

News
SpaceX returns Starship booster to factory after two major Raptor tests
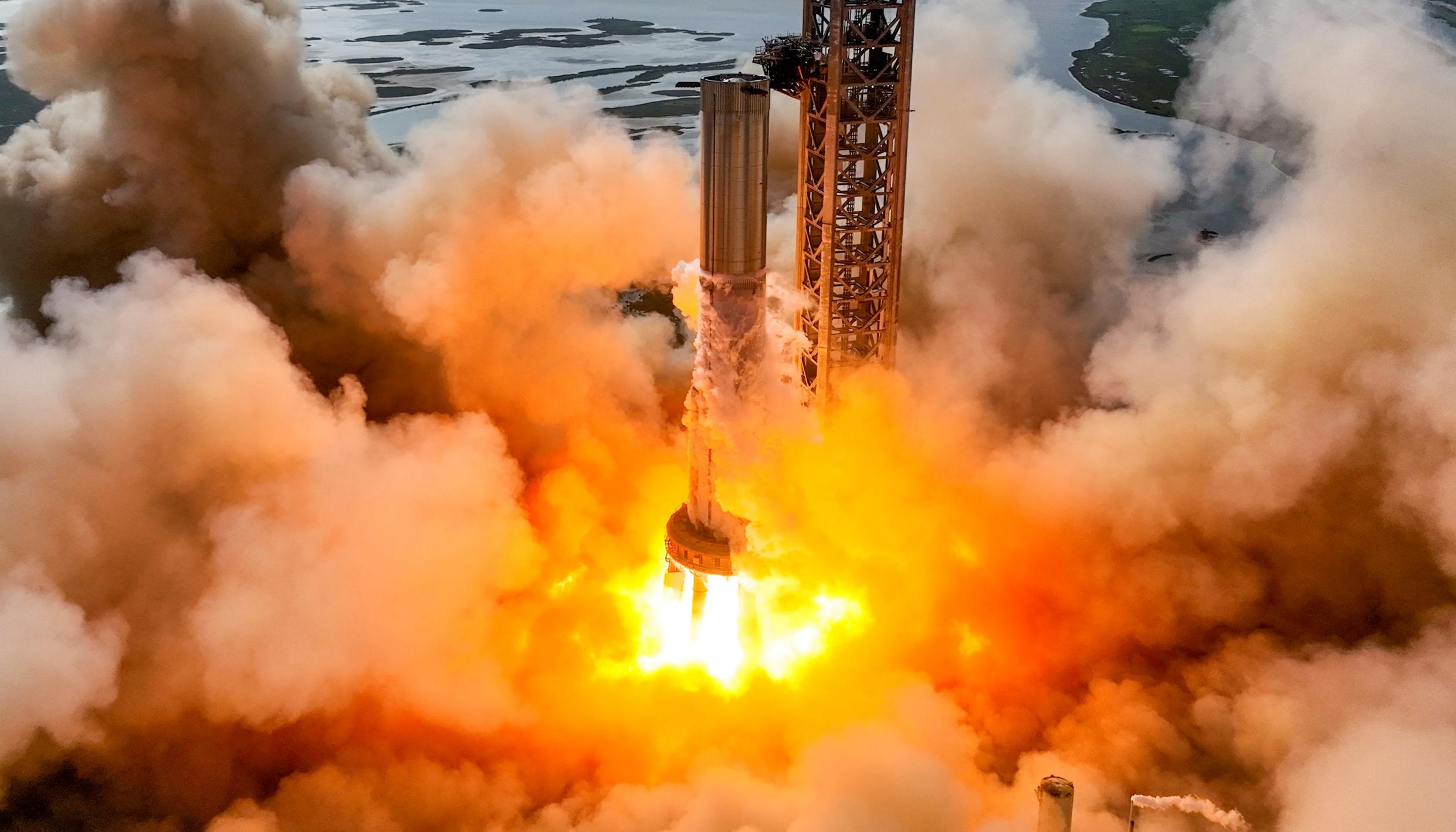
For the sixth time this year, SpaceX has returned the same Super Heavy booster prototype to its South Texas Starship factory after completing several tests.
Why is unclear. Super Heavy Booster 7 left the factory for the first time in March 2022 and has been stuck in a seemingly continuous state of testing, rework, and retesting ever since. While the pace of testing and progress was in many ways more aggressive from 2019 to mid-2021, it still can’t be said that SpaceX has been slacking off in 2022. Booster 7 alone completed more than 24 distinct tests (including six static fires) between early April and late November.
But in a shift from the first three or so years of steel Starship development, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk has ceased to be a consistent source of information on the purpose and results of many of those tests, even as NASA has begun to funnel hundreds of millions of taxpayer dollars into the Starship program. Save for occasional tidbits from SpaceX, Musk, and NASA; or deep unofficial analyses of public information, the day-to-day or week-to-week status of Starship has generally been relegated to speculation. Over the last few months, that information void has only grown larger.
The update that's rolling out to the fleet makes full use of the front and rear steering travel to minimize turning circle. In this case a reduction of 1.6 feet just over the air— Wes (@wmorrill3) April 16, 2024
Perhaps the biggest near-term update this year came from a senior NASA official on October 31st. In an advisory briefing, Mark Kirasich – Deputy Associate Administrator for Artemis Campaign Development – offered a surprising amount of detail about SpaceX’s near-term plans and even reported that Starship’s first orbital test flight was expected as early as December 2022, pending several crucial tests. But more than five weeks later, SpaceX appears to have only made a modest amount of progress towards those milestones and has yet to attempt the two most important tests.
Kirasich: First orbital Starship/Super Heavy expected in December. Still waiting for full 33 engine test, wet dress rehearsel, and FAA licensing. Will land in ocean off Hawaii. pic.twitter.com/FktCggnPEe— Marcia Smith (@SpcPlcyOnline) October 31, 2022
Nonetheless, some progress – however indeterminate without official information – has been made. As of Kirasich’s briefing, SpaceX was in the middle of a relatively minor series of cautious propellant loading tests with Booster 7 and Ship 24, which were stacked on October 20th. After three more partial full-stack tests in the first seven days of November, Ship 24 was removed. Aside from the visible steps SpaceX took after, little is known about the outcome of those propellant loading tests.
Ship 24’s fate is a different story, but Super Heavy B7 appeared to make it through full-stack testing in great shape. On November 14th, Booster 7 completed a record-breaking 14-engine static fire, doubling its previous record of seven engines and likely becoming one of the most powerful rockets in history. Musk simply stated that the “test went well”.
Poor weather undoubtedly contributed, but it would be another 15 days before Booster 7’s next test. On November 29th, after an aborted test on the 28th, SpaceX followed Booster 7’s record-breaking 14-engine static fire with a longer 13-second test of 11 Raptors. Before engine ignition, SpaceX loaded Booster 7 with around 2800 tons (~6.2M lb) of liquid oxygen (LOx) propellant in less than 90 minutes, making it a partial wet dress rehearsal (the methane tank was barely filled) as well. Musk called it “a little more progress towards Mars” and SpaceX shared a photo of the static fire on Twitter, but the results of the test – meant “to test autogenous pressurization” – were kept mostly opaque.
That uncertainty didn’t help when two of Booster 7’s 33 Raptor engines were removed immediately after the long-duration test. Then, Booster 7 was removed from Starbase’s lone ‘orbital launch mount’ on December 2nd and rolled back to the factory’s High Bay assembly facility on December 3rd. Historically, SpaceX has only returned Booster 7 to the factory to repair damage or install missing hardware. Without official information, it’s impossible to say why Booster 7 returned for the sixth time.
The most optimistic explanation is that SpaceX brought the Super Heavy booster back to the factory to fully close out its engine section heat shield, which currently has 20 missing panels for each of its outer Raptor engines. But there’s a good reason that those panels were never reinstalled. Any replacements would need to be modified to ensure that the ad-hoc system installed to prevent the conditions that led to Booster 7’s first explosion from recurring can still be used for future static fire tests. Even then, it’s unclear why SpaceX would need to reinstall those panels now for Booster 7’s upcoming 33-engine static fire(s) and full-stack wet dress rehearsal(s) when they weren’t needed for 11 and 14-engine static fires and a dozen other fire-free tests.
Depending on why Booster 7 is back at the factory, there is a precedent for it returning to the launch site as early as next week. Alternatively, if major work or repairs are required, it could be six weeks before SpaceX returns the rocket to the launch pad. Given that the full wet dress rehearsals and one or several 33-engine static fires standing between Booster 7 and flight readiness will be riskier and more challenging than any other test the prototype has completed to date, there is no real chance that Starship will be ready for its first orbital launch this year.
In fact, without detailed information, especially regarding Ship 24’s mysterious state, it’s difficult to pinpoint a viable target for Starship’s orbital launch debut more specific than the first half of 2023. But with any luck, even if it requires a substantially longer wait, SpaceX’s recent decision to make Starbase move slower and break fewer things will hopefully pay off with a successful debut sometime next year.

News
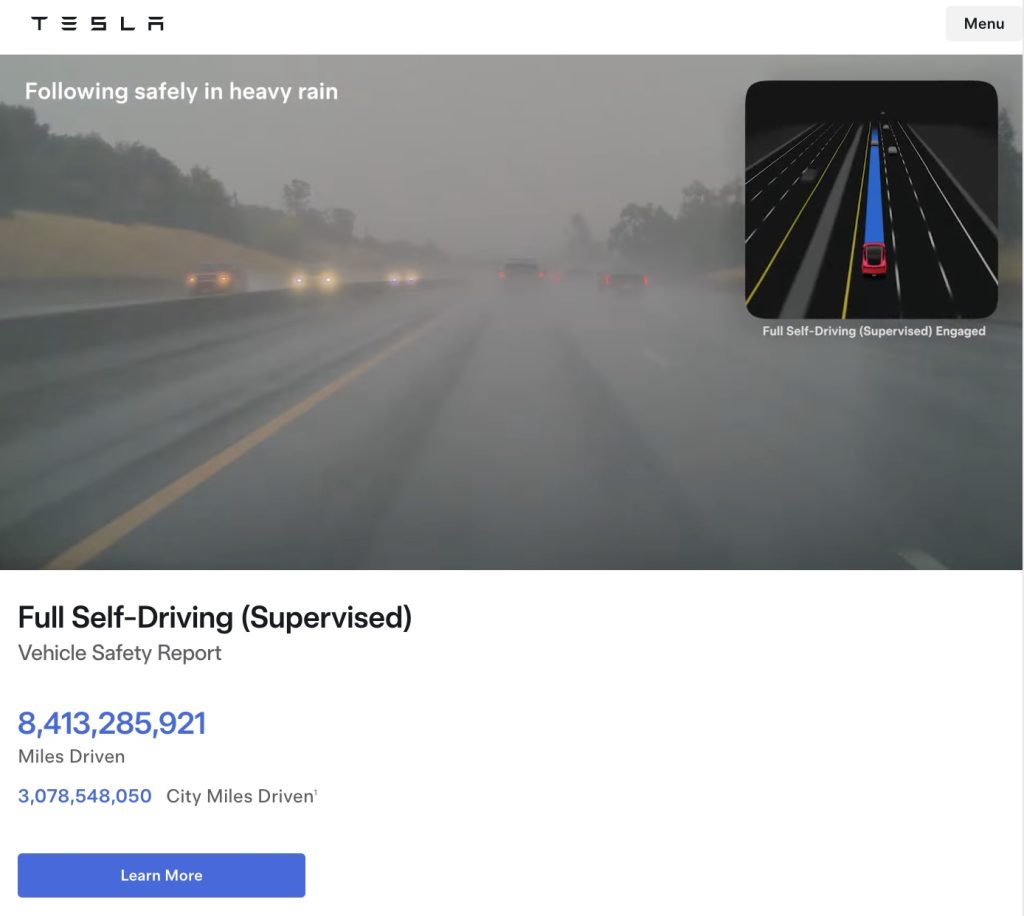
Tesla FSD (Supervised) fleet passes 8.4 billion cumulative miles
The figure appears on Tesla’s official safety page, which tracks performance data for FSD (Supervised) and other safety technologies.

Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (Supervised) system has now surpassed 8.4 billion cumulative miles.
The figure appears on Tesla’s official safety page, which tracks performance data for FSD (Supervised) and other safety technologies.
Tesla has long emphasized that large-scale real-world data is central to improving its neural network-based approach to autonomy. Each mile driven with FSD (Supervised) engaged contributes additional edge cases and scenario training for the system.
The milestone also brings Tesla closer to a benchmark previously outlined by CEO Elon Musk. Musk has stated that roughly 10 billion miles of training data may be needed to achieve safe unsupervised self-driving at scale, citing the “long tail” of rare but complex driving situations that must be learned through experience.
The growth curve of FSD Supervised’s cumulative miles over the past five years has been notable.
As noted in data shared by Tesla watcher Sawyer Merritt, annual FSD (Supervised) miles have increased from roughly 6 million in 2021 to 80 million in 2022, 670 million in 2023, 2.25 billion in 2024, and 4.25 billion in 2025. In just the first 50 days of 2026, Tesla owners logged another 1 billion miles.
At the current pace, the fleet is trending towards hitting about 10 billion FSD Supervised miles this year. The increase has been driven by Tesla’s growing vehicle fleet, periodic free trials, and expanding Robotaxi operations, among others.
With the fleet now past 8.4 billion cumulative miles, Tesla’s supervised system is approaching that threshold, even as regulatory approval for fully unsupervised deployment remains subject to further validation and oversight.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk fires back after Wikipedia co-founder claims neutrality and dubs Grokipedia “ridiculous”
Musk’s response to Wales’ comments, which were posted on social media platform X, was short and direct: “Famous last words.”

Elon Musk fired back at Wikipedia co-founder Jimmy Wales after the longtime online encyclopedia leader dismissed xAI’s new AI-powered alternative, Grokipedia, as a “ridiculous” idea that is bound to fail.
Musk’s response to Wales’ comments, which were posted on social media platform X, was short and direct: “Famous last words.”
Wales made the comments while answering questions about Wikipedia’s neutrality. According to Wales, Wikipedia prides itself on neutrality.
“One of our core values at Wikipedia is neutrality. A neutral point of view is non-negotiable. It’s in the community, unquestioned… The idea that we’ve become somehow ‘Wokepidea’ is just not true,” Wales said.
When asked about potential competition from Grokipedia, Wales downplayed the situation. “There is no competition. I don’t know if anyone uses Grokipedia. I think it is a ridiculous idea that will never work,” Wales wrote.
After Grokipedia went live, Larry Sanger, also a co-founder of Wikipedia, wrote on X that his initial impression of the AI-powered Wikipedia alternative was “very OK.”
“My initial impression, looking at my own article and poking around here and there, is that Grokipedia is very OK. The jury’s still out as to whether it’s actually better than Wikipedia. But at this point I would have to say ‘maybe!’” Sanger stated.
Musk responded to Sanger’s assessment by saying it was “accurate.” In a separate post, he added that even in its V0.1 form, Grokipedia was already better than Wikipedia.
During a past appearance on the Tucker Carlson Show, Sanger argued that Wikipedia has drifted from its original vision, citing concerns about how its “Reliable sources/Perennial sources” framework categorizes publications by perceived credibility. As per Sanger, Wikipedia’s “Reliable sources/Perennial sources” list leans heavily left, with conservative publications getting effectively blacklisted in favor of their more liberal counterparts.
As of writing, Grokipedia has reportedly surpassed 80% of English Wikipedia’s article count.
News
Tesla Sweden appeals after grid company refuses to restore existing Supercharger due to union strike
The charging site was previously functioning before it was temporarily disconnected in April last year for electrical safety reasons.

Tesla Sweden is seeking regulatory intervention after a Swedish power grid company refused to reconnect an already operational Supercharger station in Åre due to ongoing union sympathy actions.
The charging site was previously functioning before it was temporarily disconnected in April last year for electrical safety reasons. A temporary construction power cabinet supplying the station had fallen over, described by Tesla as occurring “under unclear circumstances.” The power was then cut at the request of Tesla’s installation contractor to allow safe repair work.
While the safety issue was resolved, the station has not been brought back online. Stefan Sedin, CEO of Jämtkraft elnät, told Dagens Arbete (DA) that power will not be restored to the existing Supercharger station as long as the electric vehicle maker’s union issues are ongoing.
“One of our installers noticed that the construction power had been backed up and was on the ground. We asked Tesla to fix the system, and their installation company in turn asked us to cut the power so that they could do the work safely.
“When everything was restored, the question arose: ‘Wait a minute, can we reconnect the station to the electricity grid? Or what does the notice actually say?’ We consulted with our employer organization, who were clear that as long as sympathy measures are in place, we cannot reconnect this facility,” Sedin said.
The union’s sympathy actions, which began in March 2024, apply to work involving “planning, preparation, new connections, grid expansion, service, maintenance and repairs” of Tesla’s charging infrastructure in Sweden.
Tesla Sweden has argued that reconnecting an existing facility is not equivalent to establishing a new grid connection. In a filing to the Swedish Energy Market Inspectorate, the company stated that reconnecting the installation “is therefore not covered by the sympathy measures and cannot therefore constitute a reason for not reconnecting the facility to the electricity grid.”
Sedin, for his part, noted that Tesla’s issue with the Supercharger is quite unique. And while Jämtkraft elnät itself has no issue with Tesla, its actions are based on the unions’ sympathy measures against the electric vehicle maker.
“This is absolutely the first time that I have been involved in matters relating to union conflicts or sympathy measures. That is why we have relied entirely on the assessment of our employer organization. This is not something that we have made any decisions about ourselves at all.
“It is not that Jämtkraft elnät has a conflict with Tesla, but our actions are based on these sympathy measures. Should it turn out that we have made an incorrect assessment, we will correct ourselves. It is no more difficult than that for us,” the executive said.








