

News
SpaceX’s surprise Falcon 9 drone ship landing explained ahead of Cargo Dragon launch
Speaking in a press briefing prior to NASA’s next Cargo Dragon launch, a SpaceX official shed some light on a surprise Falcon 9 drone ship landing planned for Wednesday, revealing the circumstances behind the unique decision.
A few days ago, it became clear that SpaceX and NASA and decided to perform a drone ship booster landing attempt after Cargo Dragon’s CRS-19 launch, an unusual trajectory compared to the more typical return-to-launch-site (RTLS) Landing Zone recoveries. Teslarati discussed this quandary earlier today.
“As it turns out, this Falcon 9 landing is a bit of mystery: it’s unclear why exactly SpaceX has decided to land the booster at sea instead of the usual Landing Zone recoveries that have followed most recent Cargo Dragon launches. Typically, the low insertion orbit (~200 km x ~390 km) and relatively low mass of Cargo Dragon (less than 10 tons or 22,000 lb) means that Falcon 9 has (literally) tons of propellant left over, giving it the margins needed to flip around, cancel out a huge amount of horizontal velocity, and boost 100+ km (62+ mi) back to shore.
Instead, new Falcon 9 booster B1058 is scheduled to land aboard drone ship OCISLY some 350 km (220 mi) downrange, an unusual distance. For reference, SpaceX’s May 2019 CRS-17 mission is the only time Falcon 9 has landed at sea after a CRS launch since CRS-8, the rocket’s first successful drone ship recovery. That scenario was forced because LZ-1/2 had coincidently been showered in Crew Dragon debris after C201 exploded during testing. Even then, OCISLY was stationed just 20 or so kilometers offshore, meaning that Falcon 9 B1056 still performed a routine Return To Launch Site (RTLS) landing in spirit.”
Teslarati.com — December 3rd

According to Jessica Jensen, SpaceX’s director of Dragon mission management, the actual reason behind Falcon 9 B1058’s surprise drone ship landing is relatively simple and was more or less one of the possibilities posed earlier today at Teslarati.
“[It’s] also possible that CRS-19 will follow in the footsteps of CRS-18, which sported a prototype Falcon 9 upper stage designed to push the enveloped of its orbital longevity. Falcon 9 B1056 still managed to land at LZ-1 after CRS-18, but a more ambitious follow-on test could potentially require much more propellant, accounting for the drone ship’s position further downrange “
Much as predicted, SpaceX is essentially going to perform an even more ambitious coast test, requiring significantly larger propellant margins that took away from Falcon 9’s own landing propellant budget. For whatever reason, the gray coating covering the CRS-18 upper stage’s RP-1 (refined kerosene) tank is not present on Falcon 9. Based on a picture taken of the horizontal rocket by a NASA Social CRS-19 attendee, CRS-19’s upper stage looks no different than any other.
Jensen says that the coast test will be performed for unspecified “other” customers, presumably referring to the US Air Force (USAF) and other commercial customers interested in direct-to-geostationary (GEO) launch services. Direct GEO launches require rocket upper stages to perform extremely long coasts in orbit, all while fighting the hostile vacuum environment’s temperature swings and radiation belts and attempting to prevent cryogenic propellant from boiling off or freezing solid. In simple terms, it’s incredibly difficult to build a reliable, high-performance upper stage capable of remaining fully functional after 6-12+ hours in orbit.
Although SpaceX said that the test was for “other” customers, that may well have been a cryptic way to avoid indicating that one such customer might be NASA itself. NASA is in the midst of a political battle for the Europa Clipper spacecraft’s launch contract, which is currently legally obligated to launch on NASA’s SLS rocket. Said rocket will likely cost on the order of >$2 billion per launch, meaning that simply using Falcon Heavy or Delta IV Heavy could save no less than ~$1.5 billion. Incredibly, that means that simply using a commercial launch vehicle could save NASA enough money to fund an entire Curiosity-sized Mars rover or even a majority of the cost of building a dedicated Europa lander. Such a launch would demand every ounce of Falcon Heavy’s performance, including a very long orbital coast.
Regardless of the prospective beneficiaries of SpaceX’s planned Falcon 9 upper stage test, CRS-19 is scheduled to launch no earlier than 12:51 pm EST (16:51 UTC), December 4th. High upper-level winds may delay the mission 24 hours to December 5th but for now, it remains on track for Wednesday.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
Tesla Cybercab display highlights interior wizardry in the small two-seater
Photos and videos of the production Cybercab were shared in posts on social media platform X.
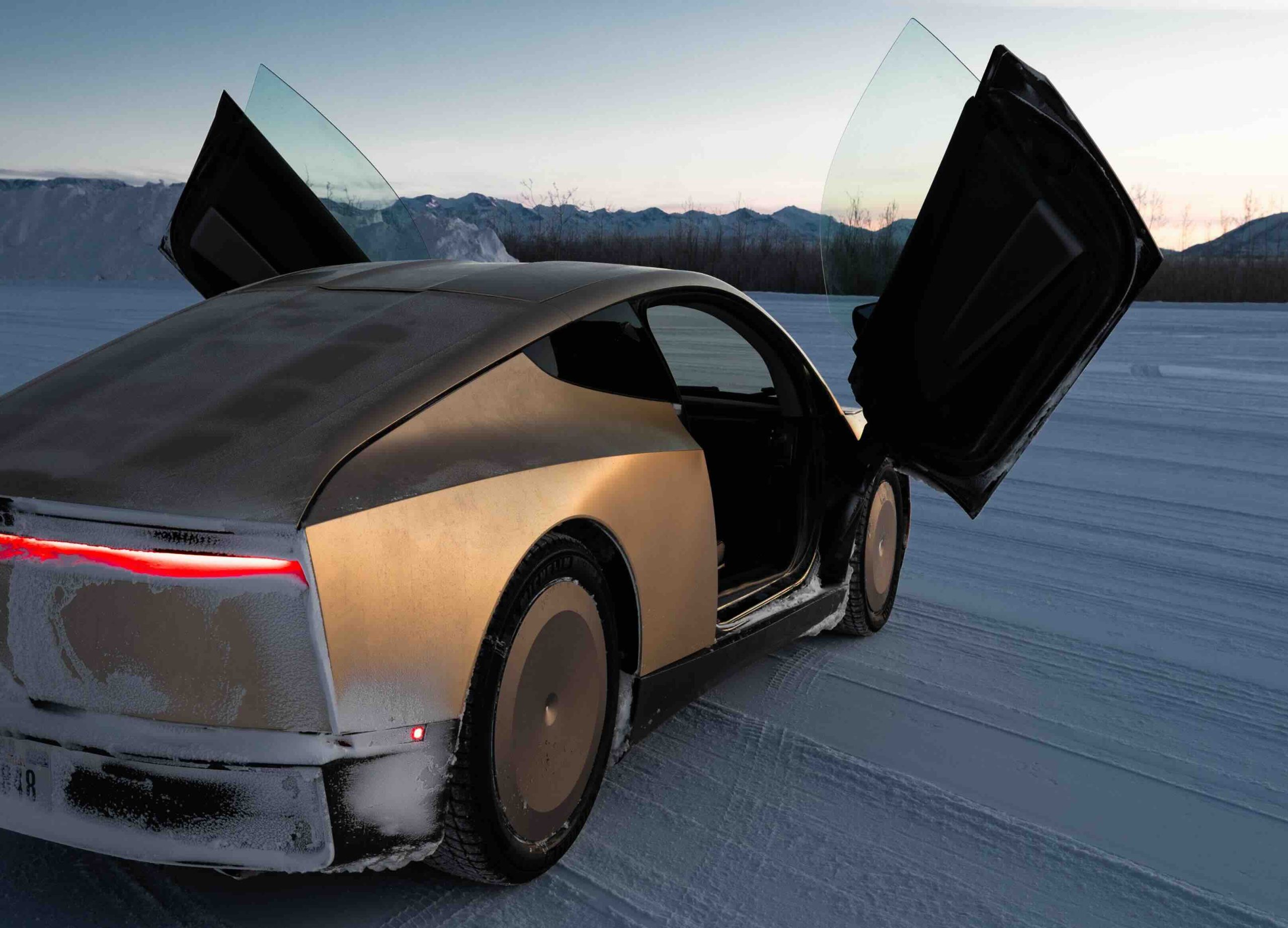

The Tesla Cybercab is currently on display at the U.S. Department of Transportation in Washington, D.C., and observations of the production vehicle are highlighting some of its notable design details.
Photos and videos of the production Cybercab were shared in posts on social media platform X.
Observers of the Cybercab display unit noted that the two-seat Robotaxi provides unusually generous legroom for a vehicle of its size. Based on the vehicle’s video, the compact two-seater appears to offer more legroom than Tesla’s larger vehicles such as the Model Y, Model X, and Cybertruck.
The Cybercab’s layout allows Tesla to dedicate nearly the entire cabin to passengers. The vehicle is designed without a steering wheel or pedals, which helps maximize interior space.
Footage from the display also highlights the Cybercab’s large center screen, which is positioned prominently in front of the passenger bench. The display appears intended to provide entertainment and ride information while the vehicle operates autonomously.
Images of the vehicle also show an additional camera integrated into the Cybercab’s C-pillar. The extra camera appears to expand the vehicle’s field of view, which would be useful as Tesla works toward fully unsupervised Full Self-Driving.
Tesla engineers have previously explained that the Cybercab was designed to be highly efficient both in manufacturing and in operation. Cybercab Lead Engineer Eric E. stated in 2024 that the Robotaxi would be built with roughly half the number of parts used in a Model 3 sedan.
“Two seats unlocks a lot of opportunity aerodynamically. It also means we cut the part count of Cybercab down by a substantial margin. We’re gonna be delivering a car that has roughly half the parts of Model 3 today,” the Tesla engineer said.
The Tesla engineer also noted that the Cybercab’s cargo area can accommodate multiple golf bags, two carry-on suitcases, and two full-size checked bags. The trunk can also fit certain bicycles and a foldable wheelchair depending on size, which is quite impressive for a small car like the Cybercab.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk’s xAI wins permit for power plant supporting AI data centers
The development was reported by CNBC, citing confirmation from the Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality (MDEQ).

Mississippi regulators have approved a permit allowing Elon Musk’s artificial intelligence company xAI to construct a natural gas power plant in Southaven. The facility is expected to support the company’s expanding AI infrastructure tied to its Colossus data center operations near Memphis.
The development was reported by CNBC, citing confirmation from the Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality (MDEQ).
According to the report, regulators “voted to approve the permit” of xAI subsidiary MZX Tech LLC to construct a power plant featuring 41 natural gas-burning turbines “after careful consideration of all public comments and community concerns.”
The Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality stated that the permit followed a regulatory review process that included public comments and community input. Jaricus Whitlock, air division chief for the MDEQ, stated that the project met all applicable environmental standards.
“The proposed PSD permit in front of the board today not only meets all state and federal permitting regulations, but goes above and beyond what is required by law. MDEQ and the EPA agree that not a single person around our facilities will be exposed to unhealthy levels of air pollution,” Whitlock stated.
The planned facility will help provide electricity for xAI’s AI computing infrastructure in the Memphis region.
The Southaven project forms part of xAI’s efforts to scale computing capacity for its artificial intelligence systems.
The company currently operates two major data centers in Memphis, known as Colossus 1 and Colossus 2, which provide computing power for xAI’s Grok AI models. xAI is also planning to build another large data center in Southaven called Macrohardrr, which would be located in a warehouse previously used by GXO Logistics.
Large-scale AI training requires substantial computing power and electricity, prompting technology companies to develop dedicated energy infrastructure for their data centers.
SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell previously stated that xAI plans to develop 1.2 gigawatts of power capacity for its Memphis-area AI supercomputer site as part of the federal government’s Ratepayer Protection Pledge. The commitment was announced during an event with United States President Donald Trump.
“As part of today’s commitment, we will take extensive additional steps to continue to reduce the costs of electricity for our neighbors. xAI will therefore commit to develop 1.2 GW of power as our supercomputer’s primary power source. That will be for every additional data center as well. We will expand what is already the largest global Megapack power installation in the world,” Shotwell said.
“The installation will provide enough backup power to power the city of Memphis, and more than sufficient energy to power the town of Southaven, Mississippi where the data center resides. We will build new substations and invest in electrical infrastructure to provide stability to the area’s grid.”
Elon Musk
Tesla China teases Optimus robot’s human-looking next-gen hands
The image was shared by Tesla AI’s account on Weibo and later reposted by Tesla community members on X.

A new teaser shared by Tesla’s China team appears to show a pair of unusually human-like hands for Optimus.
The image was shared by Tesla AI’s account on Weibo and later reposted by Tesla community members on X.
As could be seen in the teaser image, the new version of Optimus’ hands features proportions and finger structures that look strikingly similar to those of a human hand. Their appearance suggests that they might have dexterity approaching that of a human hand.
If the image reflects a new generation of Optimus’ hands, it could indicate Tesla is continuing to refine one of the most critical components of its humanoid robot.
Hands are widely viewed as one of the most difficult engineering challenges in robotics. For Optimus to perform complex real-world work, from manufacturing tasks to household activities, its hands would need to be the best in the industry.
Elon Musk has repeatedly described Optimus as Tesla’s most important long-term product. In posts on social media platform X, Musk has stated that Optimus could eventually become the first real-world Von Neumann machine.
In theory, a Von Neumann machine is a self-replicating system capable of building copies of itself using available materials. The concept was originally proposed by mathematician John von Neumann in the mid-20th century.
“Optimus will be the first Von Neumann machine, capable of building civilization by itself on any viable planet,” Musk wrote in a post on X.
If Optimus is expected to carry out complex work autonomously in the future, high levels of dexterity will likely be essential. This makes the development of advanced robotic hands a key step towards Musk’s long-term expectations for the product.








