News
World Energy Outlook: “Electric cars are happening” as global gasoline consumption peaks

A new forecast put together by The International Energy Agency (IEA) indicates that worldwide consumption of gasoline has peaked as Tesla and new players within the electric vehicle space halt demand growth in the next 25 years. IEA director Fatih Birol told press in London that the number of electric cars on the road worldwide will increase from 1 million last year to 150 million by 2040. Birol went on to say that demand for gasoline will peak very shortly if it has not already. Gasoline accounts for one in four barrels of oil consumed worldwide. “Electric cars are happening,” Birol said. The push for more efficient cars with lower carbon emissions is also spurring a decrease in demand for gasoline.
Birol’s forecast is in line with a statement made a few weeks ago by Simon Henry, CFO of Royal Dutch Shell. “We’ve long been of the opinion that demand will peak before supply,” he said. “And that peak may be somewhere between 5 and 15 years hence, and it will be driven by efficiency and substitution, more than offsetting the new demand for transport.”
According to Bloomberg, the IEA expects that gasoline consumption will drop 0.2% over the next 25 years even though the number of cars on the road worldwide is predicted to double to 2 billion vehicles during that period. Birol’s remarks came in connection with the release of the IEA’s annual World Energy Outlook for 2016.
Nevertheless, the IEA’s negative prediction for gasoline does not mean that demand for oil will cease any time soon. It still predicts overall oil demand will grow for several decades because of rising demand for so-called middle distalates — diesel, fuel oil, and jet fuel — by the shipping, trucking, aviation and petrochemical industries.
Philip Verleger, a veteran oil market analyst in Colorado, is more pessimistic about the IEA report. “Refiners across the globe can only hope that this [IEA] forecast turns out to be right, because all the indications are today that consumption is going to begin dropping not in 2030, but probably in 2020,” said Verleger. “It’s the best news a dying patient can hope to get.” Refineries are designed to maximize the production of gasoline. Changes in the marketplace may force them to invest billions to reconfigure the refining process.
Not all emissions come from automobiles and trucks. The global shipping industry is responsible for the largest amount of carbon emissions in the transportation sector. (Commercial airline numbers are not far behind.) Edward Humes, author of Door To Door looks at the total emissions impact of products the industrialized world uses each day. In an interview with NPR earlier this year, Humes says, “If you take 160 [large ships], the emissions from just those vessels, of the type of emissions that cause smog and particulate pollution, those 160 mega ships will be the equivalent of the emissions of all the cars in the world. And that’s just a tiny fraction of the worldwide fleet. Together, the cargo fleet generates about 2 to 3 percent of world carbon emissions, which would – if that fleet were a country, it would put them in the top 10 emitters of carbon dioxide in the world. In fact, it would put it ahead of Germany – the fourth-largest economy in the world.”
Elon Musk
Tesla reveals it is using AI to make factories more sustainable: here’s how
Tesla is using AI in its Gigafactory Nevada factory to improve HVAC efficiency.
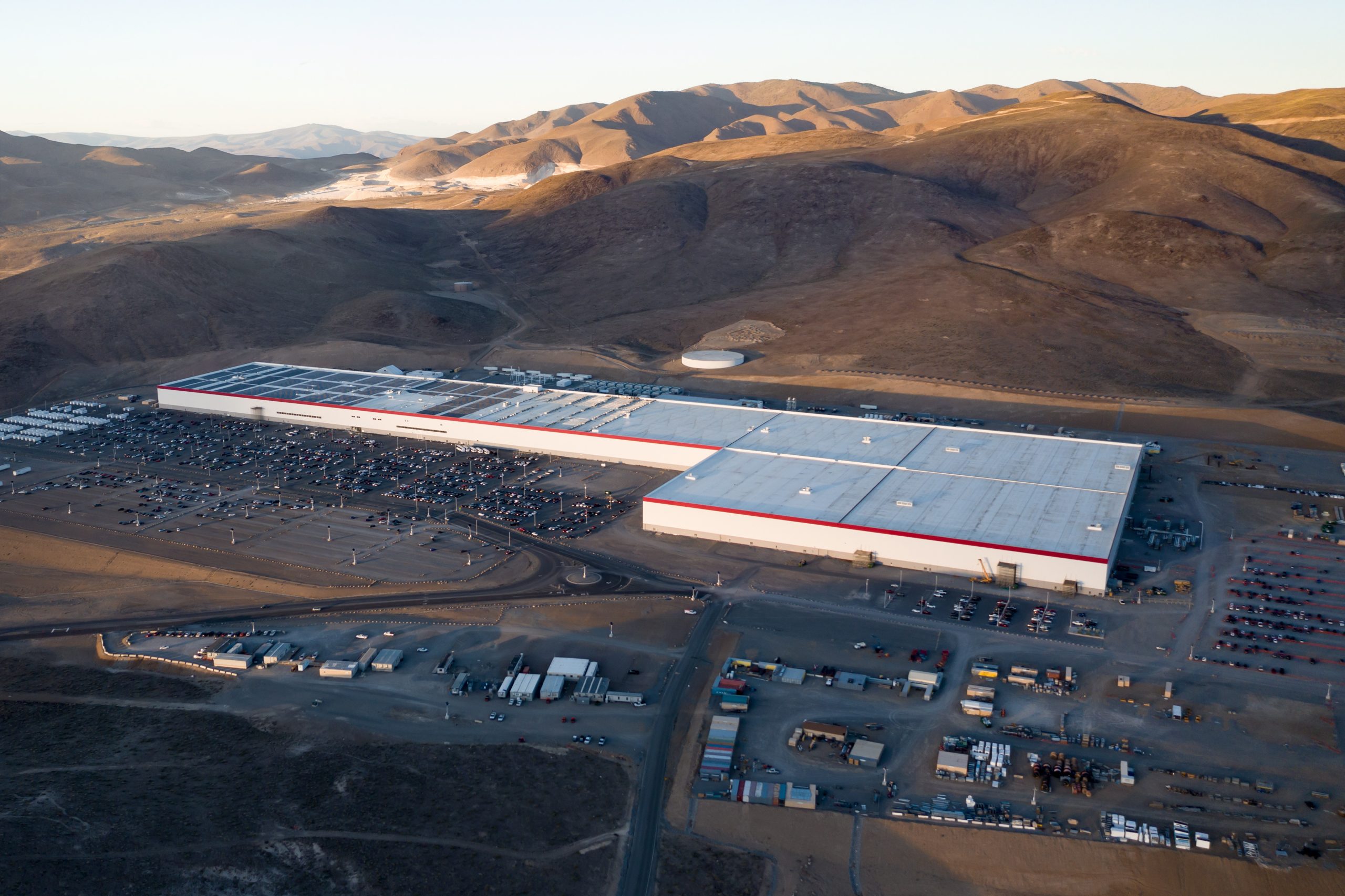

Tesla has revealed in its Extended Impact Report for 2024 that it is using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enable its factories to be more sustainable. One example it used was its achievement of managing “the majority of the HVAC infrastructure at Gigafactory Nevada is now AI-controlled” last year.
In a commitment to becoming more efficient and making its production as eco-friendly as possible, Tesla has been working for years to find solutions to reduce energy consumption in its factories.
For example, in 2023, Tesla implemented optimization controls in the plastics and paint shops located at Gigafactory Texas, which increased the efficiency of natural gas consumption. Tesla plans to phase out natural gas use across its factories eventually, but for now, it prioritizes work to reduce emissions from that energy source specifically.
It also uses Hygrometric Control Logic for Air Handling Units at Giafactory Berlin, resulting in 17,000 MWh in energy savings each year. At Gigafactory Nevada, Tesla saves 9.5 GWh of energy through the use of N-Methylpyrrolidone refineries when extracting critical raw material.
Perhaps the most interesting way Tesla is conserving energy is through the use of AI at Gigafactory Nevada, as it describes its use of AI to reduce energy demand:
“In 2023, AI Control for HVAC was expanded from Nevada and Texas to now include our Berlin-Brandenburg and Fremont factories. AI Control policy enables HVAC systems within each factory to work together to process sensor data, model factory dynamics, and apply control actions that safely minimize the energy required to support production. In 2024, this system achieved two milestones: the majority of HVAC infrastructure at Gigafactory Nevada is now AI-controlled, reducing fan and thermal energy demand; and the AI algorithm was extended to manage entire chiller plants, creating a closed-loop control system that optimizes both chilled water consumption and the energy required for its generation, all while maintaining factory conditions.”
Tesla utilizes AI Control “primarily on systems that heat or cool critical factory production spaces and equipment.” AI Control communicates with the preexisting standard control logic of each system, and any issues can be resolved by quickly reverting back to standard control. There were none in 2024.
Tesla says that it is utilizing AI to drive impact at its factories, and it has proven to be a valuable tool in reducing energy consumption at one of its facilities.
Elon Musk
Tesla analysts believe Musk and Trump feud will pass
Tesla CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump’s feud shall pass, several bulls say.

Tesla analysts are breaking down the current feud between CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump, as the two continue to disagree on the “Big Beautiful Bill” and its impact on the country’s national debt.
Musk, who headed the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) under the Trump Administration, left his post in May. Soon thereafter, he and President Trump entered a very public and verbal disagreement, where things turned sour. They reconciled to an extent, and things seemed to be in the past.
However, the second disagreement between the two started on Monday, as Musk continued to push back on the “Big Beautiful Bill” that the Trump administration is attempting to sign into law. It would, by Musk’s estimation, increase spending and reverse the work DOGE did to trim the deficit.
Every member of Congress who campaigned on reducing government spending and then immediately voted for the biggest debt increase in history should hang their head in shame!
And they will lose their primary next year if it is the last thing I do on this Earth.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) June 30, 2025
President Trump has hinted that DOGE could be “the monster” that “eats Elon,” threatening to end the subsidies that SpaceX and Tesla receive. Musk has not been opposed to ending government subsidies for companies, including his own, as long as they are all abolished.
How Tesla could benefit from the ‘Big Beautiful Bill’ that axes EV subsidies
Despite this contentious back-and-forth between the two, analysts are sharing their opinions now, and a few of the more bullish Tesla observers are convinced that this feud will pass, Trump and Musk will resolve their differences as they have before, and things will return to normal.
ARK Invest’s Cathie Wood said this morning that the feud between Musk and Trump is another example of “this too shall pass:”
BREAKING: CATHIE WOOD SAYS — ELON AND TRUMP FEUD “WILL PASS” 👀 $TSLA
She remains bullish ! pic.twitter.com/w5rW2gfCkx
— TheSonOfWalkley (@TheSonOfWalkley) July 1, 2025
Additionally, Wedbush’s Dan Ives, in a note to investors this morning, said that the situation “will settle:”
“We believe this situation will settle and at the end of the day Musk needs Trump and Trump needs Musk given the AI Arms Race going on between the US and China. The jabs between Musk and Trump will continue as the Budget rolls through Congress but Tesla investors want Musk to focus on driving Tesla and stop this political angle…which has turned into a life of its own in a roller coaster ride since the November elections.”
Tesla shares are down about 5 percent at 3:10 p.m. on the East Coast.
Elon Musk
Tesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales
Tesla CEO Elon Musk is reportedly overseeing sales in North America and Europe, Bloomberg reports.

Tesla scrambled its executives around following the exit of CEO Elon Musk’s sidekick last week, Omead Afshar. Afshar was relieved of his duties as Head of Sales for both North America and Europe.
Bloomberg is reporting that Musk is now overseeing both regions for sales, according to sources familiar with the matter. Afshar left the company last week, likely due to slow sales in both markets, ending a seven-year term with the electric automaker.
Tesla’s Omead Afshar, known as Elon Musk’s right-hand man, leaves company: reports
Afshar was promoted to the role late last year as Musk was becoming more involved in the road to the White House with President Donald Trump.
Afshar, whose LinkedIn account stated he was working within the “Office of the CEO,” was known as Musk’s right-hand man for years.
Additionally, Tom Zhu, currently the Senior Vice President of Automotive at Tesla, will oversee sales in Asia, according to the report.
It is a scramble by Tesla to get the company’s proven executives over the pain points the automaker has found halfway through the year. Sales are looking to be close to the 1.8 million vehicles the company delivered in both of the past two years.
Tesla is pivoting to pay more attention to the struggling automotive sales that it has felt over the past six months. Although it is still performing well and is the best-selling EV maker by a long way, it is struggling to find growth despite redesigning its vehicles and launching new tech and improvements within them.
The company is also looking to focus more on its deployment of autonomous tech, especially as it recently launched its Robotaxi platform in Austin just over a week ago.
However, while this is the long-term catalyst for Tesla, sales still need some work, and it appears the company’s strategy is to put its biggest guns on its biggest problems.
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Grok integration will be more realistic with this cool feature
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla China roars back with highest vehicle registrations this Q2 so far
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla dominates Cars.com’s Made in America Index with clean sweep
-
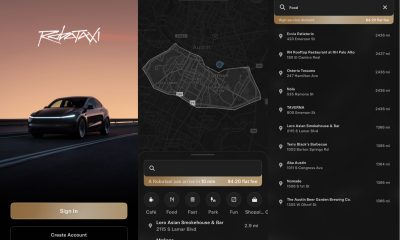
 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more















