SpaceX
SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy eyed by Europe/Japan as ULA nails spectacular Delta Heavy launch
According to RussianSpaceWeb, SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket is under serious consideration for launches of major European and Japanese payloads associated with the Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway (formerly the Deep Space Gateway).
Currently targeting launch readiness in the mid-2020s, those heavy scientific and exploratory government payloads are eyeing Falcon Heavy at the same time as the United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Delta IV Heavy – the most powerful operational rocket prior to FH’s debut – is busy wrapping up a scientific launch for NASA and prepping for another launch in September for its singular anchor customer, the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO).
https://twitter.com/_TomCross_/status/1028599075002896384
A breathtaking mission to the sun
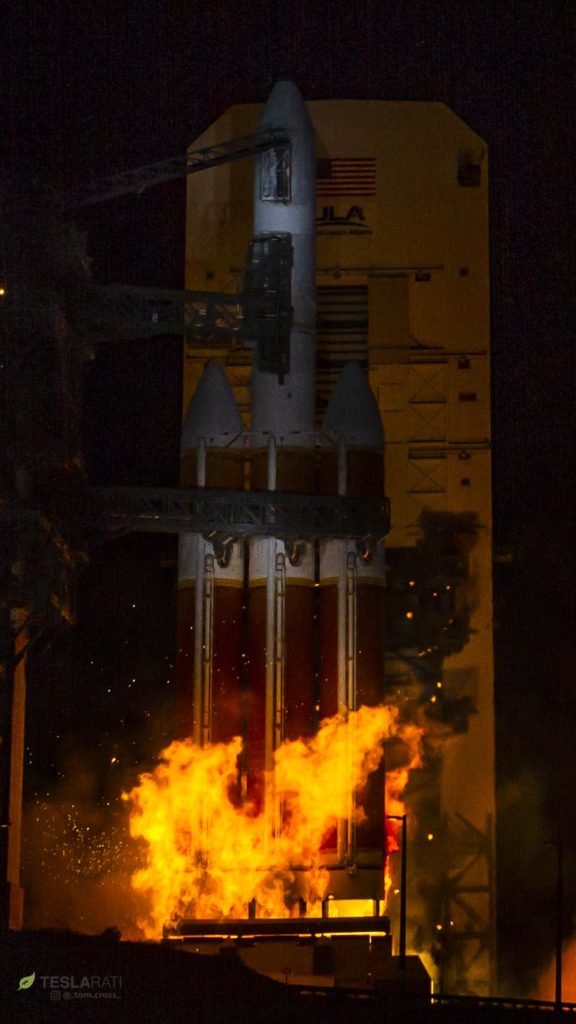
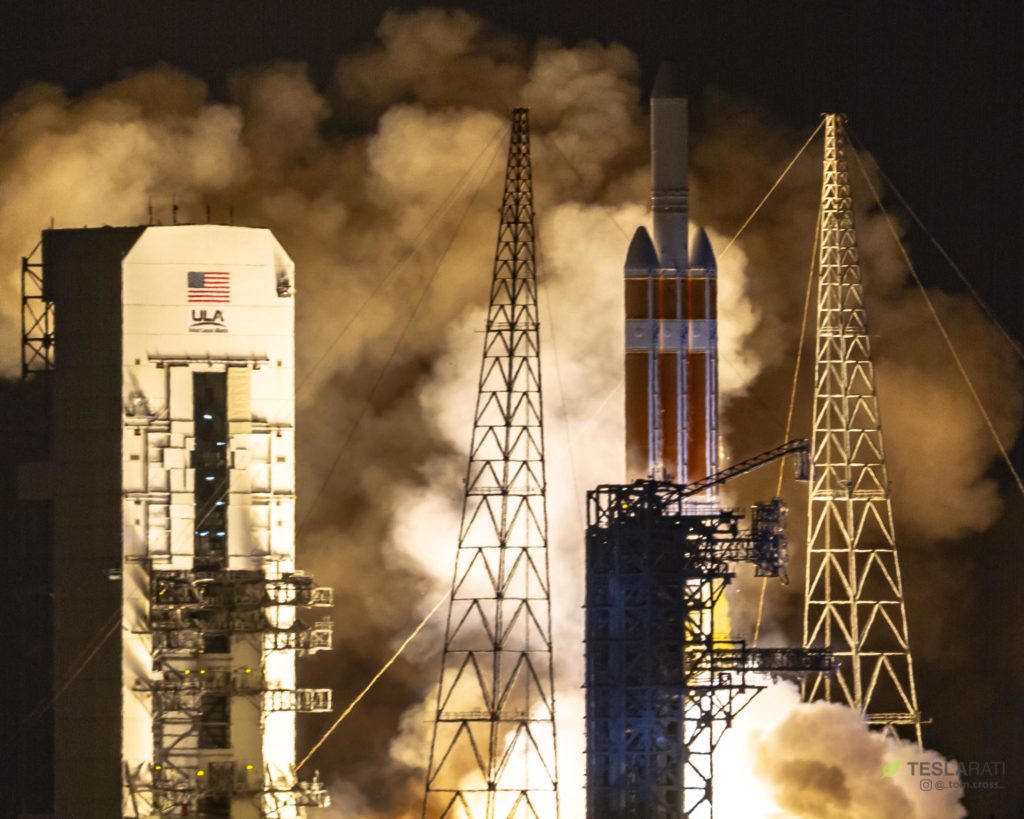
United Launch Alliance (ULA) has just completed the ninth successful launch of its Delta IV Heavy rocket, originally developed by Boeing in the 1990s and debuted in 2004 before the company’s launch vehicle subsidiary joined forces with Lockheed Martin’s own rocket branch. Delta Heavy’s August 12th mission saw the rocket send a small NASA payload known as Parker Solar Probe (PSP) on a trajectory that will eventually place the craft closer to the Sun than any human-made object before it. In pursuit of a better understanding of how exactly our solar system’s namesake functions and behaves, PSP will also become the fastest object ever created by humans, traveling at an extraordinary 200 km/s (120 mi/s) at the zenith of its deepest periapses (the point at which PSP is closest to the sun).
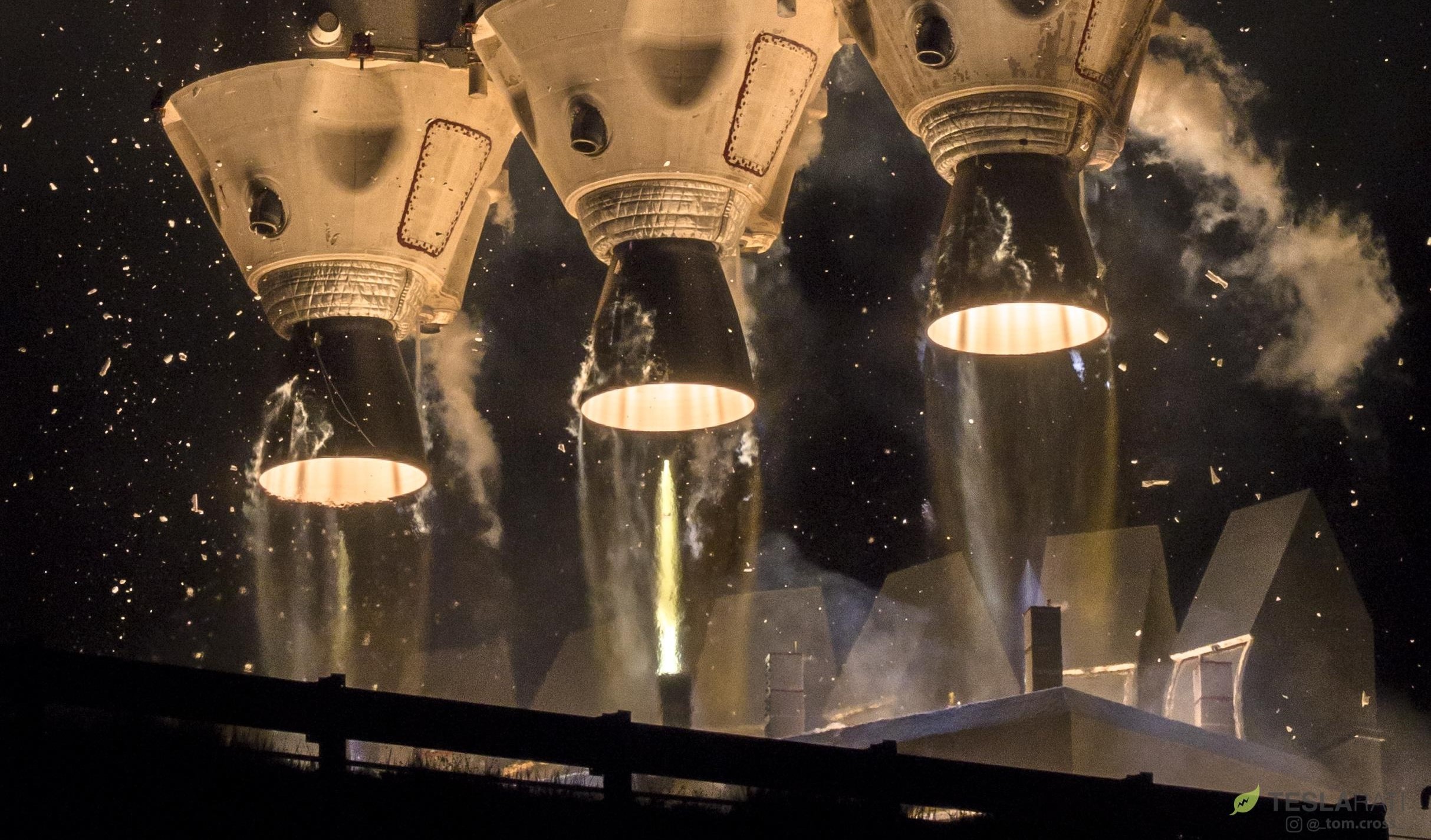
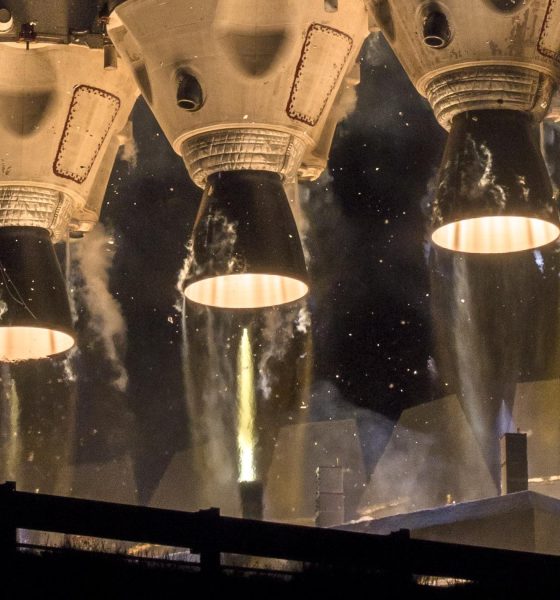
In a fitting send-off for the small heat-shielded spacecraft, Delta IV Heavy’s launch was a spectacle to behold, with clear skies and the cover of darkness combining to magnify the best of the rocket’s telltale features. Upon ignition of its three massive RS-68 rocket engines, each producing over 700,000 lb-ft of thrust, the rocket is held down for several seconds in a process that famously culminates in what appears to be self-immolation just before liftoff, a consequence of the rocket burning off excess hydrogen fuel expelled during the ignition process. Unlike Falcon 9’s dirtier kerosene-oxygen combustion, Delta Heavy’s hydrogen and oxygen fuel produce a flame that is nearly transparent, aside from a bright orange tint created by materials in each engine’s ablative (read: designed to disintegrate) nozzle.
- Delta IV Heavy opts for ‘medium-well’ just before launch. (Tom Cross)
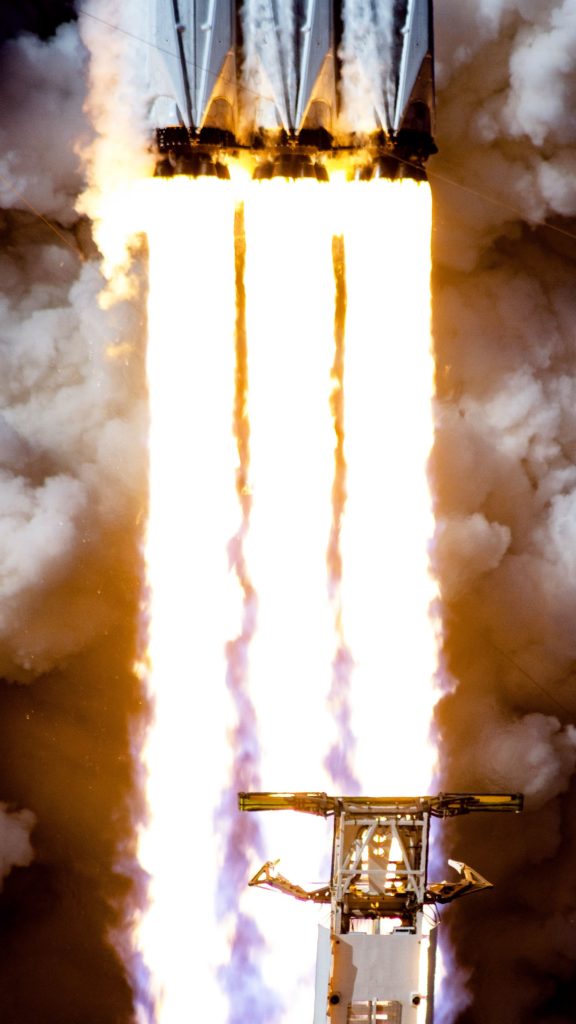
- The extraordinary might of Delta IV Heavy’s hydrolox-burning RS-68A engines, producing a combined 2.1 million pounds of thrust at liftoff. (Tom Cross)
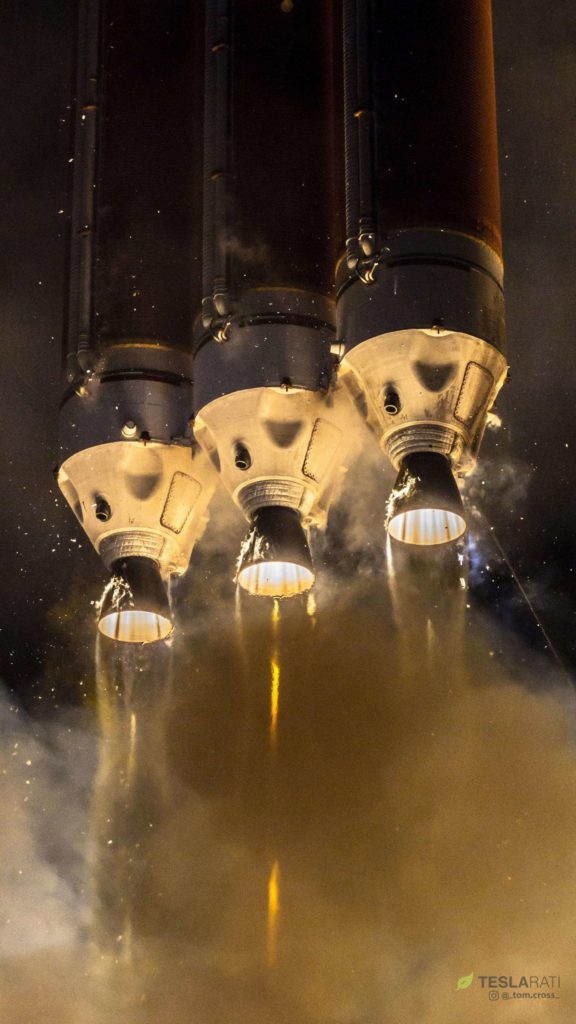
- Delta IV Heavy takes to the sky on its tenth launch, with Parker Solar Probe in tow. (Tom Cross)
- Delta IV Heavy takes to the sky on its tenth launch, with Parker Solar Probe in tow. (Tom Cross)
While Delta IV Heavy has used one of its other nine successful launches for a NASA payload (a test flight of the Orion capsule), all seven remaining missions were conducted for the USAF (1) and the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO; 6), and all six remaining missions on the rocket’s manifest also happen to be for the NRO. Put simply, Delta IV Heavy would not exist today if the NRO did not have an explicit and unflappable need for the capabilities it offers. The primary downside is cost: DIVH costs at least $350 million and usually more than $400m per launch. Thankfully for ULA, the NRO has very few problems with money, and the agency’s estimated annual budget of $10 billion (2013) is more than half of NASA’s entire budget.
After Falcon Heavy’s successful debut, Delta IV Heavy’s monopoly over heavyweight NRO and USAF payloads is rapidly coming to an end, and both agencies are almost certainly attempting to equally quickly certify SpaceX’s newest rocket for critical national security space (NSS) launches. With that influx of the slightest hint of competition, Delta IV Heavy’s ~$400 million price tag starts to look rather painful in comparison to Falcon Heavy’s cost ceiling of around $150 million, potentially much less in the event that 1-3 of its boosters are recoverable. That competition likely won’t kill Delta IV Heavy, thanks entirely to the anchor support of the NRO, but it most certainly will guarantee that Delta Heavy is retired the moment ULA’s next-gen Vulcan rocket is ready to take over, likely no earlier than 2024.
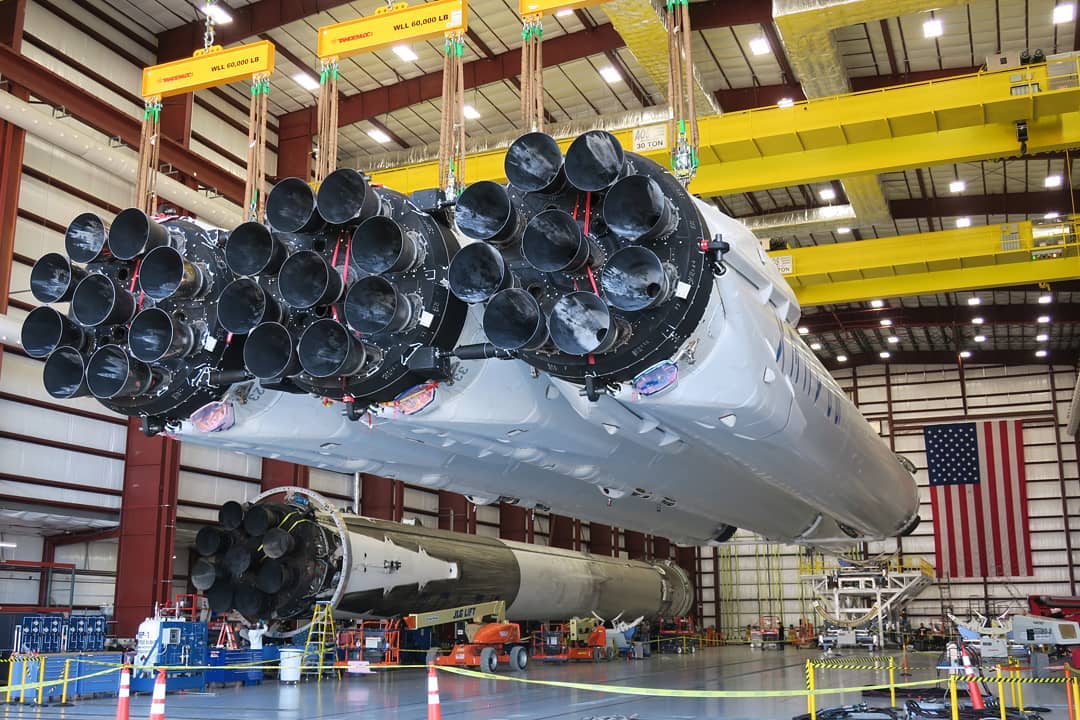

Outside of the NRO, however, there is a surprising amount of interest in Falcon Heavy for interesting (and heavy) government payloads, particularly with respect to the NASA/ESA/JAXA/Roscosmos cooperative lunar space station, known as the Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway.
Falcon Heavy enters the mix
The first payload considering Falcon Heavy for launch services is the Japanese Space Agency’s (JAXA) HTV-X, and upgraded version of a spacecraft the country developed to assist in resupplying the International Space Station (ISS). HTV-X is primarily being designed with an ISS-resupply role still at the forefront, but Russianspaceweb recently reported that JAXA is seriously considering the development of a variant of the robotic spacecraft dedicated to resupplying the Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway (LOPG; and I truly wish I were joking about both the name and acronym).
- JAXA’s first-generation HTV spacecraft on its fourth of nine planned launches, 2013. (NASA)
- JAXA’s first-generation HTV spacecraft on its fourth of nine planned launches, 2013. (NASA)
- The best available visualization of HTV-X, Japan’s upgraded and more affordable ISS resupply spacecraft. (JAXA)
As the name suggests, LOPG is fundamentally a shrunken, upgraded copy of the present-day International Space Station but with its low Earth orbit swapped for an orbit around the Moon. Why, you might ask? It happens that that question is far less sorted at this point than “how”, and there’s a fairly strong argument to be made that NASA is simply attempting to create a low-hanging-fruit destination for the chronically delayed SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft it routinely spends ~20% of its annual budget on. The alternatives to such a crewed orbital outpost are actually landing on the Moon and building a base or dramatically ramping development of foundations needed to enable the first human missions to Mars.
ARTICLE: Cislunar station gets thumbs up, new name in President's budget request – https://t.co/a1XhAPZ7ot
– By Philip Sloss.
(Numerous renders by Nathan Koga, including the epic one below) pic.twitter.com/j0cr2ze7qG
— NSF – NASASpaceflight.com (@NASASpaceflight) March 16, 2018
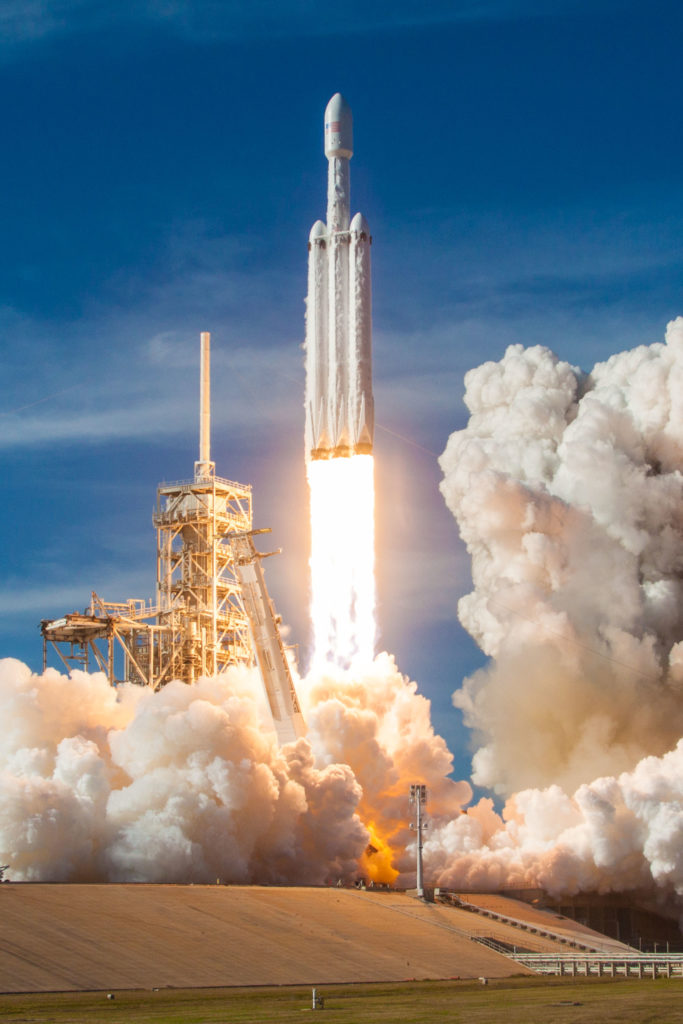
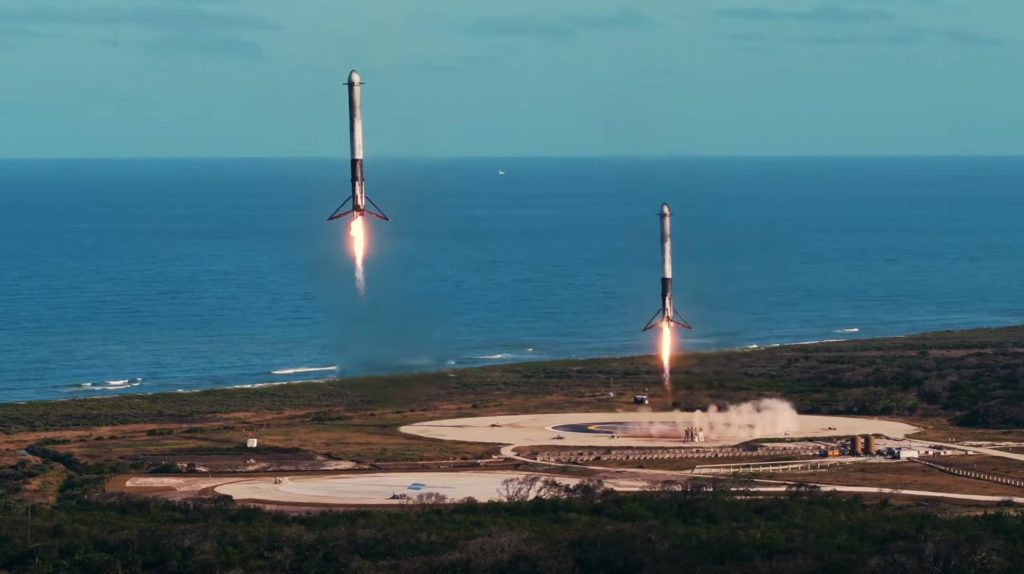
Regardless of the LOPG’s existential merits, a lot of energy (and money) is currently being funneled into planning and initial hardware development for the lunar station’s various modular segments. JAXA is currently analyzing ways to resupply LOPG and its crew complement with its HTV-X cargo spacecraft, currently targeting its first annual ISS resupply mission by the end of 2021. While JAXA will use its own domestic H-III rocket to launch HTV-X to the ISS, that rocket simply is not powerful enough to place a minimum of ~10,000 kg (22,000 lb) on a trans-lunar insertion (TLI) trajectory. As such, JAXA is examining SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy as a prime (and affordable) option: by recovering both side boosters on SpaceX’s drone ships and sacrificing the rocket’s center core, a 2/3rds-reusable Falcon Heavy should be able to send as much as 20,000 kg to TLI (lunar orbit), according to comments made by CEO Elon Musk.
- Falcon Heavy booster ice peeling away and vaporizing in the fire of the engines. (Photo: Tom Cross)
- Falcon Heavy’s launch debut from Pad 39A, February 2018. (SpaceX)
- Falcon Heavy’s side boosters seconds away from near-simultaneous landings at Landing Zones 1 and 2. (SpaceX)
That impressive performance would also be needed for another LOPG payload, this time for ESA’s 5-6 ton European System Providing Refueling Infrastructure and Telecommunications (ESPRIT) lunar station module. That component is unlikely to reach launch readiness before 2024, but ESA is already considering Falcon Heavy (over its own Ariane 6 rocket) in order to save some of the module’s propellant. Weighing 6 metric tons at most, Falcon Heavy could most likely launch ESPRIT while still recovering all three of its booster stages.
Regardless of the outcomes of those rather far-off launch contracts, it’s clear that some sort of market exists for Falcon Heavy and even more clear that its injection of competition into the stagnant and cornered heavy-lift launch segment is being globally welcomed with open arms.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!

Elon Musk
Musk company boycott proposal at City Council meeting gets weird and ironic
The City of Davis in California held a weekly city council meeting on Tuesday, where it voted on a proposal to ban Musk-operated companies. It got weird and ironic.

A city council meeting in California that proposed banning the entry of new contracts with companies controlled by Elon Musk got weird and ironic on Tuesday night after councilmembers were forced to admit some of the entities would benefit the community.
The City of Davis in California held a weekly city council meeting on Tuesday, where it voted on a proposal called “Resolution Ending Engagement With Elon Musk-Controlled Companies and To Encourage CalPERS To Divest Stock In These Companies.”
The proposal claimed that Musk ” has used his influence and corporate platforms to promote political ideologies and activities that threaten democratic norms and institutions, including campaign finance activities that raise ethical and legal concerns.”
We reported on it on Tuesday before the meeting:
California city weighs banning Elon Musk companies like Tesla and SpaceX
However, the meeting is now published online, and it truly got strange.
While it was supported by various members of the community, you could truly tell who was completely misinformed about the influence of Musk’s companies, their current status from an economic and competitive standpoint, and how much some of Musk’s companies’ projects benefit the community.
City Council Member Admits Starlink is Helpful
One City Council member was forced to admit that Starlink, the satellite internet project established by Musk’s SpaceX, was beneficial to the community because the emergency response system utilized it for EMS, Fire, and Police communications in the event of a power outage.
After public comments were heard, councilmembers amended some of the language in the proposal to not include Starlink because of its benefits to public safety.
One community member even said, “There should be exceptions to the rule.”
🚨 After the City of Davis, California, held its City Council meeting on Tuesday and voted on a resolution called “Resolution Ending Engagement With Elon Musk-Controlled Companies and To Encourage CalPERS To Divest Stock In These Companies,” it was forced to admit that it needs… pic.twitter.com/hQiCIX3yll
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 19, 2026
Community Members Report Out of Touch Mainstream Media Narratives
Many community members very obviously read big bold headlines about how horribly Tesla is performing in terms of electric vehicles. Many pointed to “labor intimidation” tactics being used at the company’s Fremont Factory, racial discrimination lawsuits, and Musk’s political involvement as clear-cut reasons why Davis should not consider his companies for future contracts.
However, it was interesting to hear some of them speak, very obviously out of touch with reality.
Musk has encouraged unions to propose organizing at the Fremont Factory, stating that many employees would not be on board because they are already treated very well. In 2022, he invited Union leaders to come to Fremont “at their convenience.”
The UAW never took the opportunity.
Some have argued that Tesla prevented pro-union clothing at Fremont, which it did for safety reasons. An appeals court sided with Tesla, stating that the company had a right to enforce work uniforms to ensure employee safety.
Another community member said that Tesla was losing market share in the U.S. due to growing competition from legacy automakers.
“Plus, these existing auto companies have learned a lot from what Tesla has done,” she said. Interestingly, Ford, General Motors, and Stellantis have all pulled back from their EV ambitions significantly. All three took billions in financial hits.
One Resident Crosses a Line
One resident’s time at the podium included this:
Another member of the community did this…a member of the City Council admonished him and it came to a verbal spat https://t.co/zWvKCiCkie pic.twitter.com/1L334qq9av
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 19, 2026
He was admonished by City Council member Bapu Vaitla, who said his actions were offensive. The two sparred verbally for a few seconds before their argument ended.
City Council Vote Result
Ultimately, the City of Davis chose to pass the motion, but they also amended it to exclude Starlink because of its emergency system benefits.
Elon Musk
California city weighs banning Elon Musk companies like Tesla and SpaceX
A resolution draft titled, “Resolution Ending Engagement With Elon Musk-Controlled Companies and To Encourage CalPERS To Divest Stock In These Companies,” alleges that Musk “has engaged in business practices that are alleged to include violations of labor laws, environmental regulations, workplace safety standards, and regulatory noncompliance.”

A California City Council is planning to weigh whether it would adopt a resolution that would place a ban on its engagement with Elon Musk companies, like Tesla and SpaceX.
The City of Davis, California, will have its City Council weigh a new proposal that would adopt a resolution “to divest from companies owned and/or controlled by Elon Musk.”
This would include a divestment proposal to encourage CalPERS, the California Public Employees Retirement System, to divest from stock in any Musk company.
A resolution draft titled, “Resolution Ending Engagement With Elon Musk-Controlled Companies and To Encourage CalPERS To Divest Stock In These Companies,” alleges that Musk “has engaged in business practices that are alleged to include violations of labor laws, environmental regulations, workplace safety standards, and regulatory noncompliance.”
It claims that Musk “has used his influence and corporate platforms to promote political ideologies and activities that threaten democratic norms and institutions, including campaign finance activities that raise ethical and legal concerns.”
If adopted, Davis would bar the city from entering into any new contracts or purchasing agreements with any company owned or controlled by Elon Musk. It also says it will not consider utilizing Tesla Robotaxis.
Hotel owner tears down Tesla chargers in frustration over Musk’s politics
A staff report on the proposal claims there is “no immediate budgetary impact.” However, a move like this would only impact its residents, especially with Tesla, as the Supercharger Network is open to all electric vehicle manufacturers. It is also extremely reliable and widespread.
Regarding the divestment request to CalPERS, it would not be surprising to see the firm make the move. Although it voted against Musk’s compensation package last year, the firm has no issue continuing to make money off of Tesla’s performance on Wall Street.
The decision to avoid Musk companies will be considered this evening at the City Council meeting.
The report comes from Davis Vanguard.
It is no secret that Musk’s political involvement, especially during the most recent Presidential Election, ruffled some feathers. Other cities considered similar options, like the City of Baltimore, which “decided to go in another direction” after awarding Tesla a $5 million contract for a fleet of EVs for city employees.
Elon Musk
Starlink restrictions are hitting Russian battlefield comms: report
The restrictions have reportedly disrupted Moscow’s drone coordination and frontline communications.

SpaceX’s decision to disable unauthorized Starlink terminals in Ukraine is now being felt on the battlefield, with Ukrainian commanders reporting that Russian troops have struggled to maintain assault operations without access to the satellite network.
The restrictions have reportedly disrupted Moscow’s drone coordination and frontline communications.
Lt. Denis Yaroslavsky, who commands a special reconnaissance unit, stated that Russian assault activity noticeably declined for several days after the shutdown. “For three to four days after the shutdown, they really reduced the assault operations,” Yaroslavsky said.
Russian units had allegedly obtained Starlink terminals through black market channels and mounted them on drones and weapons systems, despite service terms prohibiting offensive military use. Once those terminals were blocked, commanders on the Ukrainian side reported improved battlefield ratios, as noted in a New York Post report.
A Ukrainian unit commander stated that casualty imbalances widened after the cutoff. “On any given day, depending on your scale of analysis, my sector was already achieving 20:1 (casuality rate) before the shutdown, and we are an elite unit. Regular units have no problem going 5:1 or 8:1. With Starlink down, 13:1 (casualty rate) for a regular unit is easy,” the unit commander said.
The restrictions come as Russia faces heavy challenges across multiple fronts. A late January report from the Center for Strategic and International Studies estimated that more than 1.2 million Russian troops have been killed, wounded, or gone missing since February 2022.
The Washington-based Institute for the Study of War also noted that activity from Russia’s Rubikon drone unit declined after Feb. 1, suggesting communications constraints from Starlink’s restrictions may be limiting operations. “I’m sure the Russians have (alternative options), but it takes time to maximize their implementation and this (would take) at least four to six months,” Yaroslavsky noted.