SpaceX
SpaceX’s BFR Mars rocket and spaceship rendered in extraordinary fan artwork
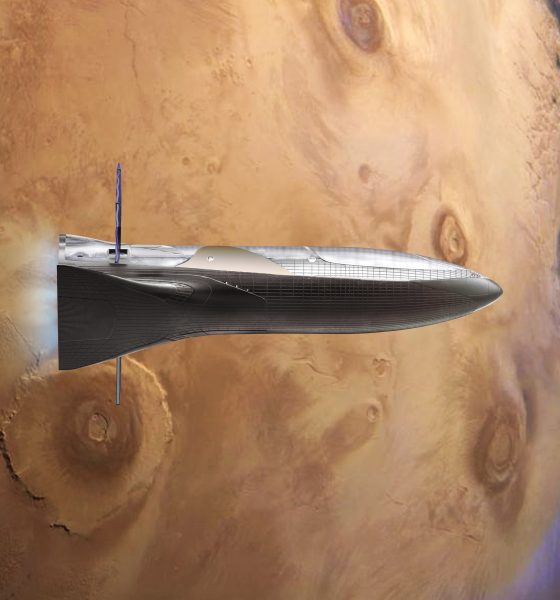
Part of a newly-formed group known as Gravitation Innovation, artist and spaceflight fan David Romax published an extraordinary series of concept artwork focused solely on SpaceX’s massive next-generation Mars rocket, known as the Big F—— Rocket (BFR). Generously published with the intent of providing SpaceX fans with a number of digital wallpapers, Romax’s work acts as an amazing companion to SpaceX’s own small collection of BFR renderings, perhaps even surpassing the company’s concept art in some cases.
David was inspired to create a series of BFR-themed wallpapers by a friend who had urged him to put his skills as a 3D modeler and artist to work for SpaceX (or at least the large community of fans built around the rocket company) by producing unofficial renders of its rockets – produce he most certainly did, and the results of his efforts are easily some of the best examples of unofficial artwork ever created by SpaceX enthusiasts.

Effectively unreleased, an updated Mars colonization video shown in 2018 replaces 2016’s ITS with the newer BFR design. (SpaceX)
Due to an understandable lack of technical detail available in the concept imagery SpaceX has thus far published for BFR and the earlier Interplanetary Transport System (ITS), Romax had to rely on aesthetic and technical intuition almost constantly over the process of producing his own artist impressions of BFR. In a number of cases, a matte painting style was used to ensure extraordinary realism by integrating real aspects of SpaceX’s current launch facilities and signatures of its active Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles and its Crew and Cargo Dragon spacecraft, reaching a level of believable detail that effortlessly surpasses similar media created by SpaceX.
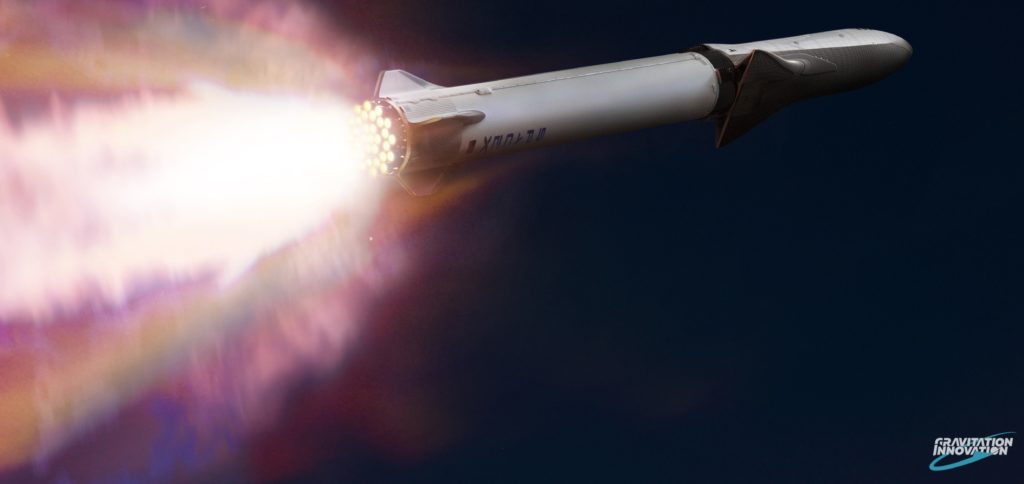
- David Romax’s artwork has blown away a number of SpaceX (and general spaceflight) fans since he shared them earlier this week. (David Romax/Gravitation Innovation)
- .While SpaceX’s own visualizations are gorgeous and thrilling in their own rights, Romax’s interpretation adds an unparalleled level of shock and awe. (SpaceX)
Of course, a comparative lack of extreme detail is really not any fault of SpaceX: given the preliminary nature of the designs of both BFR and ITS at the time they were publicly revealed (September 2016 and 2017), adding details that extended beyond the actual scope of current design work (thus treading into the realm of speculation) would be fundamentally counterproductive for a company more recently keen on showing off results over parading what can be described as ‘paper rockets’. In both the ITS and BFR reveals, CEO Elon Musk’s presentations were repeatedly (and pointedly) punctuated with truly surprising reveals of real, physical progress with mature rocket R&D programs and extensive prototype testing.
Regardless, the level of detail Romax so elegantly and seamlessly integrated into SpaceX’s preliminary Mars rocket booster and crew and cargo spaceship designs is shockingly convincing and adds a level of depth and drama that is unique in fan renderings of SpaceX’s vehicles. It certainly helps that today, nearly a year after BFR was first unveiled, SpaceX’s hardware development for BFR is far more mature. Currently, those tangible efforts range from thousands of seconds of hot-fire testing of the rocket’s Raptor propulsion system to tangible work beginning on the flight version of that advanced engine, as well as a huge temporary tent housing preliminary BFR production tooling while construction is just beginning at a different Port of Los Angeles-located plot of land intended to support the first dedicated BFR factory within 12-18 months. One step further, SpaceX’s highly reusable upgrade to Falcon 9 and Heavy, known as Block 5, has already debuted and will soon put SpaceX’s experience with rocket reuse to the test.
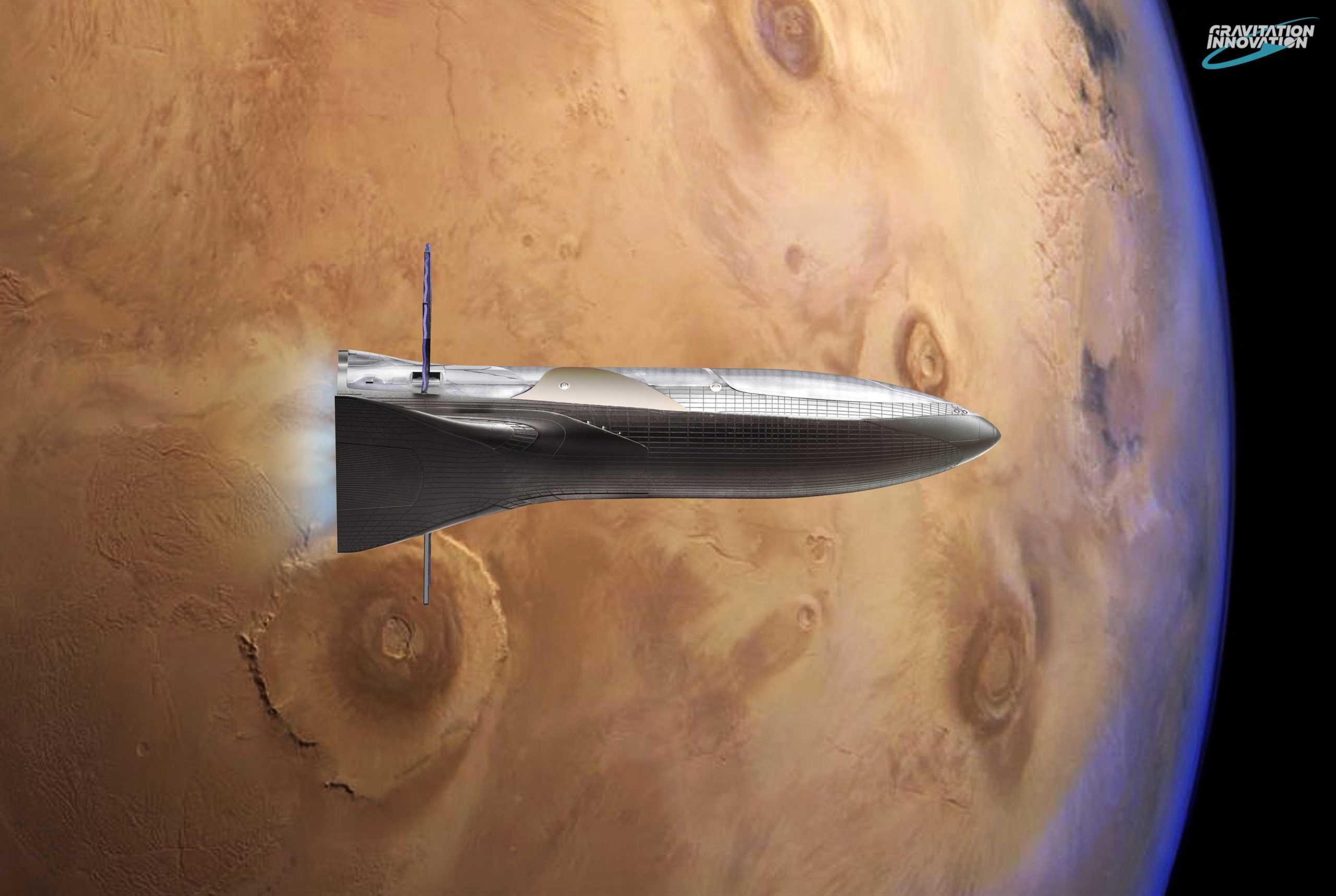
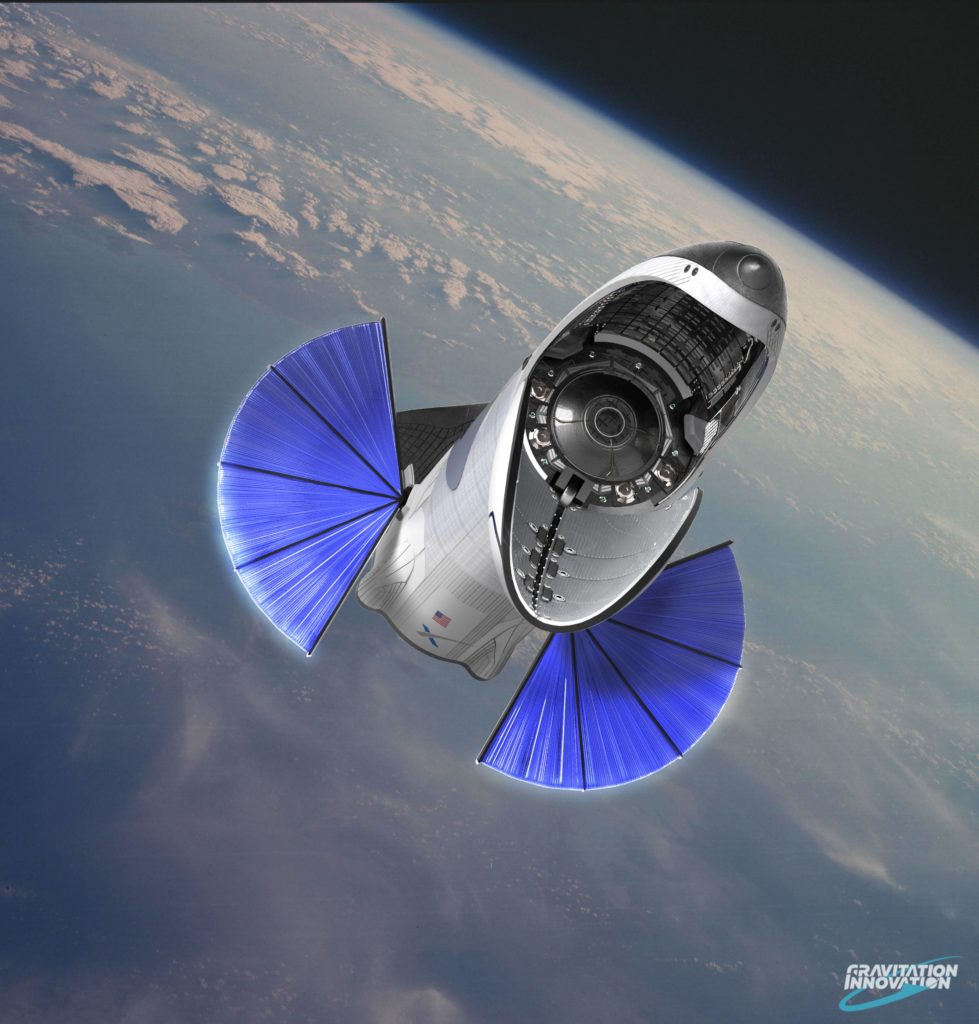
- SpaceX’s BFR. (Gravitation Innovation/David Romax)
- The cargo version of the BFS (Big F- Spaceship) rendered by David Romax, including a number of educated guesses at what it might look like and how it might function. At the request of a friend, artist David Romax put together a truly jaw-dropping collection of concept art featuring SpaceX’s BFR rocket and its Cargo and Crew spaceships. (Gravitation Innovation/David Romax)
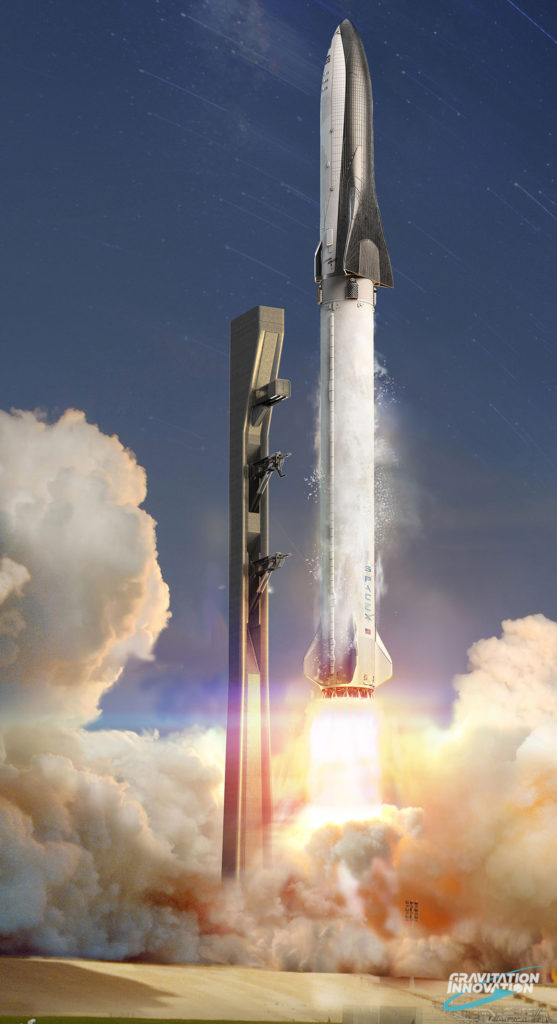
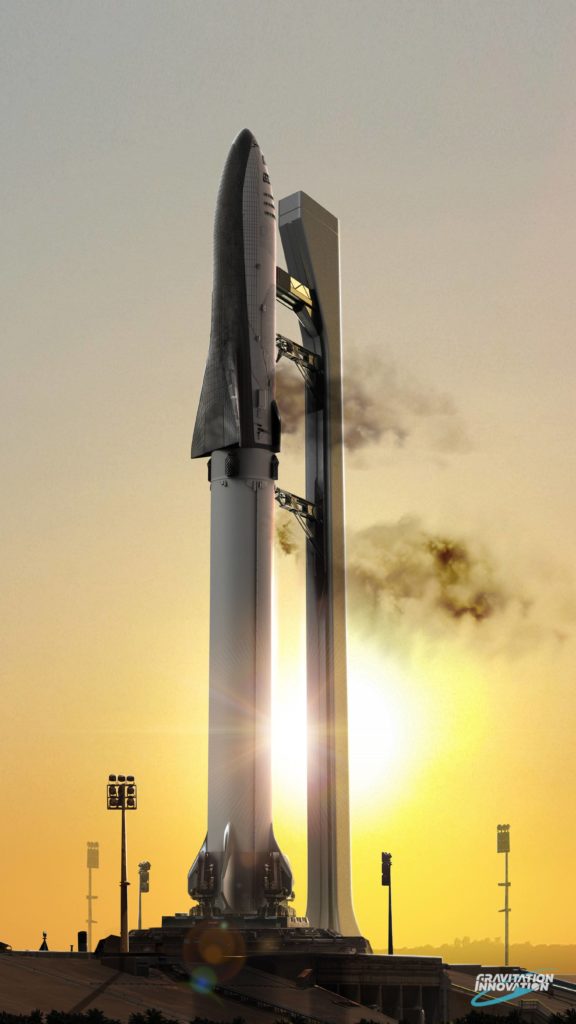
- BFR prepares for launch as the sun sets over the upgraded LC-39A, built off a concept of the future modifications included in SpaceX’s 2016 and 2017 video updates. At the request of a friend, artist David Romax put together a truly jaw-dropping collection of concept art featuring SpaceX’s BFR rocket and its Cargo and Crew spaceships. (Gravitation Innovation/David Romax)
All thanks to David Romax and Gravitation Innovation for the amazing artwork and the unflinching dedication to the future of spaceflight. Download the wallpapers in full-resolution here.
Follow us for live updates, peeks behind the scenes, and photos from Teslarati’s East and West Coast photographers.
Teslarati – Instagram – Twitter
Tom Cross – Twitter
Pauline Acalin – Twitter
Eric Ralph – Twitter

Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.
Elon Musk
Starbase after dark: Musk’s latest photo captures a Spaceport on the brink of history
SpaceX’s Starbase city in Boca Chica, Texas is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
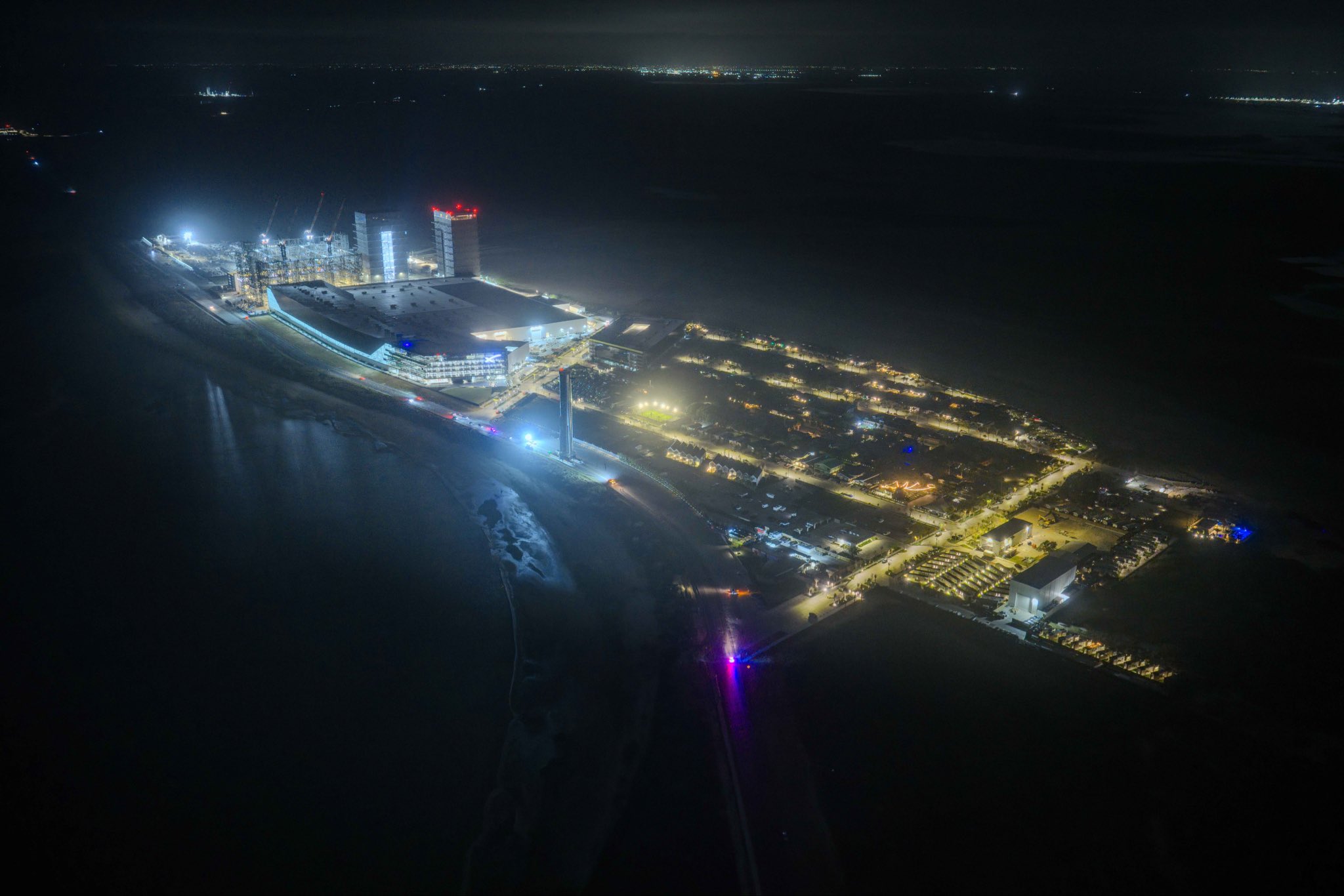

A striking nighttime photograph of SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, shared recently by Elon Musk on X, offers a dramatic glimpse of an operation that is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
The most immediately visible change in the photo is the presence of two fully erected Starship launch towers dominating the coastal skyline. The second orbital launch pad, known as Pad B, now features its fully erected tower, OLIT-3, which stands approximately 474 feet tall and incorporates an integrated water-cooled flame trench designed to minimize damage and reduce turnaround time between launches. The dual-tower silhouette against the night sky signals a decisive shift from experimental testing facility to high-cadence launch operations.
Grok Image concept of Elon Musk’s latest Starbase photo via X
Back at Starbase, Pad 2 is approaching hardware completion, with upgraded chopstick arms, a new chilldown vent system, and all 20 hold-down arms now fitted with protective doors to shield them from the intense exhaust of up to 33 Raptor 3 engines, according to a deeper dive by NASASpaceFlight.
SpaceX has also received approval to nearly double the footprint of the Starbase launch site, with groundwork already underway to add LNG liquefaction plants, expanded propellant storage, and additional ground support infrastructure.
The photo also carries a milestone civic dimension. Starbase officially became a Texas city in May 2025 after a community vote, with SpaceX employees elected as mayor and commissioners of the newly incorporated municipality. That legal status streamlines launch approvals and gives SpaceX direct control over local infrastructure decisions.
The FAA has approved an increase in launches from Starbase in Texas from five to twenty-five per year, clearing the runway for the kind of flight frequency needed to fulfill Starship’s ultimate mission of ferrying cargo and crew to the Moon, servicing the Department of Defense, deploying next-generation Starlink satellites, and eventually establishing Elon Musk’s long sought after goal of a self-sustaining human presence on Mars.
Seen from above in the dark, Starbase looks less like a test site and more like a spaceport.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk shares updated Starship V3 maiden launch target date
The comment was posted on Musk’s official account on social media platform X.

SpaceX CEO Elon Musk shared a brief Starship V3 update in a post on social media platform X, stating the next launch attempt of the spacecraft could take place in about four weeks.
The comment was posted on Musk’s official account on social media platform X.
Musk’s update suggests that Starship Flight 12 could target a launch around early April, though the schedule will depend on several remaining milestones at SpaceX’s Starbase launch facility in Texas.
Among the key steps is testing and certification of the site’s new launch tower, launch mount, and tank farm systems. These upgrades will support the next generation of Starship vehicles.
Booster 19 is expected to roll to the launch site and be placed on the launch mount before returning to the production facility to receive its 33 Raptor engines. The booster would then return for a static fire test, which could mark the first time a Super Heavy booster equipped with Raptor V3 engines is fired on the pad.
Ship 39 is expected to undergo a similar preparation process. The vehicle will likely return to the production site to receive its six engines before heading to Massey’s test site for static fire testing.
Once both stages are prepared, the booster and ship will roll out to the launch site for the first full stack of a V3 Super Heavy and V3 Starship. A full wet dress rehearsal is expected to follow before any launch attempt.
Elon Musk has previously shared how SpaceX plans to eventually recover Starship’s upper stage using the launch tower’s robotic arms. Musk noted that the company will only attempt to catch the Starship spacecraft after two successful soft landings in the ocean. The approach is intended to reduce risk before attempting a recovery over land.
“Should note that SpaceX will only try to catch the ship with the tower after two perfect soft landings in the ocean. The risk of the ship breaking up over land needs to be very low,” Musk wrote in a post on X.
Such a milestone would represent a major step toward the full reuse of the Starship system, which remains a central goal for SpaceX’s long-term launch strategy.













