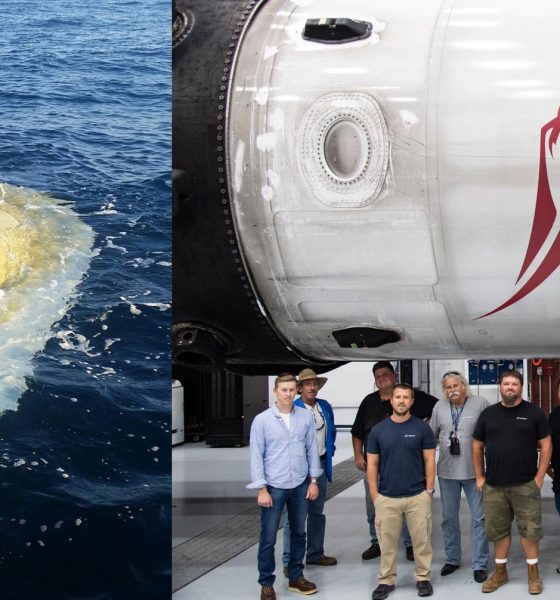

SpaceX
SpaceX Falcon 9 Block 5 booster preps for next launch as fairing fragments surface
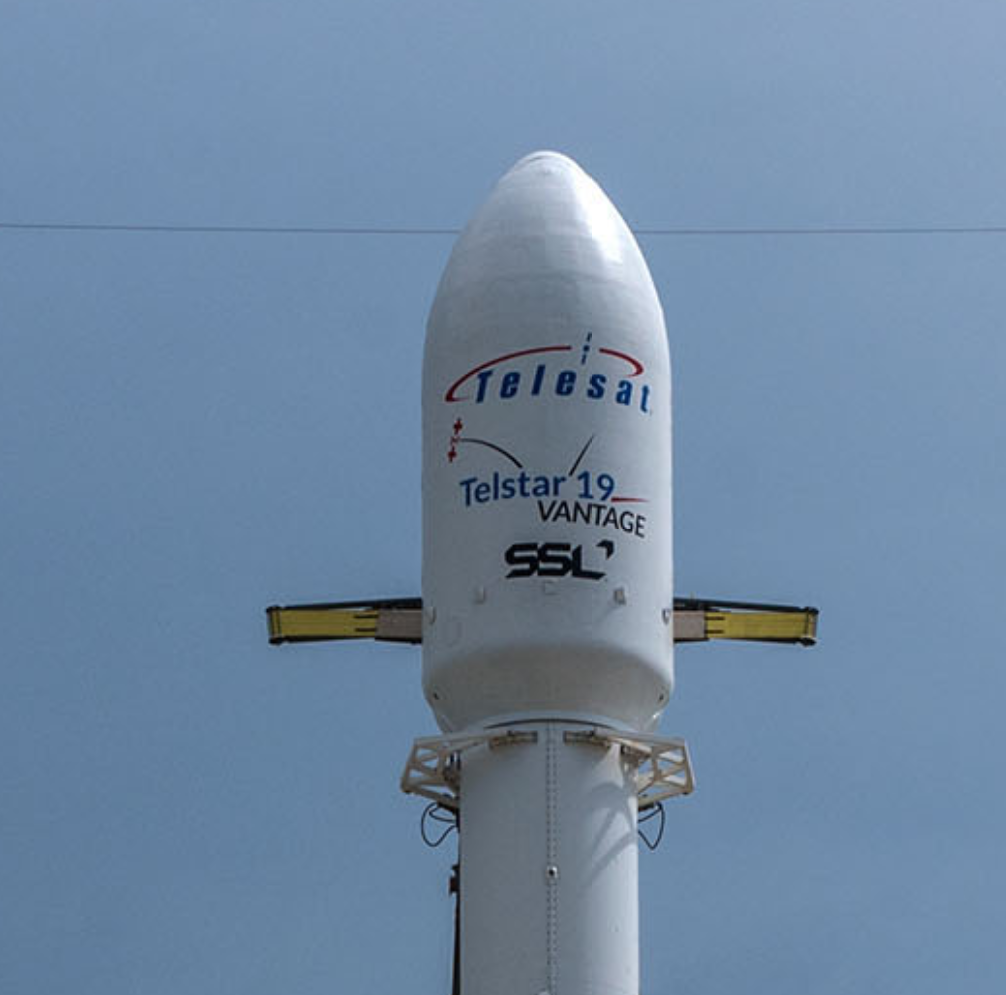
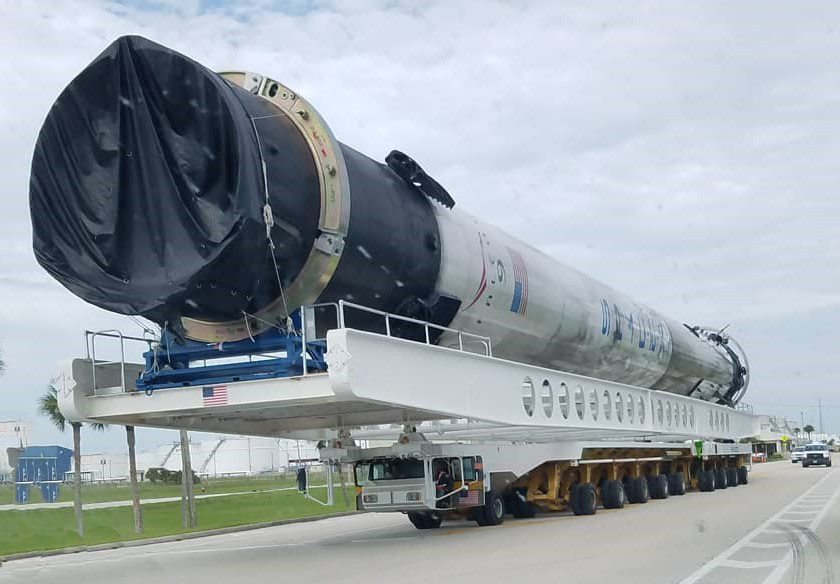
As part of a recent 10-year anniversary celebration of SpaceX’s first successful launch to reach orbit, Falcon 9 B1047 was spotted undergoing inspections and refurbishment after the Block 5 booster’s launch debut, placing the 7-ton Telstar 19V communications satellite in orbit on July 22nd.
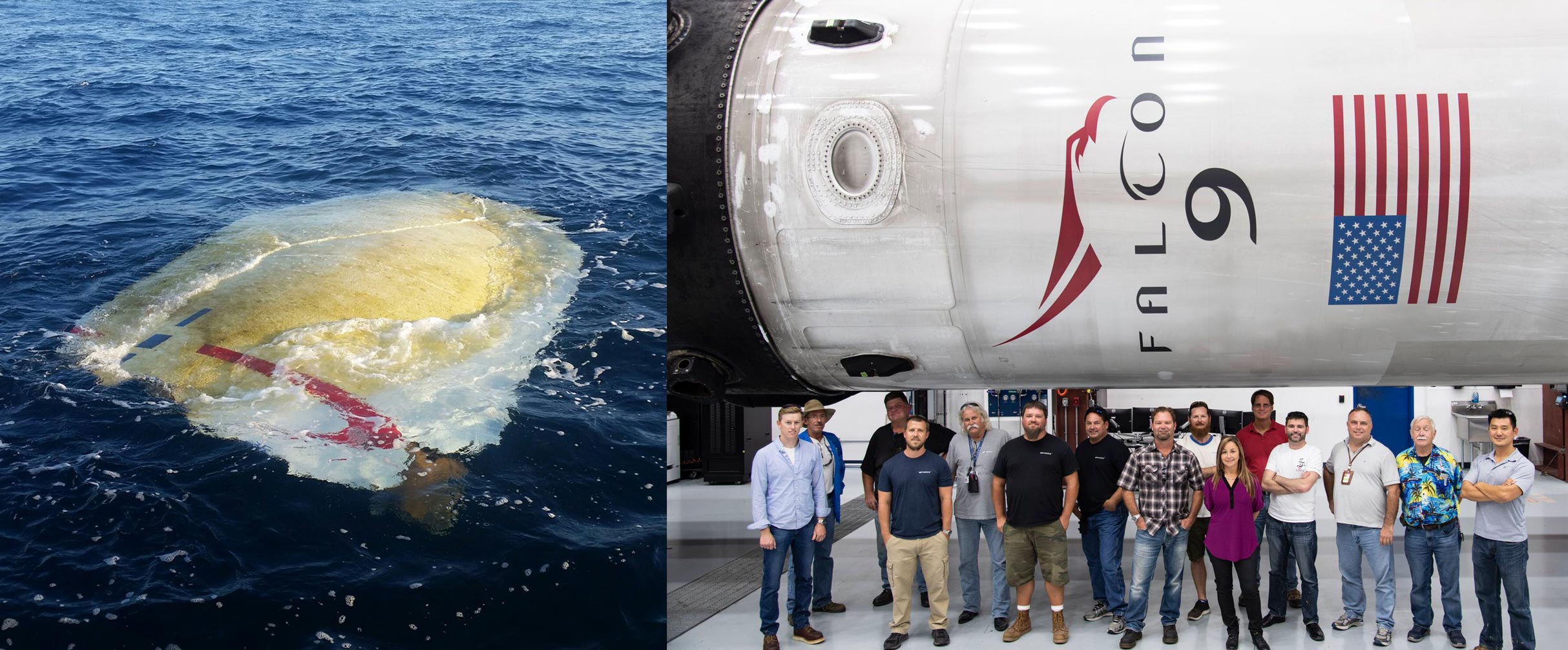
Meanwhile, a bit north of B1047’s cozy Cape Canaveral refurbishment hangar, battered fragments of a Falcon 9 payload fairing half – part of the very same Telstar 19V mission – were discovered by a fisherman off the coast of South Carolina.
https://twitter.com/SpaceXJobs/status/1045832573471969281?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw%7Ctwcamp%5Etweetembed%7Ctwterm%5E1045832573471969281&ref_url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.teslarati.com%2Fwp-admin%2Fpost.php%3Fpost%3D84909%26action%3Dedit
A tale of two halves
Around nine minutes after lifting off from SpaceX’s LC-40 pad, Falcon 9 B1047 gracefully landed on drone ship Of Course I Still Love You (OCISLY), followed soon after by confirmation of Falcon 9 Block 5’s second launch success. Perhaps a tad toasty after what one might call a ‘medium-well’ reentry, the upgraded booster was otherwise perfectly intact. A minute after B1047 separated from Falcon 9’s upper stage and Telstar 19V payload, the fairing – tasked with protecting the satellite from the stresses of high-speed atmospheric flight – was jettisoned from the second stage, splitting into two halves and falling away from the rocket in order to save precious mass on S2’s push towards orbit.
Falcon 9’s first stage separates from the upper stage for quite different reasons, cued quite literally by its propellant tanks essentially reaching “empty” – albeit an “empty” that typically includes some fumes for the booster’s safe recovery. The payload fairing, on the other hand, is detached from the second stage the moment that Falcon rises above a particular point in Earth’s atmosphere, only exposing its sensitive satellite(s) to the elements once in near-vacuum conditions. Ultimately, fairing halves separate from Falcon 9 at velocities significantly higher than that of the booster but are subjected to far more forgiving reentry conditions, requiring just a minimal of thermal protection to make it to (or just above…) the ground/ocean unscathed.
Detailed images of GO Pursuit returning to Port Canaveral this afternoon with a partial fairing half following Sunday’s launch of Falcon 9 and Telstar 19V. Damage is no surprise, as these east coast fairings — for now — land in the water. pic.twitter.com/AxkwUQH67b
— John Kraus (@johnkrausphotos) July 24, 2018
SpaceX recently began seriously attempting to recover Falcon 9 payload fairings, albeit almost exclusively during West Coast launches in order to let Mr. Steven attempt to catch the parasailing halves in the Pacific Ocean. Thus far, SpaceX engineers and technicians have not yet solved the challenging problems, although fairing halves have reportedly landed as few as 50 meters from Mr. Steven’s grasp and at least five have been recovered intact after landing gently on the ocean surface. On the East Coast, Falcon fairings are not nearly as lucky, typically alternating between smashing directly into the ocean and landing gently upon it, depending SpaceX’s need for experimental recovery data.
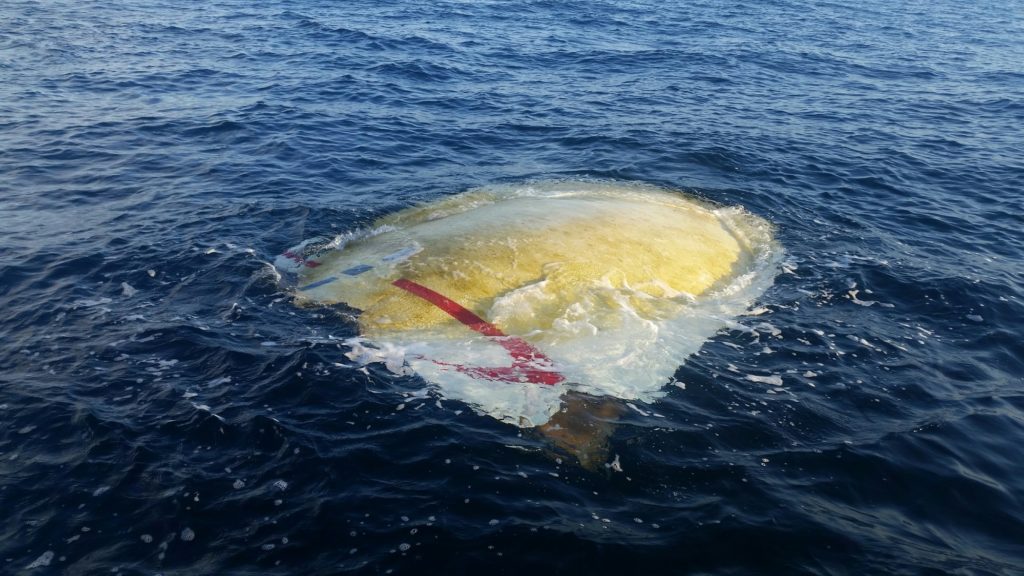
By all appearances, B1047’s fairing halves both plummeted – unarrested – into the Atlantic, shattering into pieces of fragile carbon fiber-aluminum honeycomb. Thanks to the extremely lightweight nature of their composition, even waterlogged fairing fragments tend to float almost indefinitely, winding up in far-flung places many hundreds or thousands of miles from the point of impact. A particularly large fairing fragment from Telstar 19V clearly survived its greater halve’s violent ends, floating its way 600-800 miles northwest to the coast of South Carolina. After taking photos, the fisherman rather poetically let it float away, permitting it several more weeks of freedom before washing up on some shoreline and making its way onto eBay.
- A Falcon 9 fairing fragment was discovered floating off the coast of South Carolina two months after launching with Telstar 19V. (TheHullTruth /u/gofish)
- Telstar 19V’s Falcon fairing artwork, a dead-ringer for the fairing flotsam. (SpaceX)
- B1047 returned safe and sound to Pad 39A for refurbishment less than a week after launching and landing. (Instagram /u/d_lo_ags)
Ultimately, SpaceX engineers and technicians will continue to work towards successful, reliable, and routine fairing recoveries, inevitably experiencing many failures before a functional solution is found and optimized, just like the teams that brought Falcon 9 first stage recovery from blueprint to reality. In the meantime, serendipitous events like this will continue to serve as both stark reminders of the unforgiving hurdles along the path to orbital-class rocket hardware recovery and the undeniable fact that it already can and has been done before.

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.











