

News
SpaceX’s first West Coast Falcon 9 launch in eight months now set for early 2020
After what is set to be a more than 8-month lull, SpaceX’s California launch facilities are scheduled to support a Falcon 9 launch no earlier than February 2020.
Speaking at 2019’s World Satellite Business Week, Raúl Kulichevsky – a director at the Comisión Nacional de Actividades Espaciales (CONAE), Argentina’s national space agency – confirmed that the country’s SAOCOM-1B Earth observation satellite making great progress towards that launch target.
The launch was recently pushed into January and later March of 2020 after minor satellite production delays ended plans for a late-2019 launch. On a recent positive note, Deputy Executive and Technical Director of CONAE Raúl Kulichevsky indicated that SAOCOM-1B’s Falcon 9 launch was now planned a month or so earlier than previously expected and is on track for a February 2020 liftoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB).
This small but positive schedule bump comes just a week or so after CONAE engineers and technicians wrapped up a major SAOCOM-1B integration milestone, successfully attaching the satellite’s main imaging instrument – a large phased-array radar – to its bus (the primary structure). This work is ongoing in Bariloche, Argentina, a spectacular town surrounded by the Andes mountain range and glacier-fed lakes. Aside from the electrical and mechanical integration of SAOCOM-1B’s radar and bus, the CONAE team completed the installation of thermal insulator blankets. Up next will be the attachment of two solar arrays and associated deployment tests, followed by integrated center-of-gravity measurements and vibrational/acoustic load tests.
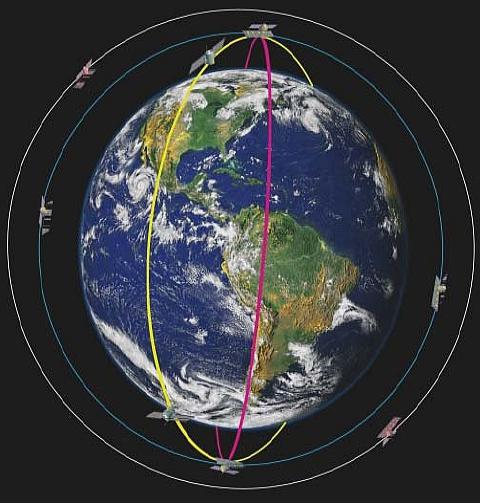
Assuming a successful launch early next year, SAOCOM-1B will join its SAOCOM-1A sister satellite in a sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), completing the L-band Satélite Argentino de Observación Con Microondas Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) constellation. In an agreement called Sistema Italo Argentino de Satélites para la Gestión de Emergencias (SIASGE), the completed SAOCOM constellation will work in conjunction with Italy’s four-satellite COSMO-SkyMed constellation to provide accurate and persistent Earth observations and support disaster monitoring efforts around the world.
CONAE hopes to eventually expand its SAOCOM constellation with the future development and deployment of two SAOCOM-2 spacecraft.
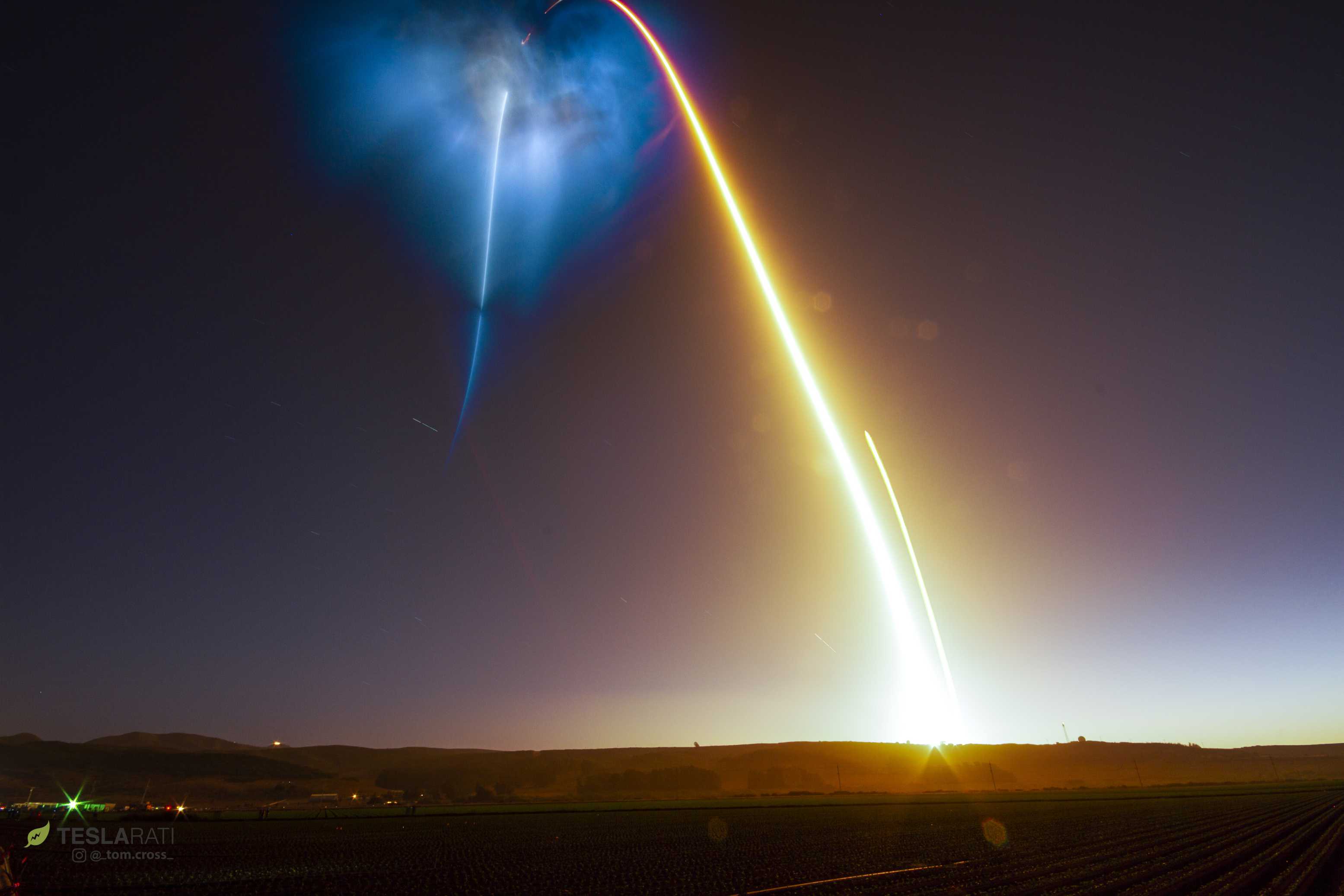
The SAOCOM-1A satellite was launched in a spectacular fashion in October 2018, producing a nebula-like cloud of sun-lit Falcon 9 exhaust that was visible for hundreds of miles. The SAOCOM-1A marked the second launch of Falcon 9 booster B1048 and also featured SpaceX’s first successful West Coast Return-to-Launch-Site (RTLS) landing.
Highly Commended for Skyscapes is Brandon Yoshizawa’s ‘Flower Power’ #astrophoto2019 pic.twitter.com/L5EVGwEfDr— Royal Museums Greenwich (@RMGreenwich) September 12, 2019
Falcon 9’s SAOCOM-1B mission will come long after SpaceX’s most recent West Coast launch – the June 2019 launch of the Canadian Space Agency’s (CSA) RADARSAT Constellation Mission (RCM). West coast observers and launch teams are sure to welcome the launch of the SAOCOM-1B mission after what is set to be more than eight months spent without a launch.
Check out Teslarati’s newsletters for prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket launch and recovery processes.
News
Tesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
Tesla seems serious about expanding its Robotaxi service to several states in the coming months.

Tesla has initiated discussions with Arizona transportation regulators to certify its driverless Robotaxi service in the state, as per a recent report from Bloomberg News. The move follows Tesla’s launch of its Robotaxi pilot program in Austin, Texas, as well as CEO Elon Musk’s recent comments about the service’s expansion in the Bay Area.
The Arizona Department of Transportation confirmed to Bloomberg that Tesla has reached out to begin the certification process for autonomous ride-sharing operations in the state. While details remain limited, the outreach suggests that Tesla is serious about expanding its driverless Robotaxi service to several territories in the coming months.
The Arizona development comes as Tesla prepares to expand its service area in Austin this weekend, as per CEO Elon Musk in a post on X. Musk also stated that Tesla is targeting the San Francisco Bay Area as its next major market, with a potential launch “in a month or two,” pending regulatory approvals.
Tesla first launched its autonomous ride-hailing program on June 22 in Austin with a small fleet of Model Y vehicles, accompanied by a Tesla employee in the passenger seat to monitor safety. While still classified as a test, Musk has said the program will expand to about 1,000 vehicles in the coming months. Tesla will later upgrade its Robotaxi fleet with the Cyercab, a two-seater that is designed without a steering wheel.
Sightings of Cybercab castings around the Giga Texas complex suggests that Tesla may be ramping the initial trial production of the self-driving two-seater. Tesla, for its part, has noted in the past that volume production of the Cybercab is expected to start sometime next year.
In California, Tesla has already applied for a transportation charter-party carrier permit from the state’s Public Utilities Commission. The company is reportedly taking a phased approach to operating in California, with the Robotaxi service starting with pre-arranged rides for employees in vehicles with safety drivers.
News
Tesla sets November 6 date for 2025 Annual Shareholder Meeting
The automaker announced the date on Thursday in a Form 8-K.

Tesla has scheduled its 2025 annual shareholder meeting for November 6, addressing investor concerns that the company was nearing a legal deadline to hold the event.
The automaker announced the date on Thursday in a Form 8-K submitted to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The company also listed a new proposal submission deadline of July 31 for items to be included in the proxy statement.
Tesla’s announcement followed calls from a group of 27 shareholders, including the leaders of large public pension funds, which urged Tesla’s board to formally set the meeting date, as noted in a report from The Wall Street Journal.
The group noted that under Texas law, where Tesla is now incorporated, companies must hold annual meetings within 13 months of the last one if requested by shareholders. Tesla’s previous annual shareholder meeting was held on June 13, 2024, which placed the July 13 deadline in focus.
Tesla originally stated in its 2024 annual report that it would file its proxy statement by the end of April. However, an amended filing on April 30 indicated that the Board of Directors had not yet finalized a meeting date, at least at the time.
The April filing also confirmed that Tesla’s board had formed a special committee to evaluate certain matters related to CEO Elon Musk’s compensation plan. Musk’s CEO performance award remains at the center of a lengthy legal dispute in Delaware, Tesla’s former state of incorporation.
Due to the aftermath of Musk’s legal dispute about his compensation plan in Delaware, he has not been paid for his work at Tesla for several years. Musk, for his part, has noted that he is more concerned about his voting stake in Tesla than his actual salary.
At last year’s annual meeting, TSLA shareholders voted to reapprove Elon Musk’s compensation plan and ratified Tesla’s decision to relocate its legal domicile from Delaware to Texas.
Elon Musk
Grok coming to Tesla vehicles next week “at the latest:” Elon Musk
Grok’s rollout to Tesla vehicles is expected to begin next week at the latest.

Elon Musk announced on Thursday that Grok, the large language model developed by his startup xAI, will soon be available in Tesla vehicles. Grok’s rollout to Tesla vehicles is expected to begin next week at the latest, further deepening the ties between the two Elon Musk-led companies.
Tesla–xAI synergy
Musk confirmed the news on X shortly after livestreaming the release of Grok 4, xAI’s latest large language model. “Grok is coming to Tesla vehicles very soon. Next week at the latest,” Musk wrote in a post on social media platform X.
During the livestream, Musk and several members of the xAI team highlighted several upgrades to Grok 4’s voice capabilities and performance metrics, positioning the LLM as competitive with top-tier models from OpenAI and Google.
The in-vehicle integration of Grok marks a new chapter in Tesla’s AI development. While Tesla has long relied on in-house systems for autonomous driving and energy optimization, Grok’s integration would introduce conversational AI directly into its vehicles’ user experience. This integration could potentially improve customer interaction inside Tesla vehicles.
xAI and Tesla’s collaborative footprint
Grok’s upcoming rollout to Tesla vehicles adds to a growing business relationship between Tesla and xAI. Earlier this year, Tesla disclosed that it generated $198.3 million in revenue from commercial, consulting, and support agreements with xAI, as noted in a report from Bloomberg News. A large portion of that amount, however, came from the sale of Megapack energy storage systems to the artificial intelligence startup.
In July 2023, Musk polled X users about whether Tesla should invest $5 billion in xAI. While no formal investment has been made so far, 68% of poll participants voted yes, and Musk has since stated that the idea would be discussed with Tesla’s board.
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk19 hours ago
Elon Musk19 hours agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla’s Omead Afshar, known as Elon Musk’s right-hand man, leaves company: reports
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”

















