Energy
A Tesla Powerwall-powered Home: Will it Pay Off?

We’ve all heard by now that the Tesla Powerwall home battery is designed to store electricity, generated from solar panels and electricity captured from utility companies during off-peak rates, and provide overall independence from the grid.
It sounds like an amazing product, and I’m sure it is, but will it pay off to own one?
Understanding the Powerwall
 The Powerwall is an energy storage unit otherwise known as a battery. It comes in two sizes today (although they can be stacked/expanded), 7kWh and 10kWh (what’s a kWh?) and costs $3,000 and $3,500, respectively. Note that the cost excludes an inverter and installation, both of which can be quite expensive to the point it can double the total out-of-pocket cost. The specs for the Powerwall come in at a whopping 220 lbs / 100 kg (unclear as to which capacity this represents) and 52.1″ x 33.9″ x 7.1″ or roughly 3.5 x 3 feet in dimension.
The Powerwall is an energy storage unit otherwise known as a battery. It comes in two sizes today (although they can be stacked/expanded), 7kWh and 10kWh (what’s a kWh?) and costs $3,000 and $3,500, respectively. Note that the cost excludes an inverter and installation, both of which can be quite expensive to the point it can double the total out-of-pocket cost. The specs for the Powerwall come in at a whopping 220 lbs / 100 kg (unclear as to which capacity this represents) and 52.1″ x 33.9″ x 7.1″ or roughly 3.5 x 3 feet in dimension.
The concept is simple, the Powerwall battery stores energy generated through your utility company when rates are the lowest (or through solar panels) and ready on tap when you need it.
Installation
Tesla notes that the cost of the Powerwall does not include the inverter or installation. An inverter alone such as the one SolarCity uses can cost around $2,000 which does not include a separate installation cost.
Installation will vary depending on the following:
- Does your residence have an existing net metering?
- Is it already wired for a generator?
- What is the distance between the photovoltaic solar panel hardware and the location to where Tesla’s Powerwall would be mounted? The shorter the distance, the less cabling to run and thus a lower installation cost.
At 200+ pounds in weight, you’ll need to ensure that there’s ample space and structural support to where the Powerwall will be installed. There also needs to be sufficient cooling space and ventilation in the mounting location.
Primary Use Cases for the Tesla Powerwall
Tesla proposes two primary use cases for the Powerwall:
- Time of Use (TOU) offset
- Backup power
Let’s explore each of these options.
Powerwall provides a Time of Use offset
In many states and countries from around the world, a Time of Use (TOU) electricity rate is available through the local utility company. The concept is simple: you pay different rates at different times of the day. During peak hours the rates are higher than they are during off hours. Many Tesla owners that live in these areas that have TOU pricing will charge their cars during the evenings when rates are typically the lowest.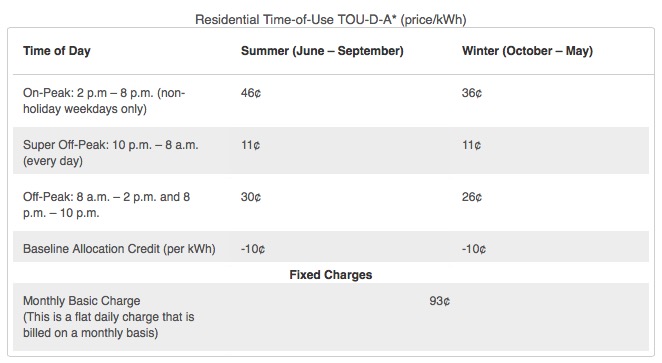
Unfortunately TOU pricing is not widespread here in Massachusetts but if you’re able to take advantage of it in your area, then the Powerwall may bring some value although it would take quite awhile to recoup the initial investment.
Taking a look at TOU rates from Southern California Edison, we can see that their off-peak rate is $0.11 while peak rate comes in at $0.46 for a difference of $0.35 per kWh. The large Powerwall unit is capable of storing 10kWh. Assuming you are able to fully charge the battery during off-peak hours each and every day, you would save approximately $3.50 per day.
Since the unit itself (without install) costs $3,500, it would take approximately 1000 days or just shy of 3 years before you “broke even”. This is assuming the utility company continues to offer off-peak rates throughout the year. Add in the installation costs and you’re looking at closer to 5 years before breaking even on the Tesla Powerwall investment
Of course, there’s the argument that having a solar panel system would allow you to charge the Powerwall battery for free through sunlight, but only if you fully ignore the cost of the solar system itself.
RELATED >>> My journey to installing a SolarCity system
Owning or leasing a solar system comes with its own break-even calculations so you’ll have to factor that into the equation with the Powerwall.
Powerwall provides backup power
The other stated potential use case for the Powerwall is to use it for backup power in the event your home power is completely cut off from the grid.
Don’t expect to power your entire house with just a single 10kWh Powerwall. Tesla’s site provides some good examples of how much power common home appliances draw. For instance the Powerwall would be able to power a typical refrigerator for 2 days. This time would of course be extended if you were able to replenish the battery through a solar system.
In the case of an extended power outage (think Zombie apocalypse), you may be able to power essential home services indefinitely with a properly sized battery and solar system.
The ability to re-fill from solar is a nice benefit, but the alternative would be a noisy gasoline powered generator.
 A 6.5kW generator can be had for for as little as $800. That generator can output 32,500kWh (50% load x 10 hours according that link). That’s 3x the power at less than 25% of the cost of Tesla’s offering. The cost for that power? About $15. The generator, unlike the Powerall, is mobile and can go anywhere you go. Generators typically have very low maintenance and can be re-filled quickly regardless of weather conditions (hurricanes, snow storms, etc – all likely conditions that will cause loss of power).
A 6.5kW generator can be had for for as little as $800. That generator can output 32,500kWh (50% load x 10 hours according that link). That’s 3x the power at less than 25% of the cost of Tesla’s offering. The cost for that power? About $15. The generator, unlike the Powerall, is mobile and can go anywhere you go. Generators typically have very low maintenance and can be re-filled quickly regardless of weather conditions (hurricanes, snow storms, etc – all likely conditions that will cause loss of power).
I have a Honda 6.5kW generator. My house has its own well, septic etc. When power goes out I fire up the generator and power the things I need. I have water, hot showers, heat (oil, fired by electric which is powered by the generator), lights etc. I have run for days off that generator in some of the worst weather conditions New England can throw at me. I’d argue if you’re serious about backup power, then a generator is still the best option.
Powerwall, as a backup power option and also from a pure cost-perspective, I feel is only a good fit for those who have a solar system installed and live in an area where the climate is more stable.

Energy
Tesla meets Giga New York’s Buffalo job target amid political pressures
Giga New York reported more than 3,460 statewide jobs at the end of 2025, meeting the benchmark tied to its dollar-a-year lease.

Tesla has surpassed its job commitments at Giga New York in Buffalo, easing pressure from lawmakers who threatened the company with fines, subsidy clawbacks, and dealership license revocations last year.
The company reported more than 3,460 statewide jobs at the end of 2025, meeting the benchmark tied to its dollar-a-year lease at the state-built facility.
As per an employment report reviewed by local media, Tesla employed 2,399 full-time workers at Gigafactory New York and 1,060 additional employees across the state at the end of 2025. Part-time roles pushed the total headcount of Tesla’s New York staff above the 3,460-job target.
The gains stemmed in part from a new Long Island service center, a Buffalo warehouse, and additional showrooms in White Plains and Staten Island. Tesla also said it has invested $350 million in supercomputing infrastructure at the site and has begun manufacturing solar panels.
Empire State Development CEO Hope Knight said the agency was “very happy” with Giga New York’s progress, as noted in a WXXI report. The current lease runs through 2029, and negotiations over updated terms have included potential adjustments to job requirements and future rent payments.
Some lawmakers remain skeptical, however. Assemblymember Pat Burke questioned whether the reported job figures have been fully verified. State Sen. Patricia Fahy has also continued to sponsor legislation that would revoke Tesla’s company-owned dealership licenses in New York. John Kaehny of Reinvent Albany has argued that the project has not delivered the manufacturing impact originally promised as well.
Knight, for her part, maintained that Empire State Development has been making the best of a difficult situation.
“(Empire State Development) has tried to make the best of a very difficult situation. There hasn’t been another use that has come forward that would replace this one, and so to the extent that we’re in this place, the fact that 2,000 families at (Giga New York) are being supported through the activity of this employer. It’s the best that we can have happen,” the CEO noted.
Energy
Tesla launches Cybertruck vehicle-to-grid program in Texas
The initiative was announced by the official Tesla Energy account on social media platform X.
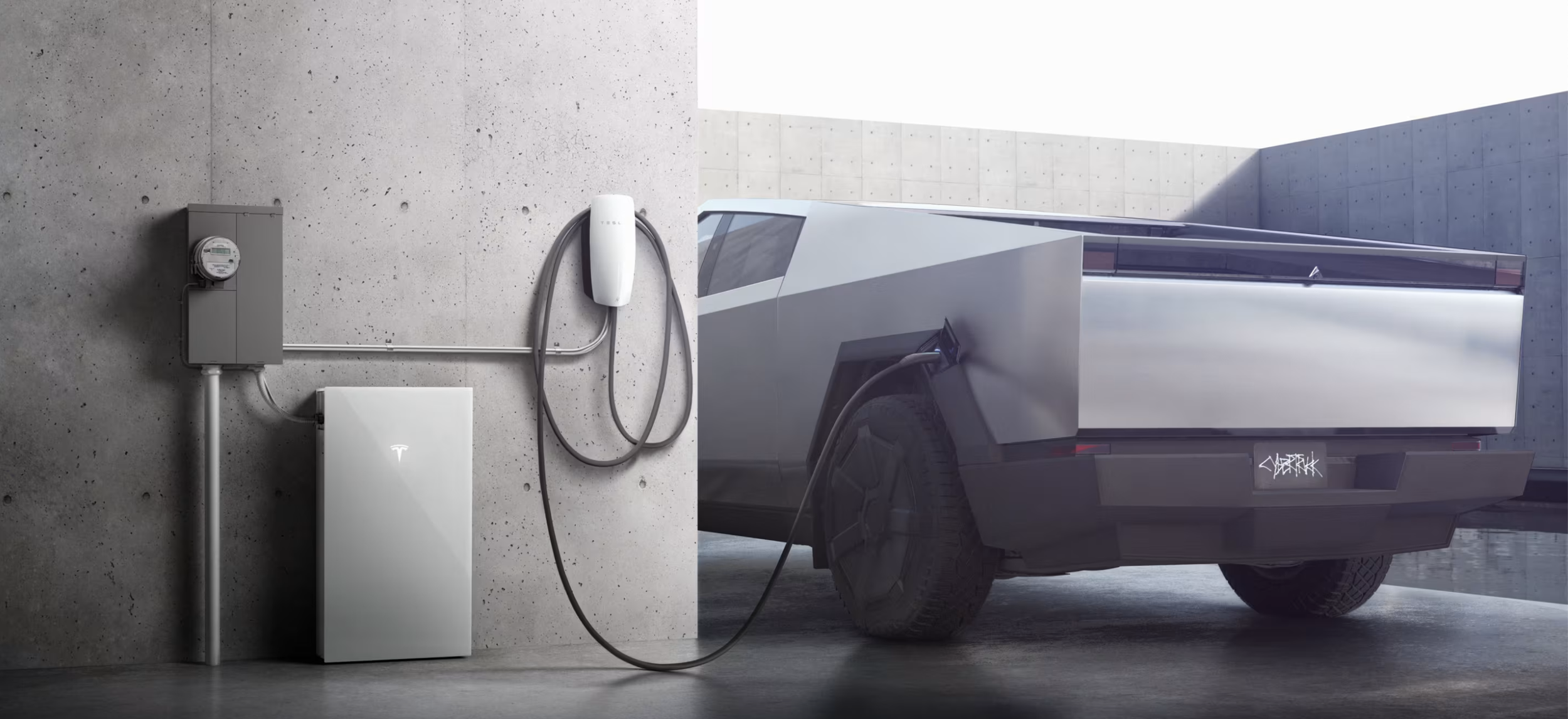

Tesla has launched a vehicle-to-grid (V2G) program in Texas, allowing eligible Cybertruck owners to send energy back to the grid during high-demand events and receive compensation on their utility bills.
The initiative, dubbed Powershare Grid Support, was announced by the official Tesla Energy account on social media platform X.
Texas’ Cybertruck V2G program
In its post on X, Tesla Energy confirmed that vehicle-to-grid functionality is “coming soon,” starting with select Texas markets. Under the new Powershare Grid Support program, owners of the Cybertruck equipped with Powershare home backup hardware can opt in through the Tesla app and participate in short-notice grid stress events.
During these events, the Cybertruck automatically discharges excess energy back to the grid, supporting local utilities such as CenterPoint Energy and Oncor. In return, participants receive compensation in the form of bill credits. Tesla noted that the program is currently invitation-only as part of an early adopter rollout.
The launch builds on the Cybertruck’s existing Powershare capability, which allows the vehicle to provide up to 11.5 kW of power for home backup. Tesla added that the program is expected to expand to California next, with eligibility tied to utilities such as PG&E, SCE, and SDG&E.
Powershare Grid Support
To participate in Texas, Cybertruck owners must live in areas served by CenterPoint Energy or Oncor, have Powershare equipment installed, enroll in the Tesla Electric Drive plan, and opt in through the Tesla app. Once enrolled, vehicles would be able to contribute power during high-demand events, helping stabilize the grid.
Tesla noted that events may occur with little notice, so participants are encouraged to keep their Cybertrucks plugged in when at home and to manage their discharge limits based on personal needs. Compensation varies depending on the electricity plan, similar to how Powerwall owners in some regions have earned substantial credits by participating in Virtual Power Plant (VPP) programs.
Cybertruck
Tesla updates Cybertruck owners about key Powershare feature

Tesla is updating Cybertruck owners on its timeline of a massive feature that has yet to ship: Powershare with Powerwall.
Powershare is a bidirectional charging feature exclusive to Cybertruck, which allows the vehicle’s battery to act as a portable power source for homes, appliances, tools, other EVs, and more. It was announced in late 2023 as part of Tesla’s push into vehicle-to-everything energy sharing, and acting as a giant portable charger is the main advantage, as it can provide backup power during outages.
Cybertruck’s Powershare system supports both vehicle-to-load (V2L) and vehicle-to-home (V2H), making it flexible and well-rounded for a variety of applications.
However, even though the feature was promised with Cybertruck, it has yet to be shipped to vehicles. Tesla communicated with owners through email recently regarding Powershare with Powerwall, which essentially has the pickup act as an extended battery.
Powerwall discharge would be prioritized before tapping into the truck’s larger pack.
However, Tesla is still working on getting the feature out to owners, an email said:
“We’re writing to let you know that the Powershare with Powerwall feature is still in development and is now scheduled for release in mid-2026.
This new release date gives us additional time to design and test this feature, ensuring its ability to communicate and optimize energy sharing between your vehicle and many configurations and generations of Powerwall. We are also using this time to develop additional Powershare features that will help us continue to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.”
Owners have expressed some real disappointment in Tesla’s continuous delays in releasing the feature, as it was expected to be released by late 2024, but now has been pushed back several times to mid-2026, according to the email.
Foundation Series Cybertruck buyers paid extra, expecting the feature to be rolled out with their vehicle upon pickup.
Cybertruck’s Lead Engineer, Wes Morrill, even commented on the holdup:
As a Cybertruck owner who also has Powerwall, I empathize with the disappointed comments.
To their credit, the team has delivered powershare functionality to Cybertruck customers who otherwise have no backup with development of the powershare gateway. As well as those with solar…
— Wes (@wmorrill3) December 12, 2025
He said that “it turned out to be much harder than anticipated to make powershare work seamlessly with existing Powerwalls through existing wall connectors. Two grid-forming devices need to negotiate who will form and who will follow, depending on the state of charge of each, and they need to do this without a network and through multiple generations of hardware, and test and validate this process through rigorous certifications to ensure grid safety.”
It’s nice to see the transparency, but it is justified for some Cybertruck owners to feel like they’ve been bait-and-switched.