News
Tesla rolls out latest Safety Score update—Here’s what’s new
Tesla’s latest Safety Score update drops one highly criticized factor, while adding weight to pieces like speeding, follow distance, and more.

Tesla has officially started rolling out a new version of its insurance program’s Safety Scores beta, improving upon a few different metrics that make up the index.
As detailed on the Tesla Insurance web page, the company has updated its Safety Scores to beta version 2.2 from the previous version 2.1. The update primarily includes improvements to how Excessive Speeding is measured, along with the removal of Forward Collision Warnings (FCW) from the formula.
In addition, Tesla has slightly increased the values of related factors such as Hard Braking and Unsafe Following Time in the v2.2 formula, perhaps in an attempt to help accommodate some of the situations previously covered by the FCW rating.
READ MORE ON TESLA INSURANCE: Tesla launches insurance discount for FSD users in these two states
Tesla’s Safety Scores are used to determine premium rates for buyers of the company’s in-house insurance program, except in California, where privacy laws prohibit the use of real-time driving data to determine premiums. The company also says that its latest formula for Safety Scores were generated using over 22 billion miles of fleet data from its cars, while the company plans to continue improving the formula as more data comes in.
At this time, Tesla Insurance is available in the following 12 states, though Safety Scores aren’t available in California for the aforementioned reason:
- Arizona
- California
- Colorado
- Illinois
- Maryland
- Minnesota
- Nevada
- Ohio
- Oregon
- Texas
- Utah
- Virginia
You can see the factors that make up Tesla’s Insurance Safety Scores below or on its website here, along with the specific formula that makes up a drivers’ 0 to 100 Safety Score.
Hard Braking
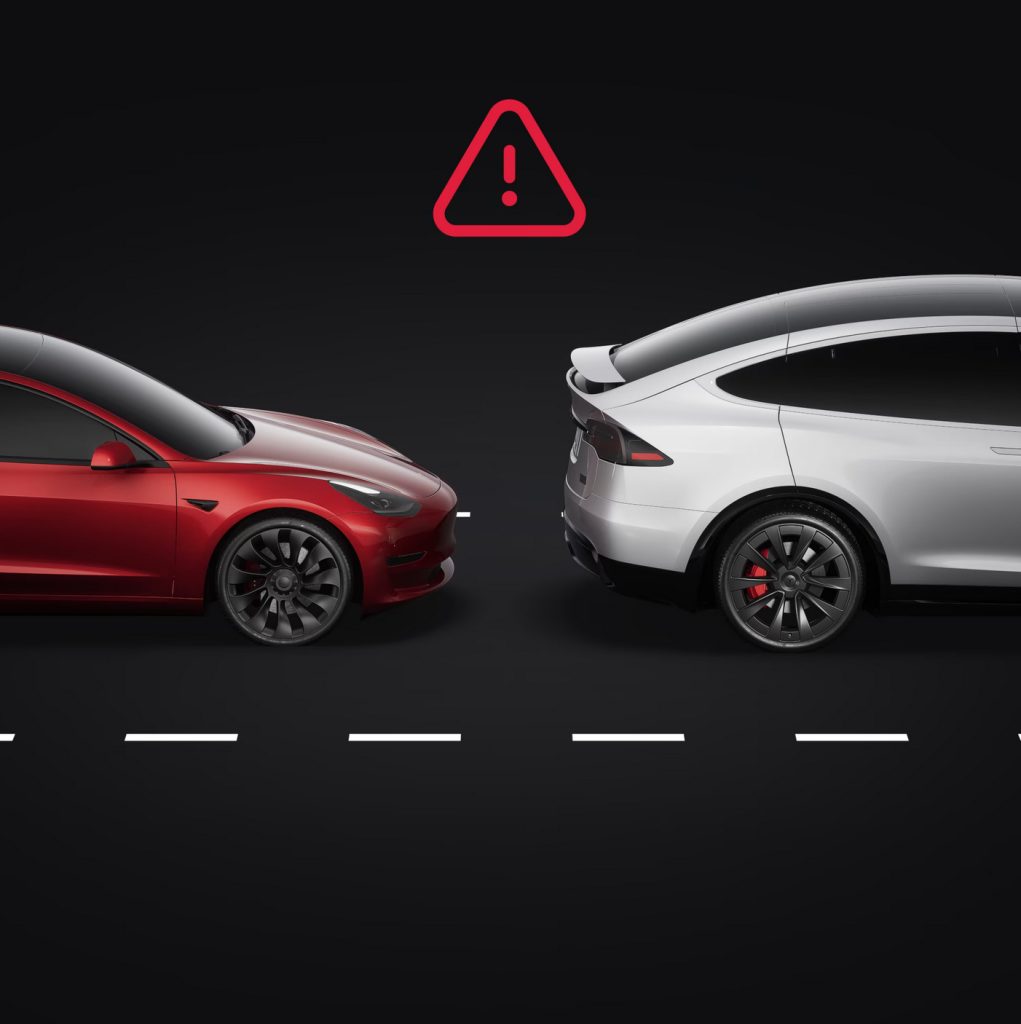

Credit: Tesla
Hard braking is defined as backward acceleration, measured by your Tesla vehicle, in excess of 0.3g. This is the same as a decrease in the vehicle’s speed larger than 6.7 mph, in one second. Hard braking is introduced into the Safety Score Beta formula as the proportion of time where the vehicle experiences backward acceleration greater than 0.3g as a percentage of the proportion of time the vehicle experiences backward acceleration greater than 0.1g (2.2 mph in one second). Hard braking while on Autopilot is not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula. For vehicles with Autopilot computer 3.0 or greater, braking while the vehicle detects yellow traffic lights is also not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula. If the vehicle is unable to detect a yellow traffic light at the time of the hard braking, the event will impact your Safety Score. The percentage shown in the app is the proportion of time spent braking done with excessive force when driving and Autopilot is not engaged. The value is capped at 5.2 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Aggressive Turning

Credit: Tesla
Aggressive turning is defined as left/right acceleration, measured by your Tesla vehicle, in excess of 0.4g. This is the same as an increase in the vehicle’s speed to the left/right larger than 8.9 mph, in one second. Aggressive turning is introduced into the Safety Score Beta formula as the proportion of time the vehicle experiences left or right acceleration greater than 0.4g as a percentage of the proportion of time the vehicle experiences left or right acceleration greater than 0.2g (4.5 mph in one second). Aggressive turning while on Autopilot is not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula. The percentage shown in the Tesla app is the proportion of time spent turning with excessive force when driving and Autopilot is not engaged. The value is capped at 13.2 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Unsafe Following
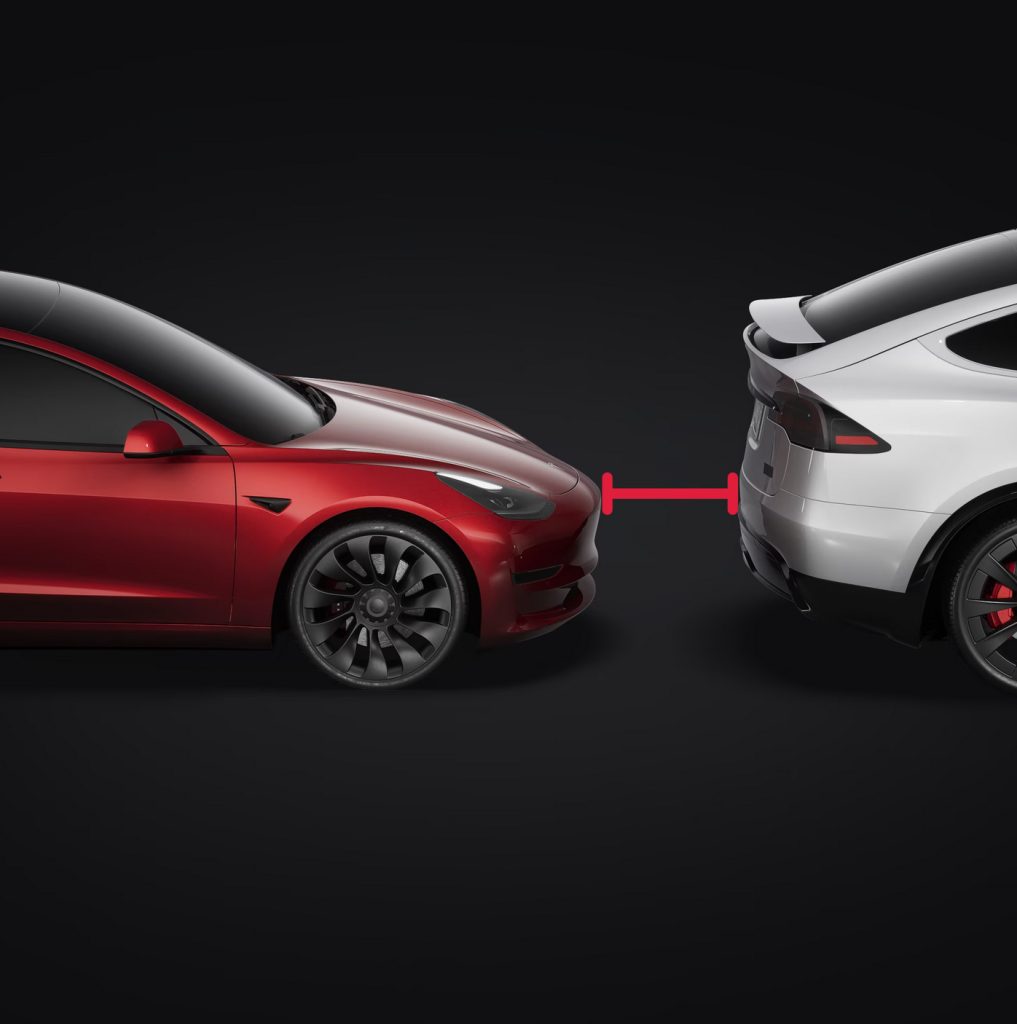

Credit: Tesla
Your Tesla vehicle measures its own speed, the speed of the vehicle in front and the distance between the two vehicles. Based on these measurements, your vehicle calculates the number of seconds you would have to react and stop if the vehicle in front of you came to a sudden stop. This measurement is called “headway.” Unsafe following is the proportion of time where your vehicle’s headway is less than 1.0 seconds relative to the time that your vehicle’s headway is less than 3.0 seconds. Unsafe following is only measured when your vehicle is traveling at least 50 mph and is incorporated into the Safety Score Beta formula as a percentage. Unsafe following while on Autopilot is not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula. The percentage shown in the Tesla app is the percentage of unsafe following when driving and Autopilot is not engaged. The value is capped at 63.2 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Excessive Speeding
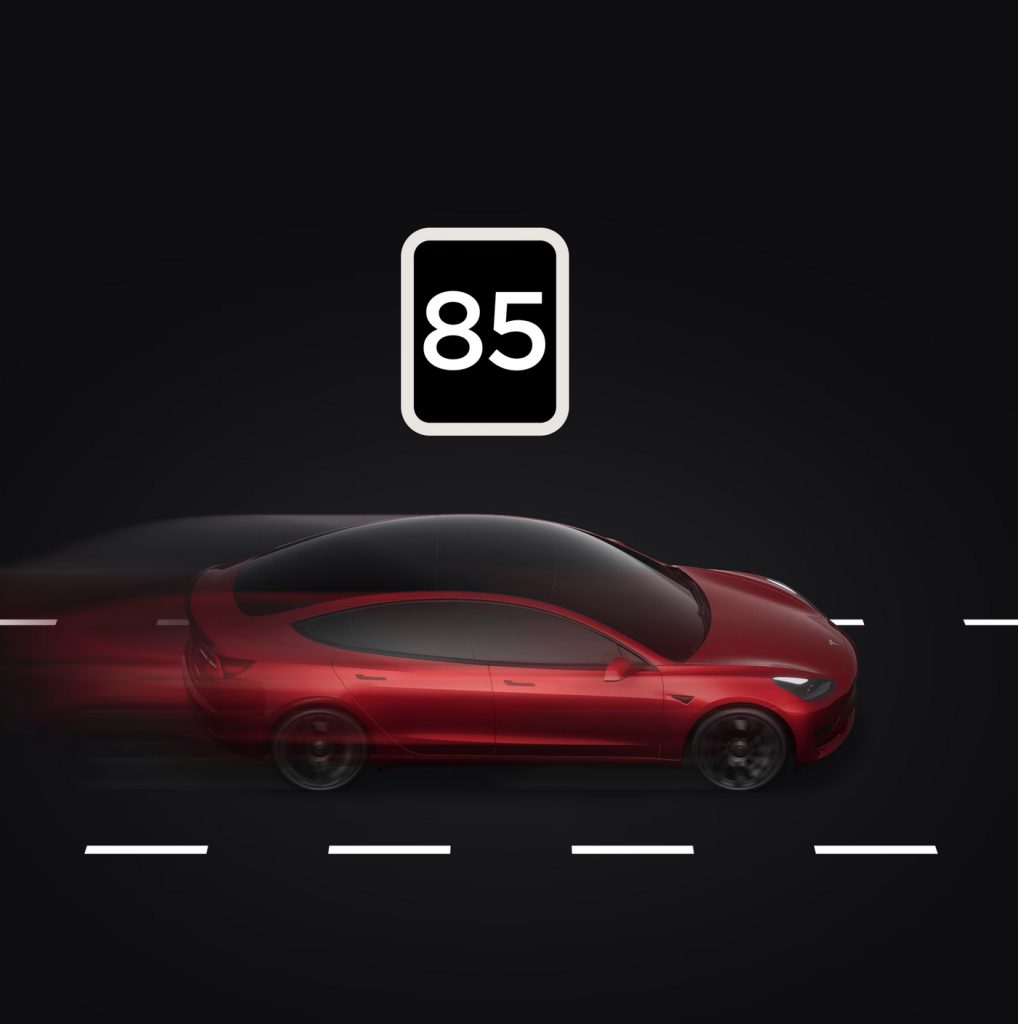

Credit: Tesla
Excessive Speeding is defined as the proportion of time spent driving in excess of 85 mph or driving 20% faster than the vehicle in front of you, when that vehicle is going over 25 mph and is within 100 meters of your vehicle. This value is expressed as a percentage of total driving time and is capped at 10.0% in the Safety Score Beta formula. Speeding while on Autopilot is not factored into the Safety Score Beta formula.
Late-Night Driving

Credit: Tesla
Late-Night Driving is defined as the number of seconds you spend driving at night (11 PM – 4 AM) divided by the number of seconds you spend driving total during the day and night. Due to the variable risk level associated with driving during each late-night hour, each hour is weighed differently, and driving at each hour will affect your Safety Score differently. For example, driving at 11 PM will not affect your Safety Score as heavily as driving at 2 AM. Drive sessions that span two days will apply to the day the trip ends. Late-Night Driving includes all driving at night (11 PM – 4 AM) including any driving done on Autopilot. The value is capped at 14.2 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Forced Autopilot Disengagement
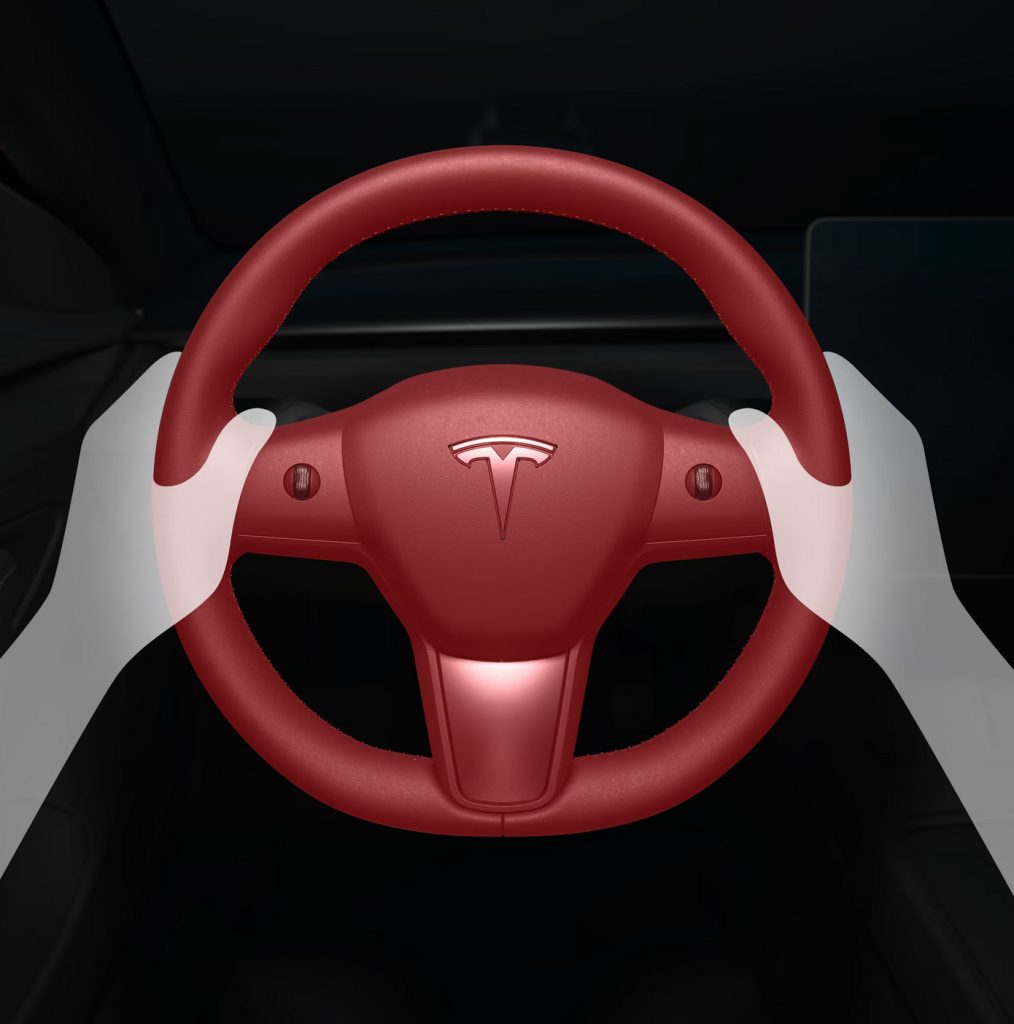

Credit: Tesla
The Autopilot system disengages for the remainder of a trip after the driver has received three audio and visual warnings. These warnings occur when your Tesla vehicle has determined that the driver has not applied sufficient resistance to the steering wheel or has become inattentive. Forced Autopilot Disengagement is introduced into the Safety Score Beta formula as a 1 or 0 indicator. The value is 1 if the Autopilot system is forcibly disengaged during a trip, and 0 otherwise.
Unbuckled Driving
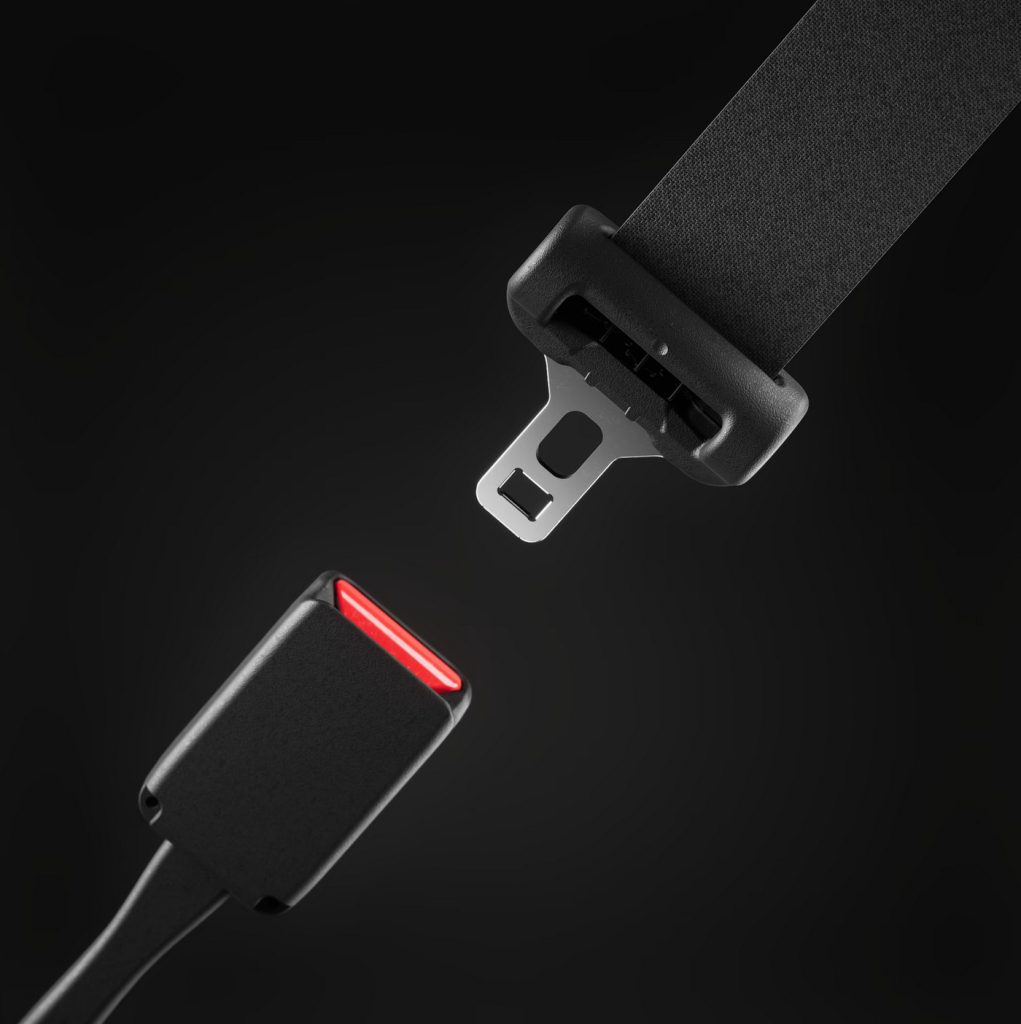

Credit: Tesla
Unbuckled Driving is defined as the proportion of time spent driving above 10 mph without fastening the driver’s seatbelt in a Tesla vehicle, as a percentage of time spent driving above 10 mph. The value shown in the Tesla app is the proportion of time driven at a speed over 10 mph, without buckling the driver’s seatbelt, as a percentage of time spent driving over 10 mph. The value is capped at 31.7 percent in the Safety Score Beta formula.
Tesla’s formula for Safety Score beta v2.2
Tesla takes the formula pictured below, dubbed its Predicted Collision Frequency (PCF), and converts it into the 0 to 100 version 2.2 Safety Score it assigns based on driver behavior. The 2.1 Safety Score formula can also be seen on the Tesla Insurance page, though the below formula is for the newly launched version 2.2.
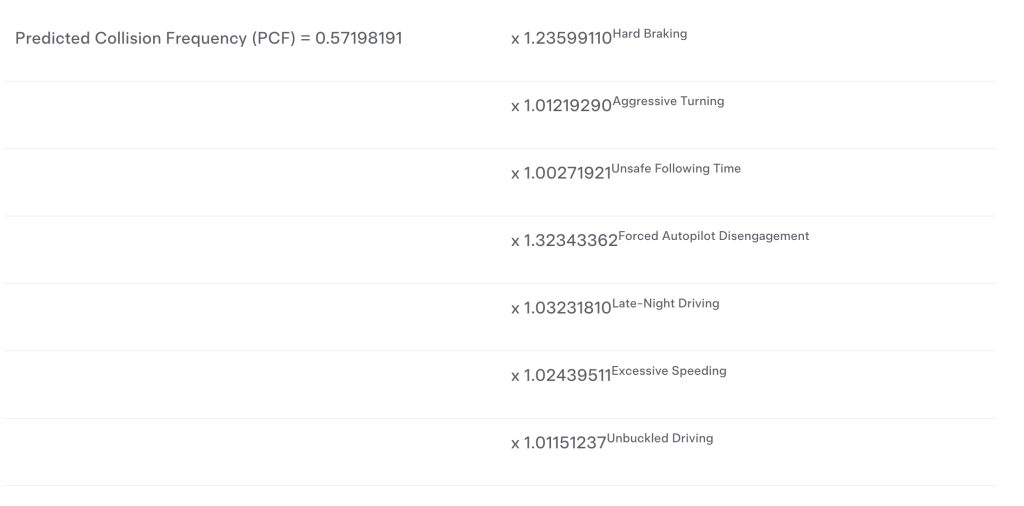
Credit: Tesla

News
Tesla’s most wanted Model Y heads to new region with no sign of U.S. entry
Unlike the standard Model Y, the “L” stretches the wheelbase by roughly 150 mm and the overall length by about 177 mm to 4,976 mm. The result is a genuine 2-2-2 seating layout that gives six adults proper legroom and cargo space — a true family hauler without the cramped third-row compromises of many three-row SUVs.
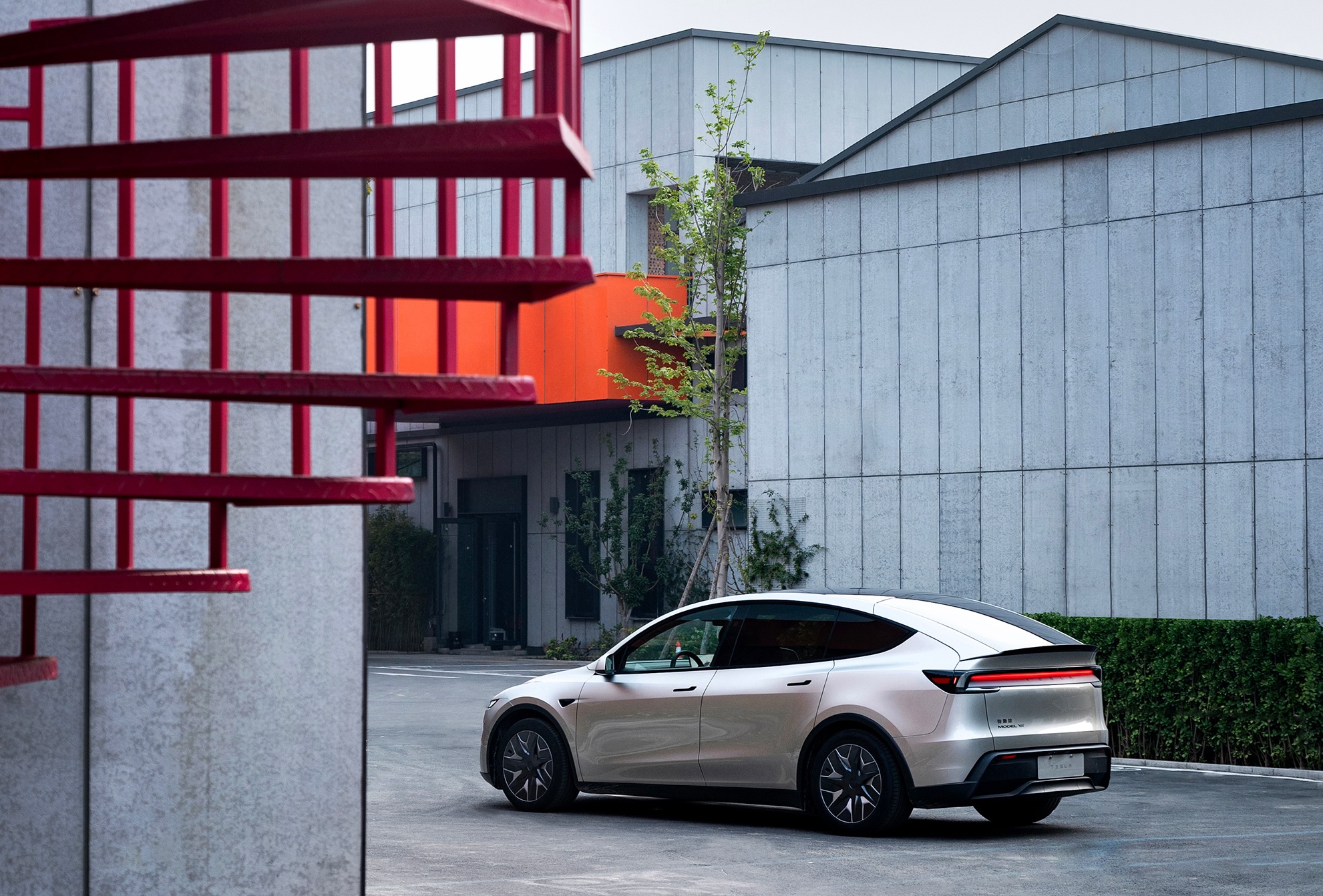

Tesla’s most wanted Model Y configuration is heading to a new region, and although U.S. fans and owners have requested the vehicle since its release last year, it appears the company has no plans to bring it to the market.
According to fresh regulatory filings, the six-seat Model Y L is coming to South Korea with signs indicating an imminent launch. The extended-wheelbase configuration, already a hit in China, just cleared energy-efficiency certification from the Korea Energy Agency, paving the way for deliveries as early as the first half of 2026.
The vehicle is already built at Tesla’s Giga Shanghai facility in China, making it an ideal candidate for the Asian market, as well as the European one, as the factory has been known as a bit of an export hub in the past.
$TSLA
BREAKING: The official launch of Tesla Model Y L in S.Korea seems to be quite imminent.Additional credentials related to Model YL were released today.
✅ Battery Manufacturer: LG Energy Solutions
✅ Number of passengers: 6 people
✅ Total battery capacity: 97.25 kWh… pic.twitter.com/hmy64XYi80— Tsla Chan (@Tslachan) March 6, 2026
It seems like Tesla was prepping for this release anyway, as the timing was no accident. A camouflaged Model Y L prototype was spotted testing on Korean highways the same day the certification dropped. Tesla has already secured similar approvals for Australia and New Zealand, with both markets expecting the larger Model Y in 2026.
Unlike the standard Model Y, the “L” stretches the wheelbase by roughly 150 mm and the overall length by about 177 mm to 4,976 mm. The result is a genuine 2-2-2 seating layout that gives six adults proper legroom and cargo space — a true family hauler without the cramped third-row compromises of many three-row SUVs.
South Korean filings list it as an all-wheel-drive imported electric passenger vehicle with a 97.25 kWh total battery capacity supplied by LG Energy Solution. Local tests show an impressive 543 km (337 miles) combined range at room temperature and 454 km (282 miles) in colder conditions, easing one of the biggest concerns for Korean EV buyers.
Tesla Model Y lineup expansion signals an uncomfortable reality for consumers
But for U.S. fans, things are not looking good for a launch in the market.
CEO Elon Musk has been blunt. The six-seater “wouldn’t arrive in the U.S. until late 2026, if ever,” he said, pointing to the company’s heavy bet on unsupervised Full Self-Driving and robotaxi platforms like the Cybercab. With the Model X slated for discontinuation, many families hoped the stretched Model Y would slide into the lineup as an affordable three-row bridge. So far, that hope remains unfulfilled.
For now, South Korean drivers will be among the first buyers outside China to enjoy the spacious, efficient Model Y L. Tesla continues its global rollout strategy, tailoring vehicles to regional tastes while North American customers keep refreshing their apps and crossing their fingers.
The Model Y L proves the appetite for practical, family-sized electric SUVs is stronger than ever. Hopefully, Tesla will listen to its fans and bring the vehicle to the U.S. where it would likely sell well.
Elon Musk
Tesla is ramping up its advertising strategy on social media
Tesla has long stood out in the automotive world for its unconventional approach to advertising—or, more accurately, its near-total avoidance of it. For over a decade, the company spent virtually nothing on traditional marketing.

Tesla seems to be ramping up its advertising strategy on social media once again. Marketing and advertising have not been a major focus of Tesla’s, something that has brought some criticism to the company from its fans.
However, the company looks to be making adjustments to that narrative, as it has at times in the past, as ads were spotted on several different platforms over the past few days.
On Facebook and YouTube, ads were spotted that were evidently placed by Tesla. On Facebook, Tesla was advertising Full Self-Driving, and on YouTube, an ad for its Energy Division was spotted:
Tesla also threw up some ads on YouTube for Energy https://t.co/19DGQMjBsA pic.twitter.com/XQRfgaDKxY
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 9, 2026
Tesla has long stood out in the automotive world for its unconventional approach to advertising—or, more accurately, its near-total avoidance of it. For over a decade, the company spent virtually nothing on traditional marketing.
In 2022, Tesla’s U.S. ad spend was roughly $152,000, a rounding error compared to General Motors’ $3.6 billion the following year.
Traditional automakers averaged about $495 per vehicle on ads; Tesla spent $0. CEOElon Musk’s stance was explicit: “Tesla does not advertise or pay for endorsements,” he posted on X in 2019. “Instead, we use that money to make the product great.”
The strategy relied on word-of-mouth from delighted owners, Elon’s massive X following, viral product launches, media frenzy, and customer referrals. A great product, Musk argued, sells itself. It does not need Super Bowl spots or billboards. Resources poured into R&D instead, with Tesla investing nearly $3,000 per car, far more than rivals.
Tesla counters jab at lack of advertising with perfect response
This reluctance wasn’t arrogance; it was philosophy, and Musk made it clear that the money was better spent on the product. Heavy spending on ads was seen as wasteful when innovation and authenticity drove organic demand. Shareholder calls for marketing budgets were ignored.
The current shift, paid Facebook ads promoting Full Self-Driving (Supervised) and YouTube Shorts offering up to $1,000 back on Powerwall batteries, marks a pragmatic evolution.
These targeted campaigns coincide with the end of one-time FSD purchases and a March 31 deadline for FSD transfer eligibility on new vehicles.
This move likely signals Tesla adapting to scale, as well as a more concerted effort to stop misinformation regarding its platform. As EV competition intensifies and the company bets big on robotaxis and energy storage, pure organic buzz may not suffice to hit adoption targets. Selective digital ads allow precise, cost-effective reach without abandoning core principles.
If successful, it could foreshadow measured expansion into marketing, boosting high-margin software and home energy revenue while preserving Tesla’s innovative edge. But, it’s nice to see the strategy return, especially as Tesla has been reluctant to change its mind in the past.
News
Tesla Model Y outsells everything in three states, but Ford dominates
The Model Y’s success here highlights accelerating mainstream adoption of electric SUVs, which offer spacious interiors, impressive range, rapid acceleration, and low operating costs.
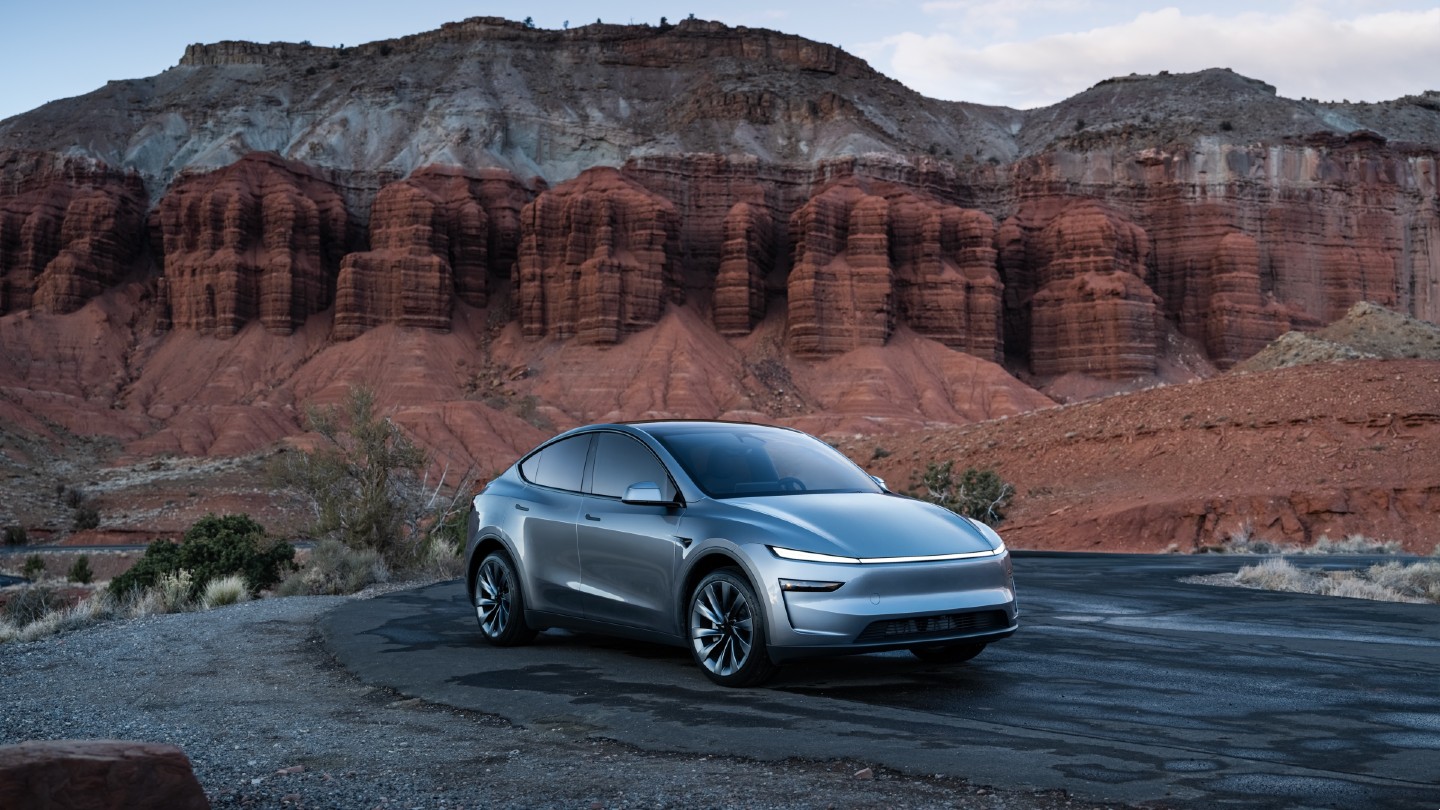

The Tesla Model Y was the best-selling vehicle in three different states in the U.S. last year, according to new data that shows the all-electric crossover outsold every other car in a few places. However, Ford widely dominated the sales figures with its popular F-Series of pickups.
According to new vehicle registration data compiled by Edmunds and visualized by Visual Capitalist, the Ford F-Series, encompassing models like the F-150, F-250, F-350, and F-450, claimed the title of best-selling vehicle in 29 states.
This dominance underscores the pickup truck’s unbreakable appeal across much of the country, particularly in rural, Midwestern, Southern, and Western states, where towing capacity, durability, and utility for work or recreation remain top priorities.
The Tesla Model Y is the best-selling vehicle in California, Washington, and Nevada
How many states will it dominate next year? https://t.co/ERyoyce42D
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 9, 2026
The F-Series has held the crown as America’s overall best-selling vehicle for decades, a streak that continued strong into 2025 despite broader market shifts.
Yet, amid this truck-heavy reality, Tesla made a notable breakthrough. The Model Y emerged as the top-selling vehicle, not just the leading EV, but the outright best-seller in three key states: California, Nevada, and Washington.
These West Coast strongholds reflect regions with robust EV infrastructure, high environmental awareness, generous incentives, and tech-savvy populations. In California alone, nearly 50 percent of new vehicle registrations were electrified, far outpacing the national average of around 25 percent.
The Model Y’s success here highlights accelerating mainstream adoption of electric SUVs, which offer spacious interiors, impressive range, rapid acceleration, and low operating costs.
Elon Musk: Tesla Model Y is world’s best-selling car for 3rd year in a row
Elsewhere, Japanese crossovers filled many gaps: Toyota’s RAV4 and Honda’s CR-V topped charts in several urban and densely populated Northeastern and Midwestern states, where fuel efficiency, reliability, and family-friendly features win out over larger trucks.
While Ford’s broad reach shows traditional preferences persist, at least for now, Tesla’s Model Y victories in high-population, influential states signal a gradual but undeniable transition toward electrification. As charging networks expand and battery technology improves, more states could follow the West Coast’s lead in the coming years.
This 2025 map captures a pivotal moment: pickup trucks still rule the majority, but EVs are carving out meaningful territory where consumer priorities align with sustainability and innovation. The road ahead promises continued competition between legacy giants and electric disruptors.








