

SpaceX
SpaceX to build small version of BFR’s spaceship for use on Falcon 9, says Elon Musk
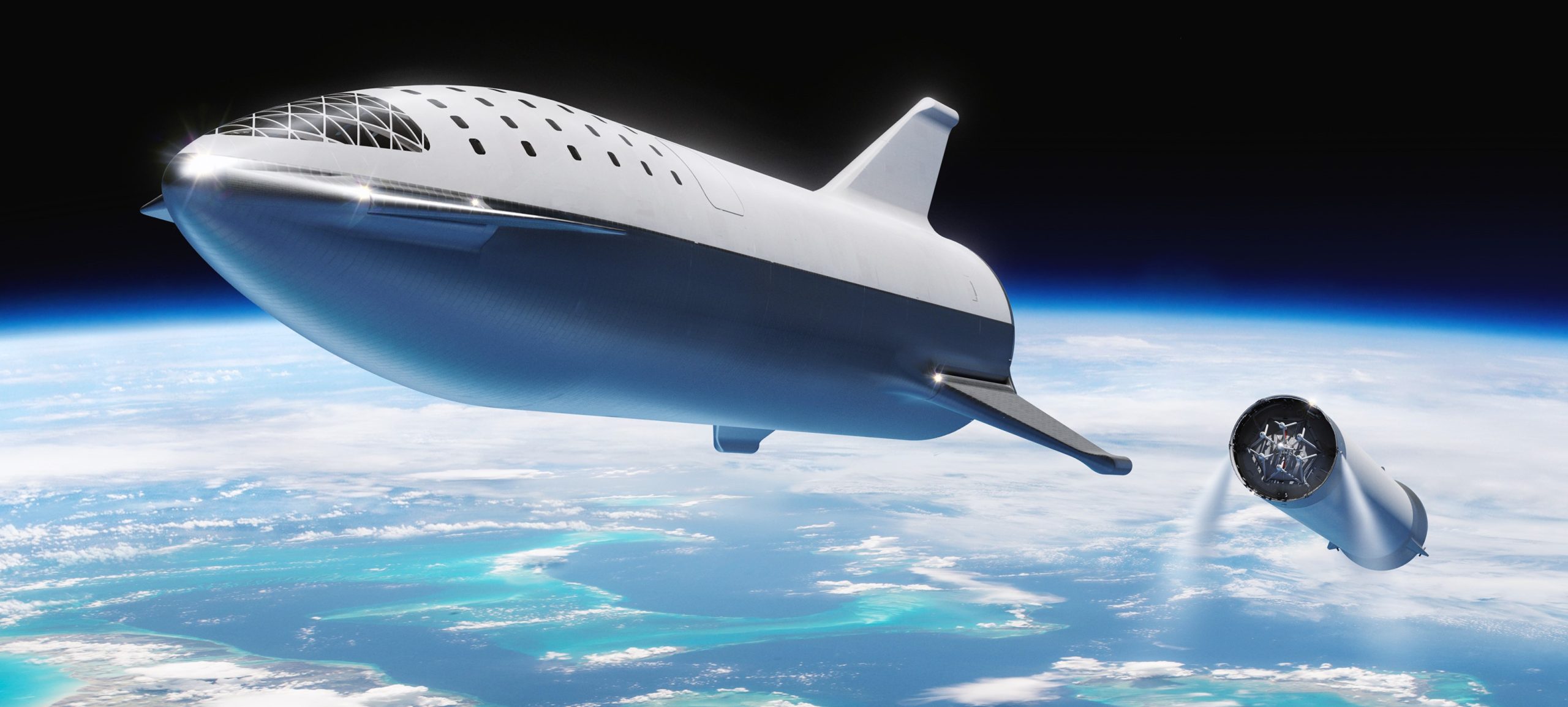
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk has taken to Twitter to announce a new development program: in order to gain experience with the new design and recovery strategy, SpaceX engineers and technicians will apparently build a miniature version of BFR’s winged spaceship able to launch atop Falcon 9 or Falcon Heavy.
According to Musk, the company aims to conduct the first orbital flight of this mini-BFS as early as June 2019, just eight months away.
Mod to SpaceX tech tree build: Falcon 9 second stage will be upgraded to be like a mini-BFR Ship
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) November 7, 2018
Described as a “SpaceX tech tree build”, Musk seems to be implying that the strategic purpose of this new development is to act as a stepping stone between Falcon 9 and BFR, two dramatically different launch vehicles relying on a variety of entirely distinct technologies. Based on the fact that Musk believes the mini-BFS could reach orbit as early as June 2019, it seems likely that the miniature spaceship will essentially just be a strengthened Falcon 9 upper stage with fins and a heat shield attached versus a more extreme departure, where the stage would literally be a mini-BFS.
In the latter scenario, SpaceX could use the opportunity to extensively test – albeit on a smaller scale – a number of immature BFR technologies, including all-composite propellant tanks, autogenous pressurization, a sea level-optimized rocket engine on an orbital upper stage, methane and oxygen (methalox) propellant, actuatable tripod fins, new heat shield materials, and more. If SpaceX has been working on this for several months, there is still a chance that those technologies will be tested on this step-change Falcon 9 S2 variant, but it seems improbable that Musk would have been able to stay totally silent on the plans during his September 2018 update to the BFR program.
- BFR’s spaceship and booster (now Starship and Super Heavy) separate in a mid-2018 render of the vehicle. (SpaceX)
- A detailed view of BFR’s booster interstage, apparent lack of grid fins, RCS pod nubs, and more. (SpaceX)
- A closeup of BFS’ nose section, featuring impressively varied tile-sizes, joining methods, and extremely precise curves on the interface between canard wings and the hull. (SpaceX)
Falcon 9 upper-stage recovery
Going off of what little information we have, it seems more likely that the “mini-BFR ship” described by Musk is an effort to realize Falcon 9 upper stage recovery and test BFR’s orbital spaceship recovery strategies than it is an extensive development platform for all critical BFR technologies. Prior to today’s tweet, Musk announced early this year (April, to be precise) that SpaceX would attempt to recovery Falcon 9’s upper stage with a “giant…balloon”, or an inflatable decelerator to use the technical terminology.
SpaceX will try to bring rocket upper stage back from orbital velocity using a giant party balloon
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) April 15, 2018
Given this new development, it’s unclear if those plans are still on – as a small spaceship, Falcon 9’s upper stage would likely be able to reenter Earth’s atmosphere without the need for something like a single-use inflatable decelerator, which would have always been a suboptimal crutch for the recovery of any orbital spacecraft, be it Falcon 9 or BFR. With this new plan, it appears that SpaceX wants to kill at least two birds with one stone, building a platform capable of flight-testing a handful of new technologies critical to BFR’s success while also potentially realizing the dream of a fully-reusable Falcon 9.
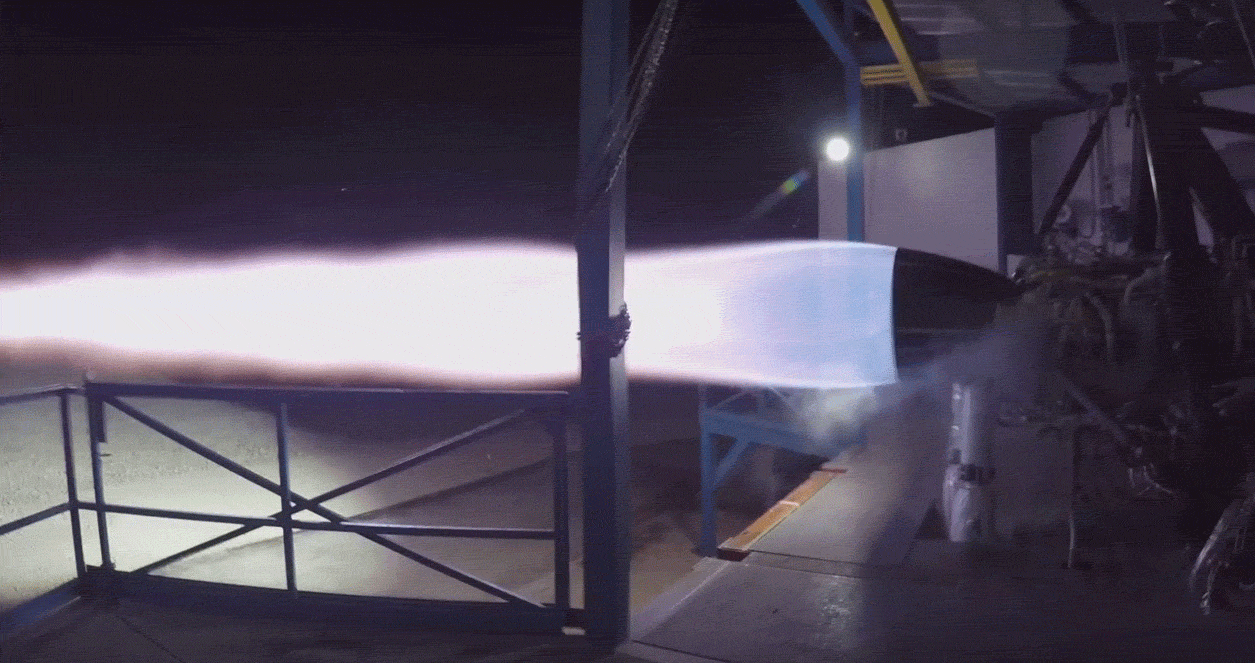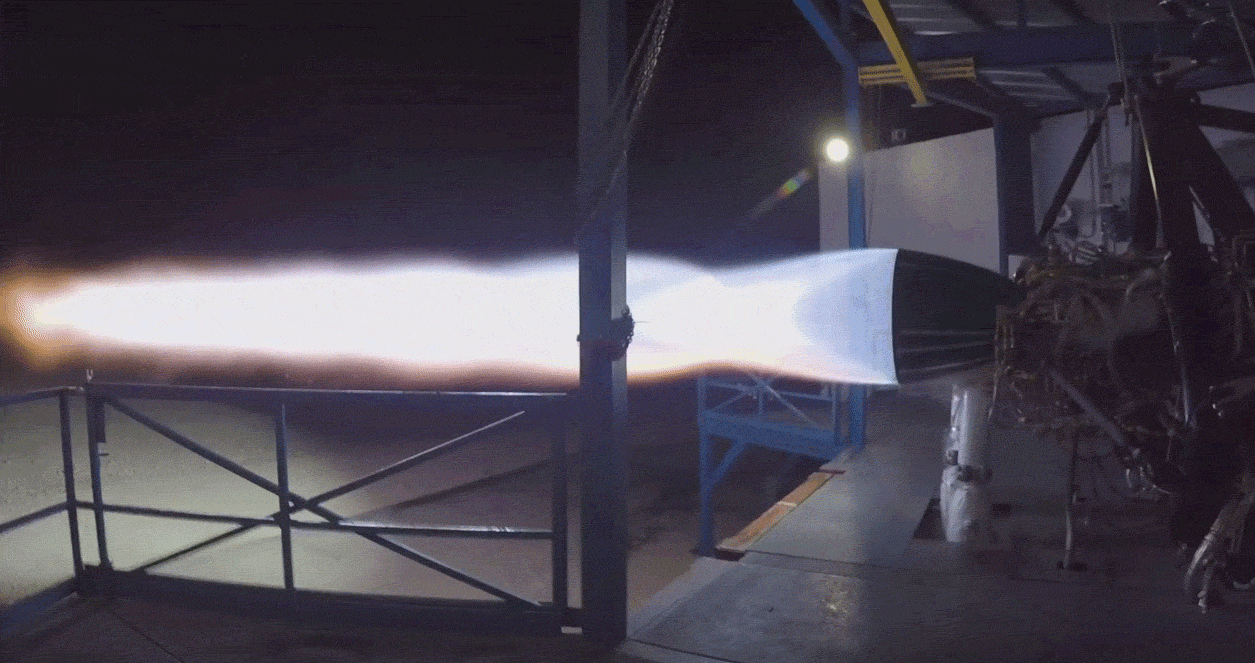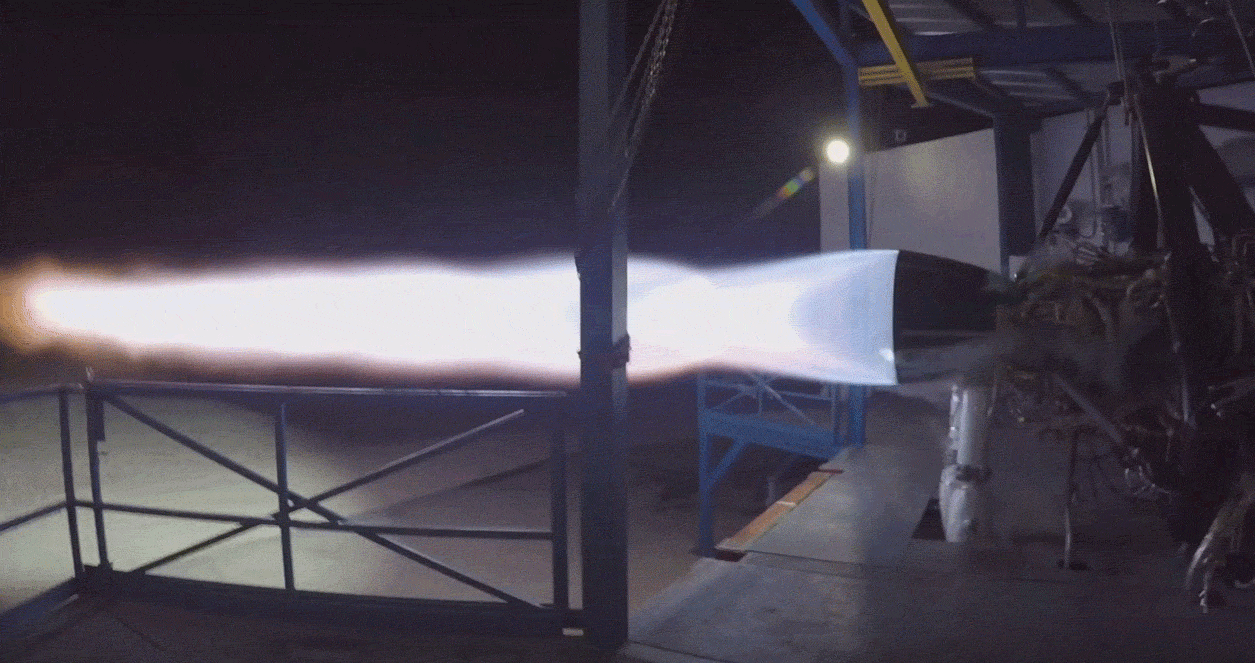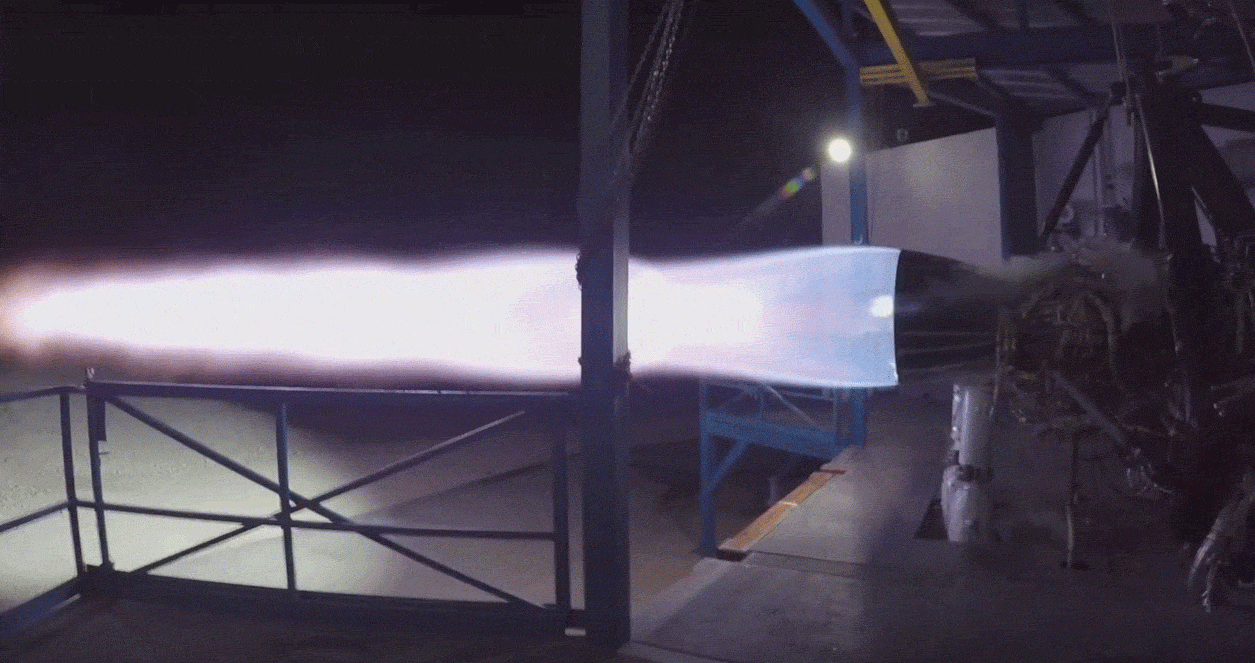
Given recent reports from Reuters that Musk has demanded that SpaceX’s Starlink team work towards the first launch of an operational batch of satellites by mid-2019, his target date for a mini-BFS Falcon 9 upper stage is likely no coincidence. Given the potential risk of being the first to launch on an unproven variant of Falcon 9, it’s possible (if not probable) that SpaceX will conduct its own launch of the rocket prior to flying paying customers – a perfect way to avoid wasting that launch would be risking a few of SpaceX’s own Starlink satellites in place of a customer’s payload.
Won’t land propulsively for those reasons. Ultra light heat shield & high Mach control surfaces are what we can’t test well without orbital entry. I think we have a handle on propulsive landings.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) November 7, 2018
Musk seems to be confident that SpaceX has effectively ‘solved’ propulsive rocket landings, stating that the purpose of this new variant will be dedicated to testing an “ultra light heat shield and high Mach control surfaces”. Judging from a number of recent job postings focused on new thermal protection systems (and affixing them to composite structures) and an official request for information (RFI) from NASA Ames about its lightweight TUFROC heat shield material, this is a major focus and one of several critical paths for BFR development.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!

Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Elon Musk
NASA watchdog says Starship development delays could affect Artemis timeline
The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before Starship can serve as a crewed lunar lander.

A NASA watchdog report stated that continued development work on SpaceX’s Starship could affect the timeline for the agency’s planned Artemis moon missions. The report noted that several technical milestones still need to be completed before the spacecraft can serve as a crewed lunar lander.
The findings were detailed in a report from NASA’s Office of Inspector General, as noted in a report from Reuters.
NASA selected SpaceX’s Starship in 2021 to serve as the Human Landing System (HLS) for its Artemis lunar program. The vehicle is intended to transport astronauts from lunar orbit to the surface of the Moon and back as part of future Artemis missions.
According to the watchdog report, Starship’s development has experienced roughly two years of schedule delays compared to earlier expectations. Still, NASA is targeting 2028 for the first crewed lunar landing using the Starship lander.
One of the most significant technical milestones for Starship’s lunar missions is in-space refueling.
To support a crewed lunar landing, multiple Starship launches will be required to deliver propellant to orbit. Tanker versions of Starship will transfer fuel to a storage depot spacecraft, which will then refuel the lunar lander.
The report noted that this approach could require more than 10 Starship launches to fully refuel the spacecraft needed for a single lunar landing mission.
NASA officials indicated that demonstrating cryogenic propellant transfer in orbit remains one of the most important technical steps before Starship can be certified for lunar missions.
SpaceX has conducted 11 Starship test flights since 2023 as the company continues developing the fully reusable launch system. A 12th test flight, this time featuring Starship V3, is expected to be held in early April.
Elon Musk
SpaceX weighs Nasdaq listing as company explores early index entry: report
The company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX is reportedly leaning toward listing its shares on the Nasdaq for a potential initial public offering (IPO) that could become the largest in history.
As per a recent report, the company is reportedly seeking early inclusion in the Nasdaq-100 index. The update was reported by Reuters, citing people familiar with the matter.
According to the publication, SpaceX is considering Nasdaq as the venue for its eventual IPO, though the New York Stock Exchange is also competing for the listing. Neither exchange has reportedly been informed of a final decision.
Reuters has previously reported that SpaceX could pursue an IPO as early as June, though the company’s plans could still change.
One of the publication’s sources also suggested that SpaceX is targeting a valuation of about $1.75 trillion for its IPO. At that level, the company would rank among the largest publicly traded firms in the United States by market capitalization.
Nasdaq has proposed a rule change that could accelerate the inclusion of newly listed megacap companies into the Nasdaq-100 index.
Under the proposed “Fast Entry” rule, a newly listed company could qualify for the index in less than a month if its market capitalization ranks among the top 40 companies already included in the Nasdaq-100.
If SpaceX is successful in achieving its target valuation of $1.75 trillion, it would become the sixth-largest company by market value in the United States, at least based on recent share prices.
Newly listed companies typically have to wait up to a year before becoming eligible for major indexes such as the Nasdaq-100 or S&P 500.
Inclusion in a major index can significantly broaden a company’s shareholder base because many institutional investors purchase shares through index-tracking funds.
According to Reuters, Nasdaq’s proposed fast-track rule is partly intended to attract highly valued private companies such as SpaceX, OpenAI, and Anthropic to list on the exchange.











