Space
Mars exploration in focus as Europe prepares ExoMars Rover for search of life
2020 may be the year humanity takes its biggest step toward finding evidence of life beyond Earth. NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) are each working on its own rover that will roam Mars’s surface in search of life.
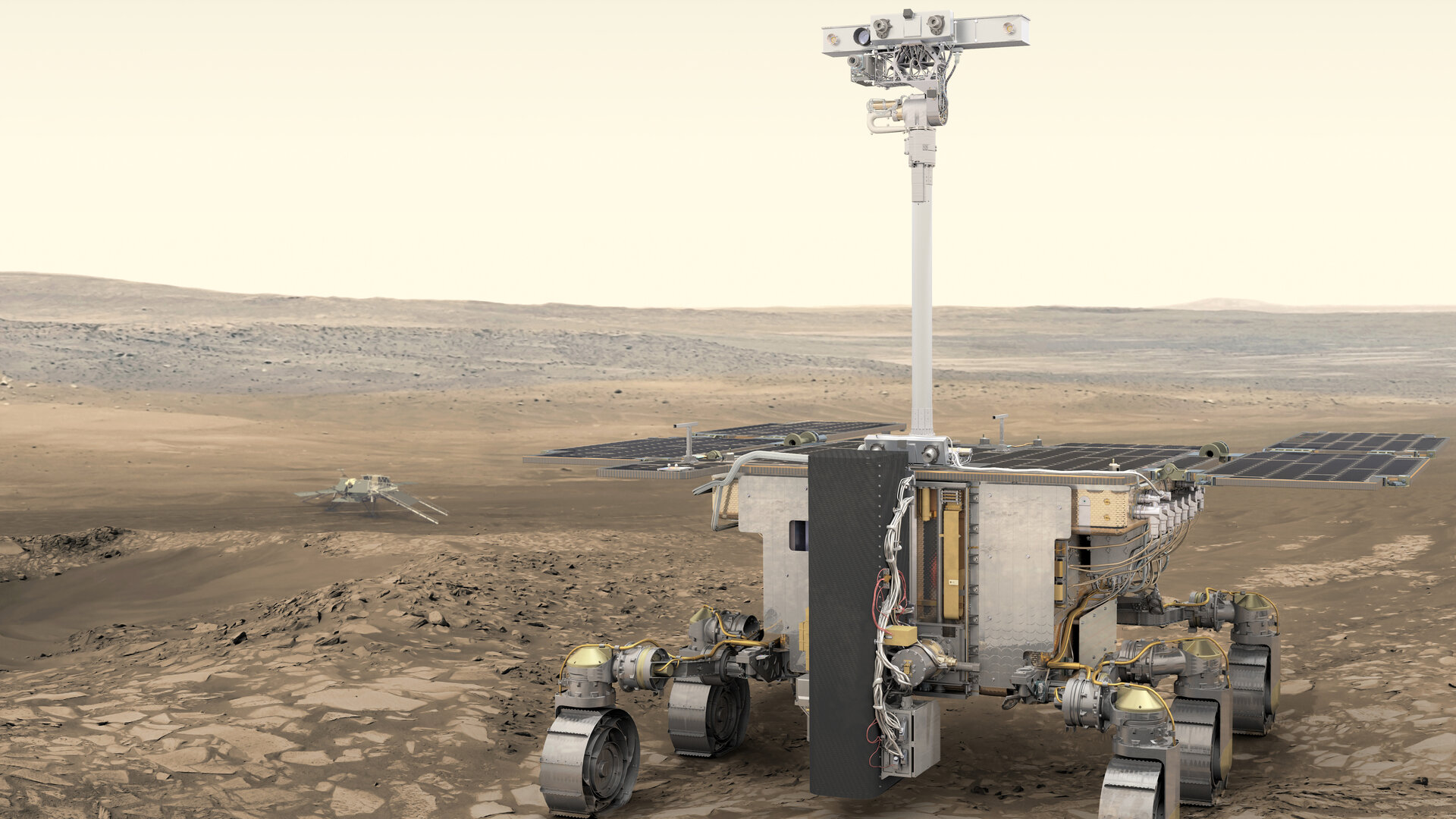
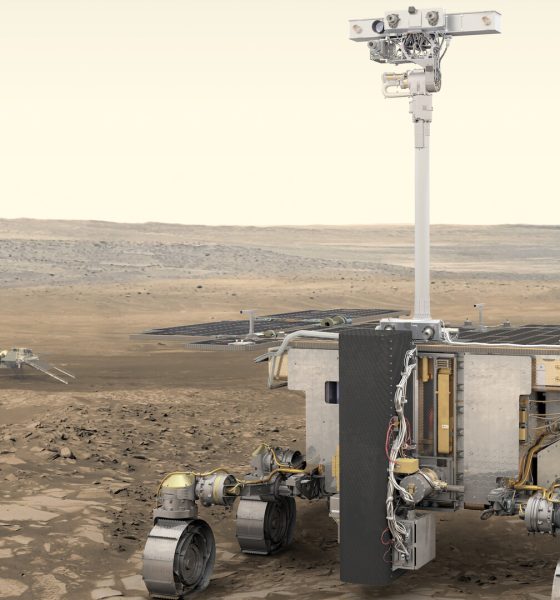
The ExoMars mission is Europe’s first Mars rover. Named after British DNA pioneer Rosalind Franklin, the golf cart-sized robot is approximately one-third the size of NASA’s planned Mars 2020 rover and will look for signs that life might have existed on Mars.
Both rovers will act as remote scientists, beaming back a wealth of data and images to Earth.
Mars 2020 will collect Martian samples for eventual return to Earth sometime in the future, while ExoMars will use its unique drill to burrow below the surface. Here, the rover will find pristine samples that were shielded from the harsh radiation bombarding Mars’s surface. Scientists are hopeful that below the surface is where we could find our first evidence of life.
A Rover’s Purpose
Mars is a hostile place. Because its atmosphere is much thinner than Earth’s, life as we know it would have a difficult time surviving on the surface.
Billions of years ago, the surface of Mars was probably quite similar to that of Earth. However, that changed when Mars lost its magnetic field, which stripped its atmosphere, and exposed its surface to intense radiation. All of which made survival above ground incredibly challenging.
Historically, Mars missions have searched for signs of life on the planet’s surface, usually at places where there are signs of ancient water. That’s because this is typically where we find life on Earth.
But since we haven’t found life on the planet’s surface yet, mission scientists propose we need to dig deeper. There may be some microbial Martians underground.
The ExoMars rover (and accompanying lander) are a follow-on to ESA’s ExoMars Orbiter mission which reached Mars in 2016. That initial mission consisted of two parts: the Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and the Schiaparelli landing demonstrator.
Landing on Mars
TGO made it to Mars and is doing great, however, Schiaparelli didn’t fare so well — the lander crashed during its descent to the Martian surface.
Landing a probe on Mars is not easy. To safely navigate the tenuous Martian atmosphere requires a combination of sophisticated landing gear, including heat shields, retrorockets, and even giant, inflatable airbags.
Despite the crash landing, Schiaparelli achieved its goal as a technology demonstrator. It also showed that the team needed to revamp the landing system before the rover launches. But, with less than a year till liftoff, the rover team is struggling with an established piece of landing architecture: parachutes.
In order to slow the rover down, the mission requires multiple parachutes — one 15 meters (49 feet) in diameter and one 35 meters (115 feet).
As the rover begins its descent, atmospheric drag will slow the craft from around 21 000 km/h (13,048 mph) to 1700 km/h (1,056 mph). That’s when the first parachute will deploy. About 20 seconds later, at about 400 km/h (248 mph), the second chute will deploy. Lastly, the braking engines will kick in about 1 km (or half a mile) above the ground, enabling the rover land safely on the Martian surface.
The entire sequence takes just six minutes.
Parachute Troubles
During high-altitude testing conducted earlier this year, the craft’s parachutes ripped as soon as they deployed. ESA engineers made several adjustments, including reinforcing both the parachutes and their storage bags with Teflon to make them deploy easier. The chutes are still tearing.
Now the agency is turning to NASA for help. ESA engineers are teaming up with the folks at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, to put the enhanced parachutes through months of rigorous testing.
In the meantime, the rover team is putting its hardware through a round of thermal testing. For 18 days it will be subjected to the same harsh temperature conditions experienced on Mars.
The parachutes are expected to finish testing sometime in April 2020; they will then be integrated with the rover and shipped to the launch site in Kazakhstan. However, if any part of the mission misses its deadline, the entire project could be sidelined until the next favorable Mars launch window — in 2022.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
Starlink gets its latest airline adoptee for stable and reliable internet access
The company said it plans to “rapidly integrate Starlink into its fleet,” and that the first Starlink-equipped aircraft will enter service this Summer.

SpaceX’s Starlink, the satellite internet program launched by Elon Musk’s company, has gotten its latest airline adoptee, offering stable and reliable internet to passengers.
Southwest Airlines announced on Wednesday that it would enable Starlink on its aircraft, a new strategy that will expand to more than 300 planes by the end of the year.
The company said it plans to “rapidly integrate Starlink into its fleet,” and that the first Starlink-equipped aircraft will enter service this Summer.
Tony Roach, Executive Vice President, Chief Customer and Brand Officer for the airline, said:
“Free WiFi has been a huge hit with our Rapid Rewards Members, and we know our Customers expect seamless connectivity across all their devices when they travel. Starlink delivers that at-home experience in the air, giving Customers the ability to stream their favorite shows from any platform, watch live sports, download music, play games, work, and connect with loved ones from takeoff to landing.”
Southwest also said that this is just one of the latest upgrades it is making to provide a more well-rounded experience to its aircraft. In addition to Starlink, it is updating cabin designs, offering more legroom, and installing in-seat power to all passengers.
Southwest became one of several airlines to cross over to Starlink, as reviews for the internet provider have raved about reliability and speed. Over the past year, Hawaiian Airlines, United Airlines, Alaska Airlines, airBaltic, Air France, JSX, Emirates, British Airways, and others have all decided to install Starlink on their planes.
This has been a major move away from unpredictable and commonly unreliable WiFi offerings on planes. Starlink has been more reliable and has provided more stable connections for those using their travel time for leisure or business.
Jason Fritch, VP of Starlink Enterprise Sales at SpaceX, said:
“We’re thrilled to deliver a connectivity experience to Southwest Airlines and its Customers that really is similar, if not better, than what you can experience in your own home. Starlink is the future of connected travel, making every journey faster, smoother, and infinitely more enjoyable.”
Starlink recently crossed a massive milestone of over 10 million subscribers.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk confirms SpaceX is not developing a phone

Despite many recent rumors and various reports, Elon Musk confirmed today that SpaceX is not developing a phone based on Starlink, not once, but twice.
Today’s report from Reuters cited people familiar with the matter and stated internal discussions have seen SpaceX executives mulling the idea of building a mobile device that would connect directly to the Starlink satellite constellation.
Musk did state in late January that SpaceX developing a phone was “not out of the question at some point.” However, He also said it would have to be a major difference from current phones, and would be optimized “purely for running max performance/watt neural nets.”
Not out of the question at some point. It would be a very different device than current phones. Optimized purely for running max performance/watt neural nets.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 30, 2026
While Musk said it was not out of the question “at some point,” that does not mean it is currently a project SpaceX is working on. The CEO reaffirmed this point twice on X this afternoon.
Musk said, “Reuters lies relentlessly,” in one post. In the next, he explicitly stated, “We are not developing a phone.”
Reuters lies relentlessly
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 5, 2026
We are not developing a phone
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 5, 2026
Musk has basically always maintained that SpaceX has too many things going on, denying that a phone would be in the realm of upcoming projects. There are too many things in the works for Musk’s space exploration company, most notably the recent merger with xAI.
SpaceX officially acquires xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise
A Starlink phone would be an excellent idea, especially considering that SpaceX operates 9,500 satellites, serving over 9 million users worldwide. 650 of those satellites are dedicated to the company’s direct-to-device initiative, which provides cellular coverage on a global scale.
Nevertheless, there is the potential that the Starlink phone eventually become a project SpaceX works on. However, it is not currently in the scope of what the company needs to develop, so things are more focused on that as of right now.
Elon Musk
Will Tesla join the fold? Predicting a triple merger with SpaceX and xAI

With the news of a merger between SpaceX and xAI being confirmed earlier this week by CEO Elon Musk directly, the first moves of an umbrella company that combines all of the serial tech entrepreneur’s companies have been established.
The move aims to combine SpaceX’s prowess in launches with xAI’s expanding vision in artificial intelligence, as Musk has detailed the need for space-based data centers that will require massive amounts of energy to operate.
It has always been in the plans to bring Musk’s companies together under one umbrella.
“My companies are, surprisingly in some ways, trending toward convergence,” Musk said in November. With SpaceX and xAI moving together, many are questioning when Tesla will be next. Analysts believe it is a no-brainer.
SpaceX officially acquires xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise
Dan Ives of Wedbush wrote in a note earlier this week that there is a “growing chance” Tesla could be merged in some form with the new conglomeration over the next 12 to 18 months.
“In our view, there is a growing chance that Tesla will eventually be merged in some form into SpaceX/xAI over time. The viewis this growing AI ecosystem will focus on Space and Earth together… and Musk will look to combine forces,” Ives said.
Let’s take a look at the potential.
The Case for Synergies – Building the Ultimate AI Ecosystem
A triple merger would create a unified “Musk Trinity,” blending Tesla’s physical AI with Robotaxi, Optimus, and Full Self-Driving, SpaceX’s orbital infrastructure through Starlink and potential space-based computer, and xAI’s advanced models, including Grok.
This could accelerate real-world AI applications, more specifically, ones like using satellite networks for global autonomy, or even powering massive training through solar-optimized orbital data centers.
The FCC welcomes and now seeks comment on the SpaceX application for Orbital Data Centers.
The proposed system would serve as a first step towards becoming a Kardashev II-level civilization and serve other purposes, according to the applicant. pic.twitter.com/TDnUPuz9w7
— Brendan Carr (@BrendanCarrFCC) February 4, 2026
This would position the entity, which could ultimately be labeled “X,” as a leader in multiplanetary AI-native tech.
It would impact every level of Musk’s AI-based vision for the future, from passenger use to complex AI training models.
Financial and Structural Incentives — and Risks
xAI’s high cash burn rate is now backed by SpaceX’s massive valuation boost, and Tesla joining the merger would help the company gain access to private funding channels, avoiding dilution in a public-heavy structure.
The deal makes sense from a capital standpoint, as it is an advantage for each company in its own specific way, addressing specific needs.
Because xAI is spending money at an accelerating rate due to its massive compute needs, SpaceX provides a bit of a “lifeline” by redirecting its growing cash flows toward AI ambitions without the need for constant external fundraising.
Additionally, Tesla’s recent $2 billion investment in xAI also ties in, as its own heavy CapEx for Dojo supercomputers, Robotaxis, and Optimus could potentially be streamlined.
Musk’s stake in Tesla and SpaceX, after the xAI merger, is also uneven. His ownership in Tesla equates to about 13 percent, only increasing as he achieves each tranche of his most recent compensation package. Meanwhile, he owns about 43 percent of the private SpaceX.
A triple merger between the three companies could boost his ownership in the combined entity to around 26 percent. This would give Musk what he wants: stronger voting power and alignment across his ventures.
It could also be a potential facilitator in private-to-public transitions, as a reverse merger structure to take SpaceX public indirectly via Tesla could be used. This avoids any IPO scrutiny while accessing the public markets’ liquidity.
Timeline and Triggers for a Public Announcement
As previously mentioned, Ives believes a 12-18 month timeline is realistic, fueled by Musk’s repeated hints at convergence between his three companies. Additionally, the recent xAI investment by Tesla only points toward the increased potential for a conglomeration.
Of course, there is speculation that the merger could happen in the shorter term, before June 30 of this year, which is a legitimate possibility. While this possibility exists but remains at low probability, especially when driven by rapid AI/space momentum, longer horizons, like 2027 or later, allow for key milestones like Tesla’s Robotaxi rollout and Cybercab ramp-up, Optimus scaling, or regulatory clarity under a favorable administration.

Credit: Grok Imagine
The sequencing matters: SpaceX-xAI merger as “step one” toward a unified stack, with a potential SpaceX IPO setting a valuation benchmark before any Tesla tie-up.
Full triple convergence could follow if synergies prove out.
Prediction markets are also a reasonable thing to look at, just to get an idea of where people are putting their money. Polymarket, for example, sits at between a 12 and 24 percent chance that a Tesla-SpaceX merger is officially announced before June 30, 2026.
Looking Ahead
The SpaceX-xAI merger is not your typical corporate shuffle. Instead, it’s the clearest signal yet that Musk is architecting a unified “Muskonomy” where AI, space infrastructure, and real-world robotics converge to solve humanity’s biggest challenges.
Yet the path is fraught with execution risks that could turn this visionary upside into a major value trap. Valuation mismatches remain at the forefront of this skepticism: Tesla’s public multiples are unlike any company ever, with many believing they are “stretched.” On the other hand, SpaceX-xAI’s private “marked-to-muth” pricing hinges on unproven synergies and lofty projects, especially orbital data centers and all of the things Musk and Co. will have to figure out along the way.
Ultimately, the entire thing relies on a high-conviction bet on Musk’s ability to execute at scale. The bullish case is transformative: a vertically integrated AI-space-robotics giant accelerates humanity toward abundance and multi-planetary civilization faster than any siloed company could.








