News
SpaceX’s BFR rocket and spaceship look more real than ever in new 4K renders
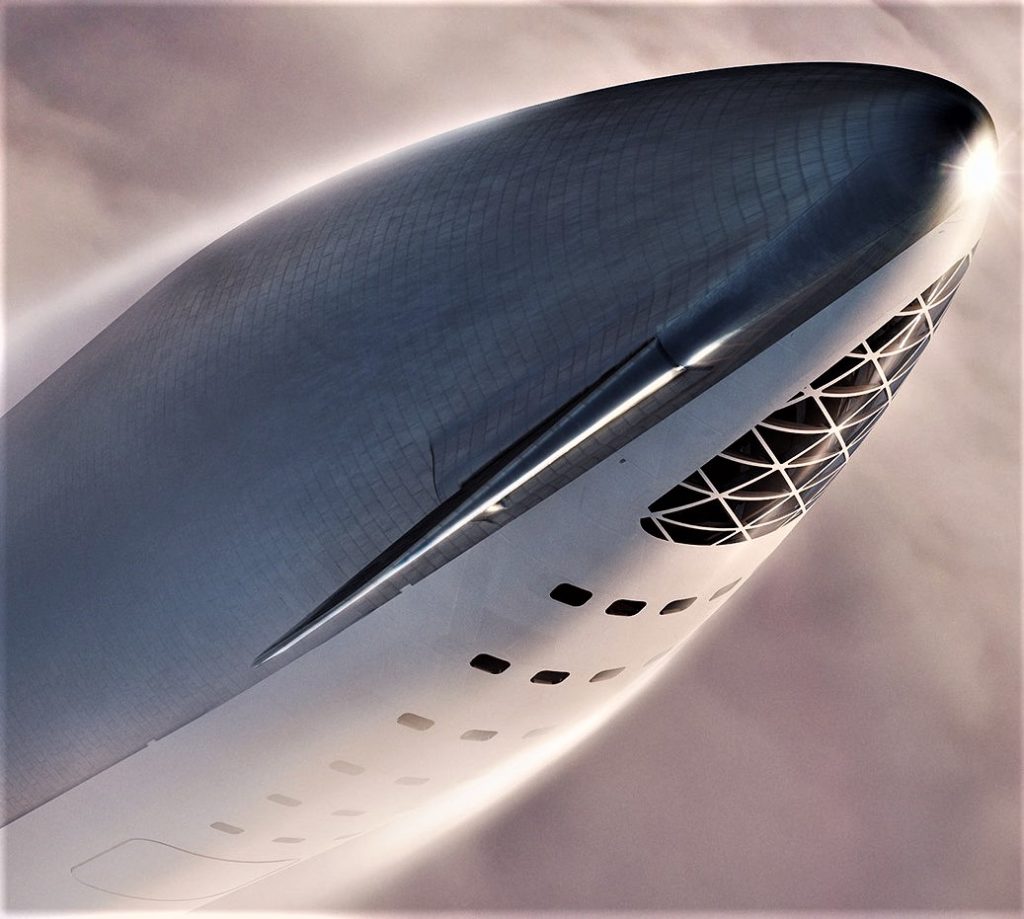
Following a September 17th presentation from CEO Elon Musk, SpaceX has published a series of uniquely detailed renders of BFR, showing off a number of new features present on the updated booster and spaceship, ranging from heat-shield tiles to Raptor pusher-rods.
To be clear, it’s possible that a skilled 3D designer took extreme artistic license and added miscellaneous trinkets and details that generally appear to look like true rocket components, but it seems unlikely that SpaceX (or Musk) would be okay with publicizing renders of a launch vehicle that go beyond the fidelity of what is already in work at an engineering level.
As such, the exceptionally detailed renders – published in 4K with a style nearly identical to Crew Dragon CGI posted recently – may directly rely on engineering-grade CAD (computer-aided design) drawings from SpaceX’s in-house BFR development team. Chances are good that that is the case to some extent, thanks largely to the fact that SpaceX has already begun fabricating full-scale structures for the first spaceship prototype. Building huge aerospace-grade subcomponents before the overall systems design has been completed is inadvisable depending on tolerances for waste, as the most likely outcome is having to build a new component when designs invariably change before any complex system’s various components work together on paper.
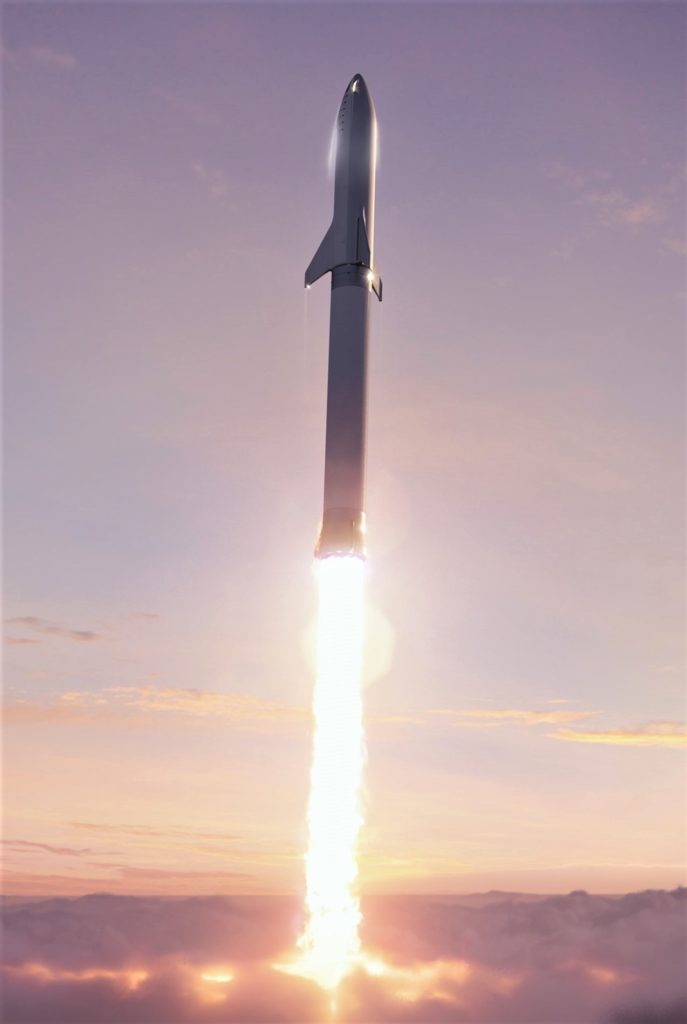
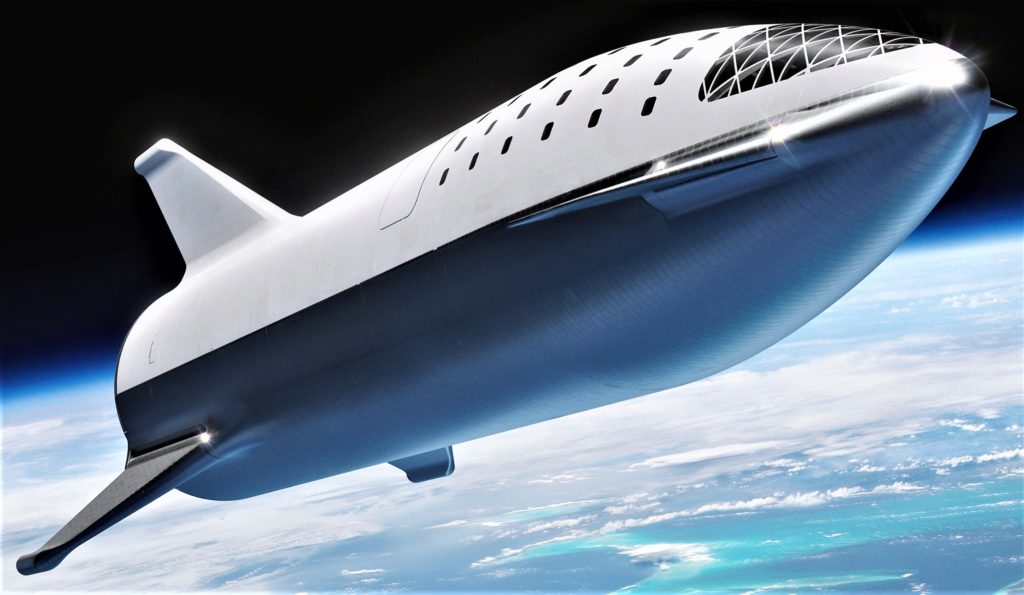
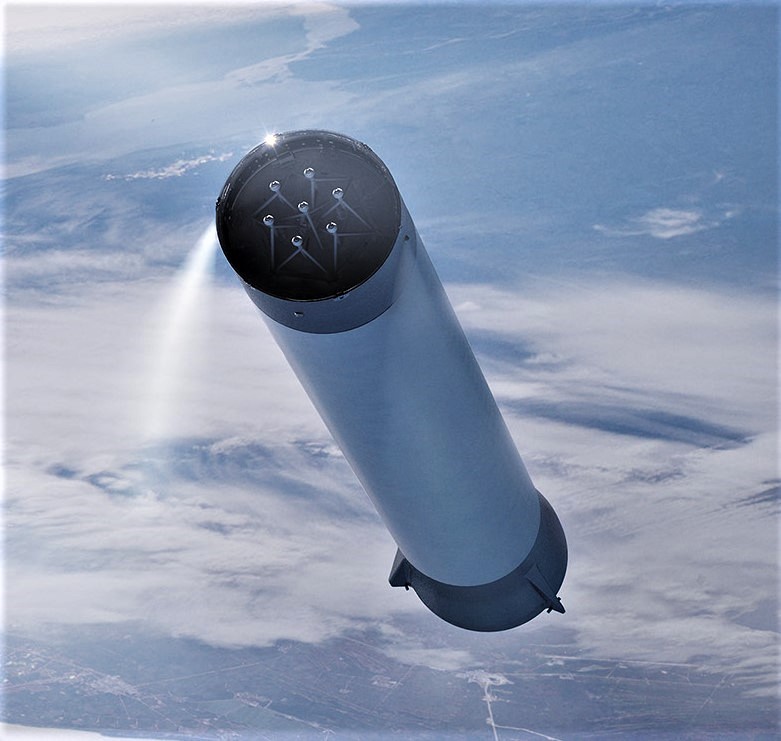
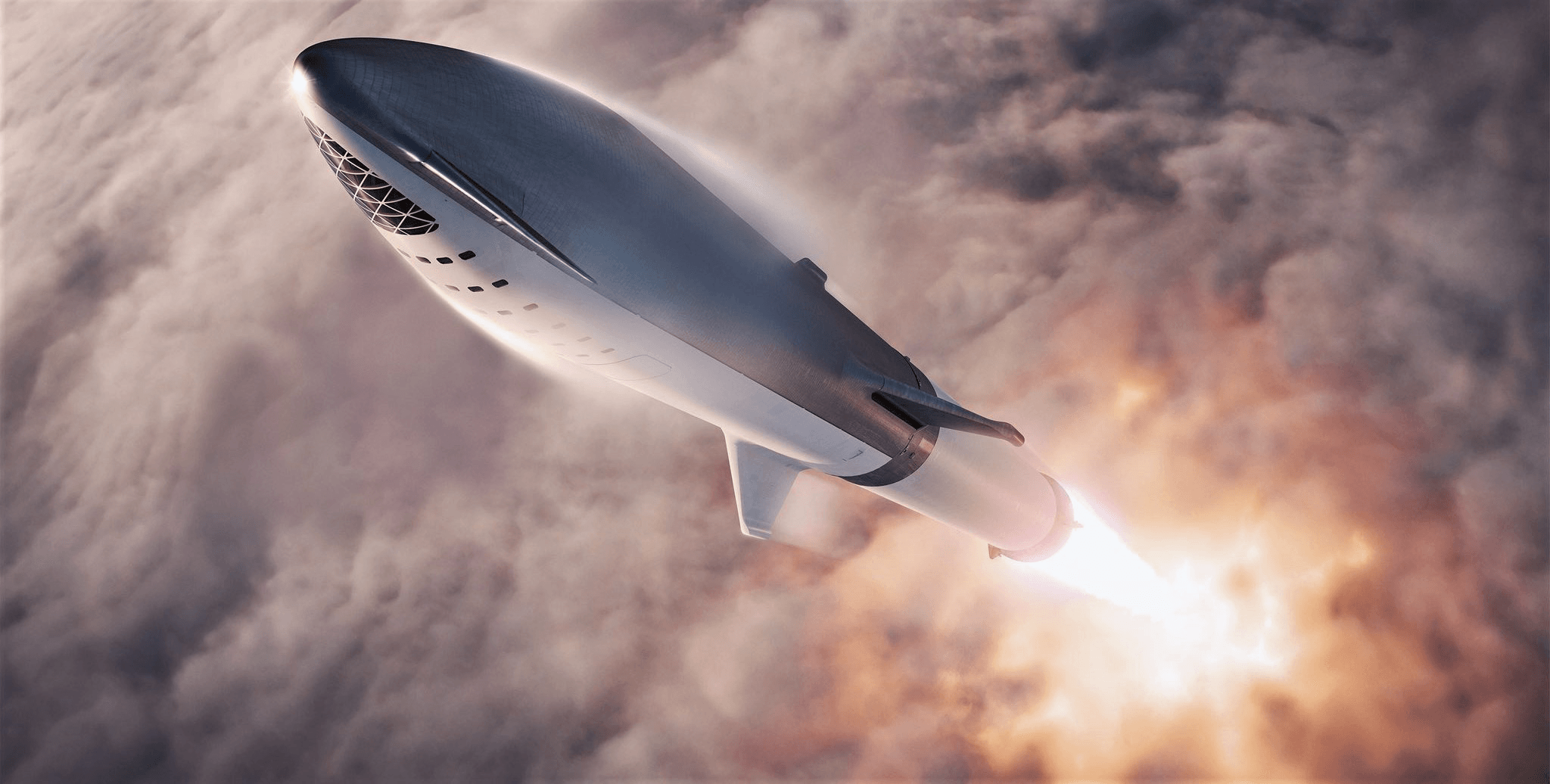
- BFR (2018) breaks through a cloud layer shortly after launch. (SpaceX)
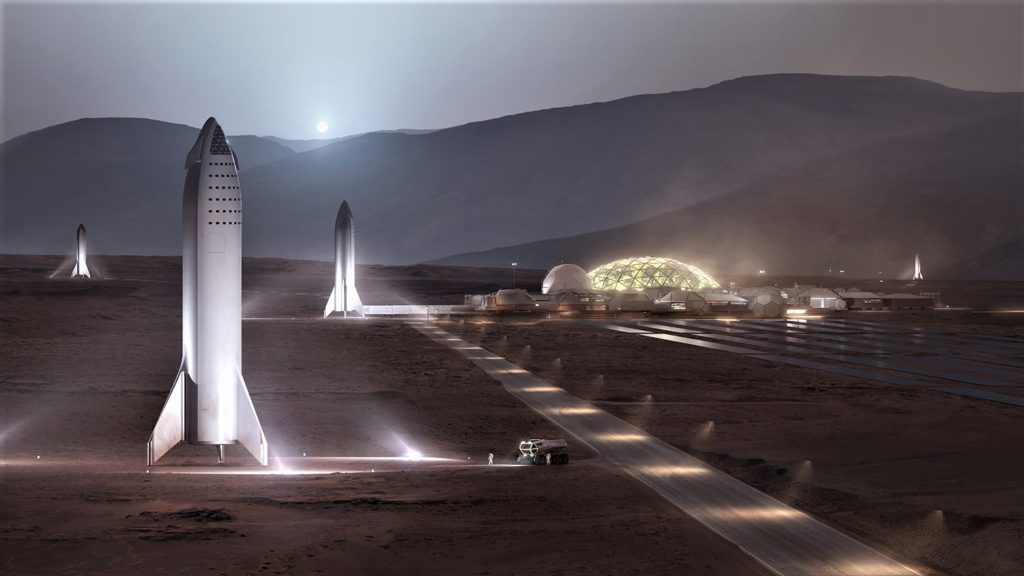
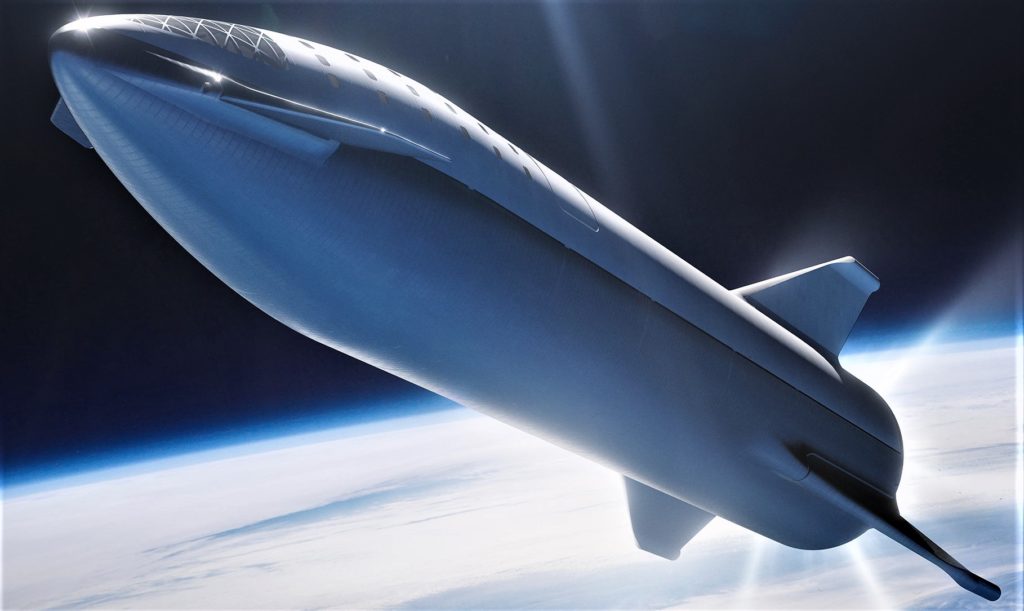
- A number of BFR (2018) spaceships seen landed at a future Mars base. (SpaceX)
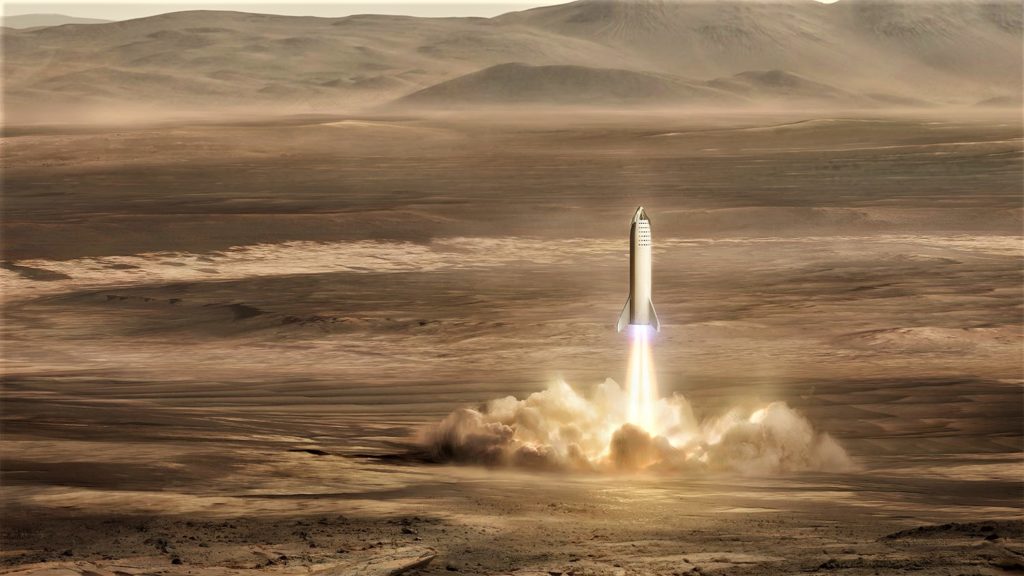
- An updated spaceship lands on Mars. (SpaceX)
At a minimum, the sheer level of detail included in these updated BFR renders points to a design that is more mature and closer to reality than anything SpaceX has shown before in its series of prospective Mars rockets presented over the last two years.
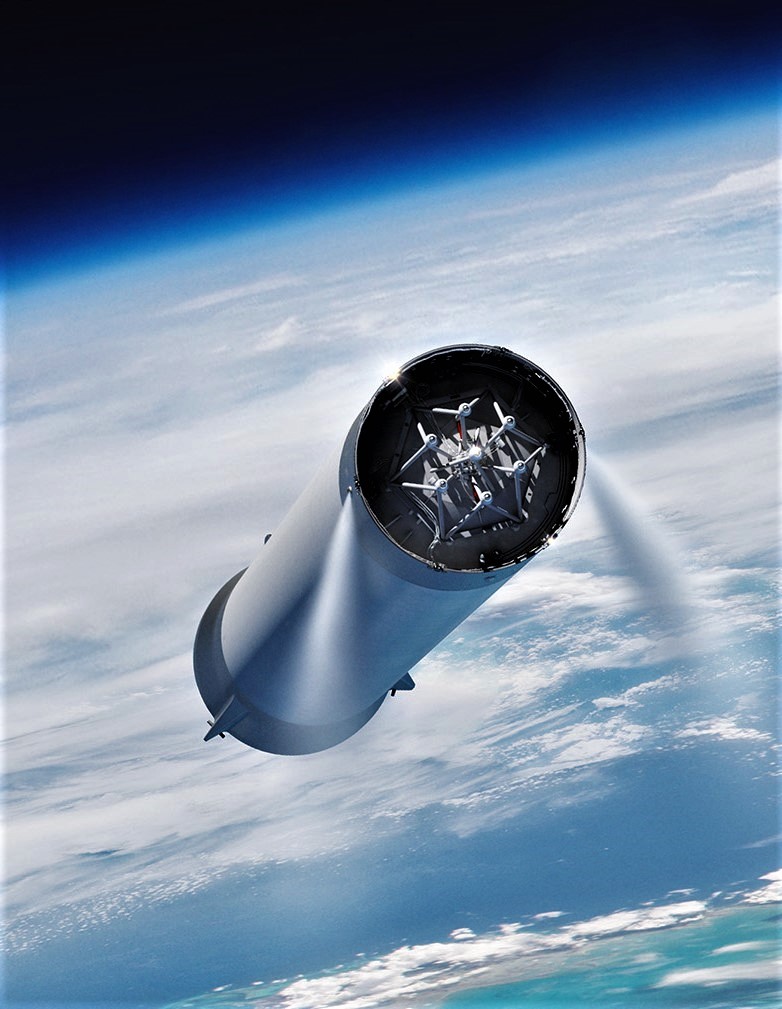
Highlights from SpaceX’s BFR (2018) renders include beautiful details of heat shield tiles, visible separation mechanisms between the spaceship and booster, an extremely detailed BFR booster interstage (featuring seven pusher rods for the upper stage’s seven Raptor engines, just like Falcon 9), and even spot-on plumes from the rocket’s thrusters.
- A closeup of BFS’ nose section, featuring impressively varied tile-sizes, joining methods, and extremely precise curves on the interface between canard wings and the hull. (SpaceX)
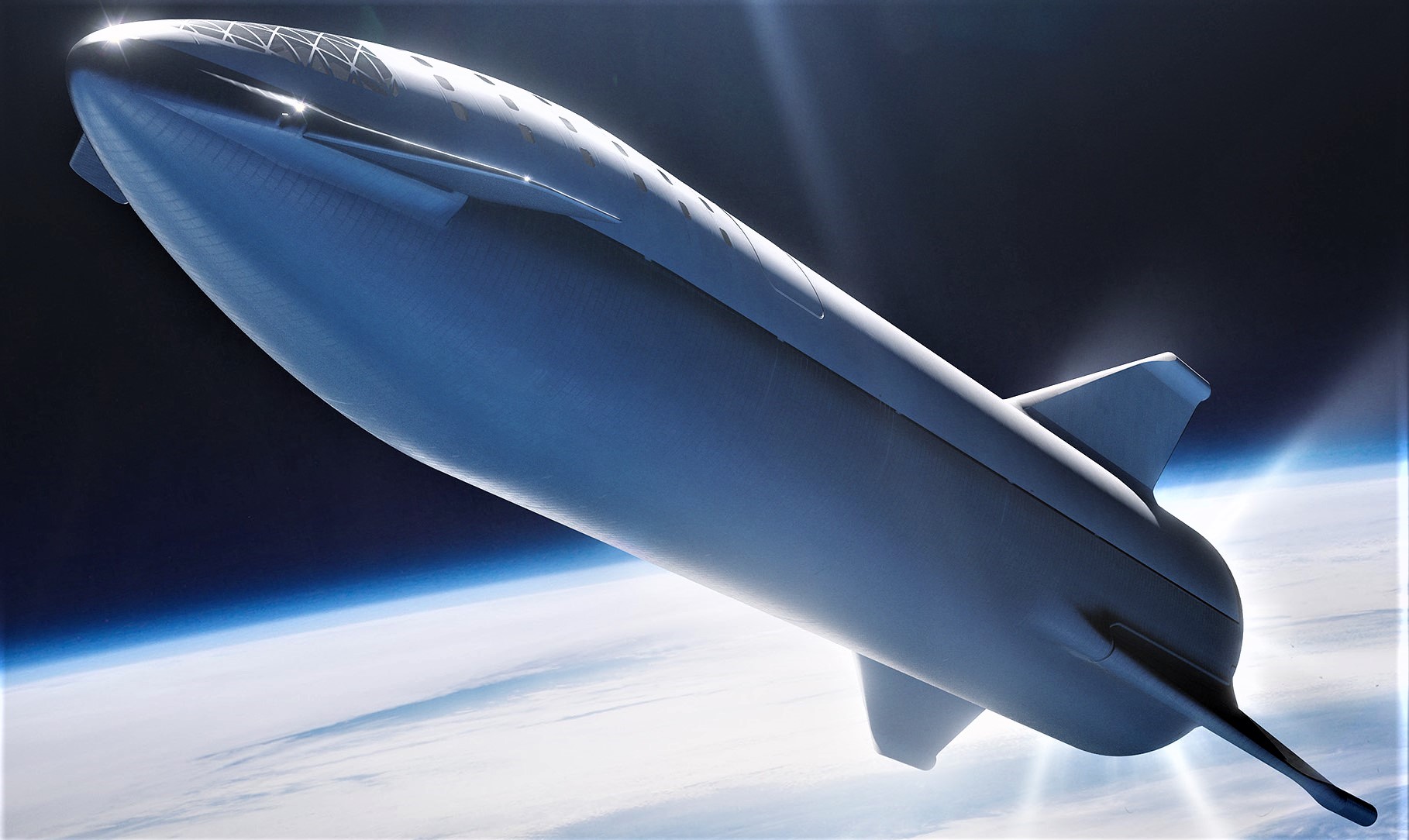
- A slightly broader overview of BFS just after separating from the booster. Note notches along the shield/skin divide, as well as very specific access panels, hatches, and smaller protuberances. (SpaceX)
- A view of BFS just after separating from its booster stage. (SpaceX)
The latter detail is particularly interesting because the thruster pods shown firing definitively take the place of where grid fins are later shown in certain slides – the most obvious conclusion is that a lower-fidelity model of BFR was used for the presentation’s animations, whereas the 3D model used for renders was far closer to the real deal. Musk did comment on Twitter that the lack of grid fins was a simple mistake on the part of the graphic designer, but it’s hard to parse that story (reasonable as it is) and the artists’ very specific decisions to place and illustrate RCS pods in action.
Good catch. They are there in the flight design, but we forgot to put them in this render.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) September 17, 2018
Perhaps SpaceX is entertaining the idea of entirely replacing grid fins with RCS (reaction control system) thrusters on the BFR booster, instead relying on its stubby aft fins for aerodynamic stability and using thrusters for course correction. One way or another, it’s extremely difficult to tell – while it’s probably best to side with Musk’s official comment, the possibility still remains that the replacement of grid fins with RCS thrusters was no accident.
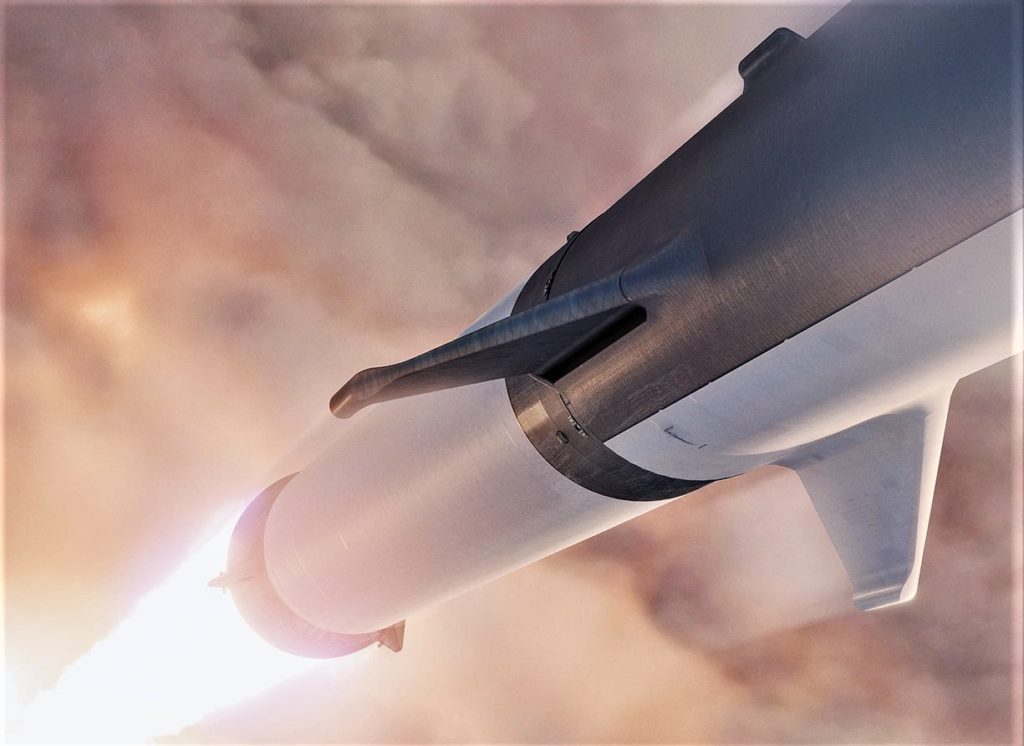
- A detailed view of BFR’s booster interstage, apparent lack of grid fins, RCS pod nubs, and more. (SpaceX)
- BFR’s booster, now known as Super Heavy. (SpaceX)
- Another view of the booster’s distinctly intentional RCS thrusters in place of grid fins. (SpaceX)
- A Falcon 9 Block 5 booster bares its interstage and pusher rod, offering a perfect illustration of its scale. (Bloomberg)
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!
News
SpaceX’s Crew-11 mission targets July 31 launch amid tight ISS schedule
The flight will lift off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

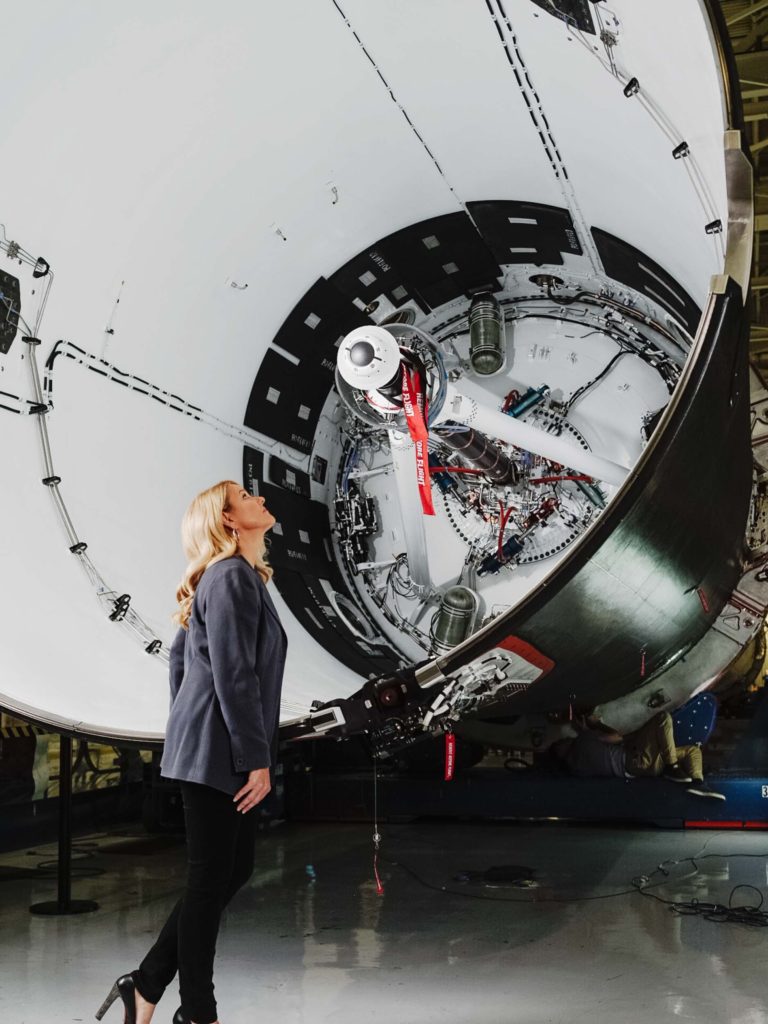
NASA and SpaceX are targeting July 31 for the launch of Crew-11, the next crewed mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The flight will lift off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using the Crew Dragon Endeavour and a Falcon 9 booster.
Crew Dragon Endeavour returns
Crew-11 will be the sixth flight for Endeavour, making it SpaceX’s most experienced crew vehicle to date. According to SpaceX’s director of Dragon mission management, Sarah Walker, Endeavour has already carried 18 astronauts representing eight countries since its first mission with NASA’s Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley in 2020, as noted in an MSN report.
“This Dragon spacecraft has successfully flown 18 crew members representing eight countries to space already, starting with (NASA astronauts) Bob (Behnken) and Doug (Hurley) in 2020, when it returned human spaceflight capabilities to the United States for the first time since the shuttle retired in July of 2011,” Walker said.
For this mission, Endeavour will debut SpaceX’s upgraded drogue 3.1 parachutes, designed to further enhance reentry safety. The parachutes are part of SpaceX’s ongoing improvements to its human-rated spacecraft, and Crew-11 will serve as their first operational test.
The Falcon 9 booster supporting this launch is core B1094, which has launched in two previous Starlink missions, as well as the private Ax-4 mission on June 25, as noted in a Space.com report.
The four-members of Crew-11 are NASA astronauts Zena Cardman and Mike Fincke, as well as Japan’s Kimiya Yui and Russia’s Oleg Platonov.
Tight launch timing
Crew-11 is slated to arrive at the ISS just as NASA coordinates a sequence of missions, including the departure of Crew-10 and the arrival of SpaceX’s CRS-33 mission. NASA’s Bill Spetch emphasized the need for careful planning amid limited launch resources, noting the importance of maintaining station altitude and resupply cadence.
“Providing multiple methods for us to maintain the station altitude is critically important as we continue to operate and get the most use out of our limited launch resources that we do have. We’re really looking forward to demonstrating that capability with (CRS-33) showing up after we get through the Crew-11 and Crew-10 handover,” Spetch stated.
Lifestyle
EV fans urge Tesla to acquire Unplugged Performance for edge in fleet and security industry
Unplugged Performance has built a name for itself by producing performance upgrades for Tesla vehicles.
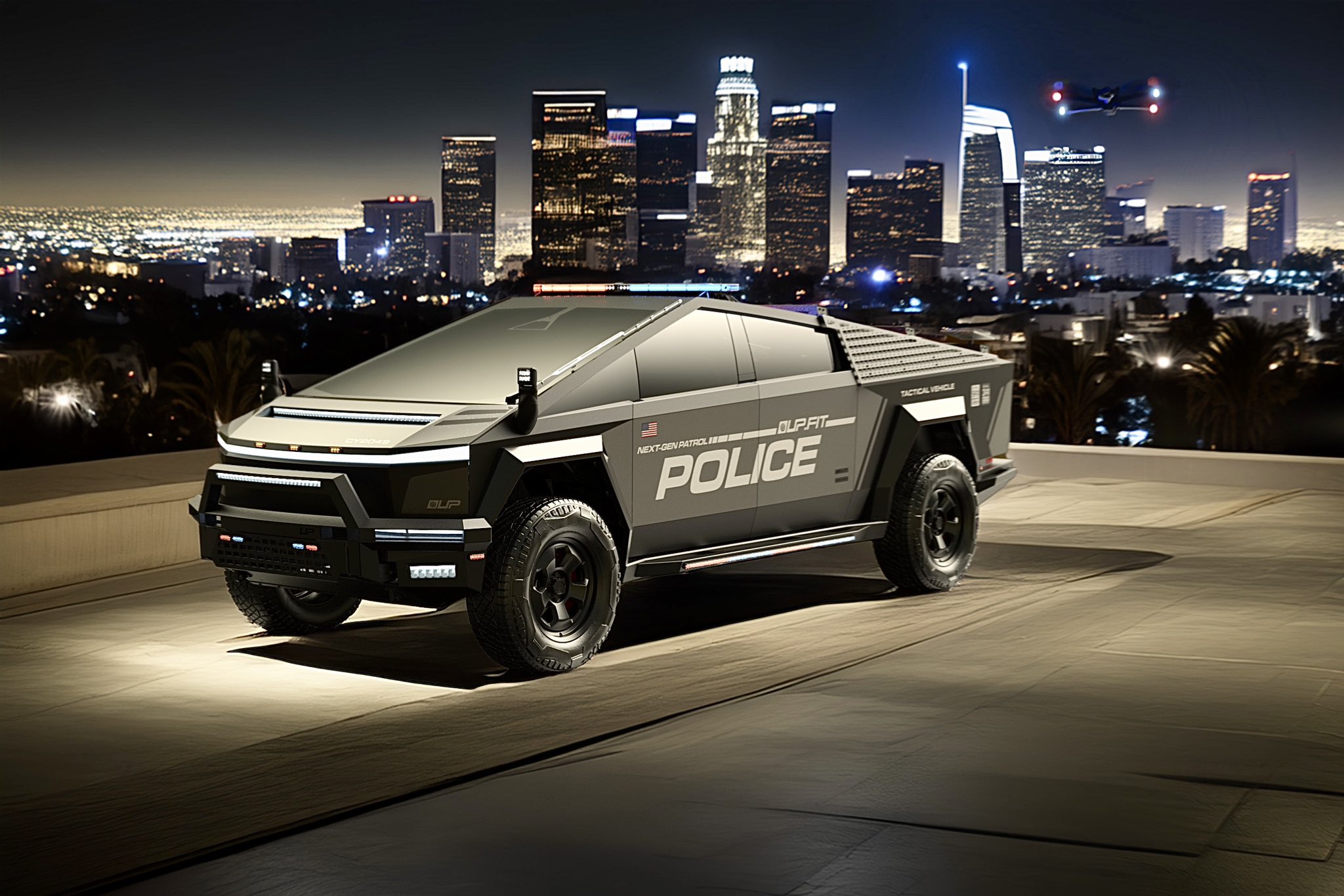

A growing number of Tesla enthusiasts and longtime community voices are calling on the electric vehicle maker to acquire Unplugged Performance, a California-based aftermarket company best known for tuning Tesla vehicles and developing specialized government fleet solutions under its UP.FIT division.
The idea was once considered a niche proposal among EV fans, but it is now gaining serious attention not just as a performance play but as a strategic move to deepen Tesla’s roots in the fleet and security industry.
A strategic fit
Unplugged Performance has built a name for itself by producing performance upgrades for Tesla vehicles, from track-optimized components to visual and aerodynamic upgrades. But in recent years, its UP.FIT division has pivoted toward a more functional future by outfitting Tesla vehicles like Model Ys for police, military, and government use.
That work has sparked growing calls for closer collaboration with Tesla, especially as the EV maker increasingly leans into autonomy, AI, and fleet services as core components of its next chapter.
“I posted this four years ago, but I think it’s more true now than ever,” wrote Whole Mars Catalog, a well-known Tesla investor and FSD Beta tester, on X. “Tesla should buy Unplugged. But not just as a Performance division. What they are doing with UP.FIT unlocks large government and commercial fleet purchases that can improve utilization.”
Tesla fans such as shareholder Sawyer Merritt echoed the sentiment, calling Unplugged a “great fit within Tesla.” adding, “They are literally located directly next to Tesla’s design studio in Hawthorne.”
Enabling the next wave
Supporters of the idea noted that integrating Unplugged into Tesla’s corporate structure could help accelerate the adoption of autonomous technologies in government sectors. With UP.FIT patrol cars already in use across some U.S. police departments, Tesla fans envisioned a future where self-driving Teslas could potentially revolutionize law enforcement, search-and-rescue, and public service logistics.
“Just imagine how autonomous patrol cars could transform policing and bring us into a safer future,” the veteran FSD tester wrote.
The benefits could also extend to Tesla’s existing consumer base. “They also have some incredible products in the works that I think will appeal to many ordinary Tesla drivers — not just those looking for performance or mods. Stuff that’s so good it should have come straight from the design studio next door,” Whole Mars Catalog noted.
Unplugged Performance, founded in 2013, shares not just a product vision with Tesla, but also geography. Its Hawthorne headquarters sits directly adjacent to Tesla’s design studio, and the two companies have maintained a close working relationship over the years. The aftermarket firm has long positioned itself as a “mission-aligned” partner to Tesla.
In response to the recent calls for acquisition, Unplugged Performance acknowledged the support from the community. “Our very existence is to support the Tesla mission with @UpfitTesla and @UnpluggedTesla,” Unplugged CEO Ben Schaffer posted on X. “We love working with Tesla and are grateful for the community’s support since 2013!”
News
Tesla debuts hands-free Grok AI with update 2025.26: What you need to know
All new Tesla vehicles delivered on or after July 12, 2025, will include Grok AI out of the box

Tesla has begun rolling out Grok, an in-car conversational AI assistant developed by xAI, to eligible vehicles starting July 12. The feature marks the most direct integration yet between Elon Musk’s artificial intelligence startup and Tesla’s consumer product lineup, offering drivers hands-free access to a chat-style companion while on the road.
Grok comes pre-installed on new vehicles
According to Tesla’s FAQ page for the feature, all new vehicles delivered on or after July 12, 2025, will include Grok AI out of the box. Owners of older vehicles may gain access through an over-the-air update, provided their vehicle meets a few hardware and software requirements.
Specifically, Grok is currently only supported on Tesla models equipped with an AMD infotainment processor and running vehicle software version 2025.26 and higher. Compatible models include the Model S, Model 3, Model X, Model Y, and Cybertruck. A Premium Connectivity subscription or active Wi-Fi connection is also required.
Tesla notes that additional vehicle compatibility may arrive in future software updates.
Grok’s features and limitations for now
Drivers can engage with Grok using the App Launcher or by pressing and holding the voice command button on the steering wheel. Grok is designed to answer questions and hold conversations using natural language, offering responses tailored to its chosen personality—ranging from “Storyteller” to the more eccentric “Unhinged.”
For fun, Tesla posted a demonstration of Grok likely running on “Unhinged” talking about what it would do to Optimus when they are on a date, much to the shock of the humanoid robot’s official social media account.
It should be noted, however, that Grok cannot currently issue commands to the vehicle itself, at least for now. Traditional voice commands for tasks like climate control, navigation, or media remain separate from Grok as of writing.
The feature is being released in Beta and does not require a Grok account or xAI subscription to activate, although that policy may change over time.
Grok privacy and in-car experience
Tesla emphasizes that interactions with Grok are securely processed by xAI and not linked to a user’s Tesla account or vehicle. Conversations remain anonymous unless a user signs into Grok separately to sync their history across devices.
Tesla has also begun promoting Grok directly on its official vehicle webpages, showcasing the feature as part of its in-car experience, further highlighting the company’s increasing focus on AI and infotainment features on its all-electric vehicles.
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk5 days ago
Elon Musk5 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla sees explosive sales growth in UK, Spain, and Netherlands in June