

News
Tesla Autopilot and FSD Beta can be a remedy for drivers with PTSD — even in their imperfect state
It took Tesla owner Matthew Kerle a whole month to get behind the wheel of a car and drive on the highway once more. And when he did, things were not the same.
Just a few weeks before, Kerle was riding in his friend’s Pontiac Grand Am when the driver approached a sharp curve too fast. It was dusk, and the road was unfamiliar. Upon realizing that they were about to crash, Kerle braced for impact, planting his feet on the car’s floor and clenching his iPhone as tightly as he could in his hand. The driver tried to slow down, but it was not enough, and the vehicle started rolling. The impact was so violent that Kerle’s iPhone and shoes were wrenched from his hands and feet.
Things moved in slow motion at that point. Kerle hoped that the vehicle would roll a couple of times and he and his friends could get out. But it was not to be. Rolling in a car is one of Kerle’s biggest fears, but he steeled himself, hoping that the vehicle would eventually stop. It did, but the rolling sensation and shower of broken glass were quickly replaced by a sudden rush of cold, dark water. Unlike in the movies where the water slowly rises when a car falls into water, Kerle and his friends were immediately submerged.
The aftermath of Kerle’s accident. (Credit: Matthew Kerle)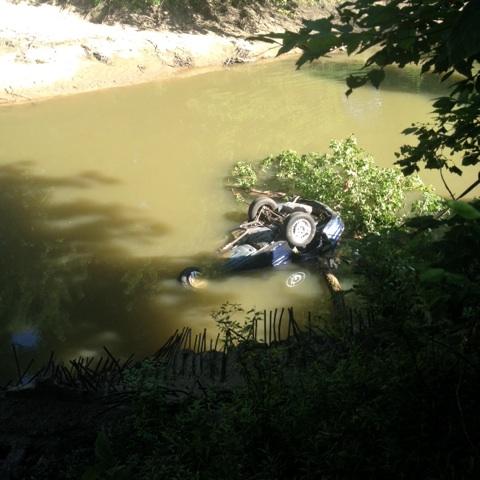
It took a significant degree of faith and some luck, but Kerle was eventually able to get out of the overturned Pontiac. Upon reaching solid ground, he saw that his four other friends were still underwater. Injured, exhausted, and shaking from the experience, Kerle called out for his friends. Fortunately, all four emerged from the water, some more injured than the others. But the group’s tribulations were not done yet, as they had to walk almost a mile to find help. Kerle ended up in the hospital, where he recovered from his injuries. But as he went home days later, he realized that things were no longer the same.
The harrowing experience with the crash and near-death experience gave Kerle PTSD. He found himself unable to drive at speed or at night. Going over railroad tracks was a trigger, and even showers were not a respite as the sound of the water hitting his ears triggered flashbacks of the accident. Kerle’s physical injuries healed, but the mental scars of his near-death experience stayed. He eventually started driving again, but it was a constant mental battle. He could drive, but there were still times when the trauma of the accident came back.
A Hidden Issue
Kerle’s experience is not unique among American drivers. A survey conducted by online insurance comparison service The Zebra revealed that about 66% of Americans experience driving anxiety, with 55% reporting that they feel it while performing common driving maneuvers. Out of those who experienced anxiety behind the wheel, 26% stated that they were most anxious when merging into the highway and 19% stated that they were most anxious when they are backing up or reversing. About 62% of Americans also reported having a past traumatic driving experience.
Dr. Rachel Cavallaro, a licensed Psychologist with Thriveworks in Boston, informed Teslarati that vehicular accidents are the leading cause of post-traumatic stress disorder in the general population. Considering that there are 6 million car accidents in the United States with over 2.5 million injuries, this is not a surprise. A study from the American Psychological Association also revealed that car accidents are the number one trauma for men and the second most frequent trauma for women. A study conducted by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) further revealed that 39.2% of motor vehicle accident survivors develop some form of PTSD as well.
Credit: The Zebra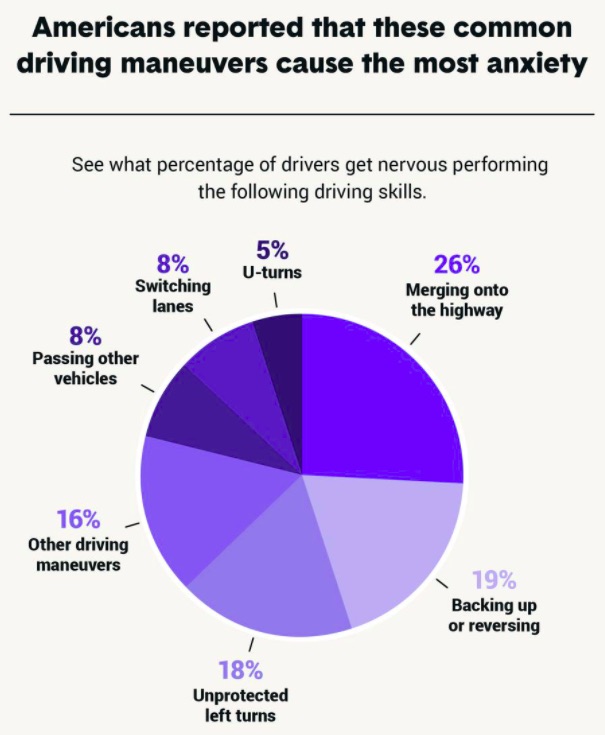
“Many people with these conditions avoid driving altogether. If they do decide to drive, they endure it with intense anxiety such as heart palpitations, sweating, muscle tension, an underlying feeling of restlessness, or irritability. These individuals may go to great lengths to avoid highways or roads they view as dangerous. For individuals who have PTSD symptoms, they may have intrusive thoughts or memories which further interfere with their ability to attend to the road. In more severe cases, the individual may experience flashbacks or dissociate,” Cavallaro said.
Needless to say, Kerle’s experiences and the challenges he faced in his recovery are shared by numerous other drivers in the United States. Jay Varela, a therapist from Thriveworks in Roanoke, outlined some of the issues typically faced by drivers who struggle with PTSD on the road, and Kerle’s experiences were on the dot.
“It can be extremely challenging for someone suffering from PTSD or driving phobia to drive a vehicle on their own. Individuals with PTSD struggle with ‘triggers’ that remind them of their traumatic experiences. Vehicular accident survivors can experience many triggers while driving, such as the makes and models of cars, weather conditions, or noises. Such triggers can lead to a fight-or-flight response. Fight-or-flight responses can make it difficult to maintain safe driving habits. Furthermore, individuals may engage in ‘safety behaviors’ to manage their symptoms. These can include stopping suddenly, driving well below the speed limit, or becoming fixated on the rearview mirror,” Varela said.
An Imperfectly Useful Solution
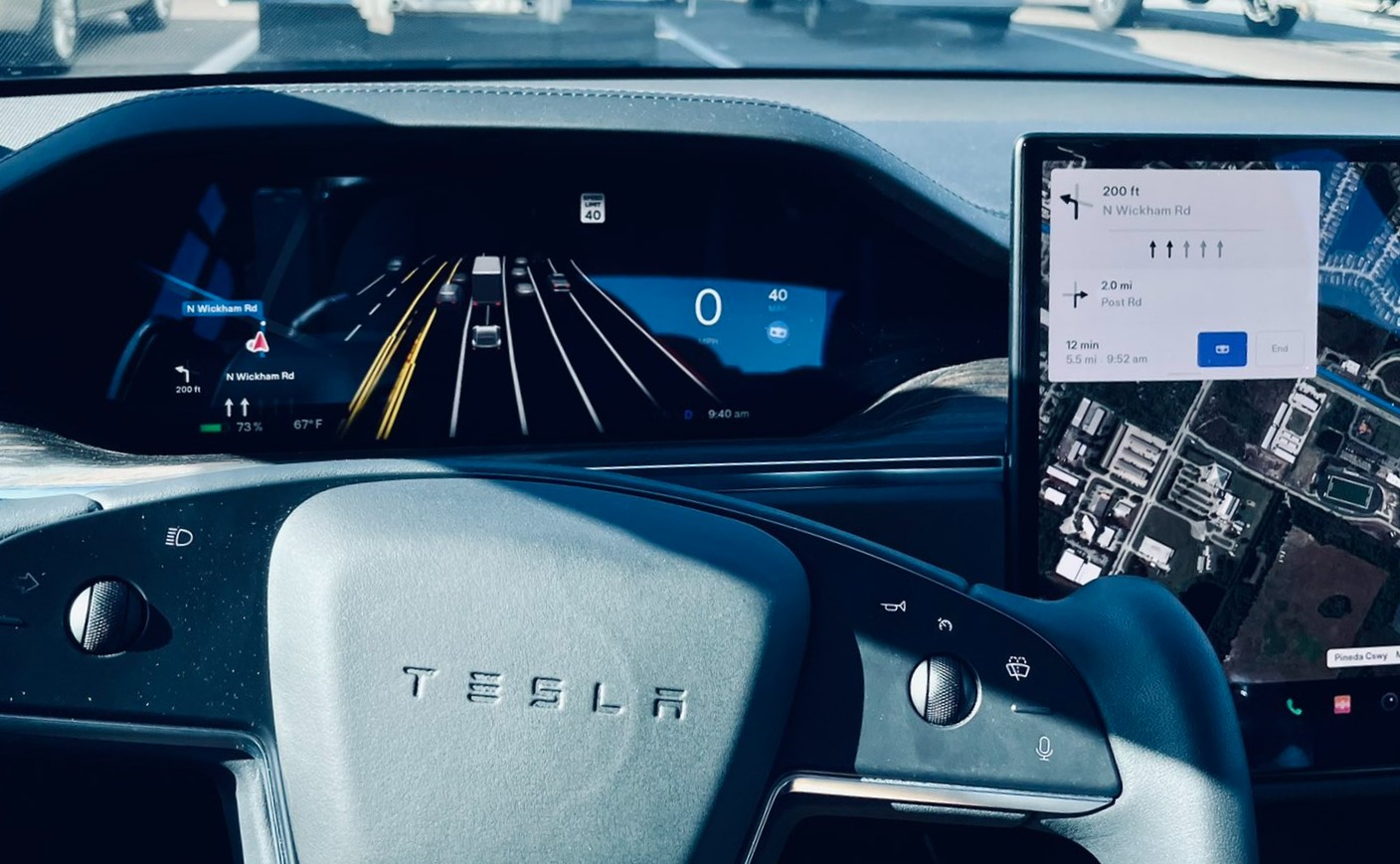
For Kerle, his driving experiences took a turn for the better in 2019 when he took delivery of his Tesla Model 3. By then, he was living in a Phoenix suburb and his commute was very long. Since electric vehicles have lane access, he figured that a Tesla could help him get to work and home faster. Kerle admitted that Tesla’s tech intrigued him, and because he is more of a tech guy than a car guy, he could not stay away from Autopilot. It should be noted that back in 2019, Autopilot is nowhere near as refined as it is today, but for Kerle, it was already life-changing.
“When you work with a system long enough, you start to understand it,” Kerle told Teslarati, adding that when he first got Autopilot, he tended to distrust the driver-assist system since it would behave differently than a human driver. But over time and as he got more used to Autopilot’s behaviors, Kerle started realizing that Tesla’s driver-assist technologies are really optimized for safety. The car may not behave like a human driver at times, but it is careful nonetheless.
“After a while, you’re like, ‘All right, I know in situations like this, here’s how it’s going to respond.’ It is going to slow down three car lengths nearby. It’s gonna make it. It’s not gonna cause an accident. And then you start to build a trust and an understanding. And so what I’d say is that you really learn what (Autopilot) does really well and areas that it might not be perfect. You can’t just blindly trust it to do everything and not pay attention, so I really view the relationship between a driver and FSD or Autopilot as a partnership, with the driver taking the role of a supervisor,” Kerle said.

Eventually, Kerle noted that even Autopilot’s rather strange behaviors are rooted in safety. He told Teslarati about an experience in which Autopilot moved over and sharply jerked back to its original lane. Initially, Kerle thought it was a bug that needed to be reported, but he soon realized that his car jerked back because a careless driver was speeding on the adjacent lane. Had he intervened then and completed the lane change, Kerle noted that he might have ended up being involved in a crash again.
“When you’re changing lanes, what do you do? You look in your mirror, you turn, you turn and look for cars, and your field of view is very narrow, and you’re taking your eyes off all of the other parts of the road. That is actually a very dangerous thing, and it causes a lot of accidents. Autopilot can see every direction. Now it understands time space. It understands based where cars are, where they’re doing to be, and what they’re doing.
“And it making a lane change is actually very safe because it understands what’s going on around it better than a human would. So I think that as supervisors, as it is shifting to become a lot better than humans in a lot of cases, one of the most dangerous things that we can do is take over when it actually has it, because we can mess it up,” Kerle said.
Kerle is now married with a growing family, so he has bought a Tesla Model X to make sure his kids are as safe as possible. He is also now part of the company’s FSD Beta program, which allows him to use automatic driving on inner-city streets.
An Infinitely Useful Work in Progress
For Cavallaro, the presence of driver-assist systems that take the stress of driving tasks is invaluable today since the systems could help reduce the fear of driving while increasing the feeling of safety. Varela adds that the presence of automated driving features in vehicles could help individuals suffering from PTSD or driving phobia maintain their independence.
“Many individuals with PTSD and/or driving phobia may feel unable to drive and this can lead to a loss of independence. Such a loss may have serious impacts on occupational, social, and overall personal functioning. Automated driving systems may help them regain their independence by reducing mental strain and safeguarding against dangerous safety behaviors,” Varela said.
Both Tesla Autopilot and FSD Beta are a work in progress, and there is also no denying the fact that the company’s self-driving efforts are running quite late. But having seen the rate of improvement in both Autopilot and FSD Beta, Kerle believes that it is just a matter of time before Tesla attains actual autonomous driving. Even in their current form and capabilities, Kerle highlighted that Autopilot and FSD Beta had shown him just how much stress manual driving could bring.

“Before I got my Model 3, because of my PTSD, I did not understand how much stress driving to work caused me. When I got FSD and when I got comfortable with it, I had significantly more energy and significantly less stress — by a significant margin — like, other people noticed. And so, I did not really understand how much stress driving and rush hour traffic for an hour each way adds to your life and how exhausting it is to your body. And FSD Beta, yes, you have to supervise and pay attention, but it still removes a massive amount of stress and exhaustion.
“I’m supervising, I’m making sure it’s driving safely, but I don’t have to worry ‘Is that car in front of me gonna slam on its brakes, and do I need to react in a quarter of a second or crash?’ ‘If I’m changing lanes, do I have to be stressed about a situation that I can’t see and can’t control, but need to see where I’m gonna crash?’ All of those little, little things that you’re constantly fixated on while you’re driving are removed to just ensuring that the system is driving properly and safely. The stress reduction is insane,” Kerle said.
A Note from the Author
As someone who deals with driving anxiety and sudden OCD tendencies on the road, this article strikes close to home. Unfortunately, Tesla is not available everywhere yet, and it’s no secret that the company’s vehicles, at least for now, still cater to buyers of premium vehicles. For those who shop at the lower end of the auto market, manual driving is still the norm, and it could be for a while. With this in mind, it is pertinent to know what to do to lessen the mental strain of driving, and where to seek help.
Ken Goodman, one of the board of directors for the Anxiety and Depression Association of America and the creator of The Anxiety Solution Series, informed Teslarati that drivers who are suffering from driving anxiety should start with easier forms of driving first, and work their way up to more difficult tasks later. Goodman noted that starting with neighborhood driving is a good idea, before transitioning to highway driving later on. Driving on the fast lane could also come later when drivers become a bit more comfortable behind the wheel.
Ultimately, however, Goodman advised that the best solution is still to see a therapist that specializes in the treatment of driving anxiety.
Cavallaro, for her part, added that Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and associated approaches could help drivers who are suffering from PTSD and driving phobia. “Cognitive Behavioral Therapy has been empirical validated and supported for PTSD as well as associated anxiety disorders. Additionally, Prolonged Exposure (PE) and Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) are specific forms of CBT that were created to treat PTSD,” she said.
Don’t hesitate to contact us with news tips. Just send a message to simon@teslarati.com to give us a heads up.

Elon Musk
What is Digital Optimus? The new Tesla and xAI project explained
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Tesla and xAI announced their groundbreaking joint project, Digital Optimus, also nicknamed “Macrohard” in a humorous jab at Microsoft, earlier this week.
This software-based AI agent is designed to automate complex office workflows by observing and replicating human interactions with computers. As the first major outcome of Tesla’s $2 billion investment in xAI, it represents a powerful fusion of hardware efficiency and advanced reasoning.
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Macrohard or Digital Optimus is a joint xAI-Tesla project, coming as part of Tesla’s investment agreement with xAI.
Grok is the master conductor/navigator with deep understanding of the world to direct digital Optimus, which is processing and actioning the past 5 secs of…
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 11, 2026
Tesla’s specialized AI acts as “System 1”—the fast, instinctive executor—processing the past five seconds of real-time computer screen video along with keyboard and mouse actions to perform immediate tasks.
xAI’s Grok model serves as “System 2,” the strategic “master conductor” or navigator, providing high-level reasoning, world understanding, and directional oversight, much like an advanced turn-by-turn navigation system.
When combined, the two can create a powerful AI-based assistant that can complete everything from accounting work to HR tasks.
Will Tesla join the fold? Predicting a triple merger with SpaceX and xAI
The system runs primarily on Tesla’s low-cost AI4 inference chip, minimizing expensive Nvidia resources from xAI for competitive, real-time performance.
Elon Musk described it as “the only real-time smart AI system” capable, in principle, of emulating the functions of entire companies, handling everything from accounting and HR to repetitive digital operations.
Timelines point to swift deployment. Announced just days ago, Musk expects Digital Optimus to be ready for user experience within about six months, targeting rollout around September 2026.
It will integrate into all AI4-equipped Tesla vehicles, enabling parked cars to handle office work during downtime. Millions of dedicated units are also planned for deployment at Supercharger stations, tapping into roughly 7 gigawatts of available power.
Oh and it works in all AI4-equipped cars, so your car can do office work for you when not driving.
We’re also deploying millions of dedicated Digital Optimus units in the field at Superchargers where we have ~7 gigawatts of available power.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 12, 2026
Digital Optimus directly supports Tesla’s broader autonomy strategy. It leverages the same end-to-end neural networks, computer vision, and real-time decision-making tech that power Full Self-Driving (FSD) software and the physical Optimus humanoid robot.
By repurposing idle vehicle compute and extending AI4 hardware beyond driving, the project scales Tesla’s autonomy ecosystem from roads to digital workspaces.
As a virtual counterpart to physical Optimus, it divides labor: software agents manage screen-based tasks while humanoid robots tackle physical ones, accelerating Tesla’s vision of general-purpose AI for productivity, Robotaxi fleets, and beyond.
In essence, Digital Optimus bridges Tesla’s vehicle and robotics autonomy with enterprise-scale AI, promising massive efficiency gains. No other company currently matches its real-time capabilities on such accessible hardware.
It really could be one of the most crucial developments Tesla and xAI begin to integrate, as it could revolutionize how people work and travel.
News
Tesla adds awesome new driving feature to Model Y
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.

Tesla is adding an awesome new driving feature to Model Y vehicles, effective on Juniper-updated models considered model year 2026 or newer.
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.
Tesla writes in the release notes for the feature:
“Your Tesla now provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.”
🚨 Tesla has added a new “Comfort Braking” update with 2026.8
“Your Tesla provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.” https://t.co/afqCpBSVeA pic.twitter.com/C6MRmzfzls
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
Interestingly, we’re not too sure what catalyzed Tesla to try to improve braking smoothness, because it hasn’t seemed overly abrupt or rough from my perspective. Although the brake pedal in my Model Y is rarely used due to Regenerative Braking, it seems Tesla wanted to try to make the ride comfort even smoother for owners.
There is always room for improvement, though, and it seems that there is a way to make braking smoother for passengers while the vehicle is coming to a stop.
This is far from the first time Tesla has attempted to improve its ride comfort through Over-the-Air updates, as it has rolled out updates to improve regenerative braking performance, handling while using Full Self-Driving, improvements to Steer-by-Wire to Cybertruck, and even recent releases that have combatted Active Road Noise.
Tesla holds a unique ability to change the functionality of its vehicles through software updates, which have come in handy for many things, including remedying certain recalls and shipping new features to the Full Self-Driving suite.
Tesla seems to have the most seamless OTA processes, as many automakers have the ability to ship improvements through a simple software update.
We’re really excited to test the update, so when we get an opportunity to try out Comfort Braking when it makes it to our Model Y.
News
Tesla finally brings a Robotaxi update that Android users will love
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android.

Tesla is finally bringing an update of its Robotaxi platform that Android users will love — mostly because it seems like they will finally be able to use the ride-hailing platform that the company has had active since last June.
Based on a decompile of software version 26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app, Tesla looks to be ready to roll out access to Android users.
According to the breakdown, performed by Tesla App Updates, the company is preparing to roll out an Android version of the app as it is developing several features for that operating system.
🚨 It looks like Tesla is preparing to launch the Robotaxi app for Android users at last!
A decompile of v26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app shows some progress on the Android side for Robotaxi 🤖 🚗 https://t.co/mThmoYuVLy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android:
“Strings like notification_channel_robotaxid_trip_name and android_native_alicorn_eta_text show exactly how Tesla plans to replicate the iOS Live Activities experience. Instead of standard push alerts, Android users are getting a persistent, dynamically updating notification channel.”
This is a big step forward for several reasons. From a face-value perspective, Tesla is finally ready to offer Robotaxi to Android users.
The company has routinely prioritized Apple releases because there is a higher concentration of iPhone users in its ownership base. Additionally, the development process for Apple is simply less laborious.
Tesla is working to increase Android capabilities in its vehicles
Secondly, the Robotaxi rollout has been a typical example of “slowly then all at once.”
Tesla initially released Robotaxi access to a handful of media members and influencers. Eventually, it was expanded to more users, so that anyone using an iOS device could download the app and hail a semi-autonomous ride in Austin or the Bay Area.
Opening up the user base to Android users may show that Tesla is preparing to allow even more users to utilize its Robotaxi platform, and although it seems to be a few months away from only offering fully autonomous rides to anyone with app access, the expansion of the user base to an entirely different user base definitely seems like its a step in the right direction.








