Investor's Corner
The Anatomy of a Tesla ($TSLA) Trader Analyst

Hi, my name is …
Marco Papa. I am a techie by trade and very much a product of the first dot com boom (and bust) of the 90’s. I originally came to this country from Italy to pursue a PhD in computer science at USC, back in 1981. I worked for 6 different dot-coms in the span of 10 years, starting as software developer, then system architect all the way to several CTO positions. All these companies, except one, no longer exist: they either were sold, or went bankrupt. But in the process I learned a lot about company valuations, private placements, and raising tens of millions of dollars from VCs, banks and brokerage houses. And yes, like many other Internet executives of the time, I owned a Ferrari 355 spider convertible. I’ll come back later to the Ferrari.
After 10 years of high-stress jobs, I decided to move to slower-paced “environments”: for the past 14 years I have held a daytime job working for state government and a nighttime job teaching Web Technologies at USC.
“Buy what you know”
But it is during the dot-com era that I started tinkering with Mutual Funds and stocks. For the initial 15 years I was an “investor”. I would purchase mutual funds and stocks and hold them for a minimum of a year. Then in 2005 something changed: I consolidated all my retirement funds from the various companies I had worked for into a single SEP-IRA at E-Trade and strangely enough, after answering a simple questionnaire, E-Trade gave me access to Level 2 Options trading. I did not know much about options then, so I subscribed to a service called the Options Oracle from The Market Guys (http://www.themarketguys.com), which recommends entry and exit points for options trades for a fee. I learned a lot, but I felt frustrated that I was trading options of companies I knew nothing about. So I decided to follow an investment method that I had learned when I used to hold shares in Fidelity Magellan Fund (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magellan_Fund), a fund with $20B of stock investments, and the best performing one between 1977 and 1990, averaging over a 29% annual return. Peter Lynch, Magellan fund manager at that time, created the investment method commonly referred to as “Buy What You Know”: invest in businesses that you understand “personally”, especially if you buy and own their products. Since that time, I have tried to follow the “Buy What You Know” method in all my investments and trades.
Interestingly it is at that time that I started making my “switch” from Windows to the Mac. My first Apple purchase was an iPod; I subsequently trashed a ThinkPad and bought a MacBook, and finally trashed an HP desktop and bought a Mac Pro. Today I own probably close to 25 Apple devices, once I count all the iPhones, iPads, Apple Extremes, Apple TVs, and Apple Watches my wife and I use daily. In 2006 I started “investing” in Apple stock. After the stock market crash of 2007, I started “trading” Apple options. Between 2006 and 2014 I made more money trading AAPL than any other stock. During that time, I added a few more stocks to my trading pattern: Netflix (NFLX), Amazon (AMZN), Google (GOOG), Facebook (FB), Starbucks (SBUX) and more recently Tesla Motors (TSLA). These are all companies that qualify for the “Buy What You Know” mantra: I either buy their products regularly or use them in my daily life.
$TSLA to P90D
I started reading about Elon Musk since he founded PayPal. I read about his promotion of sustainable energy as a way to save our planet. In 2012 I installed solar panels in my house in Redondo Beach, CA. In 2013 I replaced my energy-hog 2007-vintage Mac Pro with a low-energy Mac Pro (a.k.a. the “can”). In 2014 I switched all light bulbs in my house (over 300 of them) from incandescent to low-energy LEDs. And in 2015 I bought a red Tesla Model S P90D (a.k.a. Red Five X-wing). By now my carbon footprint is in pretty good shape.
I started trading TSLA options in early 2014. By summer of 2015 I had enough profits from option trades in TSLA, AAPL and SCO to pay in cash 2/3 of the price of my P90D.
After trading TSLA for over two years I have a few opinions on how to invest or trade it. A stock for me is a good “investment” if it can be held for about 5 years, and provide annual stock gains of 5-10% per year. If you had purchased TSLA stock at the IPO in 2010 at about $19, you would be sitting pretty at a 10-bagger at $250, 6 years later. But if you had purchased it in March 2014 at $265 you’d be about even, two years later. Twice in the past couple of years TSLA stock raised to $275, while slamming back to $140-180 in just 6 months, both times. Tesla in my opinion is not yet a good long term investment.
Part of the reasons is that good long term investments are based on “fundamental” analysis of stocks. Fundamental analysis is based on analyzing the characteristics of a company in order to estimate its “value:” high earnings, income, high profit margins, and small debt are what investors are looking for. According to a recent thestreet.com article, “Tesla Motors has a ‘sell’ rating and a letter grade of D+ at TheStreet Ratings because of the company’s deteriorating net income, generally high debt management risk, disappointing return on equity, poor profit margins and feeble earnings per share growth.”
So if I would not recommend TSLA stock as an investment, why would I even consider TSLA for my trades? Because TSLA is a wonderful stock to trade, not on the basis of “fundamental” analysis, but on the basis of “technical” analysis. In finance, technical analysis is a security analysis methodology for forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. The “value” of the company does not matter. Even just 10 years ago, trading on the basis of technical analysis was only for the pros: brokerage houses, money managers and hedge fund managers. Today individuals have access to tools, indicators, and “conditional” trades that make trading, and especially options trading, much easier and safer.
I consider myself a “swing” trader: I normally enter an option trade when at least 3 indicators are firing on all cylinders; I put conditional stops to lower my losses when the market goes against my trade, and get out of trades when indicators are turning negative.
Coming up
It turns out that TSLA is a fairly good “swing” stock, where the above methodology has worked well in the past. In the next few weeks, while covering the news about the company that can affect its stock price, I will introduce some of the tools, indicators and techniques that any trader can use to profit on TSLA. You’ll hear names like moving averages, pay-day cycles, MACD indicator, Heikin-Ashi charts, support and resistance lines. You will see that none of these are rocket science.
I will write a column, a couple of times a week, providing TSLA stock analysis, information on investing and trading TSLA stock and options, and covering TSLA earnings and all rumors and news that can affect the stock.
Now back to the Ferrari. The F355 Spider that I purchased in 1996 was priced at $137,000, had a top speed of 183mph, 375hp, 268lb-ft torque, and performed 0-60mph in 4.5s and the quarter mile in 12.9s.
The Tesla Model S P90D (Insane) I purchased in 2015 has a very similar price, $142,000, but with a top speed of 155mph, 691hp, 713lb-ft torque, and performs 0-60mph in 3.1s and the quarter mile in 11.7s. The Tesla sedan beats the Ferrari in all but the top speed rating.
But while you needed a Formula 1 driver to obtain those numbers in the Ferrari, mainly to change the gears at the exact right time, effectively anyone can get the Tesla numbers just by flooring the accelerator. The only thing I miss from the Ferrari is the “roar” of the engine; for everything else the Tesla is so much more fun.
Disclosure: I currently have no positions in any stocks mentioned, but I may plan to initiate positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Teslarati). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Elon Musk
Tesla analyst issues stern warning to investors: forget Trump-Musk feud

A Tesla analyst today said that investors should not lose sight of what is truly important in the grand scheme of being a shareholder, and that any near-term drama between CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump should not outshine the progress made by the company.
Gene Munster of Deepwater Management said that Tesla’s progress in autonomy is a much larger influence and a significantly bigger part of the company’s story than any disagreement between political policies.
Munster appeared on CNBC‘s “Closing Bell” yesterday to reiterate this point:
“One thing that is critical for Tesla investors to remember is that what’s going on with the business, with autonomy, the progress that they’re making, albeit early, is much bigger than any feud that is going to happen week-to-week between the President and Elon. So, I understand the reaction, but ultimately, I think that cooler heads will prevail. If they don’t, autonomy is still coming, one way or the other.”
BREAKING: GENE MUNSTER SAYS — $TSLA AUTONOMY IS “MUCH BIGGER” THAN ANY FEUD 👀
He says robotaxis are coming regardless ! pic.twitter.com/ytpPcwUTFy
— TheSonOfWalkley (@TheSonOfWalkley) July 2, 2025
This is a point that other analysts like Dan Ives of Wedbush and Cathie Wood of ARK Invest also made yesterday.
On two occasions over the past month, Musk and President Trump have gotten involved in a very public disagreement over the “Big Beautiful Bill,” which officially passed through the Senate yesterday and is making its way to the House of Representatives.
Musk is upset with the spending in the bill, while President Trump continues to reiterate that the Tesla CEO is only frustrated with the removal of an “EV mandate,” which does not exist federally, nor is it something Musk has expressed any frustration with.
In fact, Musk has pushed back against keeping federal subsidies for EVs, as long as gas and oil subsidies are also removed.
Nevertheless, Ives and Wood both said yesterday that they believe the political hardship between Musk and President Trump will pass because both realize the world is a better place with them on the same team.
Munster’s perspective is that, even though Musk’s feud with President Trump could apply near-term pressure to the stock, the company’s progress in autonomy is an indication that, in the long term, Tesla is set up to succeed.
Tesla launched its Robotaxi platform in Austin on June 22 and is expanding access to more members of the public. Austin residents are now reporting that they have been invited to join the program.
Elon Musk
Tesla surges following better-than-expected delivery report
Tesla saw some positive momentum during trading hours as it reported its deliveries for Q2.

Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA) surged over four percent on Wednesday morning after the company reported better-than-expected deliveries. It was nearly right on consensus estimations, as Wall Street predicted the company would deliver 385,000 cars in Q2.
Tesla reported that it delivered 384,122 vehicles in Q2. Many, including those inside the Tesla community, were anticipating deliveries in the 340,000 to 360,000 range, while Wall Street seemed to get it just right.
Tesla delivers 384,000 vehicles in Q2 2025, deploys 9.6 GWh in energy storage
Despite Tesla meeting consensus estimations, there were real concerns about what the company would report for Q2.
There were reportedly brief pauses in production at Gigafactory Texas during the quarter and the ramp of the new Model Y configuration across the globe were expected to provide headwinds for the EV maker during the quarter.
At noon on the East Coast, Tesla shares were up about 4.5 percent.
It is expected that Tesla will likely equal the number of deliveries it completed in both of the past two years.
It has hovered at the 1.8 million mark since 2023, and it seems it is right on pace to match that once again. Early last year, Tesla said that annual growth would be “notably lower” than expected due to its development of a new vehicle platform, which will enable more affordable models to be offered to the public.
These cars are expected to be unveiled at some point this year, as Tesla said they were “on track” to be produced in the first half of the year. Tesla has yet to unveil these vehicle designs to the public.
Dan Ives of Wedbush said in a note to investors this morning that the company’s rebound in China in June reflects good things to come, especially given the Model Y and its ramp across the world.
He also said that Musk’s commitment to the company and return from politics played a major role in the company’s performance in Q2:
“If Musk continues to lead and remain in the driver’s seat, we believe Tesla is on a path to an accelerated growth path over the coming years with deliveries expected to ramp in the back-half of 2025 following the Model Y refresh cycle.”
Ives maintained his $500 price target and the ‘Outperform’ rating he held on the stock:
“Tesla’s future is in many ways the brightest it’s ever been in our view given autonomous, FSD, robotics, and many other technology innovations now on the horizon with 90% of the valuation being driven by autonomous and robotics over the coming years but Musk needs to focus on driving Tesla and not putting his political views first. We maintain our OUTPERFORM and $500 PT.”
Moving forward, investors will look to see some gradual growth over the next few quarters. At worst, Tesla should look to match 2023 and 2024 full-year delivery figures, which could be beaten if the automaker can offer those affordable models by the end of the year.
Investor's Corner
Tesla delivers 384,000 vehicles in Q2 2025, deploys 9.6 GWh in energy storage
The quarter’s 9.6 GWh energy storage deployment marks one of Tesla’s highest to date.

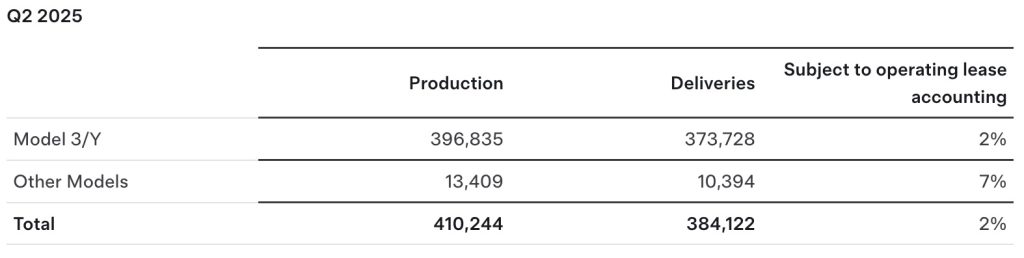
Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA) has released its Q2 2025 vehicle delivery and production report. As per the report, the company delivered over 384,000 vehicles in the second quarter of 2025, while deploying 9.6 GWh in energy storage. Vehicle production also reached 410,244 units for the quarter.
Model 3/Y dominates output, ahead of earnings call
Of the 410,244 vehicles produced during the quarter, 396,835 were Model 3 and Model Y units, while 13,409 were attributed to Tesla’s other models, which includes the Cybertruck and Model S/X variants. Deliveries followed a similar pattern, with 373,728 Model 3/Ys delivered and 10,394 from other models, totaling 384,122.
The quarter’s 9.6 GWh energy storage deployment marks one of Tesla’s highest to date, signaling continued strength in the Megapack and Powerwall segments.
Year-on-year deliveries edge down, but energy shows resilience
Tesla will share its full Q2 2025 earnings results after the market closes on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, with a live earnings call scheduled for 4:30 p.m. CT / 5:30 p.m. ET. The company will publish its quarterly update at ir.tesla.com, followed by a Q&A webcast featuring company leadership. Executives such as CEO Elon Musk are expected to be in attendance.
Tesla investors are expected to inquire about several of the company’s ongoing projects in the upcoming Q2 2025 earnings call. Expected topics include the new Model Y ramp across the United States, China, and Germany, as well as the ramp of FSD in territories outside the US and China. Questions about the company’s Robotaxi business, as well as the long-referenced but yet to be announced affordable models are also expected.
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Grok 3 partners with Oracle Cloud for corporate AI innovation
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoSpaceX and Elon Musk share insights on Starship Ship 36’s RUD
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoWatch Tesla’s first driverless public Robotaxi rides in Texas
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla has started rolling out initial round of Robotaxi invites














