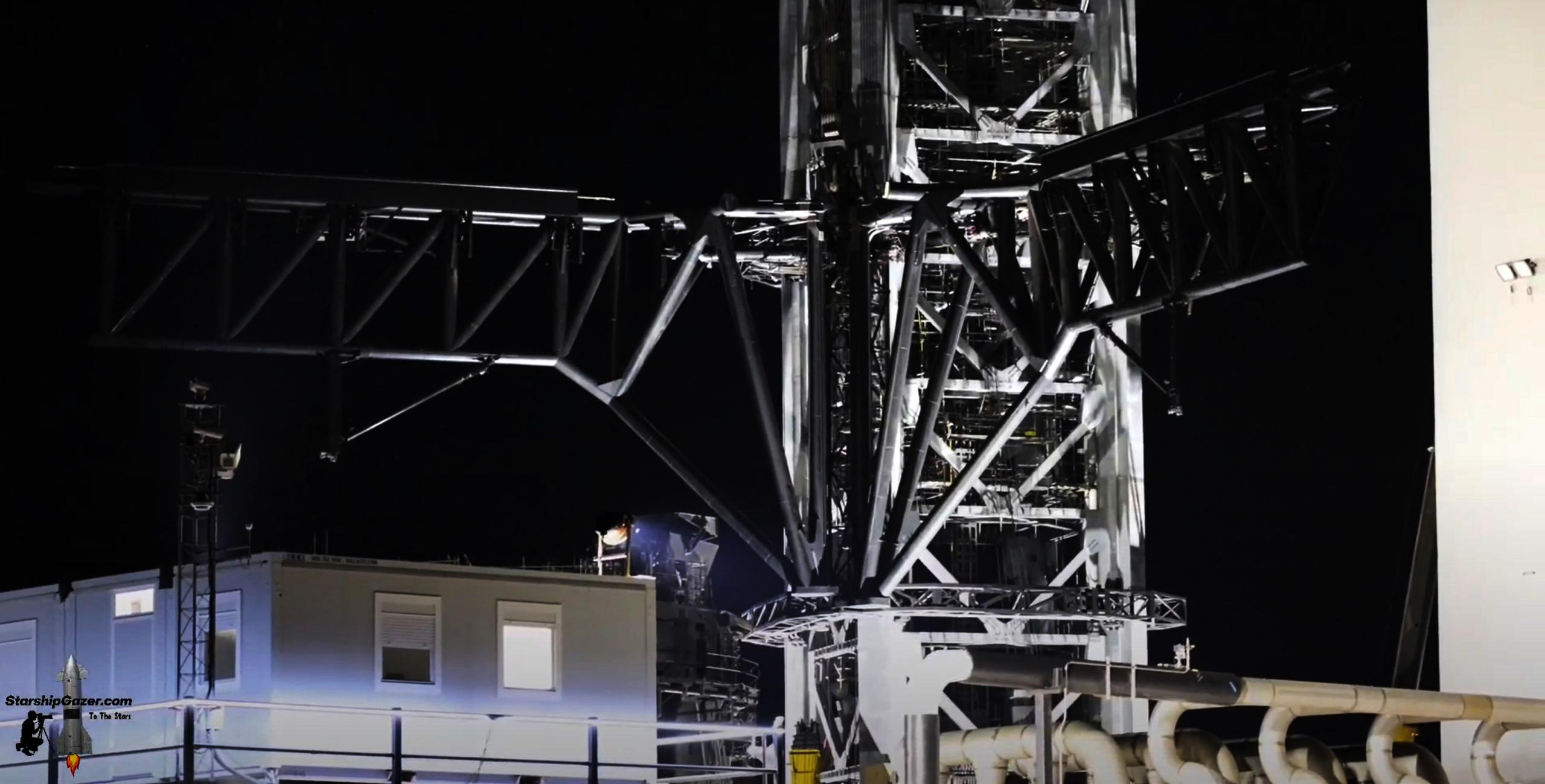
Update: Shortly after publishing, SpaceX began a much more ambitious series of tests with the Starship launch tower’s two main arms, which are designed to lift and (one day) catch Starships and Super Heavy boosters.
After lifting the arm carriage about 15m (~50 ft), several times higher than January 3rd’s far more conservative kickoff, SpaceX fired up each arm’s main hydraulic actuator and opened them about as wide as they’re able to move. Unsurprisingly, the arms’ first powered lateral movement happened very slowly, obviously telegraphing caution but probably also hinting at the start of a calibration process needed to determine their full range of motion and associate those positions with certain sensor readings or telemetry to ensure they can be safely controlled. As of midnight CST, that testing has continued well into the night.
Regardless of the purpose, substantial powered movement is a major milestone for the tower’s main arms and all but guarantees that more extensive tests and simulations are soon to come.
SpaceX has moved Starbase’s rocket-catching “chopstick” arms for the first time since they were installed on the orbital Starship pad’s ‘launch tower’ two months ago.
After a shockingly brisk three-month period of assembly, the first arm installed in late August 2021 was a lone structure designed to swing in; grab and stabilize Super Heavy with its claw; fuel and power Starship; and quickly detach and swing away from the rocket during launch. A month and a half later, SpaceX begin installing a much larger pair of more complex arms in mid-October. Unlike the Starship quick-disconnect (QD) arm, the pair of arms that followed were almost nothing like anything built as part of another rocket launch complex.
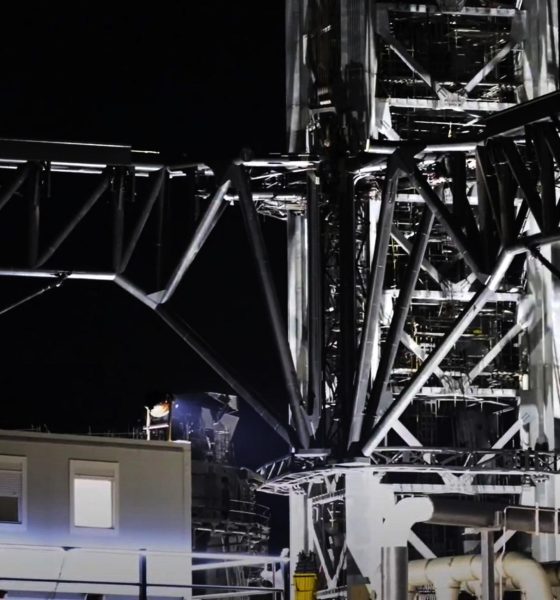
Unlike other ‘arms’ related to other rocket launch facilities, the pair SpaceX began to install on Starbase’s launch tower were colossal, measuring more than 30m (100+ ft) long and 5-10m (15-30 ft) tall. Built out of heavy-duty steel pipe and affixed to an even sturdier pair of claw-like supports that grab onto the launch tower, the combined assembly likely weighs hundreds of tons. Aside from their sheer scale, Starbase’s main tower arms are also attached to a complex system of cables and an industrial-strength ‘drawworks’ commonly used on giant oil rigs and derricks.
They also feature huge actuators that allow the two arms to open and close, revealing a bit of their purpose. While the main reason they likely exist is to provide SpaceX with an all-weather alternative to cranes for lifting, manipulating, and precisely stacking Starships and Super Heavy boosters at the launch pad, the headline – ever since Musk revealed the idea – has always been plans to use those same arms to literally catch rockets out of mid-air.
To do so, they’ll need to be able to actuate and move extremely quickly and precisely up and down the Starship launch tower, matching the velocity and autonomously determining the position of landing Super Heavy boosters (and possibly Starships) to avoid major damage or the loss of entire vehicles. While arguably an unnecessary gamble and an attempt to micro-optimize the concept of operations of a rocket that’s yet to attempt a single orbital-class launch, SpaceX’s CEO is clearly committed to the idea and – whether or not the first iteration works – has fully delivered on the first complete lift-and-catch system.
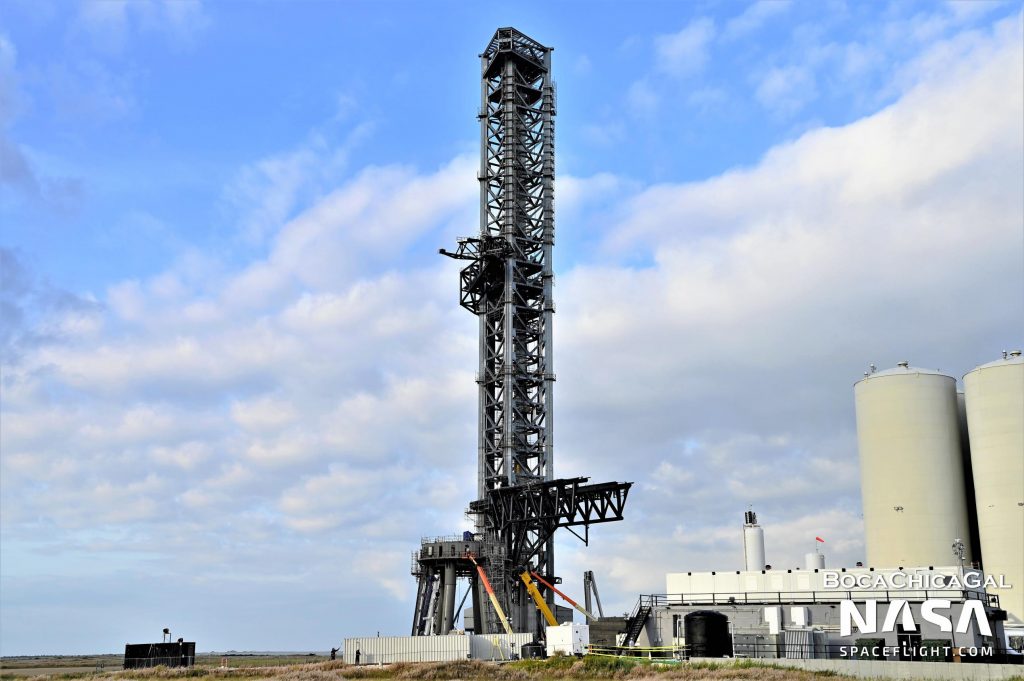
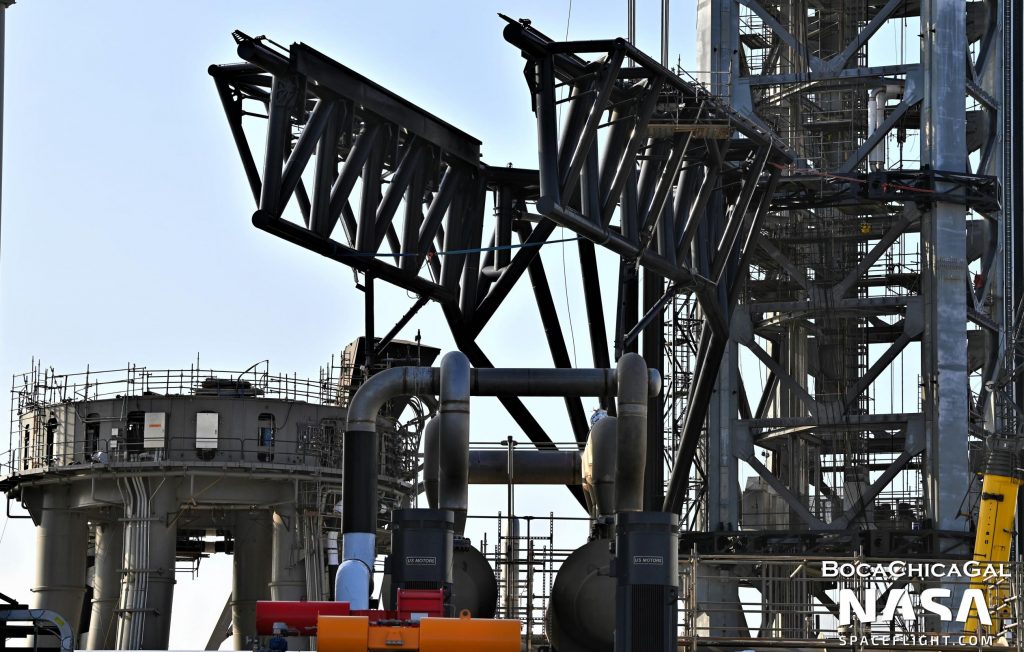


On January 3rd, 2022, after removing a large amount of scaffolding in the days prior, SpaceX briefly and slightly moved the installed arms for the first time, using the drawworks to lift the entire arm-and-carriage assembly a few meters (~6 ft) up and down the tower. Once a few minor additional steps are taken, the chopsticks could be ready for much more extensive testing, beginning with basic lift, descent, and arm actuation tests to calibrate and then proof the first-of-its-kind mechanism. Later, SpaceX will likely simulate catching rockets in a wide range of scenarios. Somewhere before, during, or after that testing, SpaceX may perform another fit test with Starship S20 and Super Heavy B4 – but this time using the arms to lift and install the stages.

Elon Musk
Musk company boycott proposal at City Council meeting gets weird and ironic
The City of Davis in California held a weekly city council meeting on Tuesday, where it voted on a proposal to ban Musk-operated companies. It got weird and ironic.

A city council meeting in California that proposed banning the entry of new contracts with companies controlled by Elon Musk got weird and ironic on Tuesday night after councilmembers were forced to admit some of the entities would benefit the community.
The City of Davis in California held a weekly city council meeting on Tuesday, where it voted on a proposal called “Resolution Ending Engagement With Elon Musk-Controlled Companies and To Encourage CalPERS To Divest Stock In These Companies.”
The proposal claimed that Musk ” has used his influence and corporate platforms to promote political ideologies and activities that threaten democratic norms and institutions, including campaign finance activities that raise ethical and legal concerns.”
We reported on it on Tuesday before the meeting:
California city weighs banning Elon Musk companies like Tesla and SpaceX
However, the meeting is now published online, and it truly got strange.
While it was supported by various members of the community, you could truly tell who was completely misinformed about the influence of Musk’s companies, their current status from an economic and competitive standpoint, and how much some of Musk’s companies’ projects benefit the community.
City Council Member Admits Starlink is Helpful
One City Council member was forced to admit that Starlink, the satellite internet project established by Musk’s SpaceX, was beneficial to the community because the emergency response system utilized it for EMS, Fire, and Police communications in the event of a power outage.
After public comments were heard, councilmembers amended some of the language in the proposal to not include Starlink because of its benefits to public safety.
One community member even said, “There should be exceptions to the rule.”
🚨 After the City of Davis, California, held its City Council meeting on Tuesday and voted on a resolution called “Resolution Ending Engagement With Elon Musk-Controlled Companies and To Encourage CalPERS To Divest Stock In These Companies,” it was forced to admit that it needs… pic.twitter.com/hQiCIX3yll
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 19, 2026
Community Members Report Out of Touch Mainstream Media Narratives
Many community members very obviously read big bold headlines about how horribly Tesla is performing in terms of electric vehicles. Many pointed to “labor intimidation” tactics being used at the company’s Fremont Factory, racial discrimination lawsuits, and Musk’s political involvement as clear-cut reasons why Davis should not consider his companies for future contracts.
However, it was interesting to hear some of them speak, very obviously out of touch with reality.
Musk has encouraged unions to propose organizing at the Fremont Factory, stating that many employees would not be on board because they are already treated very well. In 2022, he invited Union leaders to come to Fremont “at their convenience.”
The UAW never took the opportunity.
Some have argued that Tesla prevented pro-union clothing at Fremont, which it did for safety reasons. An appeals court sided with Tesla, stating that the company had a right to enforce work uniforms to ensure employee safety.
Another community member said that Tesla was losing market share in the U.S. due to growing competition from legacy automakers.
“Plus, these existing auto companies have learned a lot from what Tesla has done,” she said. Interestingly, Ford, General Motors, and Stellantis have all pulled back from their EV ambitions significantly. All three took billions in financial hits.
One Resident Crosses a Line
One resident’s time at the podium included this:
Another member of the community did this…a member of the City Council admonished him and it came to a verbal spat https://t.co/zWvKCiCkie pic.twitter.com/1L334qq9av
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 19, 2026
He was admonished by City Council member Bapu Vaitla, who said his actions were offensive. The two sparred verbally for a few seconds before their argument ended.
City Council Vote Result
Ultimately, the City of Davis chose to pass the motion, but they also amended it to exclude Starlink because of its emergency system benefits.
Elon Musk
California city weighs banning Elon Musk companies like Tesla and SpaceX
A resolution draft titled, “Resolution Ending Engagement With Elon Musk-Controlled Companies and To Encourage CalPERS To Divest Stock In These Companies,” alleges that Musk “has engaged in business practices that are alleged to include violations of labor laws, environmental regulations, workplace safety standards, and regulatory noncompliance.”

A California City Council is planning to weigh whether it would adopt a resolution that would place a ban on its engagement with Elon Musk companies, like Tesla and SpaceX.
The City of Davis, California, will have its City Council weigh a new proposal that would adopt a resolution “to divest from companies owned and/or controlled by Elon Musk.”
This would include a divestment proposal to encourage CalPERS, the California Public Employees Retirement System, to divest from stock in any Musk company.
A resolution draft titled, “Resolution Ending Engagement With Elon Musk-Controlled Companies and To Encourage CalPERS To Divest Stock In These Companies,” alleges that Musk “has engaged in business practices that are alleged to include violations of labor laws, environmental regulations, workplace safety standards, and regulatory noncompliance.”
It claims that Musk “has used his influence and corporate platforms to promote political ideologies and activities that threaten democratic norms and institutions, including campaign finance activities that raise ethical and legal concerns.”
If adopted, Davis would bar the city from entering into any new contracts or purchasing agreements with any company owned or controlled by Elon Musk. It also says it will not consider utilizing Tesla Robotaxis.
Hotel owner tears down Tesla chargers in frustration over Musk’s politics
A staff report on the proposal claims there is “no immediate budgetary impact.” However, a move like this would only impact its residents, especially with Tesla, as the Supercharger Network is open to all electric vehicle manufacturers. It is also extremely reliable and widespread.
Regarding the divestment request to CalPERS, it would not be surprising to see the firm make the move. Although it voted against Musk’s compensation package last year, the firm has no issue continuing to make money off of Tesla’s performance on Wall Street.
The decision to avoid Musk companies will be considered this evening at the City Council meeting.
The report comes from Davis Vanguard.
It is no secret that Musk’s political involvement, especially during the most recent Presidential Election, ruffled some feathers. Other cities considered similar options, like the City of Baltimore, which “decided to go in another direction” after awarding Tesla a $5 million contract for a fleet of EVs for city employees.
Elon Musk
Starlink restrictions are hitting Russian battlefield comms: report
The restrictions have reportedly disrupted Moscow’s drone coordination and frontline communications.

SpaceX’s decision to disable unauthorized Starlink terminals in Ukraine is now being felt on the battlefield, with Ukrainian commanders reporting that Russian troops have struggled to maintain assault operations without access to the satellite network.
The restrictions have reportedly disrupted Moscow’s drone coordination and frontline communications.
Lt. Denis Yaroslavsky, who commands a special reconnaissance unit, stated that Russian assault activity noticeably declined for several days after the shutdown. “For three to four days after the shutdown, they really reduced the assault operations,” Yaroslavsky said.
Russian units had allegedly obtained Starlink terminals through black market channels and mounted them on drones and weapons systems, despite service terms prohibiting offensive military use. Once those terminals were blocked, commanders on the Ukrainian side reported improved battlefield ratios, as noted in a New York Post report.
A Ukrainian unit commander stated that casualty imbalances widened after the cutoff. “On any given day, depending on your scale of analysis, my sector was already achieving 20:1 (casuality rate) before the shutdown, and we are an elite unit. Regular units have no problem going 5:1 or 8:1. With Starlink down, 13:1 (casualty rate) for a regular unit is easy,” the unit commander said.
The restrictions come as Russia faces heavy challenges across multiple fronts. A late January report from the Center for Strategic and International Studies estimated that more than 1.2 million Russian troops have been killed, wounded, or gone missing since February 2022.
The Washington-based Institute for the Study of War also noted that activity from Russia’s Rubikon drone unit declined after Feb. 1, suggesting communications constraints from Starlink’s restrictions may be limiting operations. “I’m sure the Russians have (alternative options), but it takes time to maximize their implementation and this (would take) at least four to six months,” Yaroslavsky noted.