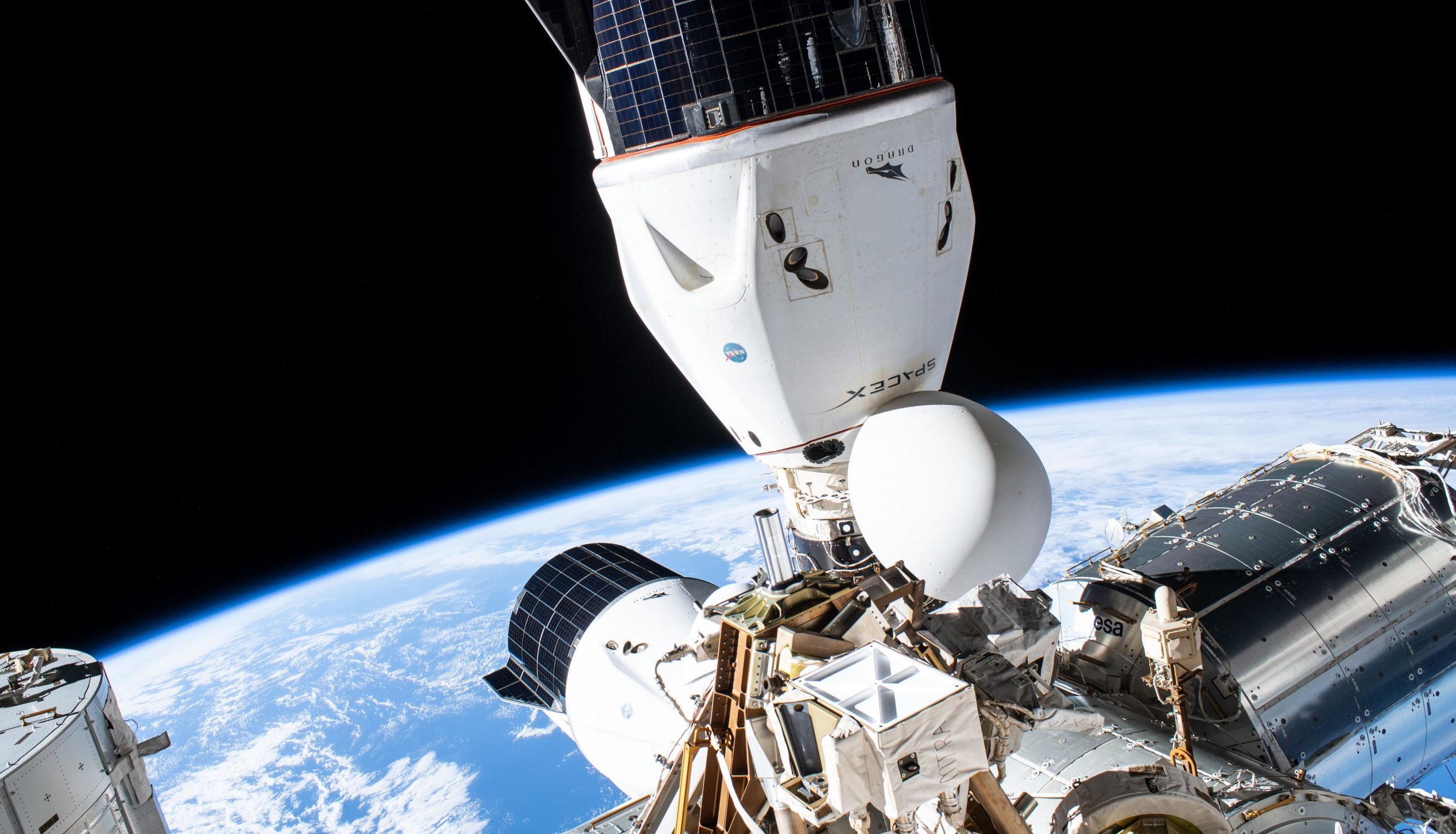


News
SpaceX a bastion of independent US, European spaceflight amid Russian threats
Russia has invaded Ukraine without provocation, triggering a series of diplomatic responses – sanctions in particular – that recently culminated in the aggressor deciding to cut ties with Europe on a number of cooperative spaceflight projects.
Dmitry Rogozin, director of Russia’s national ‘Roscosmos’ space agency, went as far as implying that the country might respond to the West’s aerospace sanctions by ending its support of the International Space Station (ISS), a move that could cause the football-field-sized structure to gradually deorbit and reenter Earth’s atmosphere. Were it not for the existence of two extraordinarily successful NASA programs and SpaceX in particular, Russia’s response – which, today, reads like a child’s tantrum – could easily have been a grave threat with far-reaching consequences.
In response to sanctions after its unprovoked invasion, Russia announced that it was withdrawing support from Europe’s French Guinea Soyuz launch operations, effectively killing Arianespace’s Soyuz offering and potentially delaying several upcoming European launches indefinitely.
As a quick side note, it’s worth noting that ULA’s lack of readily available rockets and the fact that Arianespace is likely at least a year or more away from regular Ariane 6 launches means that SpaceX may be the only Western launch provider in the world capable of filling in the gap that Arianespace’s Soyuz loss will leave. Aside from pursuing Chinese launch services, which is likely a diplomatic non-starter, the only alternative to rebooking former European Soyuz payloads on SpaceX rockets is to accept one or even several years of expensive delays.
On the other half of the coin is the International Space Station. NASA signed its first major contract with SpaceX in 2008, awarding the company $1.6 billion (and up to $3.5 billion) to launch a dozen Cargo Dragon supply missions to the ISS. Aside from effectively pulling SpaceX back from the brink of dissolution, those funds also covered a large portion of the development of its Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft and simultaneously funded Orbital Science’s (later Orbital ATK and now Northrop Grumman) Cygnus cargo spacecraft and Antares rocket.
Despite suffering two failures in 2014 and 2015, NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program has been an extraordinary success. Together, Cygnus (17) and Dragon (24) have completed 41 deliveries in the last 12 years, carrying more than 110 tons (~240,000 lb) of cargo to the ISS.
Out of sheer coincidence, on February 19th, mere days before Russia’s act of war, Northrop Grumman launched the first Cygnus spacecraft designed to help ‘re-boost’ (raise the orbit of) the International Space Station. Since NASA’s premature 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle, that task has been exclusively conducted by a combination of Russian spacecraft and the station’s Russian Zvezda module. Without regular Russian re-boost support, the station would deorbit and be destroyed. In other words, if push came to shove, the ISS could very literally fail without direct Russian involvement. Rogozin’s threat, then, was that Russia might cease to support ISS re-boosting if sanctions went too far.
However, even while ignoring the fact that NASA itself actually paid for and owns the ISS Zvezda propulsion module and in light of the first Cygnus spacecraft upgraded with a re-boost capability berthing with the station the very same week of the invasion, Russia’s threat rang decidedly hollow. Further, if Cygnus weren’t available, it’s still difficult to imagine that SpaceX wouldn’t be able to quickly develop its own Dragon re-boost capability if asked to do so.
While re-boosting is crucial, the situation has also emphasized just how little leverage Russia now has over even more important aspects of the International Space Station. Were it not for the existence of SpaceX and NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP), the situation could be even direr for Europe and the US. Despite some pressure from lawmakers to only award the CCP contract to Boeing, NASA ultimately selected Boeing and SpaceX to develop independent crew capsules capable of carrying US astronauts to and from ISS in 2014. Following a near-flawless uncrewed Crew Dragon test flight in 2019 and an equally successful crewed demo mission in 2020, SpaceX completed its first operational Crew Dragon launch in November 2020.
Since then, SpaceX has launched another two operational ‘crew rotation’ missions, meaning that the company has now singlehandedly supported all US astronaut launch and recovery operations for 16 months. Due in part to extensive mismanagement, Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft was nearly destroyed twice during its first catastrophic uncrewed test flight in December 2019. The spacecraft is still months away from a second attempt at that test flight, likely at least 9-12 months away from a hypothetical crewed test flight, and potentially 18+ months away from even less certain operational NASA astronaut launches. Further, though ULA CEO Tory Bruno claims that the company doesn’t need any support from Russia, all Atlas Vs – the rocket responsible for launching Starliner – depend on Russian-built RD-180 engines.
Further adding to the mire, even Cygnus is not immune. The first stage of the Antares rocket that mainly launches it is both built in Ukraine and dependent upon Russian Energomash RD-181 engines. Northrop Grumman only has the hardware on hand for the next two Cygnus-Antares launches, at which point the company will have to either abandon its NASA contract or find an alternative launch provider. Once again, SpaceX is the only US provider obviously capable of filling that gap on such short notice and without incurring major delays of half a year or more.

In fewer words, without SpaceX, NASA would still be exclusively dependent upon Russian Soyuz rockets and spacecraft to get its astronauts to and from the space station it spent tens of billions of dollars to help build. Even in a best-case SpaceX-free scenario, NASA might instead be dependent upon a rocket with Russian engines to launch its own astronauts. Needless to say, the presence of US astronauts on Russian launches and ULA’s use of Russian engines were already extremely sensitive issues after Russia ‘merely’ invaded Ukraine’s Crimea region in 2014.
It’s hard not to imagine that US and European responses to Russia’s aggression would have been weakened if NASA and ESA astronauts were still entirely dependent upon Russia to access the International Space Station. Further, in the same scenario, given its withdrawal from French Guinea, it’s also not implausible to imagine that Russia might have severely hampered or even fully withdrawn its support of Western access to the ISS.
Put simply, Crew Dragon – now a bastion of independent European and US human spaceflight in an age of extraordinary Russian recklessness – has arguably never been more important and SpaceX’s success never more of a triumph than they are today.
Elon Musk
Tesla begins expanding Robotaxi access: here’s how you can ride
You can ride in a Tesla Robotaxi by heading to its website and filling out the interest form. The company is hand-picking some of those who have done this to gain access to the fleet.

Tesla has begun expanding Robotaxi access beyond the initial small group it offered rides to in late June, as it launched the driverless platform in Austin, Texas.
The small group of people enjoying the Robotaxi ride-hailing service is now growing, as several Austin-area residents are receiving invitations to test out the platform for themselves.
The first rides took place on June 22, and despite a very small number of very manageable and expected hiccups, Tesla Robotaxi was widely successful with its launch.
Tesla Robotaxi riders tout ‘smooth’ experience in first reviews of driverless service launch
However, Tesla is expanding the availability of the ride-hailing service to those living in Austin and its surrounding areas, hoping to gather more data and provide access to those who will utilize it on a daily basis.
Many of the people Tesla initially invited, including us, are not local to the Austin area.
There are a handful of people who are, but Tesla was evidently looking for more stable data collection, as many of those early invitees headed back to where they live.
The first handful of invitations in the second round of the Robotaxi platform’s Early Access Program are heading out to Austin locals:
I just got a @robotaxi invite! Super excited to go try the service out! pic.twitter.com/n9mN35KKFU
— Ethan McKanna (@ethanmckanna) July 1, 2025
Tesla likely saw an influx of data during the first week, as many traveled far and wide to say they were among the first to test the Robotaxi platform.
Now that the first week and a half of testing is over, Tesla is expanding invites to others. Many of those who have been chosen to gain access to the Robotaxi app and the ride-hailing service state that they simply filled out the interest form on the Robotaxi page of Tesla’s website.
That’s the easiest way you will also gain access, so be sure to fill out that form if you have any interest in riding in Robotaxi.
Tesla will continue to utilize data accumulated from these rides to enable more progress, and eventually, it will lead to even more people being able to hail rides from the driverless platform.
With more success, Tesla will start to phase out some of the Safety Monitors and Supervisors it is using to ensure things run smoothly. CEO Elon Musk said Tesla could start increasing the number of Robotaxis to monitors within the next couple of months.
Elon Musk
Tesla analyst issues stern warning to investors: forget Trump-Musk feud

A Tesla analyst today said that investors should not lose sight of what is truly important in the grand scheme of being a shareholder, and that any near-term drama between CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump should not outshine the progress made by the company.
Gene Munster of Deepwater Management said that Tesla’s progress in autonomy is a much larger influence and a significantly bigger part of the company’s story than any disagreement between political policies.
Munster appeared on CNBC‘s “Closing Bell” yesterday to reiterate this point:
“One thing that is critical for Tesla investors to remember is that what’s going on with the business, with autonomy, the progress that they’re making, albeit early, is much bigger than any feud that is going to happen week-to-week between the President and Elon. So, I understand the reaction, but ultimately, I think that cooler heads will prevail. If they don’t, autonomy is still coming, one way or the other.”
BREAKING: GENE MUNSTER SAYS — $TSLA AUTONOMY IS “MUCH BIGGER” THAN ANY FEUD 👀
He says robotaxis are coming regardless ! pic.twitter.com/ytpPcwUTFy
— TheSonOfWalkley (@TheSonOfWalkley) July 2, 2025
This is a point that other analysts like Dan Ives of Wedbush and Cathie Wood of ARK Invest also made yesterday.
On two occasions over the past month, Musk and President Trump have gotten involved in a very public disagreement over the “Big Beautiful Bill,” which officially passed through the Senate yesterday and is making its way to the House of Representatives.
Musk is upset with the spending in the bill, while President Trump continues to reiterate that the Tesla CEO is only frustrated with the removal of an “EV mandate,” which does not exist federally, nor is it something Musk has expressed any frustration with.
In fact, Musk has pushed back against keeping federal subsidies for EVs, as long as gas and oil subsidies are also removed.
Nevertheless, Ives and Wood both said yesterday that they believe the political hardship between Musk and President Trump will pass because both realize the world is a better place with them on the same team.
Munster’s perspective is that, even though Musk’s feud with President Trump could apply near-term pressure to the stock, the company’s progress in autonomy is an indication that, in the long term, Tesla is set up to succeed.
Tesla launched its Robotaxi platform in Austin on June 22 and is expanding access to more members of the public. Austin residents are now reporting that they have been invited to join the program.
Elon Musk
Tesla surges following better-than-expected delivery report
Tesla saw some positive momentum during trading hours as it reported its deliveries for Q2.

Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA) surged over four percent on Wednesday morning after the company reported better-than-expected deliveries. It was nearly right on consensus estimations, as Wall Street predicted the company would deliver 385,000 cars in Q2.
Tesla reported that it delivered 384,122 vehicles in Q2. Many, including those inside the Tesla community, were anticipating deliveries in the 340,000 to 360,000 range, while Wall Street seemed to get it just right.
Tesla delivers 384,000 vehicles in Q2 2025, deploys 9.6 GWh in energy storage
Despite Tesla meeting consensus estimations, there were real concerns about what the company would report for Q2.
There were reportedly brief pauses in production at Gigafactory Texas during the quarter and the ramp of the new Model Y configuration across the globe were expected to provide headwinds for the EV maker during the quarter.
At noon on the East Coast, Tesla shares were up about 4.5 percent.
It is expected that Tesla will likely equal the number of deliveries it completed in both of the past two years.
It has hovered at the 1.8 million mark since 2023, and it seems it is right on pace to match that once again. Early last year, Tesla said that annual growth would be “notably lower” than expected due to its development of a new vehicle platform, which will enable more affordable models to be offered to the public.
These cars are expected to be unveiled at some point this year, as Tesla said they were “on track” to be produced in the first half of the year. Tesla has yet to unveil these vehicle designs to the public.
Dan Ives of Wedbush said in a note to investors this morning that the company’s rebound in China in June reflects good things to come, especially given the Model Y and its ramp across the world.
He also said that Musk’s commitment to the company and return from politics played a major role in the company’s performance in Q2:
“If Musk continues to lead and remain in the driver’s seat, we believe Tesla is on a path to an accelerated growth path over the coming years with deliveries expected to ramp in the back-half of 2025 following the Model Y refresh cycle.”
Ives maintained his $500 price target and the ‘Outperform’ rating he held on the stock:
“Tesla’s future is in many ways the brightest it’s ever been in our view given autonomous, FSD, robotics, and many other technology innovations now on the horizon with 90% of the valuation being driven by autonomous and robotics over the coming years but Musk needs to focus on driving Tesla and not putting his political views first. We maintain our OUTPERFORM and $500 PT.”
Moving forward, investors will look to see some gradual growth over the next few quarters. At worst, Tesla should look to match 2023 and 2024 full-year delivery figures, which could be beaten if the automaker can offer those affordable models by the end of the year.
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-
 Elon Musk1 week ago
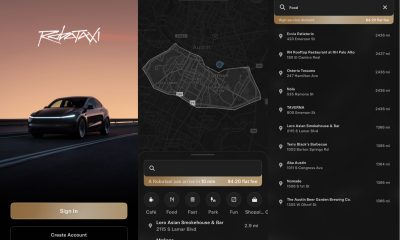
Elon Musk1 week agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla Robotaxis are becoming a common sight on Austin’s public roads
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Grok 3 partners with Oracle Cloud for corporate AI innovation
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoSpaceX President meets India Minister after Starlink approval

















