

News
SpaceX’s Starship Moon lander passes NASA review alongside Blue Origin, Dynetics
A variant of SpaceX’s Starship spacecraft optimized to land NASA astronauts on the Moon has passed the space agency’s first review alongside competing teams lead by Blue Origin and Dynetics.
Aside from reiterating the fact that NASA is drawing heavily from its experience with the Commercial Crew Program (CCP), the completion of “certification baseline reviews” for Blue Origin, Dynetics, and SpaceX’s proposed lunar landers is a significant step forward for the Human Landing System (HLS) and Artemis programs. According to NASA’s official HLS “Broad Agency Announcement” or BAA, providers must submit a vast amount of paperwork and data to pass the certification baseline review (CBR).
NASA’s acceptance criteria for CBR documentation is about as general as the space agency gets, requiring providers to demonstrate at least a basic level of maturity and expertise. Like the name suggests, it sets a baseline from which NASA and SpaceX, Dynetics, and Blue Origin’s National Team will hone in on challenges and concerns specific to each system. SpaceX’s proposal is almost certainly unique, however, given that the company is the only one anywhere close to performing actual flight tests of a (relatively) similar system.
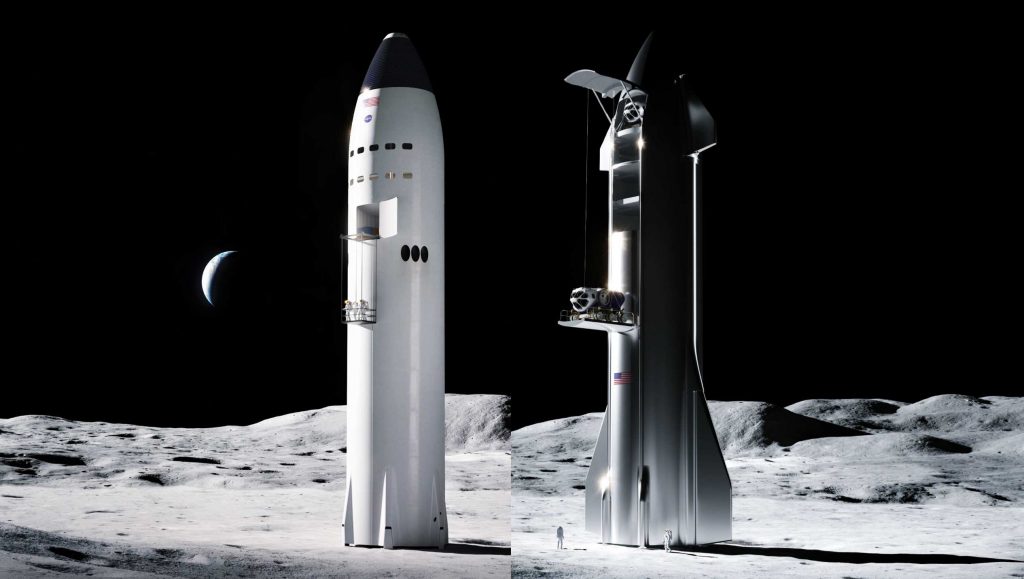

After much fanfare, NASA finally revealed its first real Human Landing System contracts on April 30th, 2020, awarding funds to Blue Origin, Dynetics, and SpaceX to develop three extremely dissimilar Moon landers. Designed to ferry NASA astronauts from a deserted lunar orbit (near-rectilinear halo orbit, NRHO). NASA initially refused to delineate the distribution of the $967 million contract.
Several news outlets later reported that Blue Origin’s “National Team” (including Draper, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman) received $567 million to develop a complex three-stage system, using Blue Origin’s existing Blue Moon lander work for the final descent stage and lander. Dynetics won $253 million to build a slightly more familiar single-stage lander and SpaceX received $135 million for a single-stage Starship-derived vehicle.
The main goal of NASA’s initial funding is to extensively characterize and understand the capabilities and characteristics of each proposal and the likelihood that each vehicle will actually be ready to land humans on the Moon by the end of 2024. The next major HLS milestone will be what the space agency calls a “continuation review,” in which NASA will likely downselect to one of the three landers above. Administrator Jim Bridenstine says that NASA may decide to proceed with more than one provider but the strong implication is that only one will exit the ~December 2020 continuation review with future funding.
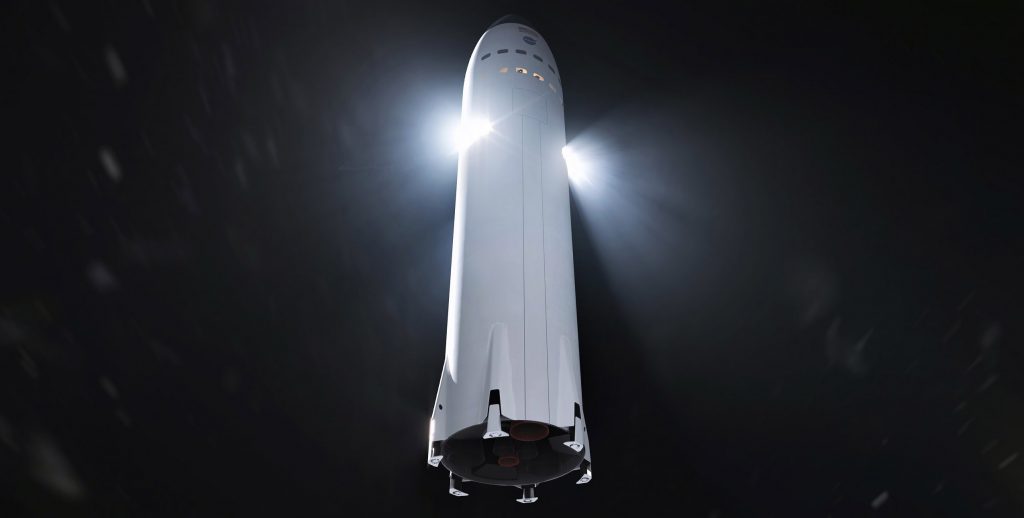
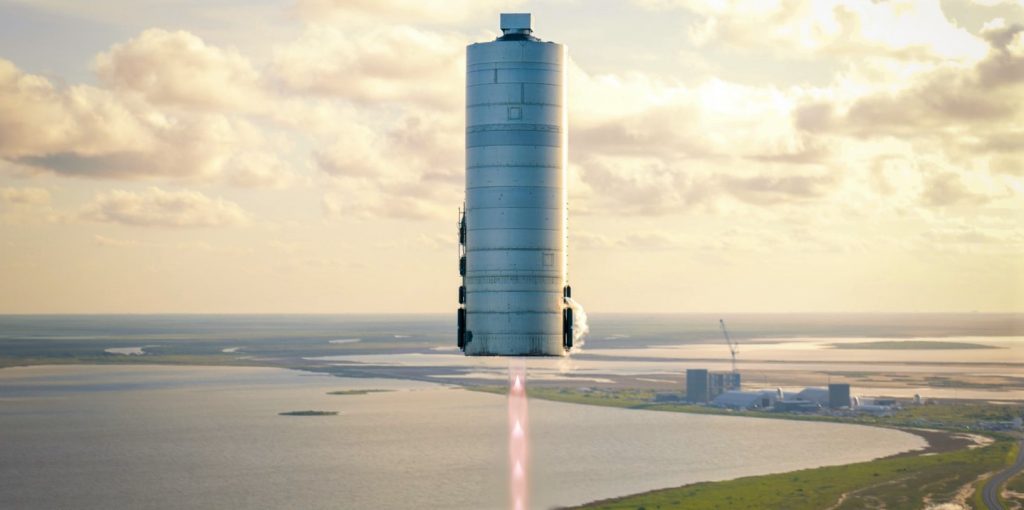


For SpaceX, it appears that the company will almost certainly field an orbit-capable Starship and Super Heavy booster with or without external help. At this point in the program, it would take a major upset for SpaceX not to be ready to start orbital Starship launch attempts in 2021. To an extent, SpaceX has proven through Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy, and Crew Dragon that it’s capable of developing reliable, reusable, industry-leading rockets and spacecraft several times more cheaply than its closest competitors.
To build a Starship safe and reliable enough that SpaceX can convince NASA to land astronauts on the Moon with it, the company will effectively have to prove that it can cut the cost of rocket production by another factor of five or ten. Time will tell where NASA’s HLS cards fall just a few months from now.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
Tesla already has a complete Robotaxi model, and it doesn’t depend on passenger count
That scenario was discussed during the company’s Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call, when executives explained why the majority of Robotaxi rides will only involve one or two people.

Tesla already has the pieces in place for a full Robotaxi service that works regardless of passenger count, even if the backbone of the program is a small autonomous two-seater.
That scenario was discussed during the company’s Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call, when executives explained why the majority of Robotaxi rides will only involve one or two people.
Two-seat Cybercabs make perfect sense
During the Q&A portion of the call, Tesla Vice President of Vehicle Engineering Lars Moravy pointed out that more than 90% of vehicle miles traveled today involve two or fewer passengers. This, the executive noted, directly informed the design of the Cybercab.
“Autonomy and Cybercab are going to change the global market size and mix quite significantly. I think that’s quite obvious. General transportation is going to be better served by autonomy as it will be safer and cheaper. Over 90% of vehicle miles traveled are with two or fewer passengers now. This is why we designed Cybercab that way,” Moravy said.
Elon Musk expanded on the point, emphasizing that there is no fallback for Tesla’s bet on the Cybercab’s autonomous design. He reiterated that the autonomous two seater’s production is expected to start in April and noted that, over time, Tesla expects to produce far more Cybercabs than all of its other vehicles combined.
“Just to add to what Lars said there. The point that Lars made, which is that 90% of miles driven are with one or two passengers or one or two occupants, essentially, is a very important one… So this is clearly, there’s no fallback mechanism here. It’s like this car either drives itself or it does not drive… We would expect over time to make far more CyberCabs than all of our other vehicles combined. Given that 90% of distance driven or distance being distance traveled exactly, no longer driving, is one or two people,” Musk said.
Tesla’s robotaxi lineup is already here
The more interesting takeaway from the Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call is the fact that Tesla does not need the Cybercab to serve every possible passenger scenario, simply because the company already has a functional Robotaxi model that scales by vehicle type.
The Cybercab will handle the bulk of the Robotaxi network’s trips, but for groups that need three or four seats, the Model Y fills that role. For higher-end or larger-family use cases, the extended-wheelbase Model Y L could cover five or six occupants, provided that Elon Musk greenlights the vehicle for North America. And for even larger groups or commercial transport, Tesla has already unveiled the Robovan, which could seat over ten people.
Rather than forcing one vehicle to satisfy every use case, Tesla’s approach mirrors how transportation works today. Different vehicles will be used for different needs, while unifying everything under a single autonomous software and fleet platform.
News
Tesla Cybercab spotted with interesting charging solution, stimulating discussion
The port is located in the rear of the vehicle and features a manual door and latch for plug-in, and the video shows an employee connecting to a Tesla Supercharger.
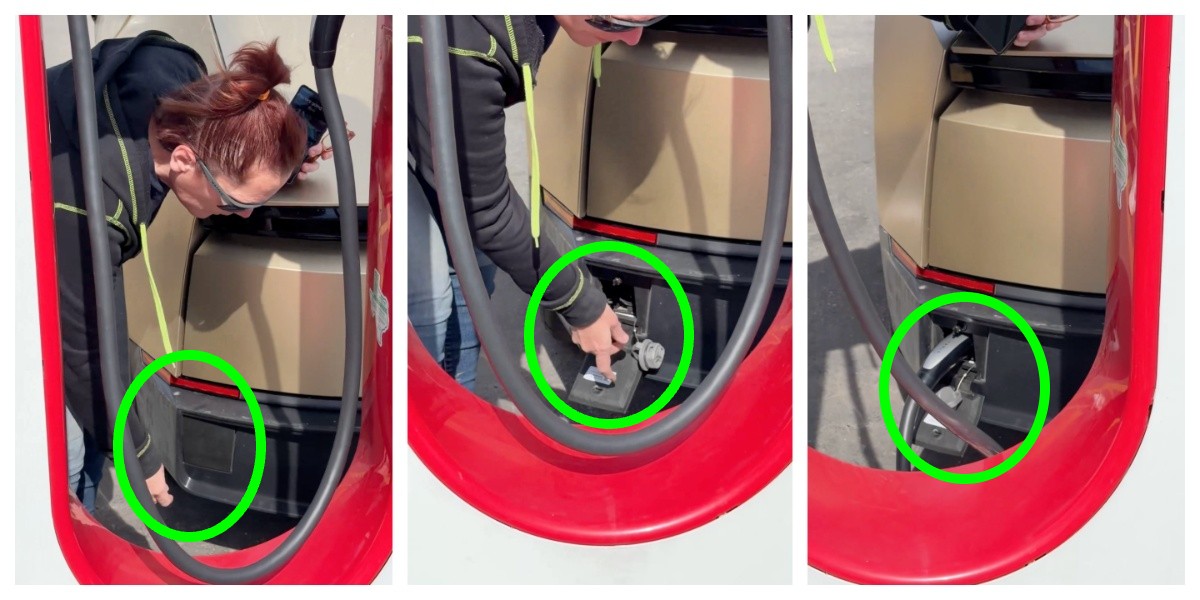
Tesla Cybercab units are being tested publicly on roads throughout various areas of the United States, and a recent sighting of the vehicle’s charging port has certainly stimulated some discussions throughout the community.
The Cybercab is geared toward being a fully-autonomous vehicle, void of a steering wheel or pedals, only operating with the use of the Full Self-Driving suite. Everything from the driving itself to the charging to the cleaning is intended to be operated autonomously.
But a recent sighting of the vehicle has incited some speculation as to whether the vehicle might have some manual features, which would make sense, but let’s take a look:
🚨 Tesla Cybercab charging port is in the rear of the vehicle!
Here’s a great look at plugging it in!!
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 29, 2026
The port is located in the rear of the vehicle and features a manual door and latch for plug-in, and the video shows an employee connecting to a Tesla Supercharger.
Now, it is important to remember these are prototype vehicles, and not the final product. Additionally, Tesla has said it plans to introduce wireless induction charging in the future, but it is not currently available, so these units need to have some ability to charge.
However, there are some arguments for a charging system like this, especially as the operation of the Cybercab begins after production starts, which is scheduled for April.
Wireless for Operation, Wired for Downtime
It seems ideal to use induction charging when the Cybercab is in operation. As it is for most Tesla owners taking roadtrips, Supercharging stops are only a few minutes long for the most part.
The Cybercab would benefit from more frequent Supercharging stops in between rides while it is operating a ride-sharing program.
Tesla wireless charging patent revealed ahead of Robotaxi unveiling event
However, when the vehicle rolls back to its hub for cleaning and maintenance, standard charging, where it is plugged into a charger of some kind, seems more ideal.
In the 45-minutes that the car is being cleaned and is having maintenance, it could be fully charged and ready for another full shift of rides, grabbing a few miles of range with induction charging when it’s out and about.
Induction Charging Challenges
Induction charging is still something that presents many challenges for companies that use it for anything, including things as trivial as charging cell phones.
While it is convenient, a lot of the charge is lost during heat transfer, which is something that is common with wireless charging solutions. Even in Teslas, the wireless charging mat present in its vehicles has been a common complaint among owners, so much so that the company recently included a feature to turn them off.
Production Timing and Potential Challenges
With Tesla planning to begin Cybercab production in April, the real challenge with the induction charging is whether the company can develop an effective wireless apparatus in that short time frame.
It has been in development for several years, but solving the issue with heat and energy loss is something that is not an easy task.
In the short-term, Tesla could utilize this port for normal Supercharging operation on the Cybercab. Eventually, it could be phased out as induction charging proves to be a more effective and convenient option.
News
Tesla confirms that it finally solved its 4680 battery’s dry cathode process
The suggests the company has finally resolved one of the most challenging aspects of its next-generation battery cells.
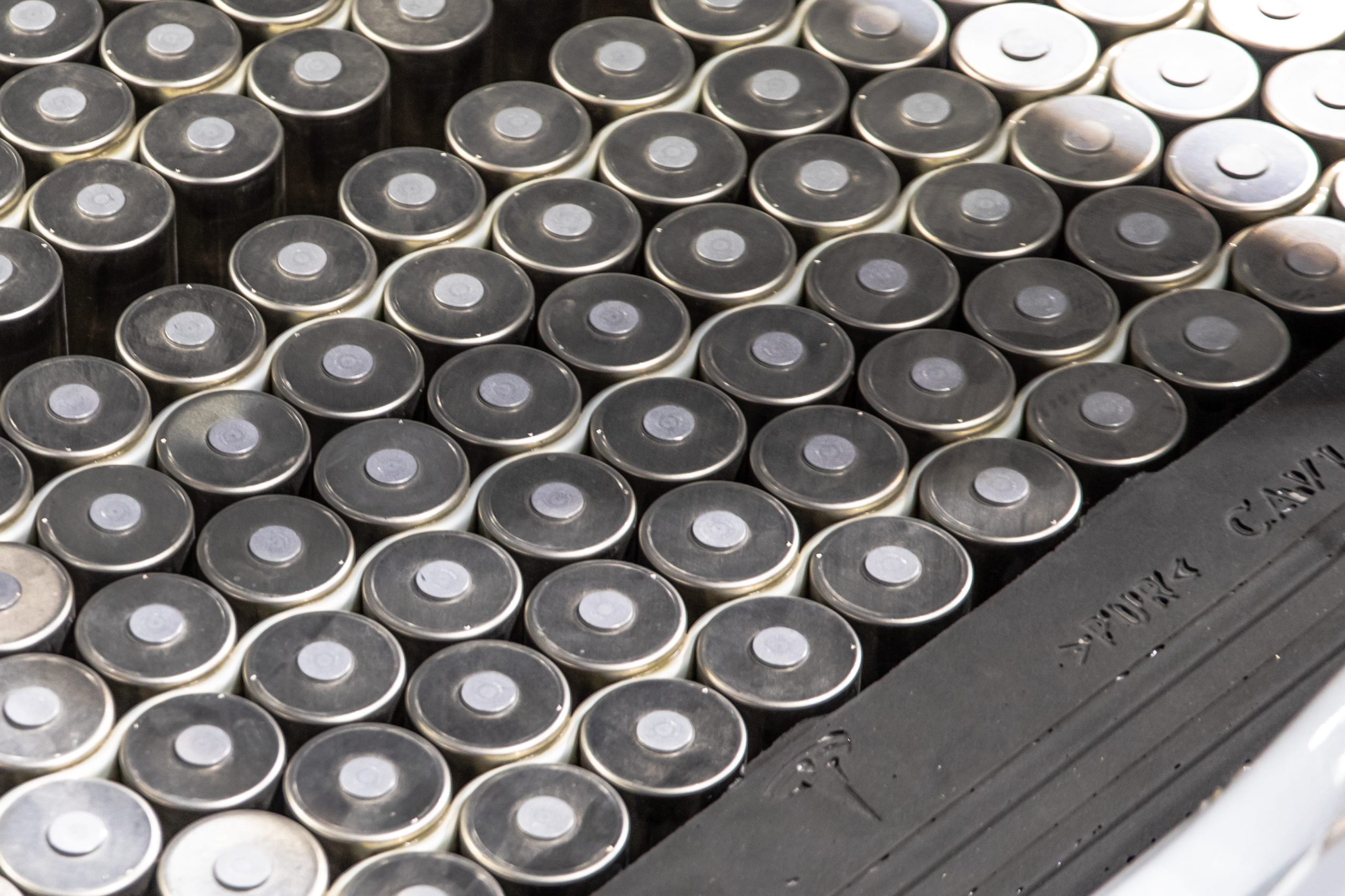

Tesla has confirmed that it is now producing both the anode and cathode of its 4680 battery cells using a dry-electrode process, marking a key breakthrough in a technology the company has been working to industrialize for years.
The update, disclosed in Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 update letter, suggests the company has finally resolved one of the most challenging aspects of its next-generation battery cells.
Dry cathode 4680 cells
In its Q4 and FY 2025 update letter, Tesla stated that it is now producing 4680 cells whose anode and cathode were produced during the dry electrode process. The confirmation addresses long-standing questions around whether Tesla could bring its dry cathode process into sustained production.
The disclosure was highlighted on X by Bonne Eggleston, Tesla’s Vice President of 4680 batteries, who wrote that “both electrodes use our dry process.”
Tesla first introduced the dry-electrode concept during its Battery Day presentation in 2020, pitching it as a way to simplify production, reduce factory footprint, lower costs, and improve energy density. While Tesla has been producing 4680 cells for some time, the company had previously relied on more conventional approaches for parts of the process, leading to questions about whether a full dry-electrode process could even be achieved.
4680 packs for Model Y
Tesla also revealed in its Q4 and FY 2025 Update Letter that it has begun producing battery packs for certain Model Y vehicles using its in-house 4680 cells. As per Tesla:
“We have begun to produce battery packs for certain Model Ys with our 4680 cells, unlocking an additional vector of supply to help navigate increasingly complex supply chain challenges caused by trade barriers and tariff risks.”
The timing is notable. With Tesla preparing to wind down Model S and Model X production, the Model Y and Model 3 are expected to account for an even larger share of the company’s vehicle output. Ensuring that the Model Y can be equipped with domestically produced 4680 battery packs gives Tesla greater flexibility to maintain production volumes in the United States, even as global battery supply chains face increasing complexity.








