News
Tesla’s race to autonomy: No one said it would be easy
Need to type up a quick memo before work? Forgot to eat breakfast before driving to school? In just a few years, driving may be a more hands-off endeavor than ever before if companies like Tesla, Uber, Volvo, Alphabet, General Motors, or Ford have anything to do about it. You could be a passenger in your own self-driving car, weaving in and out of traffic with ease and parallel parking like a pro every time. It seems like most every company even tangentially related to cars is pouring money into the race for autonomy.
The freedom of self-driving cars is still heavily dependent on regulatory whim and technological availability, but some are setting demanding goals in an effort to finish first in that race. Tesla for example, plans to showcase its Full Self-Driving Capability by driving one of its fleet cars from California to New York, without human involvement, by the end of this year. But their competitors are moneyed, motivated and many.
The Self-Driving Battle Arena
For Uber, success in autonomous driving research could be a sweet distraction from the recent troubles of the company. Its self-driving program has been based in Pittsburgh, right next to Carnegie Mellon with its highly regarded robotics program since it began in 2015. Then-CEO Travis Kalanick was determined to stay on top of the industry. “It starts with understand that the world is going to go self-driving and autonomous,” Kalanick said in a 2016 interview with Business Insider. “So if that’s happening, what would happen if we weren’t a part of that future? If we weren’t part of the autonomy thing? Then the future passes us by basically, in a very expeditious and efficient way.”
Plagued by lawsuits, investigations, and subsequent executive upheaval that saw Kalanick’s resignation from the enterprise he founded, Uber is still one of the best places for researchers and engineers to work on their projects. The company has armies of vehicles across the country, vast datasets of information from the millions of miles its cars have covered through its ride-hailing branch, and the money to fund its engineers’ work.
 This does not mean that Uber’s self-driving program has remained untouched. Waymo, the autonomous car division of Google’s parent company, Alphabet, is currently suing Uber over files allegedly by Anthony Levandowski when he moved from Waymo to Uber. According to Reuters, in recent court filings, Waymo has claimed that Uber knew of the stolen intellectual property and even conspired with Levandowski to use it. Uber denies the allegations and actually fired Levandowski on May 30, claiming he had not cooperated with their internal investigation– and probably hoping to win some goodwill from the judge who has already said Waymo had produced a convincing case.
This does not mean that Uber’s self-driving program has remained untouched. Waymo, the autonomous car division of Google’s parent company, Alphabet, is currently suing Uber over files allegedly by Anthony Levandowski when he moved from Waymo to Uber. According to Reuters, in recent court filings, Waymo has claimed that Uber knew of the stolen intellectual property and even conspired with Levandowski to use it. Uber denies the allegations and actually fired Levandowski on May 30, claiming he had not cooperated with their internal investigation– and probably hoping to win some goodwill from the judge who has already said Waymo had produced a convincing case.
It is unlikely the scandals will affect the decisions of most researchers to stay with the company. As Wired’s Aarian Marshall points out, the long timeline of building a safe autonomous car makes engineers less likely to leave at a moment’s notice in a period of executive instability. And the branch’s position in Pittsburgh rather than Silicon Valley means the roiling news is less sensationalized and the researchers less affected. The ride-sharing company’s failure to live up to certain promises, including backing one of Pittsburgh’s federal grant proposals or hiring from neighborhoods near its test tracks, have drawn ire from many local activists and politicians, as reported by the New York Times. Even so, it has helped the city break away from its steel past and into a high-tech future.
Meanwhile, Uber’s main competitor in the ride-sharing industry, Lyft, has been making strides to continue chipping away Uber’s monopoly in any field, including self-driving cars, as Uber deals with scandal after scandal. As reported by Recode, Lyft is steadily gaining ground on Uber in terms of the share of ride-hailing app downloads as its ratings in the IOS App Store rise and Uber’s falls. This recent shift in market share comes as Waymo and Lyft start a new partnership that will combine Waymo’s advanced technology with Lyft’s vast amounts of data on people, where and how they drive. “Lyft’s vision and commitment to improving the ways cities move with help Waymo’s self-driving technology reach more people, in more places,” a Waymo spokesperson told Wired. Extending Waymo’s dataset beyond the few cities, including Phoenix and Pittsburgh, allows the enterprise to collect the small details of average people’s driving habits much faster and accurately than its test drives around Silicon Valley will.
But despite Waymo’s eight years of self-driving research, it still has to play catch up to Uber in some regards. Waymo just started testing autonomous trucks earlier this month, while Uber first used a self-driving truck to deliver a shipment last August, advancing its technology quickly after it snatched up the self-driving truck startup Otto—founded by Anthony Levandowski after he left Waymo— in January of 2016. Yet, Waymo has the benefit of its parent company’s huge cash reserves and data.
Growing Pains
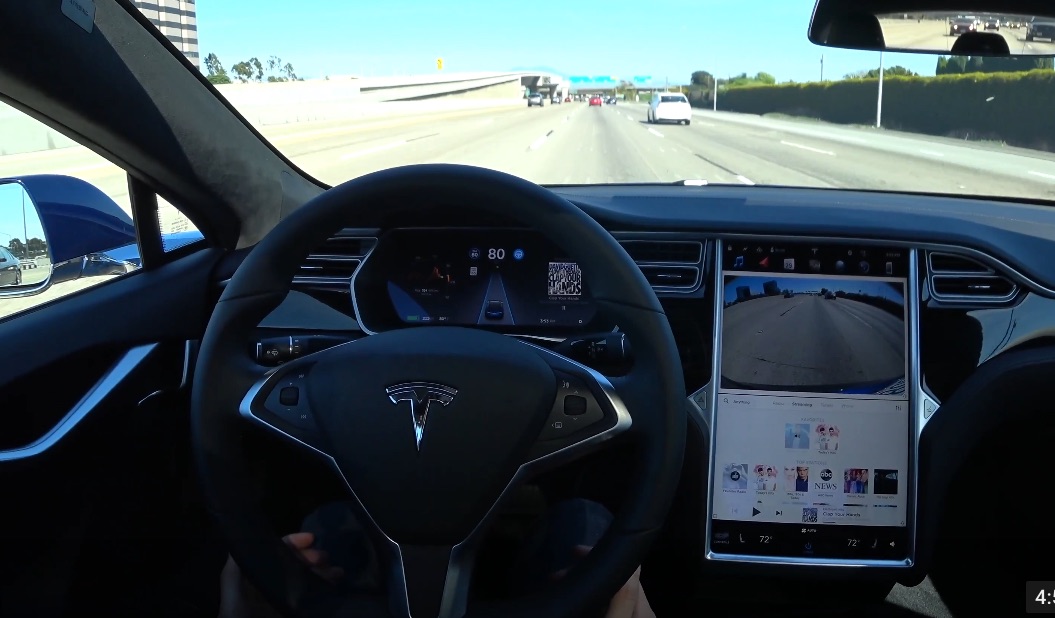
Tesla is moving its autonomous program forward at an increasingly demanding pace, trying to meet that goal of driving from Los Angeles to New York by the end of this year. It, like Uber, is going through some executive shakeup: after just six months with Tesla, Chris Lattner, Vice President of its Autopilot Software program, left the company after reported tensions with Elon Musk. Tesla explained that the former Apple engineer was not a “good fit.” It stands to mention that working under Musk is notoriously a high-pressure gig. According to LinkedIn Insights, the average tenure of a Tesla employee is only 2.2 years, while companies like General Motors keeps its employees for almost 9. But Lattner’s exit is just one example of many of talented Tesla self-driving engineers leaving the company or being poached by the competition, like Waymo.
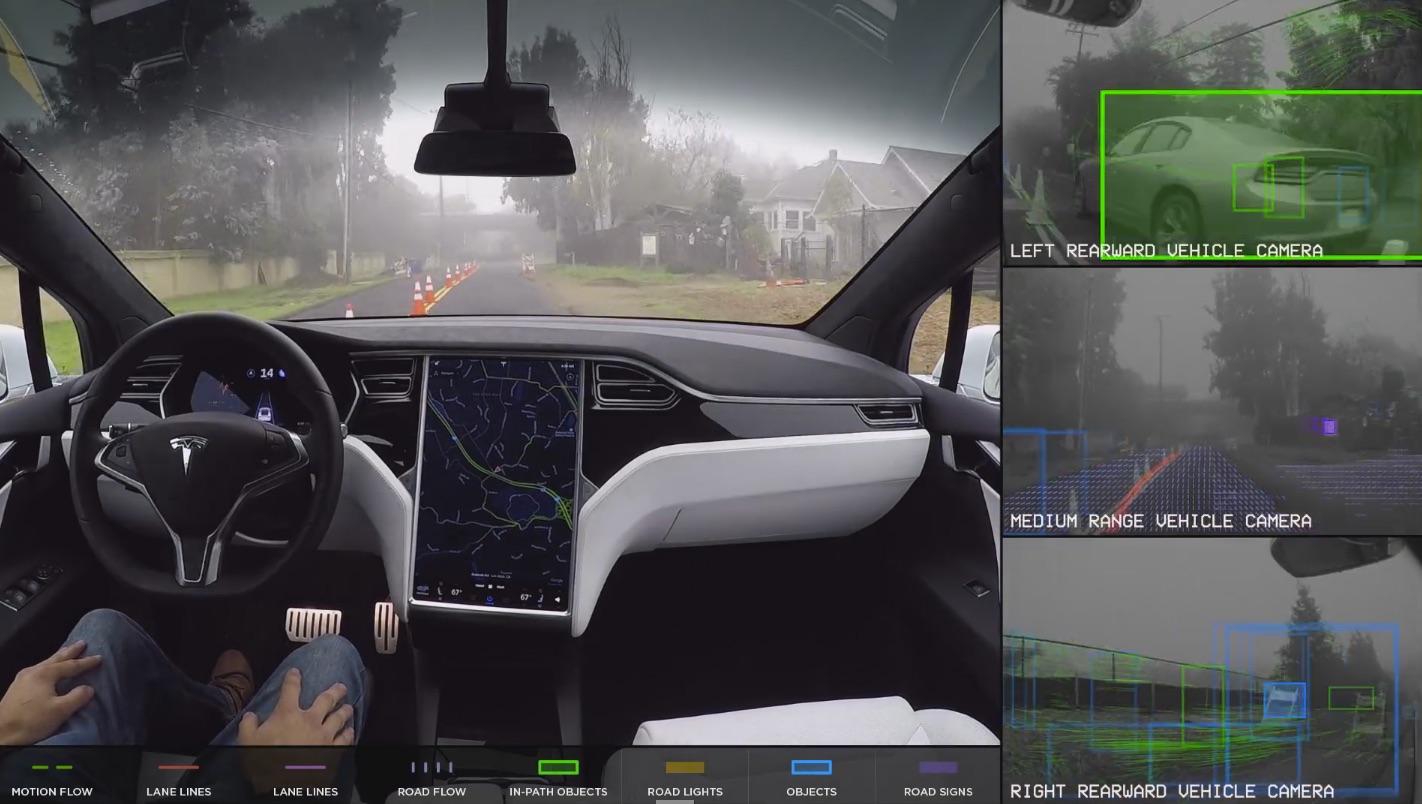
While Autopilot can do many impressive things— change lanes, brake before obstacles, and generally act as a rational human driver— it is far from perfect. The program is still technically in “public beta” testing, and rated by the National Transportation Safety Board as a 2 out of 5 on its scale of autonomy.
The fatal crash of a Model S owner Joshua Brown in May 2016 serves as a good reminder that drivers are cautioned to pay attention and keep their hands on the wheel at all times while using Autopilot. Tesla’s driving-assist feature, at the time, could not distinguish the difference between the bright sky and the white truck. Tesla and Autopilot were cleared of responsibility by the NTSB because Brown was given several warnings to take back control of the wheel. But it is a poignant example that Autopilot does not function as a self-driving car and still requires a driver’s full attention. After the accident, Tesla was forced to start developing its own hardware for Autopilot. Mobileye, which previously supplied Tesla’s image processing chips, ended its partnership in a public spat with Musk.
According to Lattner’s public resume, the transition to its own hardware presented “many tough challenges” to the Tesla team. Musk commented to shareholders in June that Tesla is “almost there in terms of exceeding the ability” of the original hardware. All of Tesla’s vehicles in production, including the upcoming Model 3, have the capability to engage Autopilot (for a price) and the necessary hardware to enable full self-driving someday. Autopilot will continue using the camera-based system that Tesla swears by, even as most of the industry focuses on developing LiDAR technology based on light and lasers.
And while Tesla prefers to work mostly alone, the rest of the industry is also pairing up, making deals, partnerships, and contracts between manufacturers, data giants, and service teams. Musk is taking a move out of Steve Jobs’ playbook by vertically integrating everything within the business, from top-to-bottom. Waymo and Honda, Lyft and Waymo, Autoliv and Volvo, Hertz and Apple, Intel and Mobileye, Audi and NVIDIA, and almost every other combination you could think of. Predictions for when the first company will reach the finish line range from within a year to two decades from now. And even if the car is made, there is still the question of if cities and states will allow autonomous vehicles to drive on their streets. The technology is closer than ever, but for now, please keep your eyes on the road.

Elon Musk
What is Digital Optimus? The new Tesla and xAI project explained
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Tesla and xAI announced their groundbreaking joint project, Digital Optimus, also nicknamed “Macrohard” in a humorous jab at Microsoft, earlier this week.
This software-based AI agent is designed to automate complex office workflows by observing and replicating human interactions with computers. As the first major outcome of Tesla’s $2 billion investment in xAI, it represents a powerful fusion of hardware efficiency and advanced reasoning.
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Macrohard or Digital Optimus is a joint xAI-Tesla project, coming as part of Tesla’s investment agreement with xAI.
Grok is the master conductor/navigator with deep understanding of the world to direct digital Optimus, which is processing and actioning the past 5 secs of…
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 11, 2026
Tesla’s specialized AI acts as “System 1”—the fast, instinctive executor—processing the past five seconds of real-time computer screen video along with keyboard and mouse actions to perform immediate tasks.
xAI’s Grok model serves as “System 2,” the strategic “master conductor” or navigator, providing high-level reasoning, world understanding, and directional oversight, much like an advanced turn-by-turn navigation system.
When combined, the two can create a powerful AI-based assistant that can complete everything from accounting work to HR tasks.
Will Tesla join the fold? Predicting a triple merger with SpaceX and xAI
The system runs primarily on Tesla’s low-cost AI4 inference chip, minimizing expensive Nvidia resources from xAI for competitive, real-time performance.
Elon Musk described it as “the only real-time smart AI system” capable, in principle, of emulating the functions of entire companies, handling everything from accounting and HR to repetitive digital operations.
Timelines point to swift deployment. Announced just days ago, Musk expects Digital Optimus to be ready for user experience within about six months, targeting rollout around September 2026.
It will integrate into all AI4-equipped Tesla vehicles, enabling parked cars to handle office work during downtime. Millions of dedicated units are also planned for deployment at Supercharger stations, tapping into roughly 7 gigawatts of available power.
Oh and it works in all AI4-equipped cars, so your car can do office work for you when not driving.
We’re also deploying millions of dedicated Digital Optimus units in the field at Superchargers where we have ~7 gigawatts of available power.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 12, 2026
Digital Optimus directly supports Tesla’s broader autonomy strategy. It leverages the same end-to-end neural networks, computer vision, and real-time decision-making tech that power Full Self-Driving (FSD) software and the physical Optimus humanoid robot.
By repurposing idle vehicle compute and extending AI4 hardware beyond driving, the project scales Tesla’s autonomy ecosystem from roads to digital workspaces.
As a virtual counterpart to physical Optimus, it divides labor: software agents manage screen-based tasks while humanoid robots tackle physical ones, accelerating Tesla’s vision of general-purpose AI for productivity, Robotaxi fleets, and beyond.
In essence, Digital Optimus bridges Tesla’s vehicle and robotics autonomy with enterprise-scale AI, promising massive efficiency gains. No other company currently matches its real-time capabilities on such accessible hardware.
It really could be one of the most crucial developments Tesla and xAI begin to integrate, as it could revolutionize how people work and travel.
News
Tesla adds awesome new driving feature to Model Y
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.

Tesla is adding an awesome new driving feature to Model Y vehicles, effective on Juniper-updated models considered model year 2026 or newer.
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.
Tesla writes in the release notes for the feature:
“Your Tesla now provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.”
🚨 Tesla has added a new “Comfort Braking” update with 2026.8
“Your Tesla provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.” https://t.co/afqCpBSVeA pic.twitter.com/C6MRmzfzls
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
Interestingly, we’re not too sure what catalyzed Tesla to try to improve braking smoothness, because it hasn’t seemed overly abrupt or rough from my perspective. Although the brake pedal in my Model Y is rarely used due to Regenerative Braking, it seems Tesla wanted to try to make the ride comfort even smoother for owners.
There is always room for improvement, though, and it seems that there is a way to make braking smoother for passengers while the vehicle is coming to a stop.
This is far from the first time Tesla has attempted to improve its ride comfort through Over-the-Air updates, as it has rolled out updates to improve regenerative braking performance, handling while using Full Self-Driving, improvements to Steer-by-Wire to Cybertruck, and even recent releases that have combatted Active Road Noise.
Tesla holds a unique ability to change the functionality of its vehicles through software updates, which have come in handy for many things, including remedying certain recalls and shipping new features to the Full Self-Driving suite.
Tesla seems to have the most seamless OTA processes, as many automakers have the ability to ship improvements through a simple software update.
We’re really excited to test the update, so when we get an opportunity to try out Comfort Braking when it makes it to our Model Y.
News
Tesla finally brings a Robotaxi update that Android users will love
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android.

Tesla is finally bringing an update of its Robotaxi platform that Android users will love — mostly because it seems like they will finally be able to use the ride-hailing platform that the company has had active since last June.
Based on a decompile of software version 26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app, Tesla looks to be ready to roll out access to Android users.
According to the breakdown, performed by Tesla App Updates, the company is preparing to roll out an Android version of the app as it is developing several features for that operating system.
🚨 It looks like Tesla is preparing to launch the Robotaxi app for Android users at last!
A decompile of v26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app shows some progress on the Android side for Robotaxi 🤖 🚗 https://t.co/mThmoYuVLy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android:
“Strings like notification_channel_robotaxid_trip_name and android_native_alicorn_eta_text show exactly how Tesla plans to replicate the iOS Live Activities experience. Instead of standard push alerts, Android users are getting a persistent, dynamically updating notification channel.”
This is a big step forward for several reasons. From a face-value perspective, Tesla is finally ready to offer Robotaxi to Android users.
The company has routinely prioritized Apple releases because there is a higher concentration of iPhone users in its ownership base. Additionally, the development process for Apple is simply less laborious.
Tesla is working to increase Android capabilities in its vehicles
Secondly, the Robotaxi rollout has been a typical example of “slowly then all at once.”
Tesla initially released Robotaxi access to a handful of media members and influencers. Eventually, it was expanded to more users, so that anyone using an iOS device could download the app and hail a semi-autonomous ride in Austin or the Bay Area.
Opening up the user base to Android users may show that Tesla is preparing to allow even more users to utilize its Robotaxi platform, and although it seems to be a few months away from only offering fully autonomous rides to anyone with app access, the expansion of the user base to an entirely different user base definitely seems like its a step in the right direction.











