
SpaceX
SpaceX’s first Starship engine suffers “expected” damage during Raptor test fire
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk says that the first full-scale Starship engine to be tested has already been pushed to the point of damage less than three weeks after the campaign began, setting the stage for the second full-scale Raptor to take over in the near future.
According to Musk, while most of the damaged pathfinder Raptor’s components should still be easily reusable, the assembly of the second finalized engine is “almost done” and that Raptor will take over near-term testing rather than waiting for repairs to the first engine. This is undoubtedly an extraordinarily aggressive test program, particularly for such a new and cutting-edge rocket propulsion system, but these latest developments are ultimately far more encouraging than they are concerning.
Merlins. The max chamber pressure run damaged Raptor SN 1 (as expected). A lot of the parts are fine for reuse, but next tests will be with SN 2, which is almost done.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 21, 2019
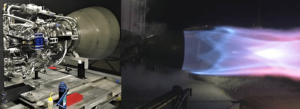
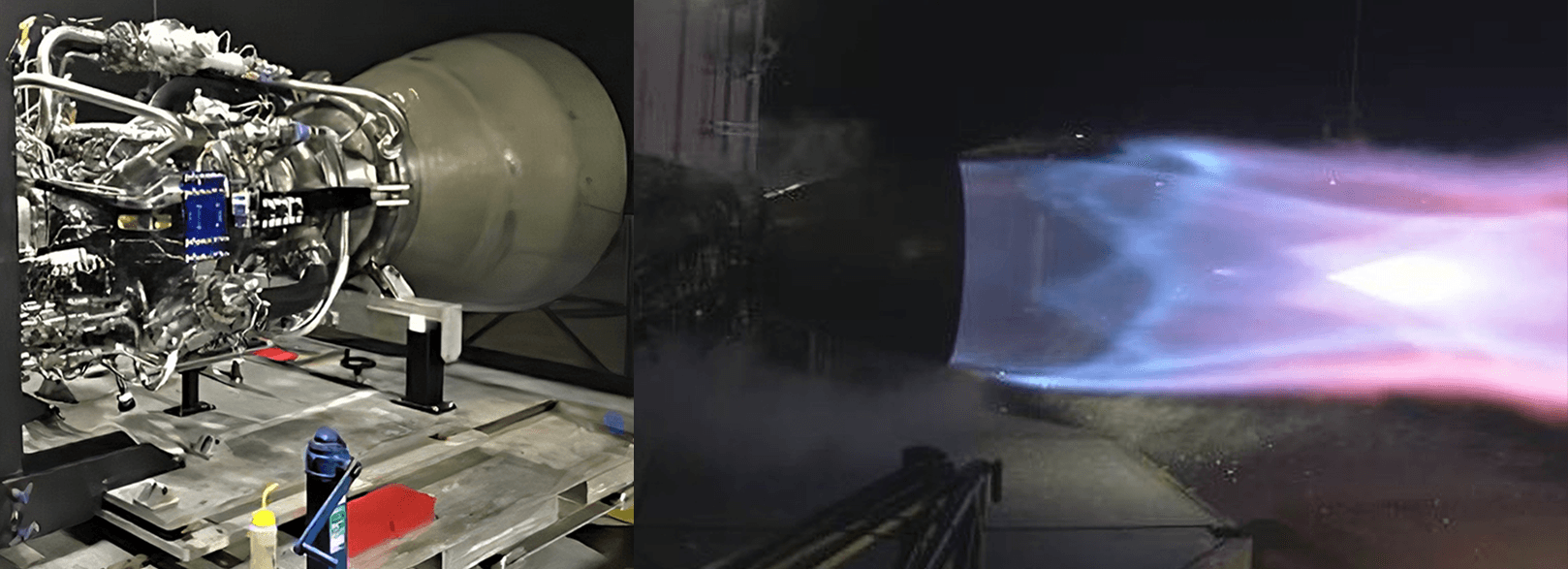
Although the Raptor engine family began integrated subscale static fires way back in September 2016, SpaceX’s propulsion team finalized Raptor’s baseline design and completed assembly, shipment, and an integrated static fire of the first full-scale engine on February 3rd, considerably less than three weeks before Musk took to Twitter. Aside from confirming that the new Raptor had been damaged during its most recent static fire several days prior, Musk indicated that the failure (unsurprisingly) was primarily attributed to the engine reaching the highest chamber pressures yet.
Raptor’s main combustion chamber (the bit directly above the nozzle) has been designed to nominally operate at and reliably withstand extraordinary pressures of 250+ bar (3600+ psi), performance that demands even higher pressures in the components that feed hot methane and oxygen gas into Raptor’s combustion chamber. One prime example hinted at by Musk in a 2018 tweet is its oxygen preburner, used to convert liquid propellant into a high-velocity gas that can then feed a dedicated oxygen turbopump. Aside from the absurdly corrosive environment created by extremely hot gaseous oxygen, the preburner must also survive pressures that could peak as high as 800+ bar, or 12,000 psi.
- SpaceX’s world-class rocket propulsion team has been progressing through early full-scale Raptor tests at an incredible speed. (SpaceX)
- Full-scale Raptor’s first static fire test, February 3rd. (SpaceX)
- Raptor’s business end with a Musk-for-scale. (Elon Musk)
- Starship revealed a trio of Raptor mockups when SpaceX technicians moved the assembly from stand to ground. (NSF – bocachicagal)
- A September 2018 render of Starship (then BFS) shows one of the vehicle’s two hinged wings/fins/legs. (SpaceX)
- BFR (2018) breaks through a cloud layer shortly after launch. (SpaceX)
A lack of technical detail means that it’s hard to know what thrust or main chamber pressure Musk had in mind when referring to exotic alloys that would be needed to survive those pressures, but the performance statistics of a Raptor with a preburner operating at 800+ bar would probably outstrip anything Musk has thus far described. In other words, it’s safe to assume that Raptor has probably not been pushed to those performance levels just yet, although it’s still a distant possibility. More likely is that 800+ bar in the oxygen preburner is an extreme stretch-goal that will take concerted research, development, and optimization to achieve, with Raptor having suffered damage somewhere below those levels while still reaching eye-watering performance figures.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 4, 2019
For an engine as complex as Raptor, there are countless dozens of potential failure modes the appearance of which would come as little surprise for an engine just days into full-scale testing. Above all else, the Raptor test schedule held by SpaceX’s world-class propulsion team – be it self-motivated or driven by reckless management-by-spreadsheet – has been fast-paced in the extreme, taking the first high-performance Raptor ever built from standstill to more than 90% thrust and chamber pressures of almost 270 bar (3900 psi) in – quite literally – less than one week. In the same period of time, more than half a dozen static fire tests (ranging from 1-10 seconds) were performed.
Within a few days of that February 10th milestone, in which Raptor reached chamber pressures comparable with the most advanced modern engines (namely RD-180/190/191), the engine was apparently pushed dramatically higher still, reaching a chamber pressure (and thus thrust) that wrought damage on some of the more sensitive parts of the engine’s plumbing. Despite the fact that the second production Raptor is apparently already “almost done”, Musk suggested that it would already feature changes (of unknown gravity) to mitigate the failure modes experienced by Raptor SN01.
SN2 has changes that should help
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 21, 2019
In an industry where NASA and contractors like Aerojet-Rocketdyne will spend months between static fire tests of Space Shuttle engines that have each literally flown multiple (if not) dozens of missions to orbit and have a demonstrated performance and reliability record that is measured in the hundreds of thousands of seconds, the speed and agility of SpaceX’s Raptor development and test program is breathtaking. What remains to be seen is just how comparably reliable and successful the end results (i.e. operational Raptor) will be, but an attitude that actively accepts and even pursues testing to destruction can ultimately only serve to benefit the finished product at the cost of destroyed hardware and many on-ground lessons learned the hard ways.
Given the immense success of SpaceX’s Merlin family of engines and the aggressive strategy of development and continuous improvement that brought it from Merlin 1A to 1D and MVacD, SpaceX is clearly not fumbling around in the dark when it comes to Raptor R&D.
Check out Teslarati’s newsletters for prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket launch and recovery processes!
News
SpaceX launches Ax-4 mission to the ISS with international crew
The SpaceX Falcon 9 launched Axiom’s Ax-4 mission to ISS. Ax-4 crew will conduct 60+ science experiments during a 14-day stay on the ISS.
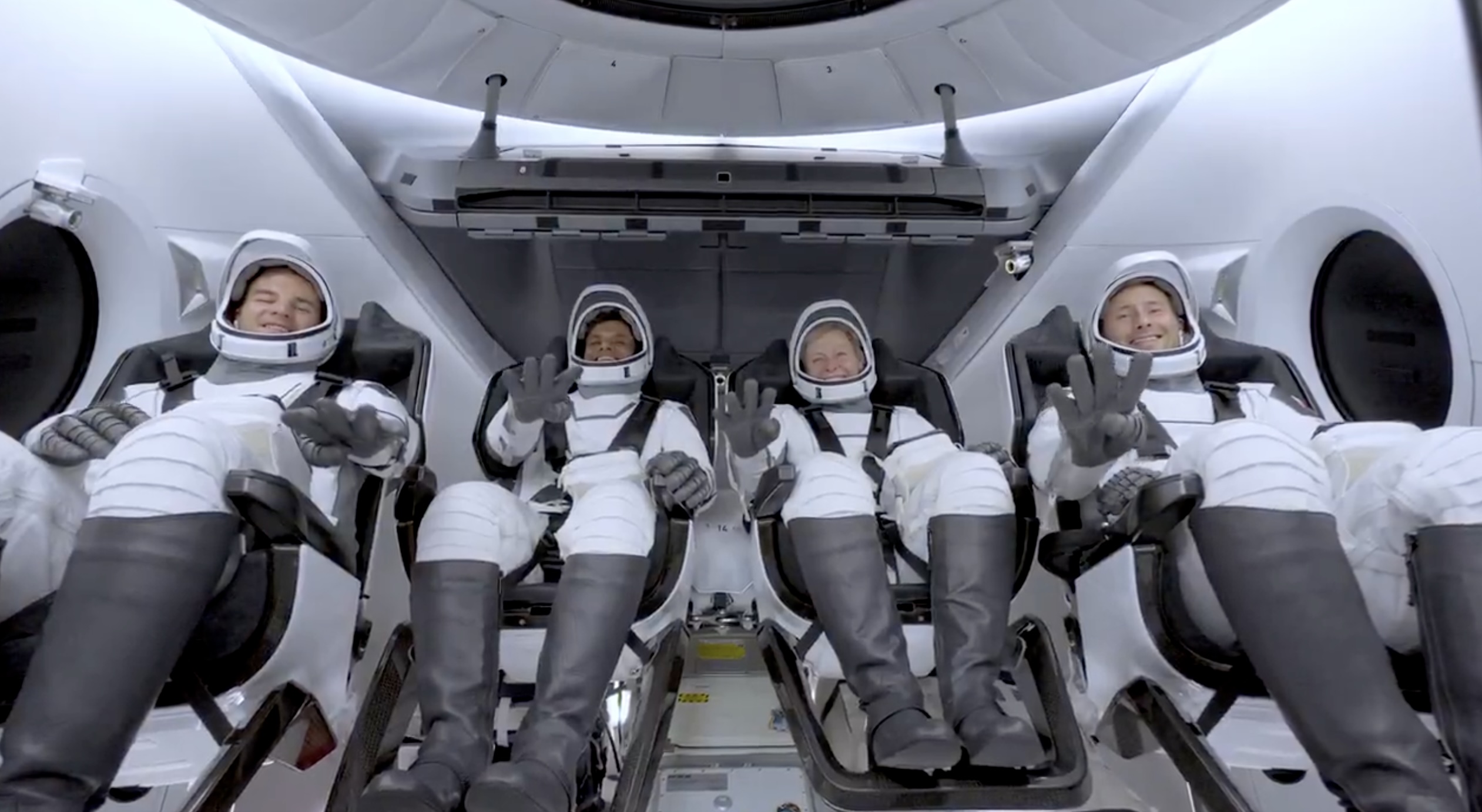

SpaceX launched the Falcon 9 rocket kickstarting Axiom Space’s Ax-4 mission to the International Space Station (ISS). Axiom’s Ax-4 mission is led by a historic international crew and lifted off from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A at 2:31 a.m. ET on June 25, 2025.
The Ax-4 crew is set to dock with the ISS around 7 a.m. ET on Thursday, June 26, 2025. Axiom Space, a Houston-based commercial space company, coordinated the mission with SpaceX for transportation and NASA for ISS access, with support from the European Space Agency and the astronauts’ governments.
The Ax-4 mission marks a milestone in global space collaboration. The Ax-4 crew, commanded by U.S. astronaut Peggy Whitson, includes Shubhanshu Shukla from India as the pilot, alongside mission specialists Sławosz Uznański-Wiśniewski from Poland and Tibor Kapu from Hungary.
“The trip marks the return to human spaceflight for those countries — their first government-sponsored flights in more than 40 years,” Axiom noted.
Shukla’s participation aligns with India’s Gaganyaan program planned for 2027. He is the first Indian astronaut to visit the ISS since Rakesh Sharma in 1984.
Axiom’s Ax-4 mission marks SpaceX’s 18th human spaceflight. The mission employs a Crew Dragon capsule atop a Falcon 9 rocket, designed with a launch escape system and “two-fault tolerant” for enhanced safety. The Axiom mission faced a few delays due to weather, a Falcon 9 leak, and an ISS Zvezda module leak investigation by NASA and Roscosmos before the recent successful launch.
As the crew prepares to execute its scientific objectives, SpaceX’s Ax-4 mission paves the way for a new era of inclusive space research, inspiring future generations and solidifying collaborative ties in the cosmos. During the Ax-4 crew’s 14-day stay in the ISS, the astronauts will conduct nearly 60 experiments.
“We’ll be conducting research that spans biology, material, and physical sciences as well as technology demonstrations,” said Whitson. “We’ll also be engaging with students around the world, sharing our experience and inspiring the next generation of explorers.”
SpaceX’s Ax-4 mission highlights Axiom’s role in advancing commercial spaceflight and fostering international partnerships. The mission strengthens global space exploration efforts by enabling historic spaceflight returns for India, Poland, and Hungary.
News
Starlink Cellular’s T-Mobile service to grow with third-party app data
From Oct 2025, T-Satellite will enable third-party apps in dead zones! WhatsApp, X, AccuWeather + more coming soon.

Starlink Cellular’s T-Mobile service will expand with third-party app data support starting in October, enhancing connectivity in cellular dead zones.
T-Mobile’s T-Satellite, supported by Starlink, launches officially on July 23. Following its launch, T-Mobile’s Starlink Cellular service will enable data access for third-party apps like WhatsApp, X, Google, Apple, AccuWeather, and AllTrails on October 1, 2025.
T-Mobile’s Starlink Cellular is currently in free beta. T-Satellite will add MMS support for Android phones on July 23, with iPhone support to follow. MMS support allows users to send images and audio clips alongside texts. By October, T-Mobile will extend emergency texting to all mobile users with compatible phones, beyond just T-Mobile customers, building on its existing 911 texting capability. The carrier also provides developer tools to help app makers integrate their software with T-Satellite’s data service, with plans to grow the supported app list.
T-Mobile announced these updates during an event celebrating an Ookla award naming it the best U.S. phone network, a remarkable turnaround from its last-place ranking a decade ago.
“We not only dream about going from worst to best, we actually do it. We’re a good two years ahead of Verizon and AT&T, and I believe that lead is going to grow,” said T-Mobile’s Chief Operating Officer Srini Gopalan.
T-Mobile unveiled two promotions for its Starlink Cellular services to attract new subscribers. A free DoorDash DashPass membership, valued at $10/month, will be included with popular plans like Experience Beyond and Experience More, offering reduced delivery and service fees. Meanwhile, the Easy Upgrade promotion targets Verizon customers by paying off their phone balances and providing flagship devices like the iPhone 16, Galaxy S25, or Pixel 9.
T-Mobile’s collaboration with SpaceX’s Starlink Cellular leverages orbiting satellites to deliver connectivity where traditional networks fail, particularly in remote areas. Supporting third-party apps underscores T-Mobile’s commitment to enhancing user experiences through innovative partnerships. As T-Satellite’s capabilities grow, including broader app integration and emergency access, T-Mobile is poised to strengthen its lead in the U.S. wireless market.
By combining Starlink’s satellite technology with strategic promotions, T-Mobile is redefining mobile connectivity. The upcoming third-party app data support and official T-Satellite launch mark a significant step toward seamless communication, positioning T-Mobile as a trailblazer in next-generation wireless services.
News
Starlink expansion into Vietnam targets the healthcare sector
Starlink aims to deliver reliable internet to Vietnam’s remote clinics, enabling telehealth and data sharing.

SpaceX’s Starlink expansion into Vietnam targets its healthcare sector. Through Starlink, SpaceX seeks to drive digital transformation in Vietnam.
On June 18, a SpaceX delegation met with Vietnam’s Ministry of Health (MoH) in Hanoi. SpaceX’s delegation was led by Andrew Matlock, Director of Enterprise Sales, and the discussions focused on enhancing connectivity for hospitals and clinics in Vietnam’s remote areas.
Deputy Minister of Health (MoH) Tran Van Thuan emphasized collaboration between SpaceX and Vietnam. Tran stated: “SpaceX should cooperate with the MoH to ensure all hospitals and clinics in remote areas are connected to the StarLink satellite system and share information, plans, and the issues discussed by members of the MoH. The ministry is also ready to provide information and send staff to work with the corporation.”
The MoH assigned its Department of Science, Technology, and Training to work with SpaceX. Starlink Vietnam will also receive support from Vietnam’s Department of International Cooperation. Starlink Vietnam’s agenda includes improving internet connectivity for remote healthcare facilities, developing digital infrastructure for health examinations and remote consultations, and enhancing operational systems.
Vietnam’s health sector is prioritizing IT and digital transformation, focusing on electronic health records, data centers, and remote medical services. However, challenges persist in deploying IT solutions in remote regions, prompting Vietnam to seek partnerships like SpaceX’s.
SpaceX’s Starlink has a proven track record in healthcare. In Rwanda, its services supported 40 health centers, earning praise for improving operations. Similarly, Starlink enabled remote consultations at the UAE’s Emirati field hospital in Gaza, streamlining communication for complex medical cases. These successes highlight Starlink’s potential to transform Vietnam’s healthcare landscape.
On May 20, SpaceX met with Vietnam’s Ministry of Industry and Trade, announcing a $1.5 billion investment to provide broadband internet, particularly in remote, border, and island areas. The first phase includes building 10-15 ground stations across the country. This infrastructure will support Starlink’s healthcare initiatives by ensuring reliable connectivity.
Starlink’s expansion in Vietnam aligns with the country’s push for digital transformation, as outlined by the MoH. By leveraging its satellite internet expertise, SpaceX aims to bridge connectivity gaps, enabling advanced healthcare services in underserved regions. This collaboration could redefine Vietnam’s healthcare infrastructure, positioning Starlink as a key player in the nation’s digital future.
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk4 days ago
Elon Musk4 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla sees explosive sales growth in UK, Spain, and Netherlands in June