

News
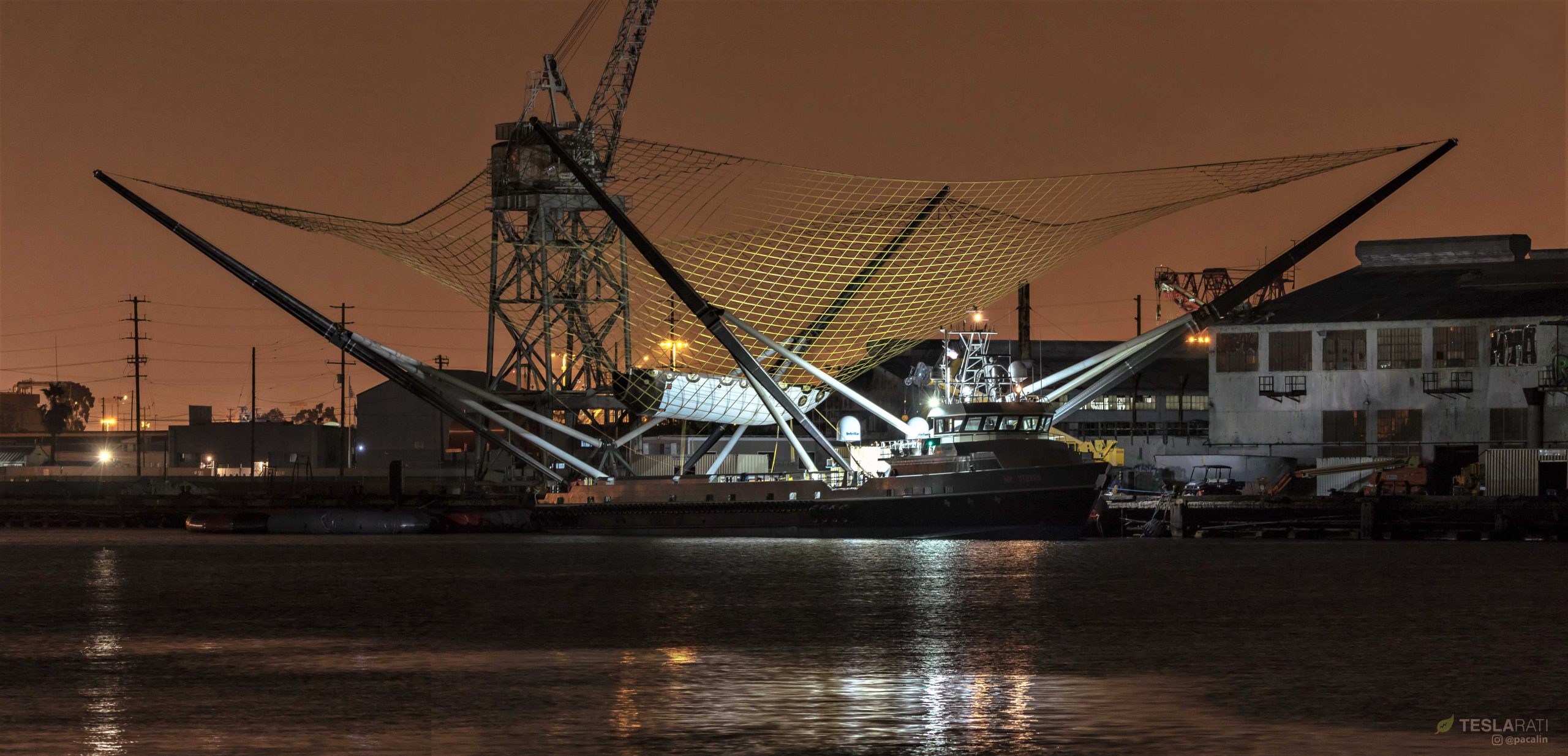
SpaceX’s Mr. Steven returns with Falcon fairing half in net after drop test practice
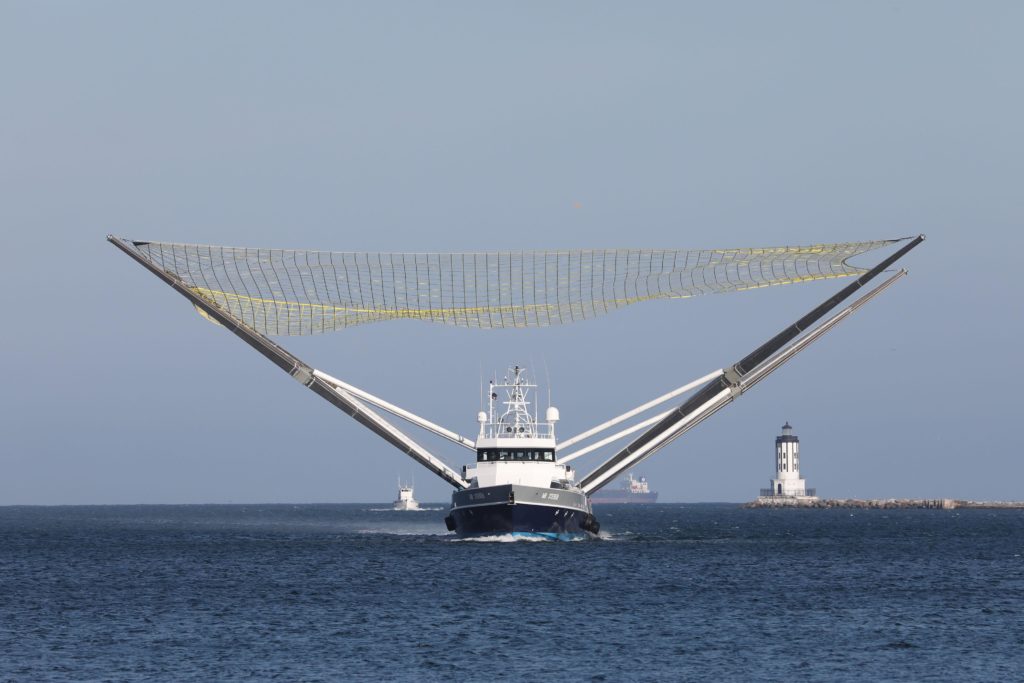
Captured in a series of photos taken by Teslarati photographers Pauline Acalin and Tom Cross over several days, SpaceX Falcon fairing recovery vessel Mr. Steven and recovery technicians and engineers have been preparing and practicing for a campaign of controlled fairing drop tests.
By using a helicopter to lift and drop a fairing into Mr. Steven’s net, SpaceX will be able to gather an unprecedented amount of data and control far more variables that might impact the success of recoveries. If the fairing is not destroyed in the process, this test series could be as long-lived as SpaceX’s Grasshopper program, used to work the largest up-front kinks out of Falcon 9 booster recovery.
Mr Steven looks ready. Should be leaving port at some point today ahead of SAOCOM-1A launch scheduled for Sunday, Oct 7, 7:21pm PT #mrsteven #SpaceX pic.twitter.com/Hk7HLmMDra
— Pauline Acalin (@w00ki33) October 6, 2018
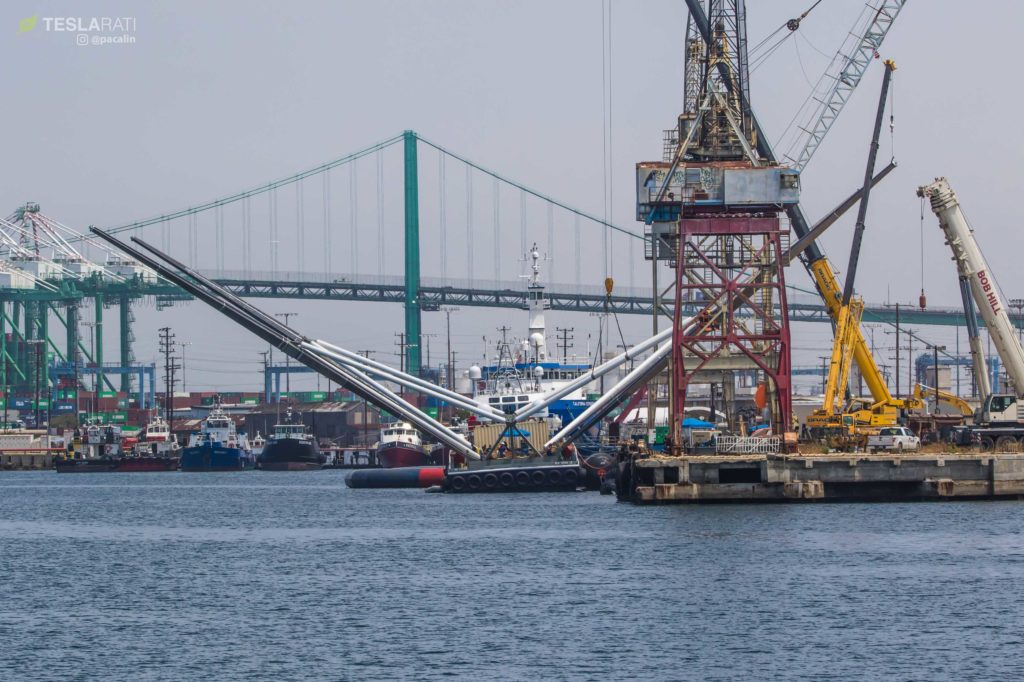
Although SpaceX technicians managed to reassemble and install Mr. Steven’s net and arm fairing recovery mechanisms in just a handful of days, finishing less than 48 hours before the West Coast launch of SAOCOM 1A, the ship remained in port for the mission, passing up its fifth opportunity to attempt recovery of one of Falcon 9’s two fairings halves. Why exactly Mr. Steven never left port is unclear and unconfirmed, although SpaceX did mention that recovery would not be attempted this time around during its official launch webcast.
The most likely explanation is mundane – sea states with average swells as large as 4m (13ft) were forecasted (and later recorded) at and around the optimal fairing recovery zone. As a Fast Supply Vessel (FSV) explicitly designed to rapidly and reliably resupply oil rigs and other maritime work areas almost regardless of weather conditions, 4m waves would normally be a tiny pittance for ships as large and heavy as Mr. Steven and would be a nonsensical reason to halt deep-sea operations.
- Thanks to their relatively high angle of attack, Mr. Steven’s newest arms should not seriously impact his stability, but there is a chance that they limit his operational envelope in high sea-states. (Chuck Bennett)
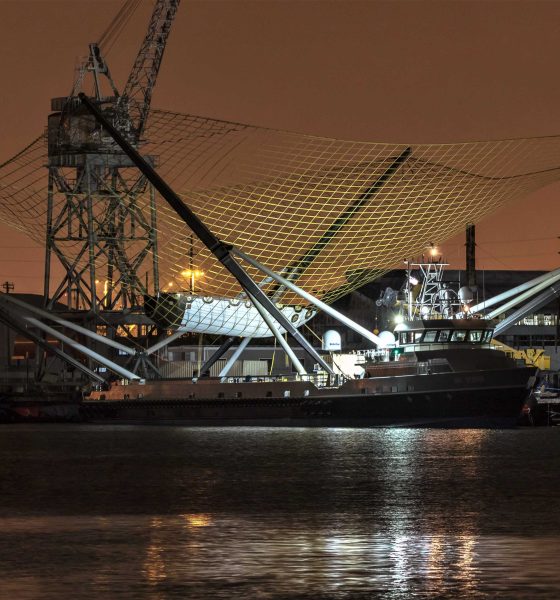
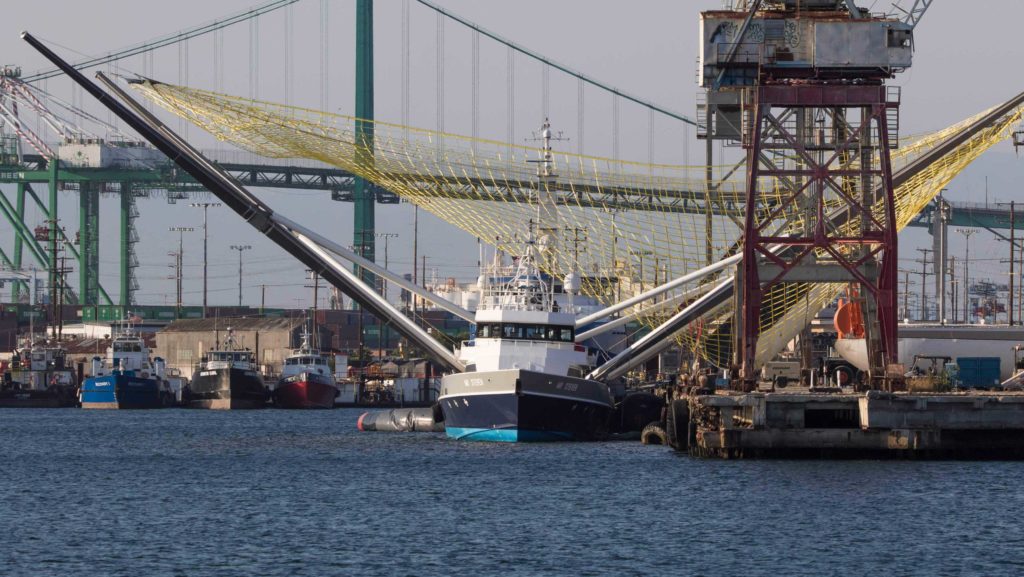
- Mr. Steven seen listing roughly 5 degrees to port during arm installation, July 10th. (Pauline Acalin)
- A few-degree list seen during fairing recovery practice, August 13th. (Pauline Acalin)
On the other hand, Mr. Steven is without a doubt the most unusual FSV in existence thanks to his massive arms and net, stretching at least 60m by 60m. Based on photos of the arm installation process, significant lists of 5+ degrees are not uncommon when arms are unbalanced during normal staggered (one-at-a-time) installations, and SpaceX quite clearly installs the first two arms on opposite sides and orientations in order to minimize installation-related listing. This indicates that his newest arms have significant mass and thus leverage over the boat’s roll characteristics, perhaps explaining why Mr. Steven has performed anywhere from 5-10 high-speed trials at sea both with and without arms installed.
Most recently, however, Mr. Steven spent a solid six weeks armless at Berth 240 while some sort of maintenance, analysis, or upgrade was undertaken with those four arms and their eight shock-absorbing booms. It’s hard to know for sure, but there are no obvious visual changes between the arms installed in July and August and those now present on his deck, and the net also looks almost identical.
Fairing drop tests?
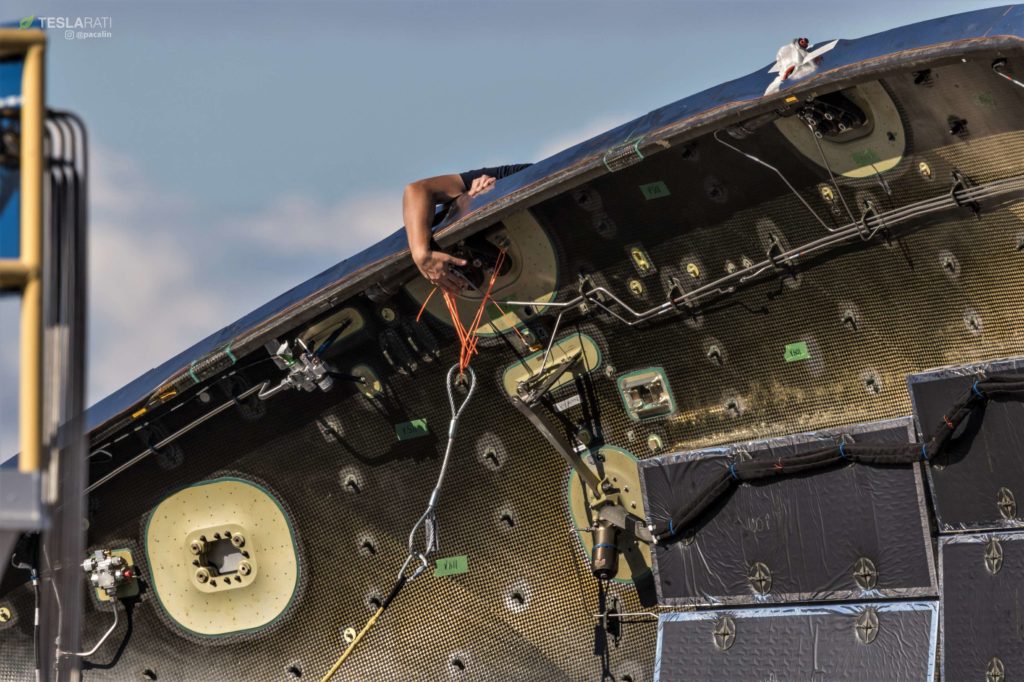
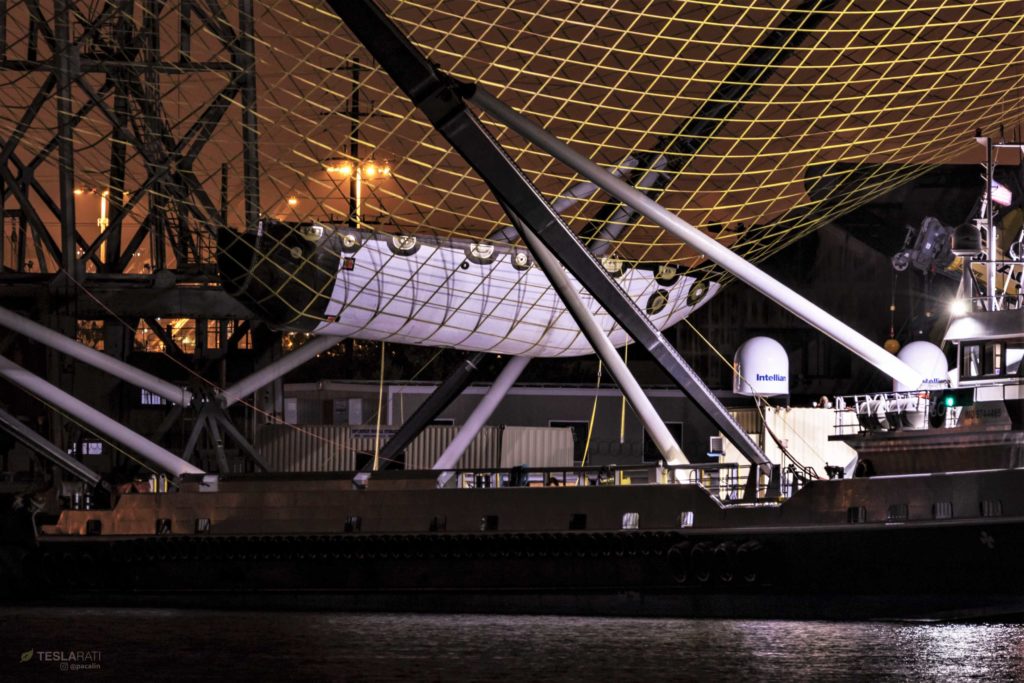
What’s less familiar these days is an oddly arranged Falcon 9 payload fairing half that has been floating around SpaceX’s Port of Los Angeles berths for the last two or so weeks. Up until October 4th, the purpose of that single half was almost entirely unclear. On October 4th, Teslarati’s entire space team (Tom, Pauline, and I) coincidentally arrived at the same time as 5-10 SpaceX technicians were working on the fairing, attaching a series of guylines and harnesses and inspecting a number of actuating mechanisms on the half.
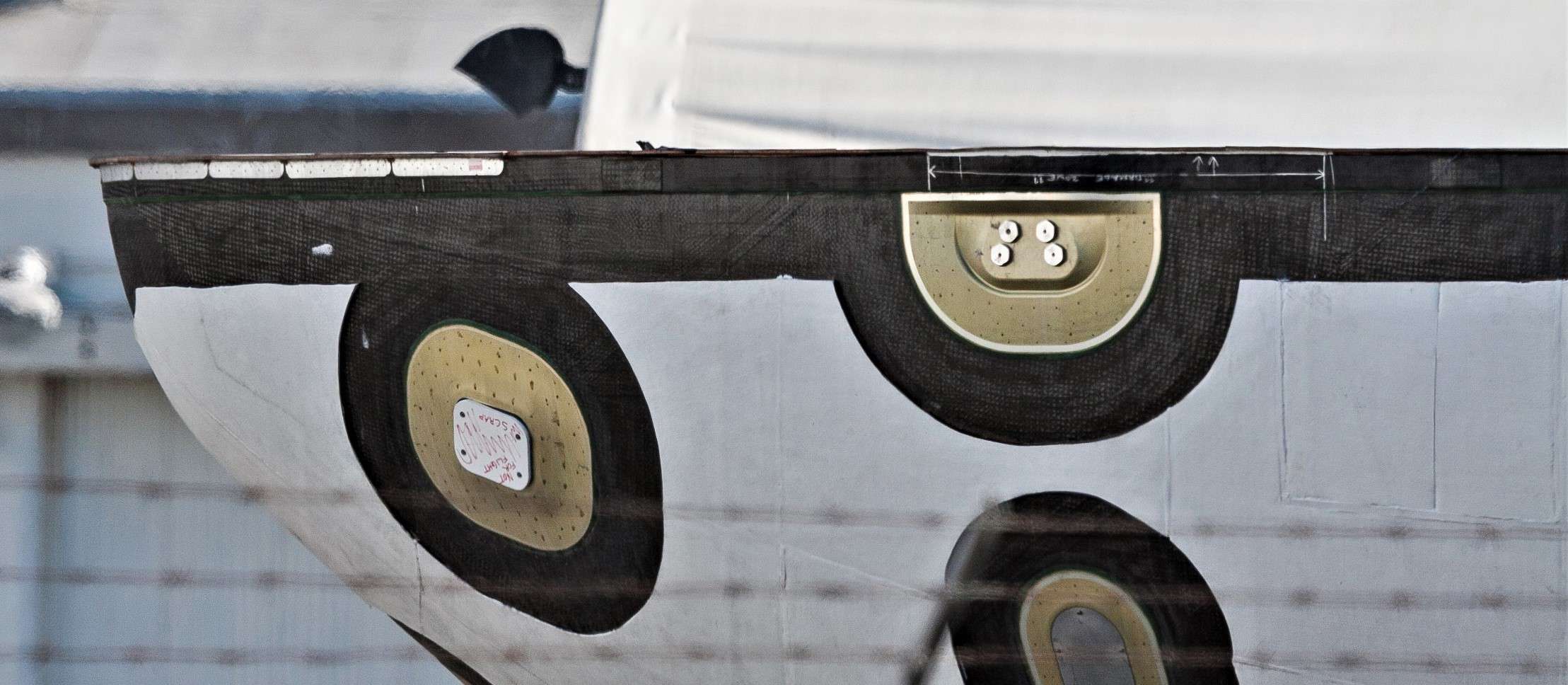

Just minutes after we arrived, a worker called out a short countdown and a wholly unexpected crashing noise sounded, followed immediately by several loud clangs as the harness connection mechanisms swung back and connected with metallic parts of the fairing. After the adrenaline wore off, the initial crashing noise was almost certainly the sound of the same mechanical jettison mechanism used to separate fairing halves ~3 minutes after the rocket lifts off.
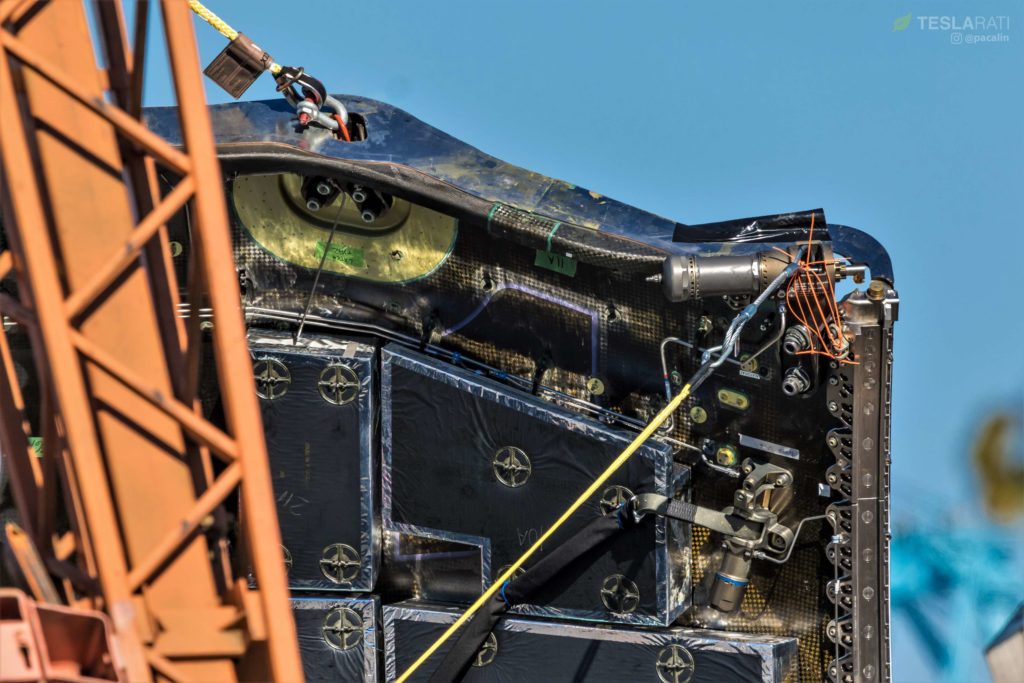
Once photos of the event could be examined more carefully, that was exactly what we found – the six harness connections were attached to the fairing by way of the same mechanical interface that allows two halves to safely attach to each other. What we had witnessed was a harness separation test, using pressurized gas stored in COPVs (the gold striped cylinders) to rapidly actuate a latch, allowing the metal harness connectors to fall away. This is further evidenced by the presence of neon orange zip-ties connecting the ends of those harnesses to any sturdy fairing structure near the connection port, an easy and (presumably) affordable way to prevent those heavy connectors from swinging down and damaging sensitive piping and components.
- An overview of the weird fairing test article just before the harnesses were jettisoned. (Pauline Acalin)
- Note the taut, yellow ropes connected to the fairing at its original serparation connector ports. (Pauline Acalin)
- Zip-ties prevented the harness connectors from smashing (too hard) into the fairing’s innards. (Pauline Acalin)
- A Falcon 9 fairing during encapsulation, when a launch payload is sealed inside the fairing’s two halves. This small satellite is NASA’s TESS, launched in April 2018. (NASA)
According to someone familiar with these activities, the purpose of that testing is to prepare for true fairing drop tests from a helicopter. The jettisonable harness would be a necessity for easy drop testing, allowing the helicopter to carry a basic cargo hook and line while technicians inside communicate with the fairing to engage its built-in separation mechanism, all while ensuring that it immediately begins a stable glide or free-fall after dropping.
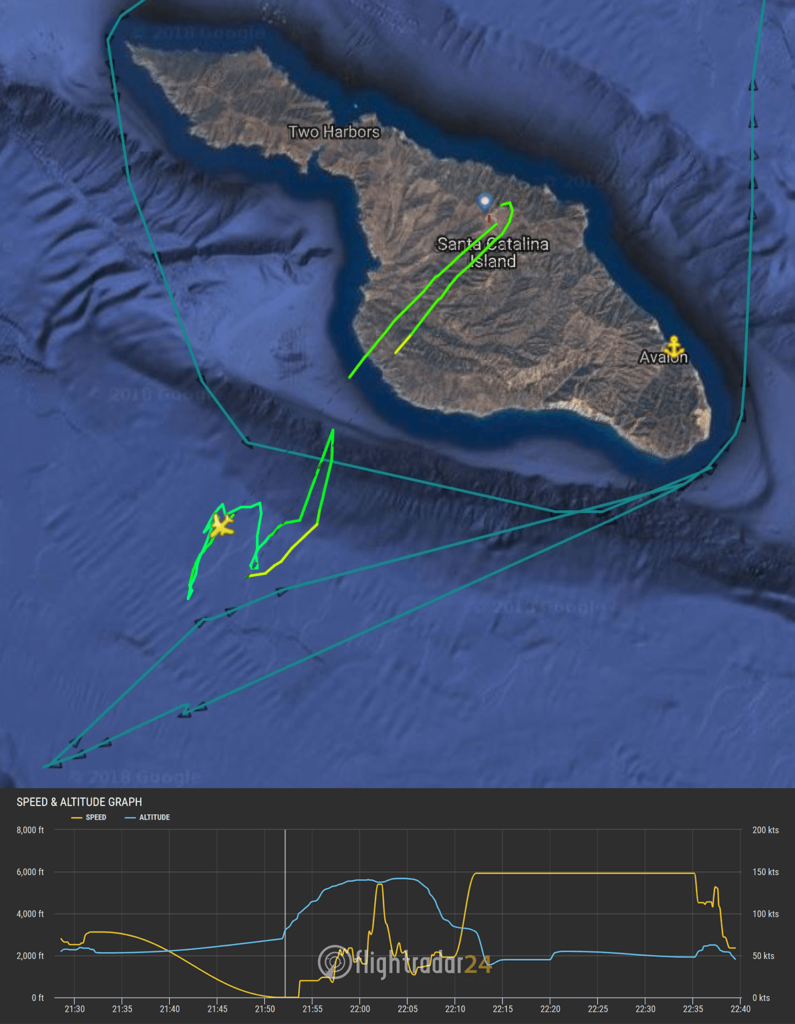
Observed on October 4th, it was at least moderately disappointing to see Mr. Steven remain in port during the spectacular Falcon 9 launch of SAOCOM 1A, October 7th. Reasons aside, roughly 12 hours after launch, Mr. Steven left on a 10+ hour cruise ~100 miles off the coast, where he repeatedly met up with tugboat Tommy and circled Santa Catalina Island once before heading back to port. Just 24 hours before launch (Oct. 6), the test fairing seen above was placed in Mr. Steven’s net for communications and harness testing – 24 hours after launch, Mr. Steven returned to Port of San Pedro after his 10-hour cruise with the same fairing half resting in his net.
- Mr. Steven returned to Port of San Pedro around 7pm on October 8th after a day spent at sea, apparently with a Falcon fairing half in tow. This is the second known time that a fairing has been in Mr. Steven’s net. (Pauline Acalin)
- An overlay of the paths of travel of a test-related helicopter and Mr. Steven, both on Oct. 8. The yellow plane is the heli at the beginning of a hover, while the gap between blue triangles in the lower left is where Mr. Steven was during that hover. (MarineTraffic + Flightradar24)
How and why it got there is unknown, as is the purpose of half a day spent boating around with the half in his net. However, a helicopter known to be involved in fairing drop tests was seen hovering and flying around Mr. Steven at the same time. Perhaps the two were practicing for real drop attempts, or perhaps the helicopter actually dropped a Falcon fairing (from > 2000 feet) and Mr. Steven successful caught it.
What is clear is that SpaceX is just getting started with efforts to perfect fairing recovery and eventually make the practice as (relatively) routine as Falcon 9 booster recovery and reuse is today. The latter was hardwon and the former will clearly be no easier.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!

News
Lucid unveils Lunar Robotaxi in bid to challenge Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
Lucid’s Lunar robotaxi is gunning for Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering.jpg)
Lucid Group pulled back the curtain on its purpose-built autonomous robotaxi platform dubbed the Lunar Concept. Announced at its New York investor day event, Lunar is arguably the company’s most ambitious concept yet, and a direct line of sight toward the autonomous ride haling market that Tesla looks to control.
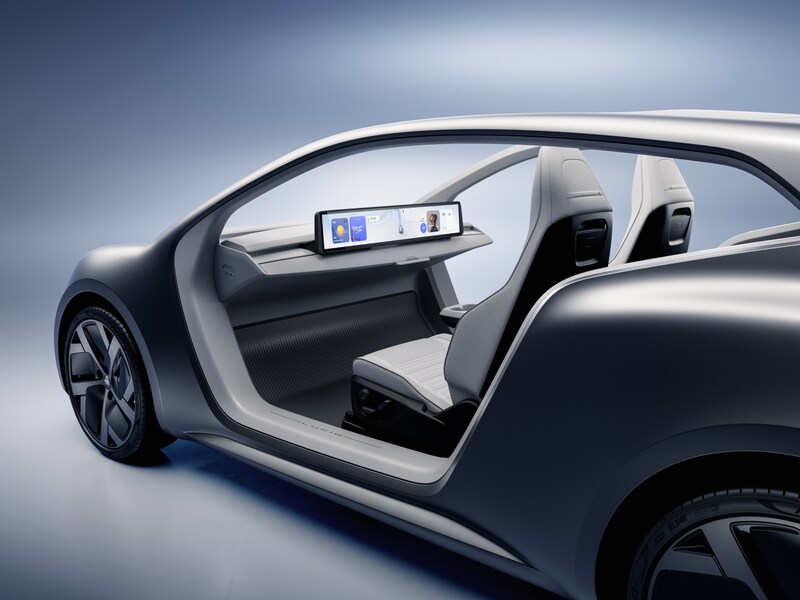

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
A comparison to Tesla’s Cybercab is unavoidable. The concept of a Tesla robotaxi was first introduced by Elon Musk back in April 2019 during an event dubbed “Autonomy Day,” where he envisioned a network of self-driving Tesla vehicles transporting passengers while not in use by their owners. That vision took another major step in October 2024 when, Musk unveiled the Cybercab at the Tesla “We, Robot” event held at Warner Bros. Studios in Burbank, California, where 20 concept Cybercabs autonomously drove around the studio lot giving rides to attendees.
Fast forward to today, and Tesla’s ambitions are finally materializing, but not without friction. As we recently reported, the Cybercab is being spotted with increasing frequency on public roads and across the grounds of Gigafactory Texas, suggesting that the company’s road testing and validation program is ramping meaningfully ahead of mass production. Tesla already operates a small scale robotaxi service in Austin using supervised Model Ys, but the Cybercab is designed from the ground up for high-volume, low-cost production, with Musk stating an eventual goal of producing one vehicle every 10 seconds.
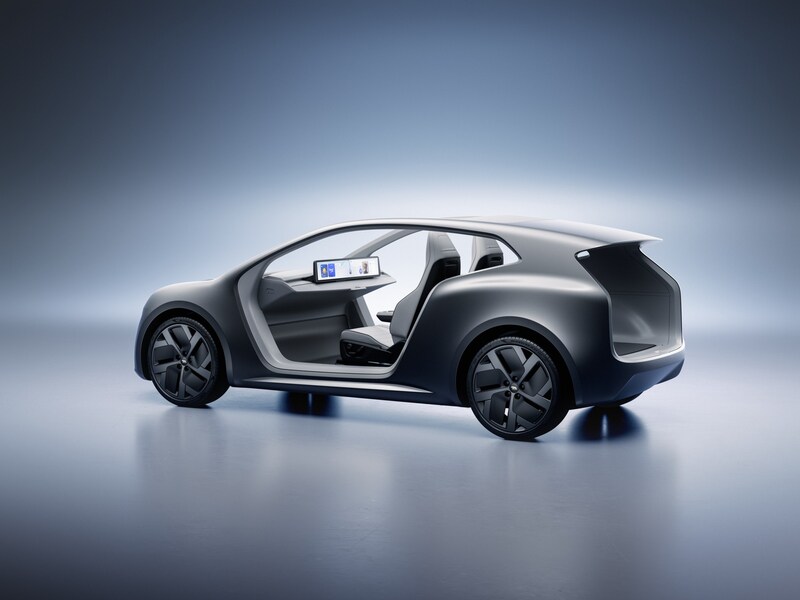

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
Into this landscape steps Lucid’s Lunar. Built on the company’s all-new Midsize EV platform, which will also underpin consumer SUVs starting below $50,000. The Lunar mirrors the Cybercab’s core philosophy of having two seats, no driver controls, and a focus on fleet economics. The platform introduces Lucid’s redesigned Atlas electric drive unit, engineered to be smaller, lighter, and cheaper to manufacture at scale.
Unlike Tesla’s strategy of building its own ride hailing network from scratch, Lucid is partnering with Uber. The companies are said to be in advanced discussions to deploy Midsize platform vehicles at large scale, with Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi publicly backing Lucid’s engineering credentials and autonomous-ready architecture.
In the investor day event, Lucid also outlined a recurring software revenue model, with an in-vehicle AI assistant and monthly autonomous driving subscriptions priced between $69 and $199. This can be seen as a nod to the software revenue stream that Tesla has long championed with its Full Self-Driving subscription.
Tesla’s Cybercab is targeting a price point below $30k and with operating costs as low as 20 cents per mile. But with regulatory hurdles still ahead, the window for competition is open. Lucid’s Lunar may not have a launch date yet, but it arrives at a pivotal moment, and when the robotaxi race is no longer viewed as hypothetical. Rather, every serious EV player needs to come to bat on the same plate that Tesla has had countless practice swings on over the last seven years.
Elon Musk
Brazil Supreme Court orders Elon Musk and X investigation closed
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.

Brazil’s Supreme Federal Court has ordered the closure of an investigation involving Elon Musk and social media platform X. The inquiry had been pending for about two years and examined whether the platform was used to coordinate attacks against members of the judiciary.
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.
According to a report from Agencia Brasil, the investigation conducted by the Federal Police did not find evidence that X deliberately attempted to attack the judiciary or circumvent court orders.
Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet concluded that the irregularities identified during the probe did not indicate fraudulent intent.
Justice Moraes accepted the prosecutor’s recommendation and ruled that the investigation should be closed. Under the ruling, the case will remain closed unless new evidence emerges.
The inquiry stemmed from concerns that content on X may have enabled online attacks against Supreme Court justices or violated rulings requiring the suspension of certain accounts under investigation.
Justice Moraes had previously taken several enforcement actions related to the platform during the broader dispute involving social media regulation in Brazil.
These included ordering a nationwide block of the platform, freezing Starlink accounts, and imposing fines on X totaling about $5.2 million. Authorities also froze financial assets linked to X and SpaceX through Starlink to collect unpaid penalties and seized roughly $3.3 million from the companies’ accounts.
Moraes also imposed daily fines of up to R$5 million, about $920,000, for alleged evasion of the X ban and established penalties of R$50,000 per day for VPN users who attempted to bypass the restriction.
Brazil remains an important market for X, with roughly 17 million users, making it one of the platform’s larger user bases globally.
The country is also a major market for Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet service, which has surpassed one million subscribers in Brazil.
Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.








![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)







