percent, up 2 points) to a commanding 4-percentage-point gap. The company also excelled in the Fossil Free & Environment category with a 50 percent score, reflecting strong progress in reducing emissions and decarbonizing operations.
Perhaps the most impressive achievement came in the batteries subsection, where Tesla posted a massive +20-point jump to reach 51 percent, becoming the first automaker ever to surpass 50 percent in this critical area.
Tesla achieved this milestone through transparency, fully disclosing Scope 3 emissions breakdowns for battery cell production and key materials like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and graphite.
The company also requires suppliers to conduct due diligence aligned with OECD guidelines on responsible sourcing, which it has mentioned in past Impact Reports.
While Tesla leads comfortably in climate and environmental performance, it scores 48 percent in human rights and responsible sourcing, slightly behind Ford’s 49 percent.
The company made notable gains in workers’ rights remedies, but has room to improve on issues like Indigenous Peoples’ rights.
Overall, the leaderboard highlights that a core group of leaders, Tesla, Ford, Volvo, Mercedes, and Volkswagen, are advancing twice as fast as their peers, proving that cleaner, more ethical EV supply chains are not just possible but already underway.
For Tesla detractors who claim EVs aren’t truly green or that the company cuts corners, this recognition from sustainability-focused NGOs delivers a powerful rebuttal.
Tesla’s vertical integration, direct supplier contracts, low-carbon material agreements (like its North American aluminum deal with emissions under 2kg CO₂e per kg), and raw materials reporting continue to set the industry standard.
As the world races toward electrification, Tesla isn’t just building cars; it’s building a more responsible future.