

Space
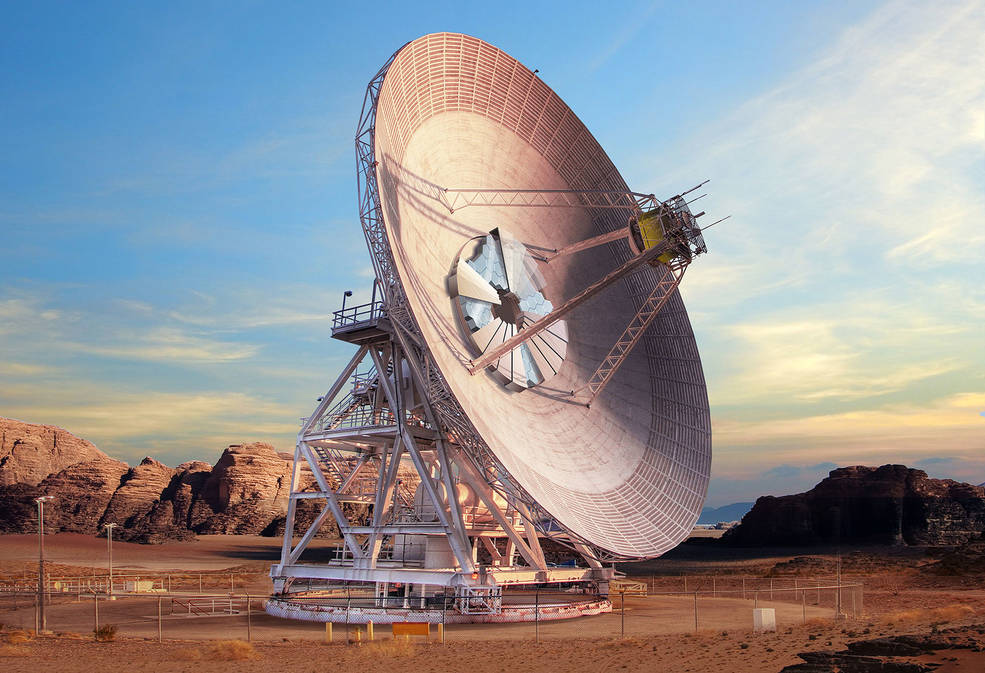
NASA ramps Mars preparations with groundbreaking for new antenna
Ever wonder how spacecraft spread throughout our solar system communicate with Earth? They do so through an international array of radio antenna known as the Deep Space Network. The network consists of 12 antennas at three separate locations: Goldstone, California; Madrid, Spain; and Canberra, Australia. NASA chose these locations because they’re each 120 degrees apart from each other, so satellites can always talk to Earth one of the stations.
“The Deep Space Network is Earth’s one phone line to our two Voyager spacecraft—both in interstellar space—all our Mars missions, and the New Horizons spacecraft that is now far past Pluto,” Jet Propulsion Laboratory Deputy Director Larry James said in a statement. “The more we explore, the more antennas we need to talk to all our missions.”
NASA is preparing for the future as more Mars missions come online and we start to send astronauts to the moon and beyond. So the space agency is adding to its current network. On Feb. 12, NASA broke ground on the new antenna, which will be added to the Goldstone site in California.
The 112-foot-wide dish, called Deep Space Station-23 (or DSS23), will take about two and half years to build. And it’s not the only addition NASA is planning. Space is getting crowded, and with the push to return to the moon and eventual plan to send humans to Mars, NASA wants to make sure it has plenty of bandwidth to communicate. To that end, the space agency aims to build an additional five antennas.
“Since the 1960s, when the world first watched live pictures of humans in space and on the Moon, to revealing imagery and scientific data from the surface of Mars and vast, distant galaxies, the Deep Space Network has connected humankind with our solar system and beyond,” said Badri Younes, NASA’s deputy associate administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, or SCaN, which oversees NASA’s networks. “This new antenna, the fifth of six currently planned, is another example of NASA’s determination to enable science and space exploration through the use of the latest technology.”

This is the first addition to Goldstone since 2003, and the new dish is being built at the complex’s Apollo site — named because its DSS-16 antenna supported NASA’s human missions to the Moon. The new dish being built will be able to support more missions with advanced technology, like lasers, which are capable of transmitting vast amounts of data from far out in the solar system as well as from astronauts on the lunar and Martian surfaces.
“Lasers can increase your data rate from Mars by about 10 times what you get from radio,” said Suzanne Dodd, director of the Interplanetary Network, the organization that manages the DSN. “Our hope is that providing a platform for optical communications will encourage other space explorers to experiment with lasers on future missions.”
Similar antennas have recently been built at the Canberra site and two are currently under construction in Madrid. The Deep Space Network is managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, and even has its own website where viewers can see which DSN dishes are talking to which spacecraft at any given time.
News
SpaceX Ax-4 Mission prepares for ISS with new launch date
SpaceX, Axiom Space, and NASA set new launch date for the Ax-4 mission after addressing ISS & rocket concerns.
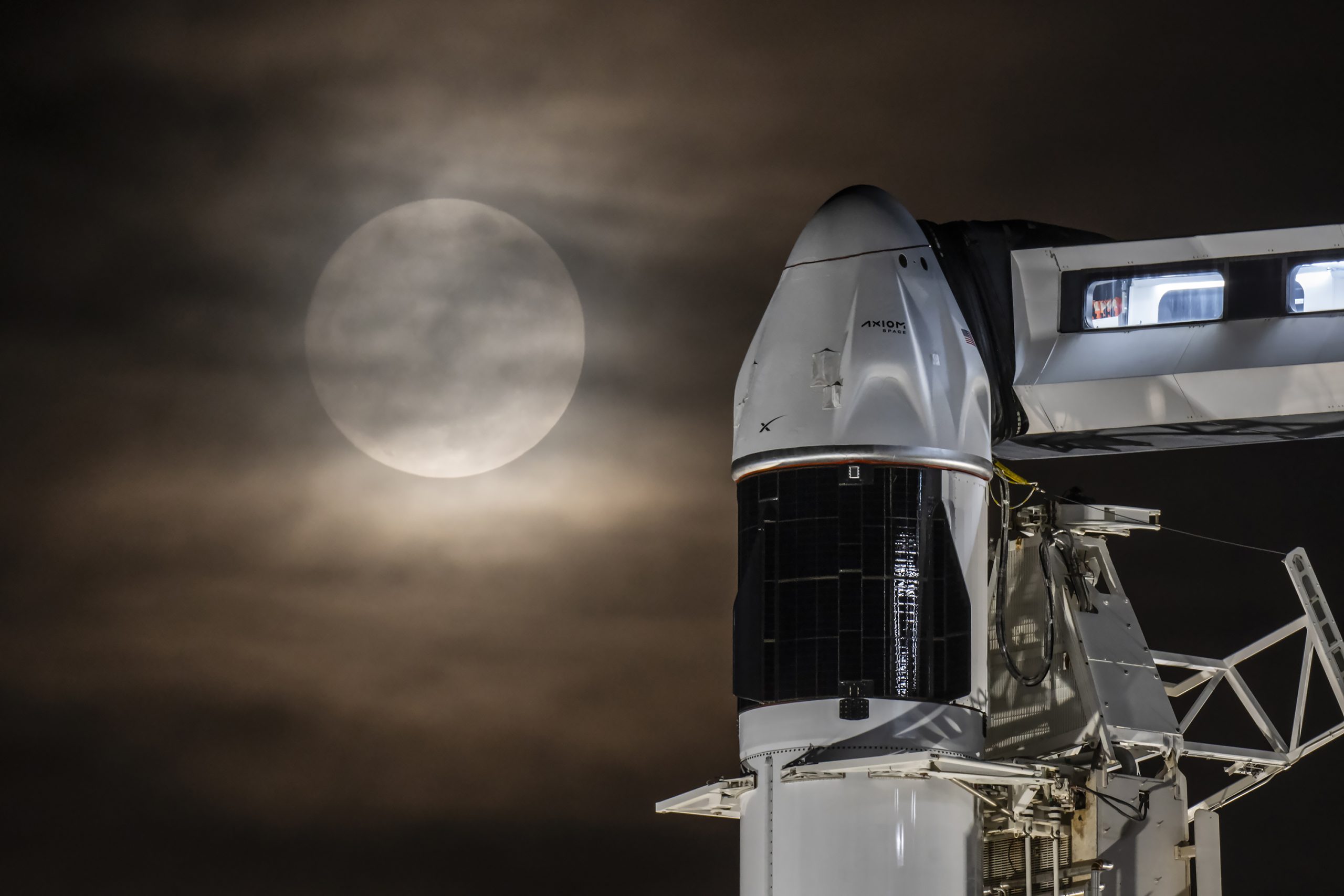

SpaceX is preparing for a new launch date for the Ax-4 mission to the International Space Station (ISS).
SpaceX, Axiom Space, and NASA addressed recent technical challenges and announced a new launch date of no earlier than Thursday, June 19, for the Ax-4 mission. The delay from June 12 allowed teams to assess repairs to small leaks in the ISS’s Zvezda service module.
NASA and Roscosmos have been monitoring leaks in the Zvezda module’s aft (back) segment for years. However, stable pressure could also result from air flowing across the hatch seal from the central station. As NASA and its partners adapt launch schedules to ensure station safety, adjustments are routine.
“Following the most recent repair, pressure in the transfer tunnel has been stable,” a source noted, suggesting the leaks may be sealed.
“By changing pressure in the transfer tunnel and monitoring over time, teams are evaluating the condition of the transfer tunnel and the hatch seal between the space station and the back of Zvezda,” the source added.
SpaceX has also resolved a liquid oxygen leak found during post-static fire inspections of the Falcon 9 rocket, completing a wet dress rehearsal to confirm readiness. The Ax-4 mission is Axiom Space’s fourth private astronaut trip to the ISS. It will launch from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on a Falcon 9 rocket with a new Crew Dragon capsule.
“This is the first flight for this Dragon capsule, and it’s carrying an international crew—a perfect debut. We’ve upgraded storage, propulsion components, and the seat lash design for improved reliability and reuse,” said William Gerstenmaier, SpaceX’s vice president of build and flight reliability.
The Ax-4 mission crew is led by Peggy Whitson, Axiom Space’s director of human spaceflight and former NASA astronaut. The Ax-4 crew includes ISRO astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla as pilot, alongside mission specialists Sławosz Uznański-Wiśniewski from Poland and Tibor Kapu from Hungary. The international team underscores Axiom’s commitment to global collaboration.
The Ax-4 mission will advance scientific research during its ISS stay, supporting Axiom’s goal of building a commercial space station. As teams finalize preparations, the mission’s updated launch date and technical resolutions position it to strengthen private space exploration’s role in advancing space-based innovation.
News
Starlink India launch gains traction with telecom license approval
Starlink just secured its telecom license in India! High-speed satellite internet could go live in 2 months.

Starlink India’s launch cleared a key regulatory hurdle after securing a long-awaited license from the country’s telecom ministry. Starlink’s license approval in India paves the way for commercial operations to begin, marking a significant milestone after a three-year wait.
The Department of Telecommunications granted Starlink a Global Mobile Personal Communication by Satellite (GMPCS) license, enabling it to roll out its high-speed internet service. Local reports hinted that Starlink plans to launch its services within the next two months. Starlink India’s services are expected to be priced at ₹3,000 per month for unlimited data. Starlink service would require a ₹33,000 hardware kit, including a dish and router.
“Starlink is finally ready to enter the Indian market,” sources familiar with the rollout plans confirmed, noting a one-month free trial for new users.
Starlink’s low-Earth orbit satellite network promises low-latency, high-speed internet that is ideal for rural India, border areas, and hilly terrains. With over 7,000 satellites in orbit and millions of global users, Starlink aims to bridge India’s digital divide, especially in areas with limited traditional broadband.
Starlink has forged distribution partnerships with Indian telecom giants Reliance Jio and Bharti Airtel to streamline deployment and retail logistics. However, the company still awaits spectrum allocation and final clearances from India’s space regulator, IN-SPACe, and national security agencies before its full launch, expected before August 2025.
India’s satellite internet market is becoming increasingly competitive, with Starlink joining rivals like OneWeb and Jio Satellite Communications. While Starlink positions itself as a premium offering, its entry has sparked debate among domestic telecom operators over spectrum pricing.
Local reports noted that other players in the industry have raised concerns over the lower regulatory fees proposed for satellite firms compared to terrestrial operators, highlighting tensions in the sector.
Starlink India’s launch represents a transformative step toward expanding internet access in one of the world’s largest markets. Starlink could redefine connectivity for millions in underserved regions by leveraging its advanced satellite technology and strategic partnerships. As the company navigates remaining regulatory steps, its timely rollout could set a new standard for satellite internet in India, intensifying competition and driving innovation in the telecom landscape.
Elon Musk
SpaceX to decommission Dragon spacecraft in response to Pres. Trump war of words with Elon Musk
Elon Musk says SpaceX will decommission Dragon as a result of President Trump’s threat to end his subsidies and government contracts.
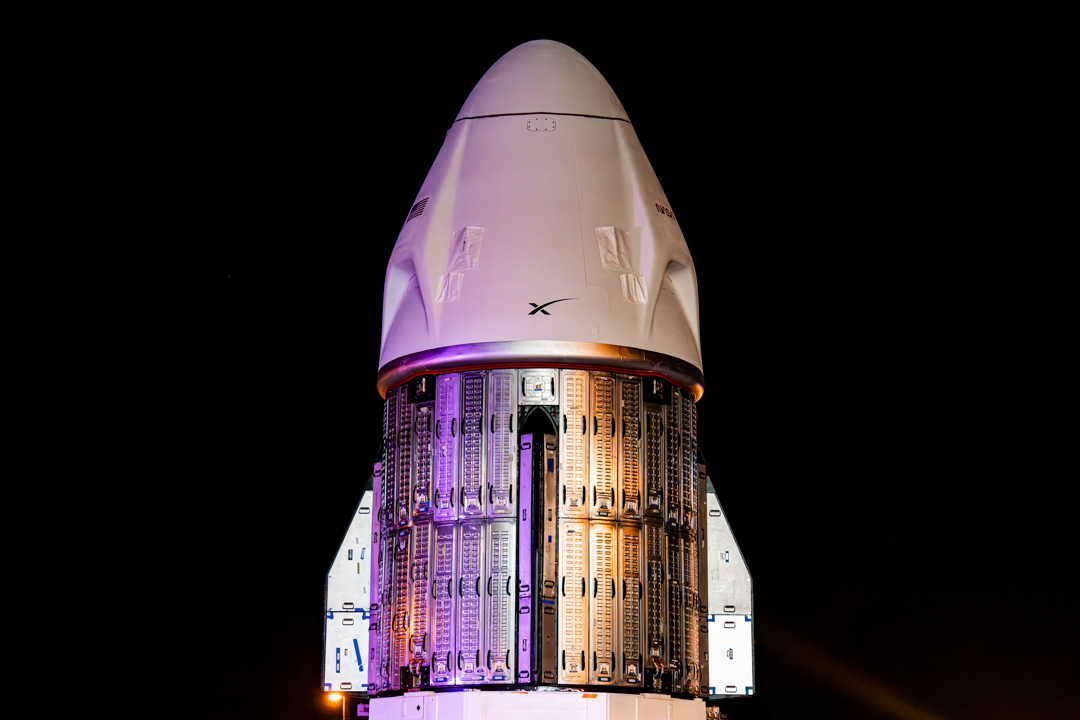
SpaceX will decommission its Dragon spacecraft in response to the intense war of words that President Trump and CEO Elon Musk have entered on various social media platforms today.
President Trump and Musk, who was once considered a right-hand man to Trump, have entered a vicious war of words on Thursday. The issues stem from Musk’s disagreement with the “Big Beautiful Bill,” which will increase the U.S. federal deficit, the Tesla and SpaceX frontman says.
How Tesla could benefit from the ‘Big Beautiful Bill’ that axes EV subsidies
The insults and threats have been brutal, as Trump has said he doesn’t know if he’ll respect Musk again, and Musk has even stated that the President would not have won the election in November if it were not for him.
President Trump then said later in the day that:
“The easiest way to save money in our Budget, Billions and Billions of Dollars, is to terminate Elon’s Government Subsidies and Contracts. I was always surprised that Biden didn’t do it!”
Musk’s response was simple: he will decommission the SpaceX capsule responsible for transporting crew and cargo to the International Space Station (ISS): Dragon.
🚨 Elon says Dragon will be decommissioned immediately due to President Trump’s threats to terminate SpaceX’s government contracts https://t.co/XNB0LflZIy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) June 5, 2025
Dragon has completed 51 missions, 46 of which have been to the ISS. It is capable of carrying up to 7 passengers to and from Earth’s orbit. It is the only spacecraft that is capable of returning vast amounts of cargo to Earth. It is also the first private spacecraft to take humans to the ISS.
The most notable mission Dragon completed is one of its most recent, as SpaceX brought NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams back to Earth after being stranded at the ISS by a Boeing Starliner capsule.
SpaceX’s reluctance to participate in federally funded projects may put the government in a strange position. It will look to bring Boeing back in to take a majority of these projects, but there might be some reluctance based on the Starliner mishap with Wilmore and Williams.
SpaceX bails out Boeing and employees are reportedly ‘humiliated’
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk5 days ago
Elon Musk5 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla sees explosive sales growth in UK, Spain, and Netherlands in June
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales

















