

News
SpaceX’s Starship rocket just took a big leap towards orbit with latest test success
A full-scale Starship rocket has passed a critical test for the first time ever, strongly suggesting that the next-generation launch vehicle could be much closer to orbital readiness than most would imagine.
To be clear, a huge amount of work remains before Starship can be deemed anywhere close to its first orbital flight tests, not the least of which is the fabrication and assembly of the first massive Super Heavy booster(s). However, after Starship SN4’s latest successful May 9th test, it’s hard to see any apparent showstoppers that can’t be handled with a combination of fairly routine testing and iterative progress, as well as time and money. There is certainly room for improvement throughout the program but SpaceX has effectively demonstrated that the biggest practical concerns about its approach to Starship are moot.
Captured live on May 9th and 10th by local resident and photographer Mary (bocachicagal) with the help of NASASpaceflight.com, SpaceX worked for about two days to reconfigure its fourth full-scale Starship prototype after two successful Raptor engine static fires and prepare it for a different kind of test. That work mainly involved removing said Raptor and replacing it with a hydraulic ram stand used to simulate the thrust of 1-3 engines without actually needing to perform a static fire test, further allowing SpaceX to simulate much longer engine operations than its spartan test pad could survive. Around 9pm CDT on May 9th (02:00 UTC, May 10), Starship SN4’s latest trial began.
Known as a cryogenic pressure and load test, it differed from a prior “cryo proof test” completed on April 26th, in which Starship was fully loaded with liquid nitrogen (more than twice as cold as dry ice), pressurized to a bit less than 5 bar (~70 psi), and stressed with hydraulic rams. About a week later, after installing a Raptor engine on a full-scale Starship prototype for the first time ever, Starship SN4 fired up said engine on May 5th – another historic first for the next-generation launch vehicle. 30 hours later, SpaceX performed another wet dress rehearsal (WDR) with liquid methane and oxygen and fired up Starship’s Raptor engine again.
After about 48 hours of reconfiguration, SpaceX moved on to a much more serious cryogenic test. As noted by CEO Elon Musk, the 4.9 bar the rocket previously reached was accepted as enough to perform a Raptor static fire test and possibly enough for a low-stress, low-altitude flight test to ~150m (500 ft). For orbital flight, however, Starship needs to withstand a minimum of 6 bar (~90 psi), while 8.5 bar (125 psi) is preferable to give the rocket the 1.4x safety factor optimal for human spaceflight.
This time, SpaceX – having successfully gathered data from two static fire tests and several wet dress rehearsals – was ready to risk Starship SN4 and pressurized it all the way to 7.5 bar (~110 psi). While ~12% shy of minimum human spaceflight standards, Starship SN4 successfully reached and maintained 7.5 bar while the ship stressed with hydraulic rams to simulate the thrust of three Raptor engines, all of which it survived fully intact. What 7.5 bar does offer, however, is a 1.25x safety factor – on the higher end of aerospace industry standards for uncrewed orbital spaceflight (i.e. cargo/satellite launches).
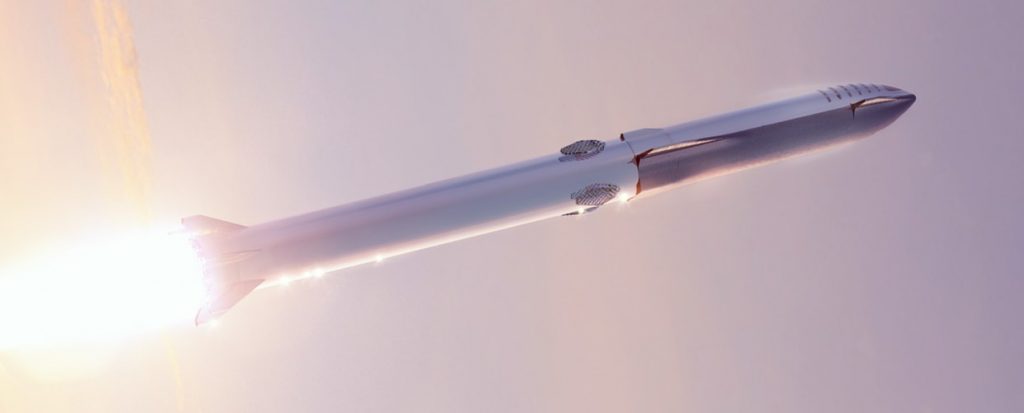

Ready for orbit?
Technically, this means that – pending much additional testing and verification with different serial prototypes and (likely) higher pressures – Starship’s stainless steel structure is effectively qualified for uncrewed orbital launches. Of course, reality is much more complex. To actually perform and survive orbital flights, SpaceX will first need to build and similarly qualify the first Super Heavy boosters and ensure that those unprecedentedly large rockets can survive and sustain ~20-30 Raptor engines firing simultaneously.
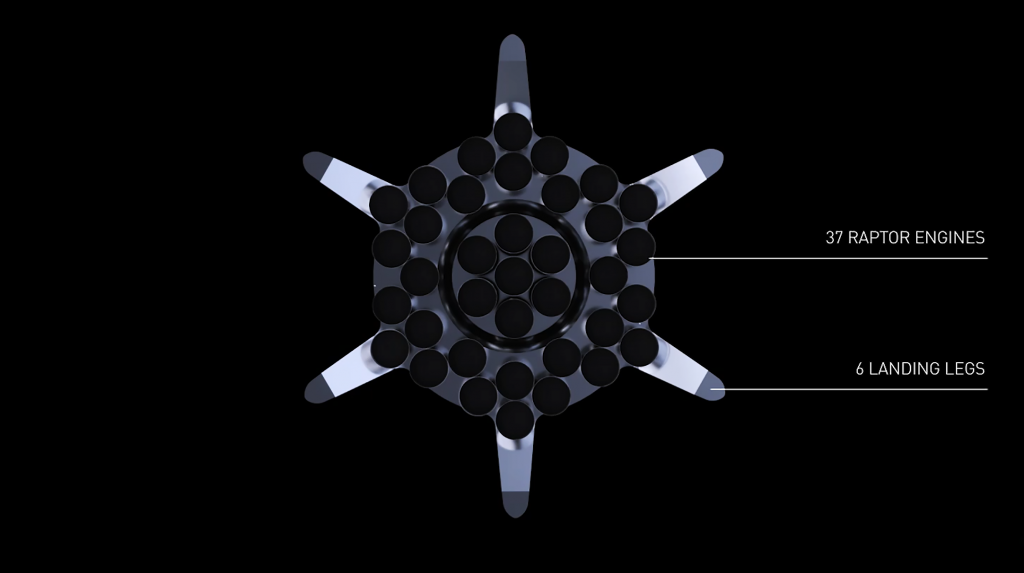
Aside from Super Heavy, it’s unknown if SpaceX has begun testing Raptor engines at the durations they will need to burn to booster Starships into orbit (TBD; likely 5-10 minutes of continuous operation). Along those lines, SpaceX also needs to build, test, and qualify Raptor’s vacuum-optimized sibling to complement the sea level version’s smaller, less-efficient nozzle. Still, Musk has already revealed that RaptorVac could be a matter of weeks from its first static fire and rocket engine development – while incredibly challenging – is more of a known quantity for SpaceX.
Perhaps the most important unknown is whether SpaceX’s recent May 2020 WDRs and static fires have used autogenous pressurization, a more efficient method of pressurizing rockets by using hot gas generated by their own engines. It’s extremely likely that SpaceX has been autogenously pressurizing Starship SN4 for its recent tests, but if that weren’t the case, it would be a big source of schedule uncertainty without significant redesign work.
Ultimately, SpaceX appears to have proven that orbital-class rockets can be built cheaply out of commodified steel in extraordinarily spartan production facilities. Many, many challenges remain but the biggest uncertainty and hurdle facing SpaceX’s Starship program and ambitions is well on its way to being fully put to rest.
Elon Musk
Tesla begins expanding Robotaxi access: here’s how you can ride
You can ride in a Tesla Robotaxi by heading to its website and filling out the interest form. The company is hand-picking some of those who have done this to gain access to the fleet.

Tesla has begun expanding Robotaxi access beyond the initial small group it offered rides to in late June, as it launched the driverless platform in Austin, Texas.
The small group of people enjoying the Robotaxi ride-hailing service is now growing, as several Austin-area residents are receiving invitations to test out the platform for themselves.
The first rides took place on June 22, and despite a very small number of very manageable and expected hiccups, Tesla Robotaxi was widely successful with its launch.
Tesla Robotaxi riders tout ‘smooth’ experience in first reviews of driverless service launch
However, Tesla is expanding the availability of the ride-hailing service to those living in Austin and its surrounding areas, hoping to gather more data and provide access to those who will utilize it on a daily basis.
Many of the people Tesla initially invited, including us, are not local to the Austin area.
There are a handful of people who are, but Tesla was evidently looking for more stable data collection, as many of those early invitees headed back to where they live.
The first handful of invitations in the second round of the Robotaxi platform’s Early Access Program are heading out to Austin locals:
I just got a @robotaxi invite! Super excited to go try the service out! pic.twitter.com/n9mN35KKFU
— Ethan McKanna (@ethanmckanna) July 1, 2025
Tesla likely saw an influx of data during the first week, as many traveled far and wide to say they were among the first to test the Robotaxi platform.
Now that the first week and a half of testing is over, Tesla is expanding invites to others. Many of those who have been chosen to gain access to the Robotaxi app and the ride-hailing service state that they simply filled out the interest form on the Robotaxi page of Tesla’s website.
That’s the easiest way you will also gain access, so be sure to fill out that form if you have any interest in riding in Robotaxi.
Tesla will continue to utilize data accumulated from these rides to enable more progress, and eventually, it will lead to even more people being able to hail rides from the driverless platform.
With more success, Tesla will start to phase out some of the Safety Monitors and Supervisors it is using to ensure things run smoothly. CEO Elon Musk said Tesla could start increasing the number of Robotaxis to monitors within the next couple of months.
Elon Musk
Tesla analyst issues stern warning to investors: forget Trump-Musk feud

A Tesla analyst today said that investors should not lose sight of what is truly important in the grand scheme of being a shareholder, and that any near-term drama between CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump should not outshine the progress made by the company.
Gene Munster of Deepwater Management said that Tesla’s progress in autonomy is a much larger influence and a significantly bigger part of the company’s story than any disagreement between political policies.
Munster appeared on CNBC‘s “Closing Bell” yesterday to reiterate this point:
“One thing that is critical for Tesla investors to remember is that what’s going on with the business, with autonomy, the progress that they’re making, albeit early, is much bigger than any feud that is going to happen week-to-week between the President and Elon. So, I understand the reaction, but ultimately, I think that cooler heads will prevail. If they don’t, autonomy is still coming, one way or the other.”
BREAKING: GENE MUNSTER SAYS — $TSLA AUTONOMY IS “MUCH BIGGER” THAN ANY FEUD 👀
He says robotaxis are coming regardless ! pic.twitter.com/ytpPcwUTFy
— TheSonOfWalkley (@TheSonOfWalkley) July 2, 2025
This is a point that other analysts like Dan Ives of Wedbush and Cathie Wood of ARK Invest also made yesterday.
On two occasions over the past month, Musk and President Trump have gotten involved in a very public disagreement over the “Big Beautiful Bill,” which officially passed through the Senate yesterday and is making its way to the House of Representatives.
Musk is upset with the spending in the bill, while President Trump continues to reiterate that the Tesla CEO is only frustrated with the removal of an “EV mandate,” which does not exist federally, nor is it something Musk has expressed any frustration with.
In fact, Musk has pushed back against keeping federal subsidies for EVs, as long as gas and oil subsidies are also removed.
Nevertheless, Ives and Wood both said yesterday that they believe the political hardship between Musk and President Trump will pass because both realize the world is a better place with them on the same team.
Munster’s perspective is that, even though Musk’s feud with President Trump could apply near-term pressure to the stock, the company’s progress in autonomy is an indication that, in the long term, Tesla is set up to succeed.
Tesla launched its Robotaxi platform in Austin on June 22 and is expanding access to more members of the public. Austin residents are now reporting that they have been invited to join the program.
Elon Musk
Tesla surges following better-than-expected delivery report
Tesla saw some positive momentum during trading hours as it reported its deliveries for Q2.

Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA) surged over four percent on Wednesday morning after the company reported better-than-expected deliveries. It was nearly right on consensus estimations, as Wall Street predicted the company would deliver 385,000 cars in Q2.
Tesla reported that it delivered 384,122 vehicles in Q2. Many, including those inside the Tesla community, were anticipating deliveries in the 340,000 to 360,000 range, while Wall Street seemed to get it just right.
Tesla delivers 384,000 vehicles in Q2 2025, deploys 9.6 GWh in energy storage
Despite Tesla meeting consensus estimations, there were real concerns about what the company would report for Q2.
There were reportedly brief pauses in production at Gigafactory Texas during the quarter and the ramp of the new Model Y configuration across the globe were expected to provide headwinds for the EV maker during the quarter.
At noon on the East Coast, Tesla shares were up about 4.5 percent.
It is expected that Tesla will likely equal the number of deliveries it completed in both of the past two years.
It has hovered at the 1.8 million mark since 2023, and it seems it is right on pace to match that once again. Early last year, Tesla said that annual growth would be “notably lower” than expected due to its development of a new vehicle platform, which will enable more affordable models to be offered to the public.
These cars are expected to be unveiled at some point this year, as Tesla said they were “on track” to be produced in the first half of the year. Tesla has yet to unveil these vehicle designs to the public.
Dan Ives of Wedbush said in a note to investors this morning that the company’s rebound in China in June reflects good things to come, especially given the Model Y and its ramp across the world.
He also said that Musk’s commitment to the company and return from politics played a major role in the company’s performance in Q2:
“If Musk continues to lead and remain in the driver’s seat, we believe Tesla is on a path to an accelerated growth path over the coming years with deliveries expected to ramp in the back-half of 2025 following the Model Y refresh cycle.”
Ives maintained his $500 price target and the ‘Outperform’ rating he held on the stock:
“Tesla’s future is in many ways the brightest it’s ever been in our view given autonomous, FSD, robotics, and many other technology innovations now on the horizon with 90% of the valuation being driven by autonomous and robotics over the coming years but Musk needs to focus on driving Tesla and not putting his political views first. We maintain our OUTPERFORM and $500 PT.”
Moving forward, investors will look to see some gradual growth over the next few quarters. At worst, Tesla should look to match 2023 and 2024 full-year delivery figures, which could be beaten if the automaker can offer those affordable models by the end of the year.
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-
 Elon Musk1 week ago
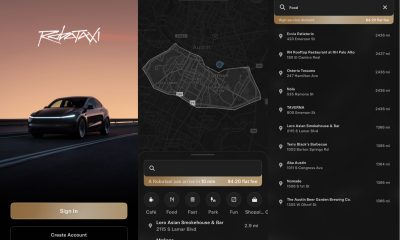
Elon Musk1 week agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla Robotaxis are becoming a common sight on Austin’s public roads
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoSpaceX President meets India Minister after Starlink approval
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Grok 3 partners with Oracle Cloud for corporate AI innovation

















