
News
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk reveals radical Starlink redesign for 60-satellite launch
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk has published the first official photo of the company’s near-final Starlink design and confirmed that Falcon 9 will launch a staggering 60 satellites on May 15th.
Known internally as Starlink v0.9, this mission will not be the first launch of operational satellites, but it will be the first internal SpaceX mission with a dedicated Falcon 9 launch. Additionally, the payload will be the heaviest yet launched by SpaceX, signifying an extraordinarily ambitious first step towards realizing the company’s ~12,000-satellite Starlink megaconstellation.
Rewriting the satellite design book
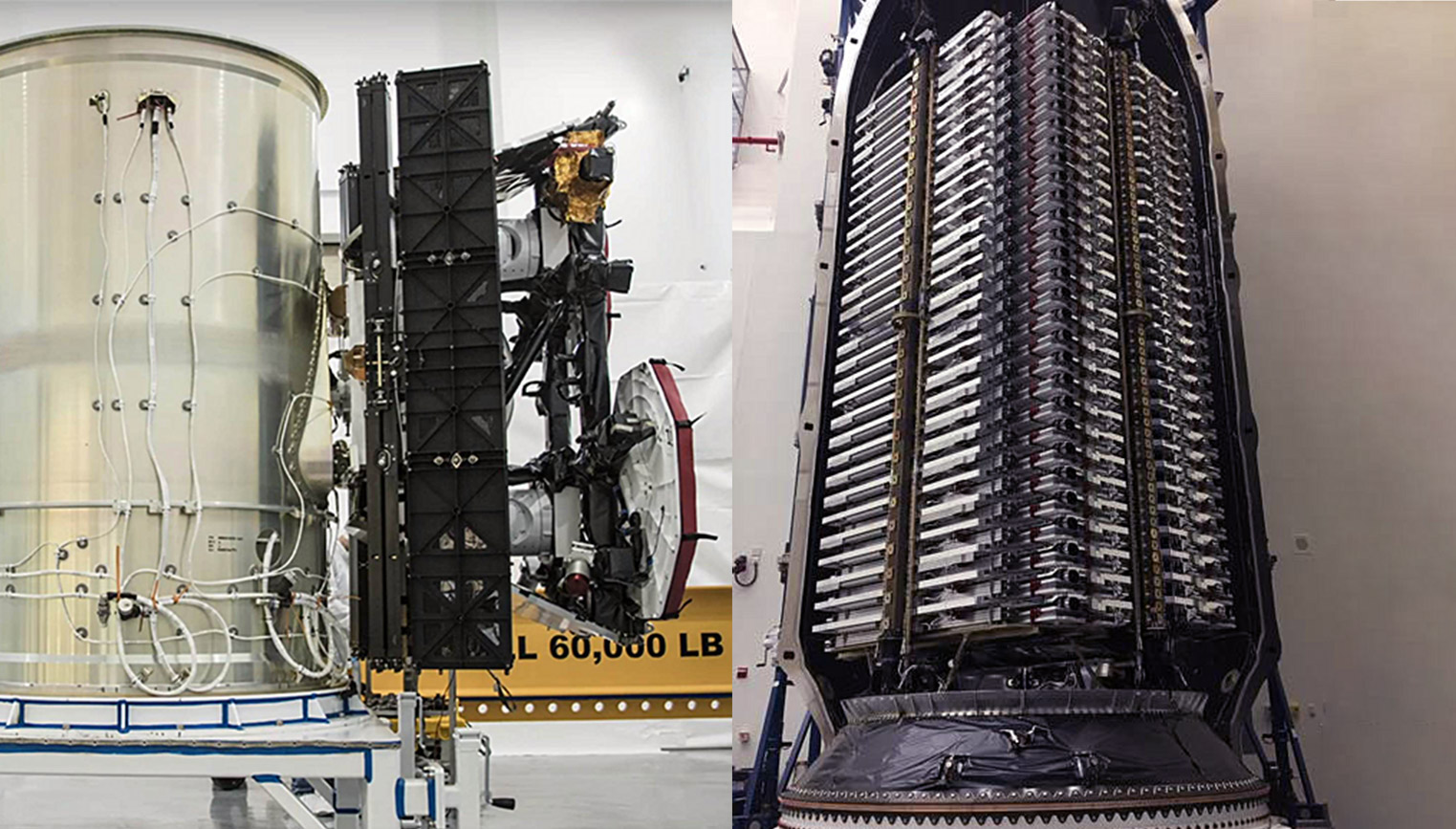
Put simply, SpaceX’s Starlink v0.9 launch is extremely unique for several reasons. Aside from the unprecedented step of launching 60 spacecraft weighing ~13,000 kg (~30,000 lb) on a developmental mission, both the form factor of each satellite and the style of dispenser/payload adapter has never been seen before. SpaceX appears to have settled on a square dispenser with four separate quadrants for satellites. The satellites themselves look truly bizarre – it’s actually difficult to discern where one spacecraft stops and the next begins.
Nevertheless, it appears that each Starlink satellite is a relatively thin rectangle, possibly with a squared top and bottom. It’s also possible that they are all around rectangular and that the dispenser instead has two main sections. Either way, the very fact that the Starlink v0.9 payload can scarcely be parsed into recognizable satellites is thrilling. Aside from the rise of smallsats and cubesats, satellite design and engineering has been relatively stagnant for decades, particularly with respect to form factors and structural layouts. Most modern satellites are simply square-ish boxes with electronics inside and payloads bolted on the outside.

By all appearances, SpaceX’s Starlink beta satellites suffer from no such tried-and-true design tropes. This is a somewhat calculated risk, as those current tried-and-true satellite design rules are conservative but decidedly proven over dozens of years of orbital experience. To throw out the satellite design textbook is to invite an increased potential for failure in order to pursue entirely new ways of thinking, designing, building, and launching spacecraft.
Even relative to fairly innovative constellations like the SpaceX-launched Iridium NEXT and OneWeb look downright mundane when examined alongside SpaceX’s inaugural Borg-cube-esque payload. SpaceX’s Starlink layout looks like nothing seen before. At the same time, it appears that the bizarre, new approach has likely maximized the density and stacking efficiency of dozens of satellites to an unprecedented degree.
Despite using the same exact Falcon fairing that has been standard for years, SpaceX has managed to cram 60 spacecraft – each weighing around 200-300 kg – into just the bottom two-thirds of the fairing, leaving a considerable amount of unused volume for future expansion.
According to President and COO Gwynne Shotwell, Starlink v0.9 satellites are extremely close to SpaceX’s true final design. However, they are still considered by SpaceX to be a “test batch” of satellites and do not have the optical (laser) interlinks that will be a critical part of Starlink’s unique constellation design. The mission is currently scheduled to launch at 10:30 pm EDT (02:30 UTC), May 15th and will have a flexible four-hour window. The mission will be preceded by a routine Falcon 9 static fire no earlier than (NET) May 13th.
Update:
According to Musk, SpaceX has actually entirely gotten rid of a satellite-dispenser middle-man, instead relying on the structure of the satellites themselves to act as their own launch adapters and deployment mechanisms. This has been done in the past on a far smaller scale – typically with 2-3 several-ton satellites – but has never been attempted at the scale SpaceX is just days away from launching.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.
News
Tesla China breaks 8-month slump by selling 71,599 vehicles wholesale in June
Tesla China’s June numbers were released by the China Passenger Car Association (CPCA) on Tuesday.

Tesla China was able to sell 71,599 vehicles wholesale in June 2025, reversing eight consecutive months of year-over-year declines. The figure marks a 0.83% increase from the 71,599 vehicles sold wholesale in June 2024 and a 16.1% jump compared to the 61,662 vehicles sold wholesale in May.
Tesla China’s June numbers were released by the China Passenger Car Association (CPCA) on Tuesday.
Tesla China’s June results in focus
Tesla produces both the Model 3 and Model Y at its Shanghai Gigafactory, which serves as the company’s primary vehicle export hub. Earlier this year, Tesla initiated a changeover for its best-selling vehicle, the Model Y, resulting in a drop in vehicle sales during the first and second quarters.
Tesla’s second-quarter China sales totaled 191,720 units including exports. While these numbers represent a 6.8% year-over-year decline for Tesla China, Q2 did show sequential improvement, rising about 11% from Q1 2025, as noted in a CNEV Post report.
For the first half of the year, Tesla sold 364,474 vehicles wholesale. This represents a 14.6% drop compared to the 426,623 units sold wholesale in the first half of 2024.
China’s competitive local EV market
Tesla’s position in China is notable, especially as the new Model Y is gaining ground in the country’s BEV segment. That being said, Tesla is also facing competition from impressive local brands such as Xiaomi, whose new YU7 electric SUV is larger and more affordable than the Model Y.
The momentum of the YU7 is impressive, as the vehicle was able to secure 200,000 firm orders within three minutes and over 240,000 locked-in orders within 18 hours. Xiaomi’s previous model, the SU7 electric sedan, which is aimed at the Tesla Model 3, also remains popular, with June deliveries surpassing 25,000 units for the ninth straight month.
While China’s EV market is getting more competitive, Tesla’s new Model Y is also ramping its production and deliveries. Needless to say, Tesla China’s results for the remaining two quarters of 2025 will be very interesting.
Elon Musk
Tesla reveals it is using AI to make factories more sustainable: here’s how
Tesla is using AI in its Gigafactory Nevada factory to improve HVAC efficiency.
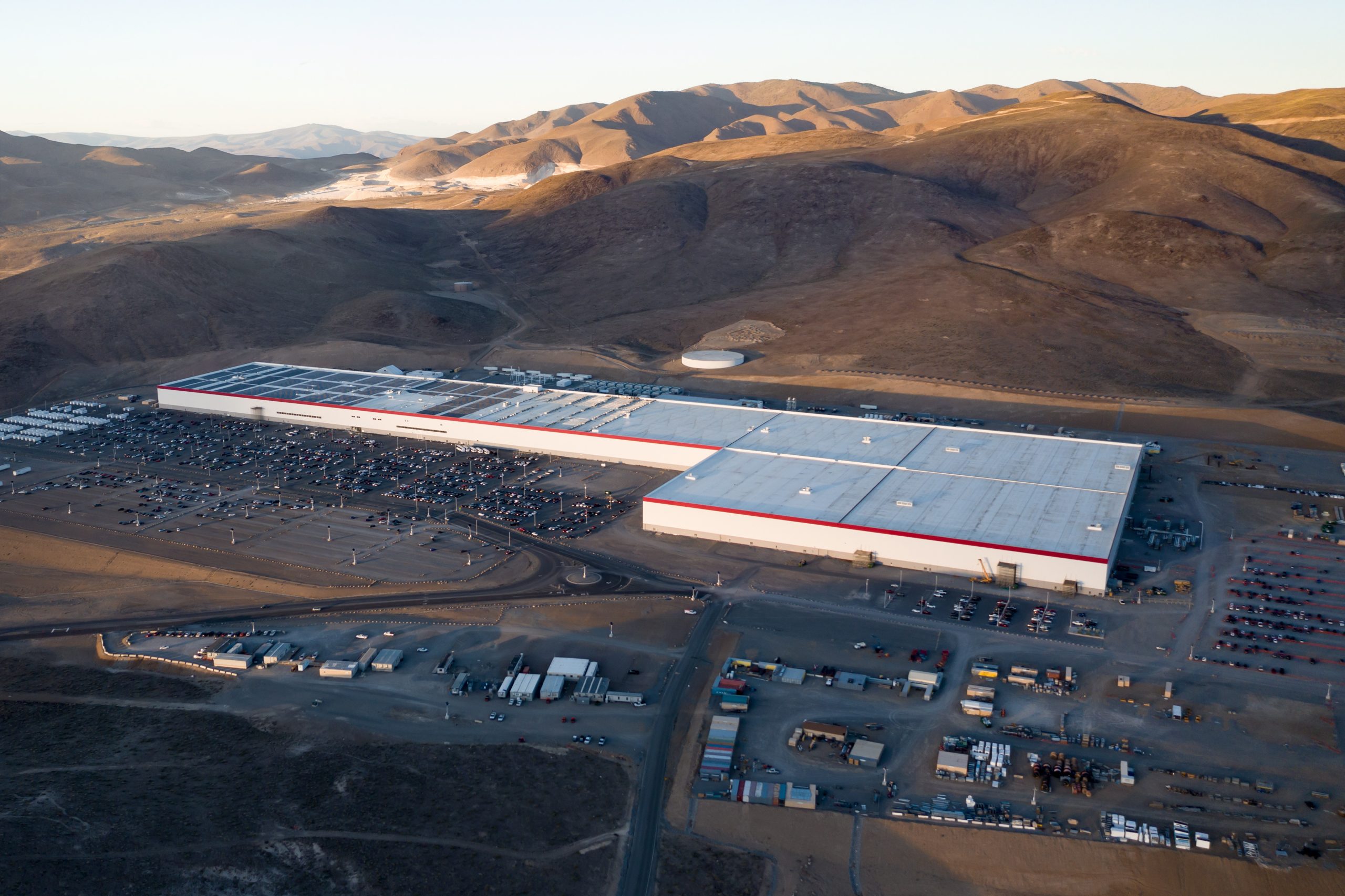

Tesla has revealed in its Extended Impact Report for 2024 that it is using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enable its factories to be more sustainable. One example it used was its achievement of managing “the majority of the HVAC infrastructure at Gigafactory Nevada is now AI-controlled” last year.
In a commitment to becoming more efficient and making its production as eco-friendly as possible, Tesla has been working for years to find solutions to reduce energy consumption in its factories.
For example, in 2023, Tesla implemented optimization controls in the plastics and paint shops located at Gigafactory Texas, which increased the efficiency of natural gas consumption. Tesla plans to phase out natural gas use across its factories eventually, but for now, it prioritizes work to reduce emissions from that energy source specifically.
It also uses Hygrometric Control Logic for Air Handling Units at Giafactory Berlin, resulting in 17,000 MWh in energy savings each year. At Gigafactory Nevada, Tesla saves 9.5 GWh of energy through the use of N-Methylpyrrolidone refineries when extracting critical raw material.
Perhaps the most interesting way Tesla is conserving energy is through the use of AI at Gigafactory Nevada, as it describes its use of AI to reduce energy demand:
“In 2023, AI Control for HVAC was expanded from Nevada and Texas to now include our Berlin-Brandenburg and Fremont factories. AI Control policy enables HVAC systems within each factory to work together to process sensor data, model factory dynamics, and apply control actions that safely minimize the energy required to support production. In 2024, this system achieved two milestones: the majority of HVAC infrastructure at Gigafactory Nevada is now AI-controlled, reducing fan and thermal energy demand; and the AI algorithm was extended to manage entire chiller plants, creating a closed-loop control system that optimizes both chilled water consumption and the energy required for its generation, all while maintaining factory conditions.”
Tesla utilizes AI Control “primarily on systems that heat or cool critical factory production spaces and equipment.” AI Control communicates with the preexisting standard control logic of each system, and any issues can be resolved by quickly reverting back to standard control. There were none in 2024.
Tesla says that it is utilizing AI to drive impact at its factories, and it has proven to be a valuable tool in reducing energy consumption at one of its facilities.
Elon Musk
Tesla analysts believe Musk and Trump feud will pass
Tesla CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump’s feud shall pass, several bulls say.

Tesla analysts are breaking down the current feud between CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump, as the two continue to disagree on the “Big Beautiful Bill” and its impact on the country’s national debt.
Musk, who headed the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) under the Trump Administration, left his post in May. Soon thereafter, he and President Trump entered a very public and verbal disagreement, where things turned sour. They reconciled to an extent, and things seemed to be in the past.
However, the second disagreement between the two started on Monday, as Musk continued to push back on the “Big Beautiful Bill” that the Trump administration is attempting to sign into law. It would, by Musk’s estimation, increase spending and reverse the work DOGE did to trim the deficit.
Every member of Congress who campaigned on reducing government spending and then immediately voted for the biggest debt increase in history should hang their head in shame!
And they will lose their primary next year if it is the last thing I do on this Earth.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) June 30, 2025
President Trump has hinted that DOGE could be “the monster” that “eats Elon,” threatening to end the subsidies that SpaceX and Tesla receive. Musk has not been opposed to ending government subsidies for companies, including his own, as long as they are all abolished.
How Tesla could benefit from the ‘Big Beautiful Bill’ that axes EV subsidies
Despite this contentious back-and-forth between the two, analysts are sharing their opinions now, and a few of the more bullish Tesla observers are convinced that this feud will pass, Trump and Musk will resolve their differences as they have before, and things will return to normal.
ARK Invest’s Cathie Wood said this morning that the feud between Musk and Trump is another example of “this too shall pass:”
BREAKING: CATHIE WOOD SAYS — ELON AND TRUMP FEUD “WILL PASS” 👀 $TSLA
She remains bullish ! pic.twitter.com/w5rW2gfCkx
— TheSonOfWalkley (@TheSonOfWalkley) July 1, 2025
Additionally, Wedbush’s Dan Ives, in a note to investors this morning, said that the situation “will settle:”
“We believe this situation will settle and at the end of the day Musk needs Trump and Trump needs Musk given the AI Arms Race going on between the US and China. The jabs between Musk and Trump will continue as the Budget rolls through Congress but Tesla investors want Musk to focus on driving Tesla and stop this political angle…which has turned into a life of its own in a roller coaster ride since the November elections.”
Tesla shares are down about 5 percent at 3:10 p.m. on the East Coast.
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Grok integration will be more realistic with this cool feature
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla China roars back with highest vehicle registrations this Q2 so far
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla dominates Cars.com’s Made in America Index with clean sweep
-
 Elon Musk1 week ago
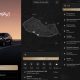
Elon Musk1 week agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more






















