
News
SpaceX sends Starship’s first vacuum Raptor engine to Boca Chica
For the first time, SpaceX has shipped a vacuum-optimized Raptor engine to its Boca Chica, Texas Starship factory days after the company’s present reiterated plans for an inaugural orbital launch attempt as early as July.
Back in March 2021, CEO Elon Musk confirmed that he’d set SpaceX a goal of attempting Starship’s first orbital launch no later than the end of July – around four and a half months distant at the time. Fifteen weeks later, though the prospects of an orbital launch attempt happening in July have practically shrunk to zero, SpaceX COO and President Gwynne Shotwell – best known for acting as a more grounded foil to Musk’s often impractical schedule estimates – reiterated that the company is still “shooting for July” for Starship’s first orbital launch attempt.
As of late June, hitting that target would require SpaceX to string together numerous extraordinary feats of engineering and rocketry in record time or attempt some extremely unorthodox corner-cutting.
The launch pad and launch vehicle hardware needed for Starship’s first space shot are currently far from ready for flight. On June 24th, Musk unexpectedly revealed that the Super Heavy booster prototype SpaceX is now in the late stages of assembly isn’t actually the booster that will carry Starship on its first space launch attempt. In other words, though dozens of rings in various states of work are strewn about SpaceX’s Boca Chica factory, the company has yet to begin assembling the massive 65m (~215 ft) tall booster required for the first orbital launch attempt.
Using Super Heavy Booster 3 (B3) as a ruler, assembly could easily take 9-10 weeks – starting whenever the process actually begins. If SpaceX started stacking Booster 4 today, in other words, it’s unlikely that the rocket would even be complete by the end of August. Barring SpaceX taking unprecedented shortcuts, completing the booster is just part of the process of preparing for flight and B4 would still need to be qualified for flight, likely involving at least one cryogenic proof and static fire test.
In a best-case scenario where SpaceX begins assembly today, manages to halve Booster 4 assembly time in one fell swoop, the sneaks the second Super Heavy ever completed through qualification testing in a single week, the orbital flight test booster still wouldn’t be ready for Starship installation (likely another unprecedented first) before mid-August.
That would then leave SpaceX five or six weeks to fully assemble Starship S20, a process that has yet to begin. Like Starship SN15, which Musk said sported “hundreds of improvements”, Musk has also stated that Ship 20 and all after it will feature another batch of upgrades needed to take Starship orbital. Starship SN15 was very gradually stacked and assembled over the course of almost four months, though that slow assembly can likely be blamed on the fact that SpaceX is busy testing Starships SN8 through SN11 and was effectively waiting to see if any other major changes might be required.
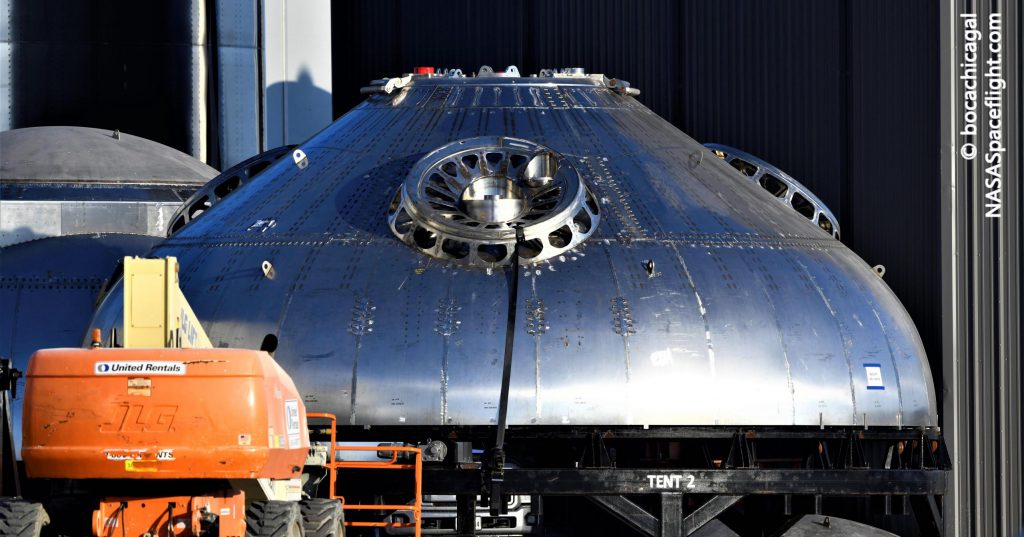

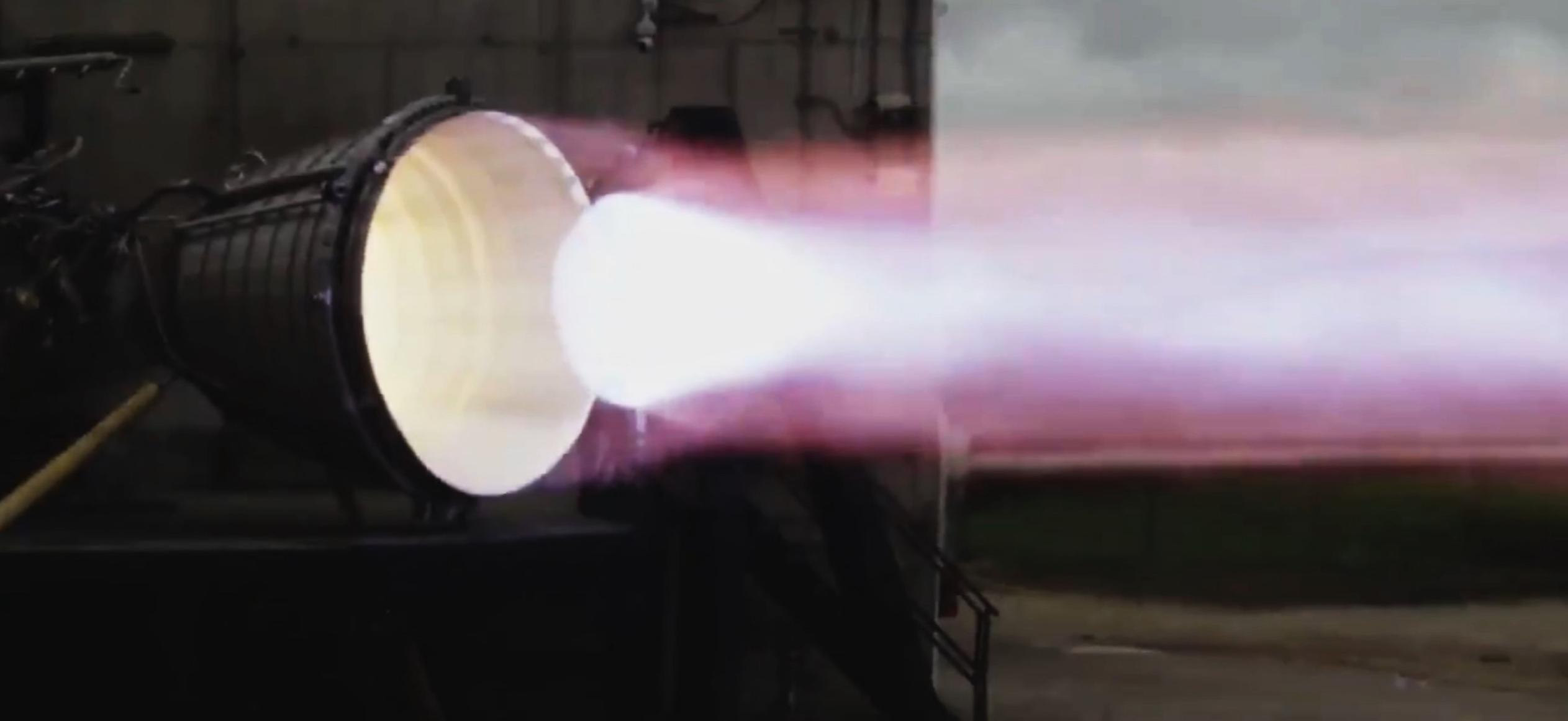
While most of S20’s upgrades are a mystery, the ship’s thrust dome – spotted in work at Boca Chica earlier this month – has already confirmed that the prototype will be the first with the necessary hardware for Raptor Vacuum engine installation. That likely means that S20 will also be the first Starship to attempt to static fire six Raptor engines*, potentially producing more thrust than a Falcon 9 booster. On June 27th, one such vacuum-optimized Raptor (RVac) arrived in Boca Chica for the first time ever, making it clear that the comparatively brand new engine may already be ready to start integrated Starship testing.
*Update: SpaceX CEO Elon Musk says that the Raptor Vacuum delivered to Boca Chica on June 27th is, in fact, meant for Starship S20, seemingly confirming that the prototype will fly with a full six Raptor engines.
Of course, beyond Starship and Super Heavy, SpaceX also has a great deal of work left to get the rocket’s first orbital-class launch facilities partially operational. SpaceX will need to complete and activate at least one or two more custom-built propellant storage tanks, sleeve those three or four tanks with three or four massive thermos-like ‘shells,’ complete thousands of feet of insulated plumbing and wiring, finish a massive ‘launch table,’ install that table on a six-legged ‘launch mount;’ outfit that table and mount with an array of power, avionics, hydraulics, and fueling equipment and plumbing; complete a ~145m (~475 ft) ‘integration tower,’ and perform the first fit checks and shakedown tests with a real booster or Starship.
Only then will SpaceX be able to attempt Starship’s first space launch. All told, it might not be literally impossible for SpaceX to complete all the above work in less than five weeks, but it’s safe to say that the odds of that happening could probably make a lottery ticket blush. Regardless, if Starship reaches orbit at any point before the end of 2021, it would beat out simpler “next-generation” rockets like Ariane 6, ULA’s Vulcan, and Blue Origin’s New Glenn despite beginning concerted development years later and with a far less certain funding situation.
News
Tesla launches in India with Model Y, showing pricing will be biggest challenge
Tesla finally got its Model Y launched in India, but it will surely come at a price for consumers.
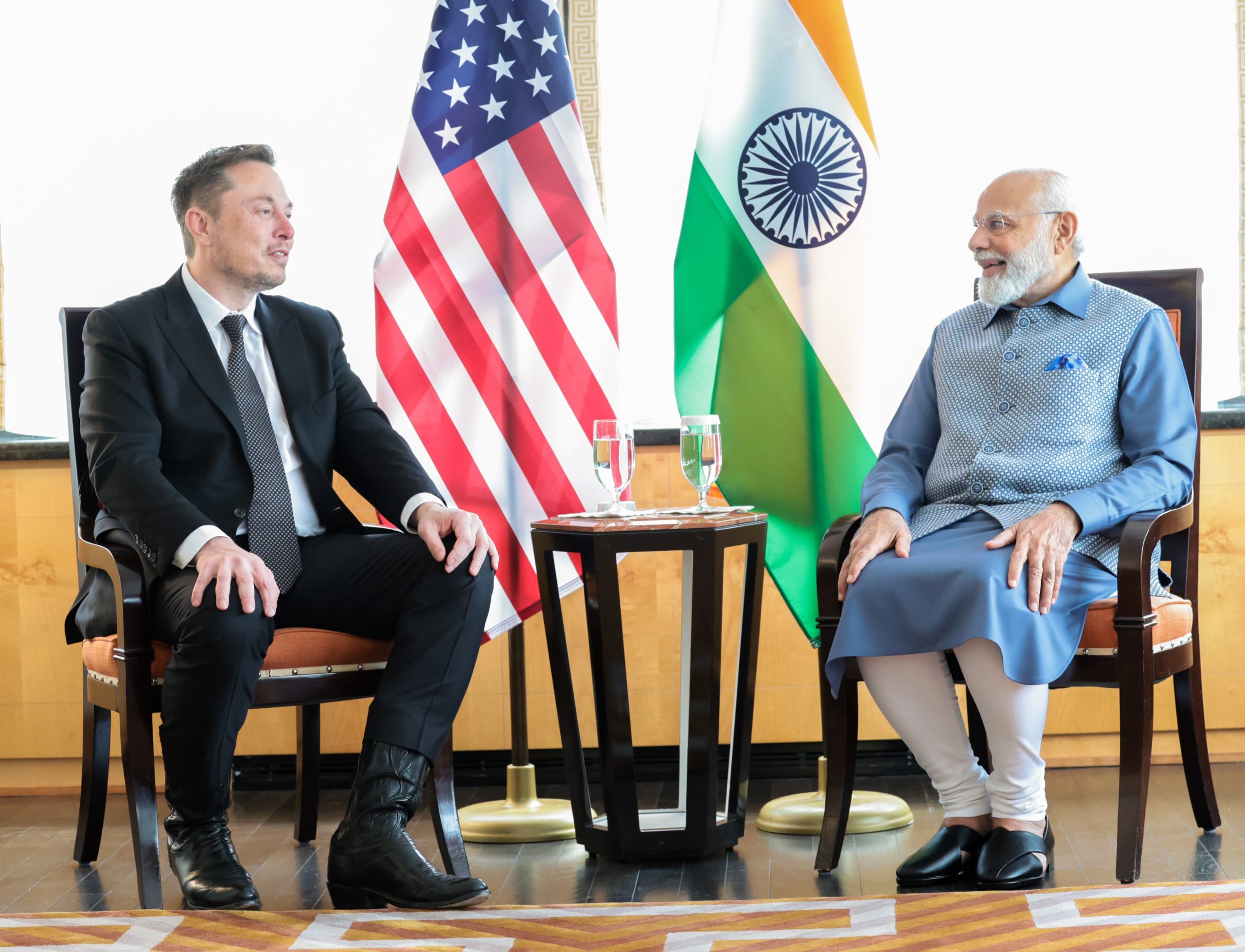

Tesla has officially launched in India following years of delays, as it brought its Model Y to the market for the first time on Tuesday.
However, the launch showed that pricing is going to be its biggest challenge. The all-electric Model Y is priced significantly higher than in other major markets in which Tesla operates.
On Tuesday, Tesla’s Model Y went up for sale for 59,89,000 rupees for the Rear-Wheel Drive configuration, while the Long Range Rear-Wheel Drive was priced at 67,89,000.
This equates to $69,686 for the RWD and $78,994 for the Long Range RWD, a substantial markup compared to what these cars sell for in the United States.
🚨 Here’s the difference in price for the Tesla Model Y in the U.S. compared to India.
🚨 59,89,000 is $69,686
🚨 67,89,000 is $78,994 pic.twitter.com/7EUzyWLcED— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 15, 2025
Deliveries are currently scheduled for the third quarter, and it will be interesting to see how many units they can sell in the market at this price point.
The price includes tariffs and additional fees that are applied by the Indian government, which has aimed to work with foreign automakers to come to terms on lower duties that increase vehicle cost.
Tesla Model Y seen testing under wraps in India ahead of launch
There is a chance that these duties will be removed, which would create a more stable and affordable pricing model for Tesla in the future. President Trump and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi continue to iron out those details.
Maharashtra Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis said to reporters outside the company’s new outlet in the region (via Reuters):
“In the future, we wish to see R&D and manufacturing done in India, and I am sure at an appropriate stage, Tesla will think about it.”
It appears to be eerily similar to the same “game of chicken” Tesla played with Indian government officials for the past few years. Tesla has always wanted to enter India, but was unable to do so due to these import duties.
India wanted Tesla to commit to building a Gigafactory in the country, but Tesla wanted to test demand first.
It seems this could be that demand test, and the duties are going to have a significant impact on what demand will actually be.
Elon Musk
Tesla ups Robotaxi fare price to another comical figure with service area expansion
Tesla upped its fare price for a Robotaxi ride from $4.20 to, you guessed it, $6.90.

Tesla has upped its fare price for the Robotaxi platform in Austin for the first time since its launch on June 22. The increase came on the same day that Tesla expanded its Service Area for the Robotaxi ride-hailing service, offering rides to a broader portion of the city.
The price is up from $4.20, a figure that many Tesla fans will find amusing, considering CEO Elon Musk has used that number, as well as ’69,’ as a light-hearted attempt at comedy over the past several years.
Musk confirmed yesterday that Tesla would up the price per ride from that $4.20 point to $6.90. Are we really surprised that is what the company decided on, as the expansion of the Service Area also took effect on Monday?
But the price is now a princely $6.90, as foretold in the prophecy 😂
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) July 14, 2025
The Service Area expansion was also somewhat of a joke too, especially considering the shape of the new region where the driverless service can travel.
I wrote yesterday about how it might be funny, but in reality, it is more of a message to competitors that Tesla can expand in Austin wherever it wants at any time.
Tesla’s Robotaxi expansion wasn’t a joke, it was a warning to competitors
It was only a matter of time before the Robotaxi platform would subject riders to a higher, flat fee for a ride. This is primarily due to two reasons: the size of the access program is increasing, and, more importantly, the service area is expanding in size.
Tesla has already surpassed Waymo in Austin in terms of its service area, which is roughly five square miles larger. Waymo launched driverless rides to the public back in March, while Tesla’s just became available to a small group in June. Tesla has already expanded it, allowing new members to hail a ride from a driverless Model Y nearly every day.
The Robotaxi app is also becoming more robust as Tesla is adding new features with updates. It has already been updated on two occasions, with the most recent improvements being rolled out yesterday.
Tesla updates Robotaxi app with several big changes, including wider service area
News
Tesla Model Y and Model 3 dominate U.S. EV sales despite headwinds
Tesla’s two mainstream vehicles accounted for more than 40% of all EVs sold in the United States in Q2 2025.

Tesla’s Model Y and Model 3 remained the top-selling electric vehicles in the U.S. during Q2 2025, even as the broader EV market dipped 6.3% year-over-year.
The Model Y logged 86,120 units sold, followed by the Model 3 at 48,803. This means that Tesla’s two mainstream vehicles accounted for 43% of all EVs sold in the United States during the second quarter, as per data from Cox Automotive.
Tesla leads amid tax credit uncertainty and a tough first half
Tesla’s performance in Q2 is notable given a series of hurdles earlier in the year. The company temporarily paused Model Y deliveries in Q1 as it transitioned to the production of the new Model Y, and its retail presence was hit by protests and vandalism tied to political backlash against CEO Elon Musk. The fallout carried into Q2, yet Tesla’s two mass-market vehicles still outsold the next eight EVs combined.
Q2 marked just the third-ever YoY decline in quarterly EV sales, totaling 310,839 units. Electric vehicle sales, however, were still up 4.9% from Q1 and reached a record 607,089 units in the first half of 2025. Analysts also expect a surge in Q3 as buyers rush to qualify for federal EV tax credits before they expire on October 1, Cox Automotive noted in a post.
Legacy rivals gain ground, but Tesla holds its commanding lead
General Motors more than doubled its EV volume in the first half of 2025, selling over 78,000 units and boosting its EV market share to 12.9%. Chevrolet became the second-best-selling EV brand, pushing GM past Ford and Hyundai. Tesla, however, still retained a commanding 44.7% electric vehicle market share despite a 12% drop in in Q2 revenue, following a decline of almost 9% in Q1.
Incentives reached record highs in Q2, averaging 14.8% of transaction prices, roughly $8,500 per vehicle. As government support winds down, the used EV market is also gaining momentum, with over 100,000 used EVs sold in Q2.
Q2 2025 Kelley Blue Book EV Sales Report by Simon Alvarez on Scribd
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoTesla debuts hands-free Grok AI with update 2025.26: What you need to know
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 Elon Musk5 days ago
Elon Musk5 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales















